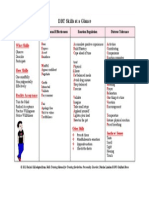
DBT Handout
Diunggah oleh
api-251536652Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DBT Handout
Diunggah oleh
api-251536652Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy: Validation as Acceptance vs.
Change
Sarah Penny, Tina Stephenson & Stacey Wilson The way forward is to simultaneously accept the client and push for change ationale !or the Develop"ent o! DBT Linehan realized CBT wasnt effective in her work with clients with Borderline Personality isorder !BP "# who typically e$perience emotion dysregulation !Linehan % e$ter&'azza# ())*+ ,an i-k# ().(" o #"otion dysregulation is an ina/ility to change or regulate emotional cues# e$periences# actions# ver/al0non&ver/al responses o Pervasive e"otion dysregulation is an ina/ility to regulate emotions across a wide range of emotions# pro/lems and situational conte$ts leading to maladaptive /ehaviours !i1e1 suicidal# /inge0purge# su/stance a/use" !2oerner# ().." o The $iosocial theory proposes that emotion dysregulation arises from the com/ination of vulnera/le /iology and invalidating social environments !i1e1 poor fit# chaotic home# a/usive home# etc1" !2oerner# ().." BT is essentially CBT with the addition of acceptance and mindfulness techni3ues o BT takes the -udgment out of CBT so that clients thinking isnt wrong or distorted o BT acknowledges that there is a pro/lem with the way the clients think# /ut the therapist first encourages clients acceptance rather than -udging# then helps them to look at how they can make changes to more /alanced thinking !,an i-k# ().("
Theoretical %rientation 4ntroduced /y 'arsha Linehan in .556 BT is /ased primarily in a /ehaviourist theoretical /ackground with roots in CBT# /ut it also contains elements of client¢ered theory# 7en practices# and dialectical philosophy !Linehan % e$ter&'azza# ())*+ ,an i-k# ().("
Client Populations 4nitially created to treat the multi&diagnostic# difficult to treat suicidal# self&harming# and BP clients !Linehan % e$ter&'azza# ())*# p16**" BT has also /een found to /e effective for clients with eating disorders# depression# su/stance use# /i&polar disorder# oppositional defiant disorder# PT8 # and an$iety !9ederici % :isniewski# ().6+ Pistorello# 9ruzzetti# 'acLane# ;allop % 4verson# ().(+ :agner# <izvi % =arned# ())>"
Core Treat"ent Strategies Behavioural Change Strategies o Change&oriented strategies that weave together /ehavioural principles and protocols from CBT o 9or e$ample# /ehavioural chain analysis# self&monitoring# etc1 !2oerner# ().." Validation Strategies o ?cceptance&oriented strategies that are derived from the client¢ered and 7en traditions
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson ( o @mpathy A communicating the clients perspective is valid in some way !2oerner# ().." Dialectical Strategies o ? com/ination of change and acceptance strategies o The primary dialectic in BT is /etween change and acceptance o The tension /etween the need to accept clients true vulnera/ilities and yet encourage them to make necessary changes to live a life worth living !,an i-k# ().(" #valuation o! &ntervention #!!ectiveness ?merican Psychiatric ?ssociation !())B" considers BT to /e an evidence&/ased and empirically supported treatment for BP and suicidal and self&harming /ehaviors To date# more than a dozen <andomized Controlled Trials have found efficacy of BT for the treatment of BP !<izvi et al1# ().6" <eductions seen in self&harming /ehaviors# hopelessness# depression# fre3uency and length of hospitalizations# treatment drop out# anger# depression and suicidal ideation !2liem# 2roger % 2osfelder# ().)+ <izvi et al1# ().6" 8tudies have also shown potential efficacy for the use of BT for depression# an$iety# comor/id BP and su/stance a/use# eating disorders !@ " without comor/id BP # and adolescents# however# further studies are needed !'acPherson# Cheavens % 9ristad# ().6+ <izvi et al1# ().6"
