Test Bank Chapter 21
Diunggah oleh
anonymousHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Test Bank Chapter 21
Diunggah oleh
anonymousHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
CHAPTER 21
Conceptual Questions C1. In an RLC circuit, the maximum current is 1 amp. What is the average current? a. 2 A b. (1 / 2 ) A c. (1/2) A d. None of the above. C2. In an RC circuit, which of the following is a possible phase angle? a. 45 b. 45 c. 135 d. 135 C3. In a 60-Hz RLC circuit, the phase angle is positive. The values of the resistance, inductance, and the capacitance are now doubled. Which of the following is now true about the phase angle? a. It is still positive. b. It could be zero. c. It will be negative. d. It could be positive, negative, or zero, but it cannot be greater than its original value. C4. A monochromatic light ave in vacuum has !re"uenc# f$ and avelength $. %hich o! the !ollo ing are also possible !re"uenc# and avelength combinations !or a monochromatic light ave in vacuum& C a.2f$, 2$ b. f$/2, $/2 c. 2f$, $/2 d. 'one o! the above are possible. C(. An RLC circuit has resistance R$, inductance L$, and capacitance C$. I! the resistance value is no doubled, hich values o! inductance and capacitance ill result in the same resonant !re"uenc# as be!ore. C a. 2L$, 2C$ b. L$/2, C$/2 c. 2L$, C$/2 d. 2L$, C$
103
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 21.1 Resistors in an AC Circuit 1. What is the effective (rms) current value for an AC current with an amplitude of 10 A? a. 28 A b. 3.1 A c. 7.1 A d. 14 A 2. In an AC series circuit, the current in a pure resistor differs in phase with the applied voltage by what angle? a. zero b. 45 c. 90 d. 180 3. The rate of heat dissipation in an AC circuit with resistance, R, and effective current, Irms, is given by which of the following? a. 0.5 (Irms)2R b. (Irms)2R c. 2.0 (Irms)2R d. 4.0 (Irms)2R 4. An AC voltage source, with a peak output of 200 V, is connected to a 50- resistor. What is the effective (or rms) current in the circuit? a. 2.8 A b. 4.0 A c. 5.6 A d. 2.0 A 5. An AC voltage source, with a peak output of 200 V, is connected to a 50- resistor. What is the rate of energy dissipated due to heat in the resistor? a. 200 W b. 400 W c. 566 W d. 800 W
104
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 6. The rms current is equal to the direct current that: a. produces the same average voltage across a resistor as in an AC circuit. b. dissipates an equal amount of energy in a resistor at the same rate as in an AC circuit. c. provides the same average current in a resistor as in an AC circuit. d. results in the same peak power in a resistor as in an AC circuit. 7. An AC voltage source, with a peak output of 120 V, results in dissipation of energy in a resistor at rate of 100 W. What is the value of the resistance? a. 144 b. 120 c. 100 d. 72 8. The peak voltage of an AC source is 200 V. What is the rms voltage? a. 282 V b. 200 V c. 141 V d. 100 V 9. In the typical household AC voltage of 120 V, what is the peak voltage? a. 240 V b. 170 V c. 120 V d. 85 V 21.2 Capacitors in an AC Circuit 10. The frequency in an AC series circuit is doubled. By what factor does this change the capacitive reactance? a. 1/2 b. 1/4 c. 2 d. 4 11. In an AC series circuit the capacitive reactance is 200 and frequency is 100 Hz. What is the capacitance? a. 3.2 F b. 6.28 F c. 8.0 F d. 50.0 F
105
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 12. A 12.0-F capacitor is connected to an AC source with an rms voltage of 120 V and a frequency of 60.0 Hz. What is the rms current in the capacitor? a. 1.41 A b. 0.768 A c. 0.543 A d. 0 A 13. When a 50-F capacitor is attached to an AC source, its capacitive reactance is 40 . If instead a 100-F capacitor is attached to the same source, what will be its capacitive reactance? a. 80 ) b. 57 ) c. 28 ) d. 20 ) 14. In a capa citor in an AC circuit, the voltag e * a. b. c. d. leads the curre nt b# +$ . lags the curre nt b# +$ . ma # lead or lag the curre nt dep e n di n g on the !re"u e n c #. is in pha s e ith ,$.,- o! the curre n t.
