Structure of Business Plans Executive Summary
Diunggah oleh
ranydiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Structure of Business Plans Executive Summary
Diunggah oleh
ranydiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
STRUCTURE AND KEY ELEMENTS OF A BUSINESS PLAN
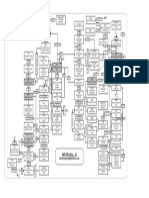
Despite their many differences, all business plans have certain elements in common that all potential investors expect to find (Exhibit 1). Additionally, an appendix is often included that contains detailed information, often presented in the form of tables or graphs. Within this more or less required structure, the business plan is free to grow in its own direction. In Phase I, competitors only worked on a few key elements and individual topics. In Phase II, new elements are added while the topics from the previous phases are expanded, and, gradually, the plan fills with content.
ELEMENTS OF A BUSINESS PLAN
Phase 1
Business
Phase 2
Business
Part of this phase
Concept 1 Executive summary 2 Product or service 3 Management team 4 Market and competition 5 Marketing and sales 6 Business system and organization 7 Implementation schedule 8 Opportunities and risks 9 Financial planning and financing
Pl an
Exhibit 9
1. Executive sum m ar y
"A good executive summary gives me a sense of why this is an interesting venture. I look for a very clear statement of the long-term mission, an overview of the people, the technology, and the fit to market."
Ann Winblad, Venture Capitalist
The executive summary is designed to pique the interest of decision makers. It should contain a brief overview of the most important aspects of the business plan. In particular, it should highlight the product or service, the value to the customer, the relevant markets, management expertise, financing requirements, and possible return on investment. Venture capitalists look at the executive summary first, though they usually j ust skim it. The quality of the summary itself is not likely to make them invest in your proj ect, yet it can convince them not to. A clear, obj ective, and concise description of your intended startup, which must be easy to comprehend,
especially by the technical layperson, will show them that you know your business. Therefore, prepare your summary with the utmost care; it may well decide whether the rest of your business plan is read. The executive summary is an independent element of the business plan: Do not confuse it with the introduction of your business concept on the title page. Look at your executive summary with a critical eye repeatedly especially after all other aspects of your business plan have been completed. Ask yourself if you have described your business idea as clearly, compellingly, and concisely as you can. Your readers should be able to read and comprehend the summary in five to 10 minutes. Test it. Give your executive summary to someone who has no previous knowledge of your business concept or its technical or scientific basis.
KEY QUESTIONS:Executive sum m ar y W hat is your business idea? In what way does it fulfill the criterion of uniqueness? W ho are your target customers? W hat is the value for those customers? W hat market volume and growth rates do you forecast? W hat competitive environment do you face? W hat additional stages of development are needed? How much investment is necessary ( estimated) ? W hat longterm goals have you set? How high do you estimate your financing needs? W hat are the sales,cost,and profit situations? W hat are the most important milestones along the way to your goal? W hat test customers have you approached/ could you approach? W hat distribution channels will you use? W hat partnerships would you like to enter into? W hat opportunities and risks do you face? W hat is the picture on patents? Summarize the results of your detailed business planning and state your exact financing needs! How will you delegate management tasks? How much production capacity is necessary? How will the implementation of your business idea be organized? List your next,concrete steps!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Need of SPMDokumen3 halamanNeed of SPMranydi0% (2)
- Waste MGMNT Motherson PSTNDokumen88 halamanWaste MGMNT Motherson PSTNranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Web TechnologiesDokumen112 halamanWeb TechnologiesranydiBelum ada peringkat
- BITSAT 2012 Sample PaperDokumen29 halamanBITSAT 2012 Sample PaperHarsh GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Business Plans Executive SummaryDokumen2 halamanStructure of Business Plans Executive SummaryranydiBelum ada peringkat
- ACT Festival 2011: New Delhi Mumbai Bengaluru KolkataDokumen21 halamanACT Festival 2011: New Delhi Mumbai Bengaluru KolkataranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Web TechnologiesDokumen93 halamanWeb TechnologiesranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Autocad SurfacingDokumen3 halamanAutocad SurfacingranydiBelum ada peringkat
- DMAICDokumen8 halamanDMAICranydiBelum ada peringkat
- QualifyTutorial Aircraft FittingDokumen6 halamanQualifyTutorial Aircraft FittingranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 Working DrawingDokumen63 halamanChapter 12 Working Drawingapi-200253170Belum ada peringkat