Contraindications and #thical Considerations ? strong /ackground in /ehavioural therapy is recommended !2oerner % Linehan# ().." Criticized for /eing resource&intensive and costly !=ad-ipavlou % Cgrodniczuk# ().)" iscussing parasuicidal acts in group setting can foster a contagion effect !Linehan# ()))" Caution must /e e$ercised when applying only portions of BT with clients !<izvi et al1# ().6" Clinicians must /e transparent a/out offering components of BT rather than the full treatment in order not to mislead clients# or leave them with the view that they have failed BT# when they didnt receive full treatment !<izvi et al1# ().6" 4f offering a component of BT to a client as an intervention# the clinician must advise the client they are only going to receive a portion of the treatment# and must provide a rationale as to why they are choosing a specific component !<izvi et al1# ().6" Dot advised to offer the full BT protocol as a private practitioner# given that a treatment team is re3uired for consultation and to maintain a dialectical /alance elivering a skills group independently would likely contri/ute to therapist /urn&out !<izvi et al1# ().6"1
Purpose and &ntended %utco"e o! DBT BTs overarching treatment rationale is to teach and support emotion regulation and to reinstate the natural organizing and communicative functions of emotion to create a life worth living !=ayes# 'asuda# Bissett# Luoma % ;uerrero# ())E+ 2oerner# ().(" BT treatment targets specific goals in therapy in highest to lowest priority .1 8uicidal and non&suicidal self&harming (1 Behaviours that interfere with therapy 61 8uicide ideation and misery E1 'aintaining treatment gains
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson 6 F1 Cther goals as the client identifies !,an i-k# ().(" Contains !our treat"ent "odesG ." individual therapy# (" skills training# 6" client&therapist consultation outside sessions+ and E" therapist consultation team meetings Contains !ive stages o! therapy that typically occurs over the course of a year or moreG .1 Pretreat"ent when goals are set and a commitment to therapy is o/tained (1 Stage & when the goal is to assist client in o/taining /asic capa/ilities and increasing /ehavioral skills in four categories of skills !as discussed /elow" 61 Stage &&# which focuses on emotional pro/lems# such as trauma&related affects through e$posure E1 Stage &&&# which focuses on ac3uiring living skills in such areas as employment# education# and interpersonal relationships F1 Stage &V# which focuses on enhancing living skills with contentment and -oy# while acknowledging life difficulties !=ayes et al1# ())E+ 2oerner# ().(" %ur Selected DBT &ntervention: What is Validation' BT defines validation as empathy plus the communication that the clients perspective is valid in some way !2oerner# ().(# p1 ..." o :ith empathy# you accurately understand the world from the clients perspective o :ith validation you also actively communicate that the clients perspective makes sense given their conte$t !2oerner# ().(" The therapist must simultaneously align with the clients goals and remain open to whats valid a/out the clients response without reinforcing dysfunctional /ehaviour# without evoking such emotional reactivity that the therapeutic task is derailed# and without dropping a focus on needed change !2oerner# ().("
