Design Lab - Equilibrium
Diunggah oleh
Suhas DonthiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Design Lab - Equilibrium
Diunggah oleh
Suhas DonthiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EQUILIBRIUM DESIGN LAB!
SUHAS DONTHI MANJUNATHA
AIM: To investigate the effect on equilibrium with the change in concentration of the reactants.
RESEARCH QUESTION: To determine if change in concentration affects the equilibrium between the products (FeSCN2+ (aq)) and reactants (Fe3+ (aq) + SCN1- (aq)) in the following reaction
You are assuming that I have any !"#$%&'()%$%*+,-%&'()%! !"*+,.$%&'()! idea what you are talking about.
HYPOTHESIS: As the concentration of the reactants is decreased the equilibrium move towards the side of the reactants and when the concentration is increased the equilibrium moves to the other side.
! !
BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Equilibrium is the state at that occurs in a closed system when the forward and reverse reactions of a reversible reaction occur at the same rate. According to Le Chatliers principle if the concentration of a species is increased, then the equilibrium moves towards the other side causing the concentration to fall to a value between the original concentration and increased value. Conversely when the concentration of the species is reduced the equilibrium shifts towards the side of the equilibrium on which it occurs causing the concentration to increase to a value between the original concentration and the reduced value.
! !
CHANGE INCREASE IN CONCENTRAION DECREASE IN CONCENTRATION
EFFECT ON EQUILIBRIUM SHIFTS TO THE OPPOSITE SIDE SHIFTS TO THE SAME SIDE
APPARATUS: 1. 3 Test tubes 2. Beaker 3. Measuring Cylinder 4. Iron Nitrate-Fe(NO3)3! 5. Potassiumthiocynate-KSCN 6. Ammonium Chloride (NH4Cl) 7. Tap water
! !
VARIABLES:
INDEPENDANT Concentration of reactions:!
DEPENDANT Colour
CONTROLLED Temperature Pressure
! !
1. Fe3+! 2. KSCN
EQUILIBRIUM DESIGN LAB!
CONTROLLED VARIABLE Temperature
SUHAS DONTHI MANJUNATHA
METHOD TO CONTROL Perform the temperature in the same room, with same conditions. Checking constantly with thermometer can improve the accuracy. Pressure can be controlled by performing all the trails under the same conditions. Preferably at 1atm.
Pressure
PROCEDURE: 1. Measure 1.0 ml of 0.20 M KSCN and 1.0 ml of 0.20 M Fe(NO3)3. 2. Add 1.0 ml of 0.20 M Fe(NO3)3 to 1.0 ml of 0.20 M KSCN. 3. Dilute the solution by accurately measuring and adding tap water until moderately orange-red color is attained and record the volume added. 4. Place 5.0 ml of the diluted solution into each of three test tubes. Perform the indicated operations (below) and compare the three solutions (using one of these three as a color standard) by looking down the tube from above, with a white paper background. Correlate each observation with Le Chteliers Principle and the above equilibrium. 5. Add a few drops of 0.20 M Fe(NO3)3 to the first test tube and note down the observation. 6. To the second 5.0 ml portion add a few drops of 0.20 M KSCN and note down the observations. 7. Add a spatula of ammonium chloride which reduces the concentration of Fe3+ 8. Repeat the experiment 4 more times for improved results. 9. Compare the results and relate it to the Le Chatliers Principle.
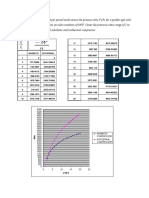
SAMPLE RESULT TABLE:
CHANGE IN CONCENTRATION Fe3+ SCN Fe3+ OBSERVATION CAUSE SHIFT OF EQUILIBRIUM
!
Note down values for each trail in a similar table for all 5 trails.