21.3 Inductors in an AC Circuit 15. In the inductor of a 60-Hz AC series circuit, the peak voltage precedes the peak current in each cycle by what time interval? a. 2.1 103 s b. 4.2 103 s c. 8.3 103 s d. 1.7 103 s 16. In an AC series circuit, the voltage in the inductor differs in phase with the voltage in the capacitor by what angle? a. zero b. 45 c. 90 d. 180 17. In an AC series circuit the inductive reactance is 50 and the frequency is 100 Hz. What is the inductance in the circuit? a. 80 mH b. 240 mH c. 500 mH d. 740 mH
106
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 18. The current in an inductor connected to an AC voltage source lags the voltage. This lag is caused by the: a. back emf in the coil. b. voltage across the coil. c. time required for electrical signals to travel through all the coils of an inductance. d. resistance of the coil. 21.4 The RLC Series Circuit 19. What is the impedance of an AC series circuit that is constructed of a 10.0- resistor along with 12.0 inductive reactance and 7.0 capacitive reactance? a. 37.0 b. 27.7 c. 27.1 d. 11.2 20. What is the phase angle of an AC series circuit that is constructed of a 10.0- resistor along with 12.00 inductive reactance and 7.00 capacitive reactance? a. 26.6 b. 18.4 c. 87.0 d. 63.4 21. An AC series circuit has 12.0 resistance, 15.00 inductive reactance and 10.00 capacitive reactance. If an effective (rms) emf of 120 V is applied, what is the effective (rms) current value? a. 5.31 A b. 9.23 A c. 10.8 A d. 26.0 A 22. Consider an AC series circuit containing a coil, capacitor and resistance. Tripling the frequency will change the inductive reactance by what factor? a. 1/3 b. 1.0 c. 1.73 d. 3.0
107
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 23. Consider an AC series circuit containing a coil, capacitor and resistance. Tripling the frequency will change the capacitive reactance by what factor? a. 1/3 b. 1.0 c. 1.73 d. 3.0 24. Consider an AC series circuit containing a coil, capacitor and resistance. Tripling the frequency will change the circuit's impedance by what factor? a. 1/3 b. 1.0 c. 3.0 d. Information is insufficient to determine answer. 25. A resistor and capacitor are connected in series with an applied AC voltage source. Separate voltmeter readings across the resistor and capacitor give values of 50 V and 75 V (rms), respectively. What is the effective (rms) voltage of the source? a. 25 V b. 63 V c. 90 V d. 125 V 26. A resistor, inductor, and capacitor are connected in series, each with effective (rms) voltage of 65 V, 140 V, and 80 V, respectively. What is the value of the effective (rms) voltage of the applied source in the circuit? a. 48 V b. 88 V c. 95 V d. 285 V 27. A resistor, inductor, and capacitor are connected in series, each with an effective (rms) voltage of 65 V, 140 V, and 80 V, respectively. What is the magnitude of the phase angle in this circuit? a. 22 b. 28 c. 37 d. 43 28. In an AC circuit, the ratio of average current to maximum current is: a. zero. b. 0.5. c. 0.707. d. 1.0.