What Does Validation Do' <educes physiological arousal !down®ulates emotion" Cues adaptive emotions to fire which regulates emotion# meaning that the clients whole system reorganizes !2oerner# ().(" Hsed genuinely and with skill# it reduces physiological arousal that is a normal effect of invalidation and it can cue more adaptive emotions to fire !2oerner# ().(" o ?ctive# disciplined# precise validation is re3uired to motivate emotion regulation and there/y create conditions for other change !Linehan# .55>"
(o) to Validate' 8earch for the valid 2now thy client !what is valid0invalid for him0her" ,alidate the valid# invalidate the invalid V alue others A sk 3uestions * isten and reflect & dentify with others D iscuss emotions A ttend to nonver/als T urn the mind
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson # ncourage participation Validation +uidelines Linehan !.55>" listed si$ levels of validation and advised therapists to validate at the highest possi/le levelG .1 (1 61 E1 *evel , Listen with Complete ?wareness# Be ?wake *evel - ?ccurately <eflect the Clients Communication *evel . ?rticulate Donver/alized @motions# Thoughts# or Behavior Patterns *evel / escri/e =ow the Clients Behavior 'akes 8ense in Terms of Past Learning =istory or Biology F1 *evel 0 ?ctively 8earch for the :ays That the Clients Behavior 'akes 8ense in the Current Circumstances# and Communicate B1 *evel 1 Be <adically ;enuine What Validation is 2ot ?greeing or giving in Personalizing clients e$perience Taking on clients distress I9i$ing the client Cheerleading0encouraging ,alidating the Iinvalid e!erences
?merican Psychiatric ?ssociation1 !())B"1 ?merican Psychiatric ?ssociation practice guidelines for the treatment of psychiatric disordersG Compendium ())B !pp1 .((6J.6.E"1 :ashington# CG ?uthor1 9ederici# ?1 % :isniewski# L1 !().6"1 ?n intensive BT program for patients with multidiagnostic eating disorder presentationsG ? case series analysis1 International Journal of Eating Disorders, 46, 6((&66.1 doiG .)1.))(0eat1((..(1 =ayes# 81 C1# 'asuda# ?1# Bissett# <1# Luoma# K1# % ;uerrero# L1 91 !())E"1 BT# 9?P# and ?CTG =ow empirically oriented are the new /ehavior therapy technologiesL Behavior Therapy, 35# 6F& FE1 doiG.)1.).B1(98)))F&>*5E1(*)E1(5*)))6&) =ad-ipavlou# ;1# % Cgrodniczuk# K1 81 !().)"1 Promising psychotherapies for personality disorders1 Canadian Journal of Psy hiatry, 55!E"# ()(&(.)1 <etrieved from httpG00ezpro$y1li/1ucalgary1ca0loginLurlMhttpG00search1pro3uest1com0docview0(((*)(E5BL accountidM5*6* 2liem# 81# 2roger# C1# % 2osfelder# K1 !().)"1 ialectical /ehavior therapy for /orderline personality disorderG ? meta&analysis using mi$ed&effects modeling1 Journal of Consulting and Clini al Psy hology, !", 56BJ5F.1 doiG.)1.)6>0a))(.).F
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson 2oerner# 21 !().("1 Doing diale ti al #ehavior therapy$ % pra ti al guide1 Dew Nork# DNG The ;uilford Press1 Linehan# '1 '1 !.55>"1 ,alidation and psychotherapy1 4n ?1 Bohart % L1 ;reen/erg !@ds1"# E&pathy re onsidered$ 'e( dire tions in psy hotherapy !pp1 6F6J 65("1 :ashington# CG ?merican Psychological ?ssociation1 Linehan# '1 '1 !()))"1 The empirical /asis of dialectical /ehavior therapyG evelopment of new treatments versus evaluation of e$isting treatments1 Clini al Psy hology$ ) ien e and Pra ti e, !# ..6J..51 doiG .)1.)560clipsy1>1.1..6
Linehan# '1'1 % e$ter& 'azza# @1T1 !())*"1 ialectical /ehavior therapy for /orderline personality disorder1 4n# Clini al *and#oo+ of Psy hologi al Disorders$ % step,#y step treat&ent &anual -4th ed./ avid =1 Barlow !ed1" Dew Nork# DNG The ;uilford Press1 'acPherson# =1 ?1# Cheavens# K1 81# % 9ristad# '1 ?1 !().6"1 ialectical /ehavior therapy for adolescentsG Theory# treatment adaptations# and empirical outcomes1 Clini al Child and 0a&ily Psy hology 1evie(, 26# F5J*)1 doiG.)1.))>0s.)FB>&).(&).(B&> Pistorello# K1# 9ruzzetti# ?1# 'acLane# c1# ;allop# <1# % 4verson# 21 '1 !().