1,0,0. 60%
Research question incomplete. No mention of how to control variables Ow is relevant data collected from method proposed?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NEW:EquilibriumDokumen4 halamanNEW:EquilibriumAnkur SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab #11: Determination of A Chemical Equilibrium Constant: ObjectivesDokumen0 halamanLab #11: Determination of A Chemical Equilibrium Constant: ObjectivesPablo BernalBelum ada peringkat
- Equilibrium Constant For Hydrolysis Lab6finalDokumen9 halamanEquilibrium Constant For Hydrolysis Lab6finalapi-534386927Belum ada peringkat
- Le Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen7 halamanLe Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlfred RogerBelum ada peringkat
- Rate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidDokumen6 halamanRate of Reaction Between Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric AcidSimon WayneBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Bio Enzyme Catalase Lab Ap 1Dokumen16 halamanAp Bio Enzyme Catalase Lab Ap 1api-233187566100% (1)
- AP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDokumen5 halamanAP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesJonathan Chen100% (2)
- Chemical Kinetics Methodology, RDRDokumen7 halamanChemical Kinetics Methodology, RDRKhayzel MelanoBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Kinetics ExperimentDokumen7 halamanSample Kinetics ExperimentVenus PondevidaBelum ada peringkat
- The Determination of Keq For FeSCN2Dokumen3 halamanThe Determination of Keq For FeSCN2Jürgen Nicholas Schwarze100% (1)
- AP Chemistry - Acid Dissociation Constant Ka LabDokumen4 halamanAP Chemistry - Acid Dissociation Constant Ka LabJonathan Chen83% (6)
- Blood PerssureDokumen16 halamanBlood Perssuretmondol34256Belum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundDokumen13 halamanExperiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundMuhammad Azri HaziqBelum ada peringkat
- NMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionDokumen8 halamanNMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionOldbooklover100% (2)
- Hydrolysis of Tert-Butyl Chloride and Solvent EffectDokumen7 halamanHydrolysis of Tert-Butyl Chloride and Solvent EffectangelbenavidezBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Repot Analytical 1Dokumen2 halamanLab Repot Analytical 1yangkmjBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationDokumen6 halamanChem Lab - A Velocity Constant TitrationMiguel Ackah-Yensu50% (2)
- Lab Report 1 Diffusion Across Biological Membrances SimulationDokumen7 halamanLab Report 1 Diffusion Across Biological Membrances SimulationAmeena Ali50% (2)
- Formal Chemistry Lab ReportsDokumen4 halamanFormal Chemistry Lab ReportsAram IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Exp. 2 c230 S - 07 Keq of FeSCNDokumen10 halamanExp. 2 c230 S - 07 Keq of FeSCNdenciopoBelum ada peringkat
- ORG LAB Melting Point Determination2009Dokumen8 halamanORG LAB Melting Point Determination2009Yunkai DayBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabDokumen8 halamanAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564Belum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4 FWRDokumen5 halamanExperiment 4 FWRSarah HermosuraBelum ada peringkat
- Rate Law Determination of The Crystal Violet Reaction by Dan HolmquistDokumen4 halamanRate Law Determination of The Crystal Violet Reaction by Dan HolmquistPaul Schumann0% (1)
- A Classification of Experimental DesignsDokumen15 halamanA Classification of Experimental Designssony21100% (1)
- Joshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportDokumen13 halamanJoshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportJoshua HaholonganBelum ada peringkat
- Surface TensionDokumen5 halamanSurface Tensiondoulat2000Belum ada peringkat