108
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 29. A 50- resistor, a 0.1-H inductor, and a 10-F capacitor are connected in series to a 60-Hz source. The rms current in the circuit is 3 A. Find the rms voltage across the resistor, the inductor, and the capacitor. a. 150 V, 113 V, 796 V (all rms) b. 0.06 V, 80 V, 562 V (all rms) c. 150 V, 113 V, 562 V (all rms) d. 60 V, 80 V, 796 V (all rms) 30. A series circuit has equal values for resistance, capacitive reactance, and inductive reactance. The phase angle for this circuit is: a. 60. b. 60. c. 180. d. not given. 31. In an RLC series circuit the capacitive reactance is 24 . If the AC frequency doubles, what will be the resulting capacitive reactance? a. 24 b. 12 c. 48 d. Additional information is need to find the value. 32. In an RLC series circuit the phase angle between the current and voltages is 30. If the AC frequency doubles, what is the resulting phase angle? a. 30 b. more than 30 c. less than 30 d. Additional information is needed to reach a determination. 33. In an RLC series circuit, if the AC frequency is increased to a very large value, what value does the phase angle between the current and voltage approach? a. 90 b. 0 c. 90 d. 45 34 In an RLC series circuit, if the AC frequency is decreased to a very small value, what value does the phase angle between the current and voltage approach? a. 90 b. 0 c. 90 d. 45
109
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
21.5 Power in an AC Circuit 35. An AC series circuit has 12.0 resistance, 15.00 inductive reactance and 10.00 capacitive reactance. If an effective (rms) emf of 120 V is applied, what is the power output? a. 1 540 W b. 1 300 W c. 1 160 W d. 1 020 W 36. The power dissipated in an AC series circuit increases as the phase angle approaches what value? a. zero b. 45 c. 90 d. 180 37. The power factor in an AC series circuit is equal to which of the following ratios? a. resistance to inductive reactance b. capacitive reactance to inductive reactance c. inductive reactance to capacitive reactance d. resistance to impedance 38. A resistor, inductor and capacitor are connected in series, each with effective (rms) voltage of 65 V, 140 V and 80 V, respectively. If the resistor is rated at 24 , what is the average power dissipated in the circuit? a. 88 W b. 176 W c. 238 W d. 323 W 39. What is the average power dissipation in a series RC circuit if R = 5.00 k, C = 2.00 F, and V = (170 V) cos 300t? a. 2.60 W b. 2.74 W c. 28.2 W d. 157 W
110
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 40. A 200- resistor is connected in series with a 10- F capacitor and a 60-Hz, 120-V (rms) line voltage. If electrical energy costs 5.0 per kWh, how much does it cost to leave this circuit connected for 24 hours? a. 62 b. 31 c. 5.2 d. 3.1 21.6 Resonance in a Series RLC Circuit 41. Resonance occurs in an AC series circuit when which of the following conditions is met? a. resistance equals capacitive reactance b. resistance equals inductive reactance c. capacitive reactance equals inductive reactance d. capacitive reactance equals zero 42. An AC series circuit contains a resistor of 20 , a capacitor of 0.75 F and an inductor of 120 mH. What frequency should be used to create a resonance condition in the circuit? a. 160 Hz b. 320 Hz c. 640 Hz d. 530 Hz 43. A series RLC AC circuit is at resonance. It contains a resistor of 30 , a capacitor of 0.35 F and an inductor of 90 mH. If an effective (rms) voltage of 150 V is applied, what is the effective (rms) current when the circuit is in resonance? a. 3.3 A b. 5.0 A c. 9.4 A d. 16.1 A 44. An AC series circuit contains a resistor of 20 , an inductor of 30 mH and a variable capacitor. If the frequency of the applied voltage is 500 Hz, to what setting should the capacitor be set if resonance is achieved? a. 0.8 F b. 1.6 F c. 2.4 F d. 3.4 F
111
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 45. A series RLC circuit in a radio is in resonance with AM 600 kHz. If the radio station is changed to AM 1 200 kHz, by what factor must the capacitance be multiplied to again achieve resonance? a. 4 b. 2 c. 1/2 d. 1/4 46. Find the resonant frequency for a series RLC circuit where R = 20.0 , C = 10.0 F, and L = 4.0 mH. a. 507 Hz b. 796 Hz c. 1.59 kHz d. 5.00 kHz 47. What is the average power dissipation in an RLC series circuit in which R = 100 , L = 0.1 H, and C = 10 F driven at resonance by a 100-V (rms) source? a. 100 W b. 500 W c. 1 000 W d. 2 W 48. An AM radio tuning circuit has a coil with an inductance of 6.00 mH and a capacitor set at 7.50 106 F. What frequency will it detect? a. 550 kHz b. 750 kHz c. 1 060 kHz d. 1 520 kHz 49. An FM radio tuning circuit has a coil with an inductance of 0.003 0 mH. What is the value of the capacitance if the set is tuned to 98 MHz? a. 1.8 106 F b. 12 106 F c. 0.98 106 F d. 0.88 106 F 50. Which of the following combinations of circuit components can be used to make a tuner for a radio, to select the desired frequency? a. fixed inductor, variable resistor b. fixed resistor, variable inductor c. fixed inductor, variable capacitor d. fixed capacitor, variable resistor