("1 ialectical /ehavior therapy ! BT" applied to college studentsG ? randomized clinical trial1 Kournal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology# *)!B"# ecem/er ().(# p 5*(J55E1 C4G .)1.)6>0a))(5)5B <izvi# 81 L1# 8teffel# L1 '1# % Carson&:ong# ?1 !().6"1 ?n overview of dialectical /ehavior therapy for professional psychologists1 Professional Psy hology$ 1esear h and Pra ti e, 44!("# >6J*)1 doiG.)1.)6>0a))(5*)* ,an i-k# 81 !().("1 DBT &ade si&ple$ % step,#y,step guide to diale ti al #ehavioural therapy1 Cakland# C?G Dew =ar/inger Pu/lications :agner# ?1 :1# <izvi# 81 L1# % =arned# '1 81 !())>"1 ?pplications of dialectical /ehavior therapy to the treatment of comple$ trauma&related pro/lemsG :hen one case formulation does not fit all1 Journal 3f Trau&ati )tress, 45!E"# 65.&E))1 doiG.)1.))(0-ts1()(B* ,an i-k# 81 !().(/. Cal&ing the e&otional stor&$ 6sing diale ti al #ehavior therapy to &anage your e&otions and #alan e your life. Cakland# C?G Dew =ar/inger Pu/lications1 DBT We$ esources httpG00www1soundstrue1com0podcast0transcripts0erin&olivo1phpLcamefromhomeMcamefromhome httpG00www1mind1org1uk0mentalOhealthOa&z0*)6)OdialecticalO/ehaviourOtherapy httpG00www1d/tselfhelp1com0html0overview(1html
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson DBT T A2SC &PT 32oerner# ().(# p1 .6("
>
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
.)
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
..
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
.(
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
.6
Penny# 8tephenson % :ilson
.E
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy for Emotional Intelligence: DBT Therapy for Calming the Emotional Storms Inside and Overcoming Anxiety SymptomsDari EverandDialectical Behavior Therapy for Emotional Intelligence: DBT Therapy for Calming the Emotional Storms Inside and Overcoming Anxiety SymptomsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Treatment Planning from a Reality Therapy PerspectiveDari EverandTreatment Planning from a Reality Therapy PerspectiveBelum ada peringkat
- Visual CBT: Using Pictures to Help You Apply Cognitive Behaviour Therapy to Change Your LifeDari EverandVisual CBT: Using Pictures to Help You Apply Cognitive Behaviour Therapy to Change Your LifePenilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (3)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Rewire Your Brain With 8 Cbt Mindfulness Techniques to Overcome Social Anxiety, Depression and Insomnia Through Positive Thinking and Self DisciplineDari EverandCognitive Behavioral Therapy: Rewire Your Brain With 8 Cbt Mindfulness Techniques to Overcome Social Anxiety, Depression and Insomnia Through Positive Thinking and Self DisciplinePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (9)
- DBT Distress Tolerance SkillsDokumen2 halamanDBT Distress Tolerance SkillsSophia Veleda100% (2)
- DBT 2B6C0EC8d01Dokumen2 halamanDBT 2B6C0EC8d01drgvenkman100% (11)
- 6 Levels of Validation for Understanding PerspectivesDokumen1 halaman6 Levels of Validation for Understanding PerspectivesGeorgia Hart100% (3)
- DBT Adult Diary CardDokumen2 halamanDBT Adult Diary CardShelly Clemons100% (8)
- DBT Skills Training Quick Reference Sheet by Rachel GillDokumen1 halamanDBT Skills Training Quick Reference Sheet by Rachel Gillsofsof007100% (14)
- Question Bank For DBTDokumen27 halamanQuestion Bank For DBTRahul MishraBelum ada peringkat
- DBT-SP Skills Training Manual v3 4Dokumen154 halamanDBT-SP Skills Training Manual v3 4Tatiana Buianina100% (3)
- DBT Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanDBT Cheat SheetTessa Vanderhart95% (38)
- NAMI Illinois State Conference Fundamentals of DBTDokumen30 halamanNAMI Illinois State Conference Fundamentals of DBTlucaspki100% (1)