- Rhs Science Lab Report GuidelinesDokumen2 halamanRhs Science Lab Report Guidelinesapi-268599570Belum ada peringkat
- Recombinant ReportDokumen4 halamanRecombinant Report门门Belum ada peringkat
- C3 IrnmrDokumen10 halamanC3 IrnmrAldi StefanusBelum ada peringkat
- Amylase Experiment Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanAmylase Experiment Lab ReportCHLOE IANNAH CALVADORESBelum ada peringkat
- 1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityDokumen13 halaman1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityShaniCoolestBelum ada peringkat
- Conclusion CPP Bubble Cap DistillationDokumen2 halamanConclusion CPP Bubble Cap DistillationAhmad KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Enzyme ConcentrationDokumen16 halamanEnzyme ConcentrationSya Subi100% (1)
- Post Lab 8 - Chem 8Dokumen3 halamanPost Lab 8 - Chem 8Christi ViajeBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Transition Temperature of Salt Hydrates: PrincipleDokumen2 halamanDetermination of Transition Temperature of Salt Hydrates: PrincipleDelin Shaji JohnBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Fruit JuicesDokumen8 halaman11 Fruit JuicesthangesspBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry ReportDokumen5 halamanChemistry ReportAngel Trisha Mae DelMundoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Dokumen7 halamanLab 4 Determination of An Equilibrium Constant 1Mohammad IzadiBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDokumen12 halamanReactions of Alkyl HalidesDarwin MangabatBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3Dokumen8 halamanEffect of PH On Enzyme Activity Lab 3api-340907023Belum ada peringkat
- WM Chemistry Ia Final Risma RemsudeenDokumen12 halamanWM Chemistry Ia Final Risma RemsudeenPriyanshi PeelwanBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Chem Lab Formula of A HydrateDokumen5 halamanAp Chem Lab Formula of A Hydrateapi-2598549080% (1)
- Lab 2Dokumen5 halamanLab 2tariqwaece100% (1)
- Respiration Lab ADADokumen7 halamanRespiration Lab ADAtimothy charlton0% (1)
- Vibration - Rotation Spectroscopy of HCL and DCLDokumen9 halamanVibration - Rotation Spectroscopy of HCL and DCLAngela LamasBelum ada peringkat
- Heat of SolutionDokumen1 halamanHeat of Solutionsimonatics08Belum ada peringkat
- Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDokumen3 halamanTitration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesMatthew Runyon50% (2)
- Science - Temperature of Sodium Thiosulphate and Rate of ReactionDokumen4 halamanScience - Temperature of Sodium Thiosulphate and Rate of ReactionSmartPurdyBelum ada peringkat
- Ex 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme ActivityDokumen2 halamanEx 4 Effect of PH On Enzyme ActivityRochel CaduyacBelum ada peringkat
- (Chem 17.1) FR ValerioDokumen5 halaman(Chem 17.1) FR ValerioRupert ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 2 - DilutionDokumen6 halamanExp 2 - DilutionSiti FatimahBelum ada peringkat
- Anal Chem 3 - Test 1-2016Dokumen4 halamanAnal Chem 3 - Test 1-2016Buhle BuhleBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3Dokumen14 halamanExperiment 3HafiniHambaliBelum ada peringkat
- Phase Diagram of A Three Component Liquid System: Experiment No. 5Dokumen7 halamanPhase Diagram of A Three Component Liquid System: Experiment No. 5Ellaine TejadaBelum ada peringkat
- Methods in Environmental Analysis III - ElectrogravimetryDokumen20 halamanMethods in Environmental Analysis III - ElectrogravimetryseyseaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 11Dokumen3 halamanLab Report 11PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Chem. 14.1 - Expt. 9 Chem Lab Report - Chemical EquilibriumDokumen3 halamanChem. 14.1 - Expt. 9 Chem Lab Report - Chemical EquilibriumRomi Necq S. Abuel40% (5)