- NX6 Modeling Tutorial - 080826Dokumen9 halamanNX6 Modeling Tutorial - 080826vijayem1Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007Dokumen20 halamanEngineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007ranydiBelum ada peringkat
- DrawingsDokumen32 halamanDrawingssharath_870% (1)
- Engineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007Dokumen20 halamanEngineering Drawing-Marking Schemes Science Subjects-XII-2007ranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Training Programme - On POKA YOKE - 12th March 2010Dokumen93 halamanTraining Programme - On POKA YOKE - 12th March 2010ranydi0% (2)
- Orthographic ReadingDokumen43 halamanOrthographic ReadingranydiBelum ada peringkat
- GD&T Tutorials PDFDokumen24 halamanGD&T Tutorials PDFranydiBelum ada peringkat
- DFDDokumen19 halamanDFDranydiBelum ada peringkat
- CATIA V5 Assembly DraftingDokumen34 halamanCATIA V5 Assembly DraftingPratik PatelBelum ada peringkat
- CATIA V5 FE Tutorial Release 14Dokumen25 halamanCATIA V5 FE Tutorial Release 14mhamouda100% (65)
- GMAT Sentence Correction (2003) BBSDokumen125 halamanGMAT Sentence Correction (2003) BBSAnda MărășescuBelum ada peringkat
- IIFT 10 SolDokumen1 halamanIIFT 10 SolranydiBelum ada peringkat
- c10 ProE WF 5.0Dokumen31 halamanc10 ProE WF 5.0ranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Requested FileDokumen5 halamanRequested FileranydiBelum ada peringkat
- c10 ProE WF 5.0Dokumen31 halamanc10 ProE WF 5.0ranydiBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- PPCDokumen27 halamanPPCPRAMATHESH PANDEY100% (1)
- Economics NumericalsDokumen9 halamanEconomics NumericalsIshaan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Data Analytics by RevoU 1659413996Dokumen11 halamanCase Study Data Analytics by RevoU 1659413996Vicky NopatBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report AcknowledgementDokumen5 halamanProject Report Acknowledgementcity cyberBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation of Final Business Plan: Enrico BotejuDokumen12 halamanPresentation of Final Business Plan: Enrico BotejuMinh Phan HoàngBelum ada peringkat
- ASR Quizzer 6 - Planning and Risk AssessmenttDokumen18 halamanASR Quizzer 6 - Planning and Risk AssessmenttInsatiable LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing 8Th Edition Lamb Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen67 halamanMarketing 8Th Edition Lamb Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdelwyngiselle43r100% (10)
- Objectives of Advertisement: Omer Maroof Enrollment No: 110130Dokumen7 halamanObjectives of Advertisement: Omer Maroof Enrollment No: 110130Aadil Ahmad ZargarBelum ada peringkat
- Mutual Aid Pact Internally Provided Backup Empty Shell Recovery Operations Center ConsiderationsDokumen2 halamanMutual Aid Pact Internally Provided Backup Empty Shell Recovery Operations Center ConsiderationsRedBelum ada peringkat
- Intelligent Data Catalog For Axon, IICS and EDPDokumen35 halamanIntelligent Data Catalog For Axon, IICS and EDPShivraj choudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3 ICSDokumen8 halamanAssignment 3 ICSauni fildzahBelum ada peringkat
- LodnaareaDokumen4 halamanLodnaareaAnwesha SenBelum ada peringkat
- Final Paper DraftDokumen112 halamanFinal Paper DraftMasresha TasewBelum ada peringkat
- IRLLDokumen27 halamanIRLLVaalu MuthuBelum ada peringkat
- Break Even Analysis BDokumen10 halamanBreak Even Analysis BFrederick Gbli100% (1)
- PrivatizationDokumen11 halamanPrivatizationKrisha Mae CaguranganBelum ada peringkat
- MHR - Case5Dokumen2 halamanMHR - Case5RIYA ROSE JOSEPH 2228146Belum ada peringkat
- The New Government Accounting System ManualDokumen37 halamanThe New Government Accounting System ManualArahbellsBelum ada peringkat
- Estimating Earnings and Cash FlowDokumen38 halamanEstimating Earnings and Cash FlowashuuuBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Project 2Dokumen37 halamanMarketing Project 2Hetik PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Sap PM TablesDokumen1 halamanSap PM TablesSimón PlazaBelum ada peringkat
- 90%Dokumen2 halaman90%Vijay VijayarajaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - Introduction To International Business TradeDokumen13 halamanLecture 3 - Introduction To International Business TradeCAMELLEBelum ada peringkat
- SM CF Final PPDokumen726 halamanSM CF Final PPjosephhouse0990Belum ada peringkat
- Air Traffic Controller Staffing ReportDokumen22 halamanAir Traffic Controller Staffing ReportBill RuminskiBelum ada peringkat
- Vikash Marketing Plans of SpicejetDokumen9 halamanVikash Marketing Plans of SpicejetvikashpgdmBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Call CentersDokumen17 halamanStrategic Call CentersAnonymous ztFU1l8HxyBelum ada peringkat
- Subject Code:: Prepared byDokumen6 halamanSubject Code:: Prepared byDarmmini MiniBelum ada peringkat
- Solavei MarketingDokumen254 halamanSolavei MarketingKelvin WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Pratap Mehta CaseDokumen13 halamanPratap Mehta CaseMyrna ChristyBelum ada peringkat