- Foııng: Scanned by CamscannerDokumen5 halamanFoııng: Scanned by CamscannerMonika Meilutė-Ribokė100% (4)
- DBT Teaching GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanDBT Teaching Guidelinesarjun.lnmiit50% (2)
- DBT-SP Skills Training Manual v3 4Dokumen131 halamanDBT-SP Skills Training Manual v3 4popoviciaida100% (9)
- DEAR MAN GIVE FAST Worksheet PDFDokumen2 halamanDEAR MAN GIVE FAST Worksheet PDFclarimachado91% (11)
- DBT ToolsDokumen20 halamanDBT Toolsjorge torres88% (8)
- Family Skills ModuleDokumen21 halamanFamily Skills ModuleAmy Powers100% (1)
- Radical Acceptance DBTDokumen3 halamanRadical Acceptance DBTPenelope Chambers92% (12)
- DBT Skills WorksheetsDokumen7 halamanDBT Skills WorksheetsMonika Meilutė-Ribokė100% (4)
- DBT Skills Flash Cards Visual ReviewDokumen14 halamanDBT Skills Flash Cards Visual ReviewBeyza Gül89% (9)
- Diary Card Sample - Marsha LinehanDokumen2 halamanDiary Card Sample - Marsha LinehanMaurice Azzano100% (20)
- Understanding DBTDokumen35 halamanUnderstanding DBTBen Fenty100% (1)
- DBT WorkbookDokumen57 halamanDBT Workbookmelodyfathi100% (11)
- DBT Skills Diary CardDokumen1 halamanDBT Skills Diary Cardmary grace banaBelum ada peringkat
- DBT Skills Mods Pt3Dokumen41 halamanDBT Skills Mods Pt3Ionelia Pașa100% (8)
- DBT Workshop PDFDokumen36 halamanDBT Workshop PDFNica Nario Asuncion100% (2)
- ACT For Interpersonal Problems: Using Mindfulness, Acceptance, and Schema Awareness To Change Interpersonal BehaviorsDokumen9 halamanACT For Interpersonal Problems: Using Mindfulness, Acceptance, and Schema Awareness To Change Interpersonal BehaviorsNew Harbinger Publications48% (21)
- DBT 2 - Completed2Dokumen264 halamanDBT 2 - Completed2jakir100% (4)
- DBTDokumen210 halamanDBTKatheryn P100% (31)
- Behavioral Chain Anaylsis Worksheet (By Seth Axelrod) PDFDokumen1 halamanBehavioral Chain Anaylsis Worksheet (By Seth Axelrod) PDFclarimachado100% (1)
- Dialetical Behaviour TherapyDokumen76 halamanDialetical Behaviour TherapyJoão Perestrelo100% (11)
- DBT Skills CheatsheetDokumen5 halamanDBT Skills CheatsheetA100% (16)
- Learn DBT The WorkbookDokumen37 halamanLearn DBT The WorkbookSonali Nahata100% (5)
- Function of Emotion Worksheet PDFDokumen1 halamanFunction of Emotion Worksheet PDFMaryBelum ada peringkat
- DBT Skills Modules PlanDokumen1 halamanDBT Skills Modules Planmathoni100% (1)
- Initials - Date Started - To - Date Completed. Please Check Each Behavior For Each Day On A Scale (0-5 See Below)Dokumen1 halamanInitials - Date Started - To - Date Completed. Please Check Each Behavior For Each Day On A Scale (0-5 See Below)Ciupi Tik100% (1)
- CBT WorksheetsDokumen10 halamanCBT WorksheetsМарія Щербініна100% (15)
- The Handbook of Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Theory, Research, and EvaluationDari EverandThe Handbook of Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Theory, Research, and EvaluationJamie BedicsBelum ada peringkat
- DBT Assignment Workbook F0220Dokumen218 halamanDBT Assignment Workbook F02201collection100% (43)
- CBT and DBT For AnxietyDokumen161 halamanCBT and DBT For Anxietyalimsher100% (8)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Paulette Aasen, PH.DDokumen38 halamanDialectical Behavior Therapy: Paulette Aasen, PH.Dcbt878Belum ada peringkat
- Zen Principles and Mindfulness Practice in Dialectical Behavior TherapyDokumen8 halamanZen Principles and Mindfulness Practice in Dialectical Behavior Therapyvoland34100% (3)
- DBT Emotional Regulation Group 4 HandoutsDokumen5 halamanDBT Emotional Regulation Group 4 HandoutsAngela McKimson100% (2)
- DBT PresentationDokumen7 halamanDBT Presentationapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- DBT Skills at A Glance by Rachel Gill PDFDokumen1 halamanDBT Skills at A Glance by Rachel Gill PDFPinki Tuscaderro (aka Rachel Gill)Belum ada peringkat