- Exp 3Dokumen3 halamanExp 3Crystal VangelineBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of Chemical EquilibriumDokumen3 halamanA Study of Chemical EquilibriumMike ArangoBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument Panel - Standard: 1988 Toyota CelicaDokumen26 halamanInstrument Panel - Standard: 1988 Toyota CelicaToua Yaj100% (1)
- US Hex Bolt SizesDokumen2 halamanUS Hex Bolt SizesYana Jarang OlBelum ada peringkat
- Java SampleExamQuestionsDokumen18 halamanJava SampleExamQuestionshmasryBelum ada peringkat
- Metco 16C 10-040Dokumen8 halamanMetco 16C 10-040JSH100Belum ada peringkat
- First-Man-Up User ManualDokumen24 halamanFirst-Man-Up User ManualJoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- Brickwork ApparatusDokumen4 halamanBrickwork ApparatusRoslie AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- OK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFDokumen2 halamanOK Flux 231 (F7AZ-EL12) PDFborovniskiBelum ada peringkat
- Dse5510 Installation InstDokumen2 halamanDse5510 Installation Instricardo_dionisi2700Belum ada peringkat
- Meinberg ManualDokumen214 halamanMeinberg ManualLeonard NicolaeBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Engineering Jobs in Bangladesh - Careerjet - Com.bdDokumen4 halamanEnvironmental Engineering Jobs in Bangladesh - Careerjet - Com.bdamrin jannatBelum ada peringkat
- TSA Surface Preparation and ApplicationDokumen7 halamanTSA Surface Preparation and ApplicationMythri Metallizing Pvt Ltd Projects100% (1)
- Hot Water Recirculation PumpsDokumen22 halamanHot Water Recirculation Pumpsniaz kilamBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Condenser Eng2Dokumen5 halamanSurface Condenser Eng2MuhammadFikriBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Indian Near Surface Geophysics BrochureDokumen4 halaman1st Indian Near Surface Geophysics BrochureAdarsh TanejaBelum ada peringkat
- Nitrogen Purge Manifold For C2H2Dokumen3 halamanNitrogen Purge Manifold For C2H2Abdullah FazilBelum ada peringkat
- IA SeriesDokumen20 halamanIA Seriessina20795Belum ada peringkat
- BX-74 / BX-78: Sliding Gate Operator BX SeriesDokumen24 halamanBX-74 / BX-78: Sliding Gate Operator BX SeriesStefce PetrovBelum ada peringkat
- WS500 Operator WorkstationDokumen2 halamanWS500 Operator WorkstationNayants GuzmánBelum ada peringkat
- Below Which Not More Than 5 Percent of The Test Results Are Expected To Fall"Dokumen13 halamanBelow Which Not More Than 5 Percent of The Test Results Are Expected To Fall"shravan iitmBelum ada peringkat
- A Research Paper On Design and Analysis of Shaftless Steam TurbineDokumen5 halamanA Research Paper On Design and Analysis of Shaftless Steam TurbineEditor IJTSRDBelum ada peringkat
- 9.16. Prepare A Plot of Work Per Pound Mole Versus The Pressue Ratio PDokumen6 halaman9.16. Prepare A Plot of Work Per Pound Mole Versus The Pressue Ratio PttussenoBelum ada peringkat
- 592-A2GA DesbloqueadoDokumen27 halaman592-A2GA DesbloqueadoVicktor GranadosBelum ada peringkat
- Msi ms-7222 Rev 3.0 SCH PDFDokumen30 halamanMsi ms-7222 Rev 3.0 SCH PDFRodney RibeiroBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Electrical LayoutDokumen1 halamanSample Electrical LayoutBentesais Bente UnoBelum ada peringkat
- Hayward Super II Pump Model SP3005X7 ManualDokumen14 halamanHayward Super II Pump Model SP3005X7 ManualhsmerkelBelum ada peringkat
- D-Link DI-524 ManualDokumen92 halamanD-Link DI-524 ManualhadzicinetBelum ada peringkat
- Invalid Keyword Argument Python - December 25 2017Dokumen3 halamanInvalid Keyword Argument Python - December 25 2017Kaleab TekleBelum ada peringkat
- Recommendation Handling of Norit GL 50Dokumen9 halamanRecommendation Handling of Norit GL 50Mátyás DalnokiBelum ada peringkat
- Acidizing TreatmentsDokumen93 halamanAcidizing TreatmentsPeña Lucia100% (2)
- DP Chipset 15045 DriversDokumen592 halamanDP Chipset 15045 DriversRajesh1146Belum ada peringkat