- Nimh4 S-DBT Diary CardDokumen1 halamanNimh4 S-DBT Diary CardTreva100% (2)
- DBT CoachDokumen12 halamanDBT CoachTreva100% (1)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Control Your Emotions, Overcome Mood Swings And Balance Your Life With DBTDari EverandDialectical Behavior Therapy: Control Your Emotions, Overcome Mood Swings And Balance Your Life With DBTPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (2)
- CBT Coping Skills Therapy ManualDokumen120 halamanCBT Coping Skills Therapy Manualdleon2694% (34)
- W3 DBT and Emotion Dysregulation PDFDokumen14 halamanW3 DBT and Emotion Dysregulation PDFpb141161100% (1)
- DBTDokumen14 halamanDBTTirtea Lorena100% (2)
- DBT Distress Tolerance Skills PDFDokumen19 halamanDBT Distress Tolerance Skills PDFpb141161100% (1)
- DBT WCCL PDFDokumen2 halamanDBT WCCL PDFTreva86% (7)
- Radically Open Dialectical Beha - Thomas R. Lynch PDFDokumen450 halamanRadically Open Dialectical Beha - Thomas R. Lynch PDFZoya Zvyagintseva89% (37)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Feeling Good Again by Overcoming Mood Swings, Gaining Emotional Control with the DBT TherapyDari EverandDialectical Behavior Therapy: Feeling Good Again by Overcoming Mood Swings, Gaining Emotional Control with the DBT TherapyPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- CBT WorkbookDokumen32 halamanCBT Workbooksoheilesm45692% (25)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) & Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): How CBT, DBT & ACT Techniques Can Help You To Overcoming Anxiety, Depression, OCD & Intrusive ThoughtsDari EverandCognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) & Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): How CBT, DBT & ACT Techniques Can Help You To Overcoming Anxiety, Depression, OCD & Intrusive ThoughtsPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide to DBT and Using Behavioral Therapy to Manage Borderline Personality DisorderDari EverandDialectical Behavior Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide to DBT and Using Behavioral Therapy to Manage Borderline Personality DisorderBelum ada peringkat
- Hieberts Counselling SkillsDokumen1 halamanHieberts Counselling Skillsapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Thesis PosterDokumen1 halamanThesis Posterapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Counselling ProcessDokumen1 halamanCounselling Processapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Feminist Therapy Code of Ethics Revised 1999Dokumen4 halamanFeminist Therapy Code of Ethics Revised 1999api-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Penny Sarah Assignment 3Dokumen15 halamanPenny Sarah Assignment 3api-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Gender Race and Class ArticleDokumen23 halamanGender Race and Class Articleapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Crpos Code of EthicsDokumen1 halamanCrpos Code of Ethicsapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Pennys CV Webpage VersionDokumen4 halamanPennys CV Webpage Versionapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- DBT PresentationDokumen7 halamanDBT Presentationapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- Stong Interest Inventory FinalDokumen13 halamanStong Interest Inventory Finalapi-251536652Belum ada peringkat
- He Imes Eader: White House: Bin Laden UnarmedDokumen44 halamanHe Imes Eader: White House: Bin Laden UnarmedThe Times LeaderBelum ada peringkat
- Check List of PMKVY Training Centers in Yamunanagar - Sarkari Yojana 2017Dokumen4 halamanCheck List of PMKVY Training Centers in Yamunanagar - Sarkari Yojana 2017Harsh GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Vs Maxicorp DigestedDokumen2 halamanMicrosoft Vs Maxicorp DigestedRoosevelt Guerrero0% (1)
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDokumen13 halamanUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Rape (Investigation and Trial) Ordinance, 2020Dokumen12 halamanAnti-Rape (Investigation and Trial) Ordinance, 2020Farman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen6 halamanChapter 4Michael ChiuBelum ada peringkat
- Western MovementDokumen5 halamanWestern MovementKee Jeon DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- English Act 3 Scene 2Dokumen3 halamanEnglish Act 3 Scene 2Anonymous QN2QVwNBelum ada peringkat
- Jadavpur University 2017 Ma English Entrance Question PaperDokumen6 halamanJadavpur University 2017 Ma English Entrance Question PaperZeventricBelum ada peringkat
- People vs. NuñezDokumen28 halamanPeople vs. NuñezLourdes LescanoBelum ada peringkat
- United States v. Rashella Reed, 11th Cir. (2014)Dokumen5 halamanUnited States v. Rashella Reed, 11th Cir. (2014)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Letter Sent To Senator Kamala Harris Requesting Her Office To Investigate DOJ CorruptionDokumen3 halamanLetter Sent To Senator Kamala Harris Requesting Her Office To Investigate DOJ CorruptionBilly EarleyBelum ada peringkat
- Identities Spatially Constructed in Relation to SexualityDokumen9 halamanIdentities Spatially Constructed in Relation to SexualityWoon Wei SengBelum ada peringkat
- Current California State Bar Disbarments Suspensions As of May 2011Dokumen12 halamanCurrent California State Bar Disbarments Suspensions As of May 2011JudgebustersBelum ada peringkat
- Union Bank Vs DBP (Obligations and Contracts - Compensation)Dokumen5 halamanUnion Bank Vs DBP (Obligations and Contracts - Compensation)Bruce Wayne100% (4)
- Rapscallion MovesSheet 03082023 1Dokumen2 halamanRapscallion MovesSheet 03082023 1We KnowBelum ada peringkat
- Michael Rubens BloombergDokumen3 halamanMichael Rubens BloombergMarina Selezneva100% (1)
- The Bishop's kindness and generosity testedDokumen9 halamanThe Bishop's kindness and generosity testedGangadhar MamadapurBelum ada peringkat
- Vu Tra Giang - 20070149 - INS3022 - 02Dokumen7 halamanVu Tra Giang - 20070149 - INS3022 - 02Hương GiangBelum ada peringkat
- Julious Caesar TranscriptDokumen1 halamanJulious Caesar TranscriptningruanantaBelum ada peringkat
- Alma Jose v. AvellanaDokumen7 halamanAlma Jose v. AvellanaAya ArceBelum ada peringkat
- People of The Philippines vs. Jose Belmar Umapas Y Crisostomo GR. No. 215742, March 22, 2017 FactsDokumen1 halamanPeople of The Philippines vs. Jose Belmar Umapas Y Crisostomo GR. No. 215742, March 22, 2017 FactsdnzrckBelum ada peringkat
- Compilation of Agrarian Law Cases 2020-2021 BDokumen27 halamanCompilation of Agrarian Law Cases 2020-2021 BMaestro LazaroBelum ada peringkat
- Libya Geographical LocationDokumen7 halamanLibya Geographical LocationAffan AzamBelum ada peringkat
- Arabic Grammar HAALDokumen2 halamanArabic Grammar HAALIfrah IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- 82 Lagman V Medialdea (2017)Dokumen7 halaman82 Lagman V Medialdea (2017)Courtney TirolBelum ada peringkat
- Dubai Aviation Exhibition and Sponsorship 2019Dokumen4 halamanDubai Aviation Exhibition and Sponsorship 2019Ali KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Nuisance - 7 - Zorilla - Ramcar V MillarDokumen13 halamanNuisance - 7 - Zorilla - Ramcar V MillarRalph Christian ZorillaBelum ada peringkat
- (L4) Nullity - Void and Voidable MarriagesDokumen20 halaman(L4) Nullity - Void and Voidable MarriagesRoberto GuiseppiBelum ada peringkat
- A Famous Speech by ShakespeareDokumen22 halamanA Famous Speech by ShakespeareSaleemah MsskinnyfiberBelum ada peringkat