112
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
51. When an RLC series circuit is in resonance, its impedance is: a. zero. b. equal to its resistance. c. a maximum. d. /2 . 52. A series RLC circuit has a inductive reactance of 4 and a capacitive reactance of . By what factor should the AC frequency be changed to put this circuit into resonance? a. 4 b. c. d. This circuit cannot be made to achieve resonance. 21.7 The Transformer 53. The primary winding of an electric train transformer has 400 turns, and the secondary has 50. If the input voltage is 120 V(rms), what is the output voltage? a. 480 V b. 60 V c. 15 V d. 10 V 54. A transformer consists of a 500-turn primary coil and a 2 000-turn secondary coil. If the current in the secondary is 3.00 A, what is the primary current? a. 0.750 A b. 1.33 A c. 12.0 A d. 48.0 A 55. An AC power generator produces 50 A (rms) at 3 600 V. The voltage is stepped up to 100 000 V by an ideal transformer, and the energy transmitted through a long-distance power line with a total resistance of 100 . What is the rms current in the long-distance line? a. 1.0 A b. 1.8 A c. 24 A d. 1 000 A
113
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 56. An AC power generator produces 25 A (rms) at 3 600 V. The energy is transmitted through a long-distance power line, which has a total resistance of 100 . What percentage of the power delivered by the generator is dissipated as heat in the long-distance line if a step-up transformer is not used? a. 0.09% b. 1.8% c. 32% d. 69% 57. A transformer is to be designed to increase the 30-kV (rms) output of a generator to the transmission line voltage of 345 kV (rms). If the primary winding has 80 turns, how many turns must the secondary have? a. 6 b. 70 c. 920 d. 9 200 58. An ideal transformer is one that: a. has a turn ratio, N2/N1, equal to 1. b. works with direct current. c. experiences no power loss. d. has an output frequency of 60 Hz. 21.8 Maxwells Predictions 21.9 Hertzs Confirmation of Maxwells Predictions 59. Which one of the following scientists made the theoretical prediction that electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum at the speed of light? a. Hertz b. Faraday c. Maxwell d. Lenz 60. Which one of the following scientists first built and operated devices that could emit and detect man-made electromagnetic radiation? a. Hertz b. Ampere c. Maxwell d. Lenz
114
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 61. Maxwell developed his theory of electromagnetism by combining previous discoveries. He added his own original hypothesis that: a. electric charges produce electric fields. b. moving electric charges produce magnetic fields. c. changing electric fields produce magnetic fields. d. changing magnetic fields produce electric fields. 62. Maxwell guessed that visible light was an electromagnetic wave because of its: a. frequency. b. wavelength. c. speed. d. energy. 21.10 Production of Electromagnetic Waves by an Antenna 21.11 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 63. An electromagnetic wave is made up of which of the following oscillating quantities? a. electrons only b. electric fields only c. magnetic fields only d. electric and magnetic fields 64. An electromagnetic wave with a peak electric field component of 1.2 102 N/C has what associated peak magnetic field value? (0 = 8.85 1012 C2/Nm2, 0 = 4 107 Tm/A and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 4.0 107 T b. 3.6 1010 T c. 2.5 106 T d. 2.8 1011 T 65. Which condition of motion must be met with regard to a charged particle if it is in the process of emitting electromagnetic radiation? a. moves at constant velocity b. accelerates c. moves at the speed of light d. moves parallel to a uniform magnetic field
115
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
66. The electric field, E , in an electromagnetic wave is oriented in what direction with respect to its associated magnetic field, B ?
a. b. c. d. E E E E parallel to B anti-parallel to B perpendicular to B at a 45 angle to B
67. An electromagnetic wave with a peak magnetic field component of 1.5 107 T has an associated peak electric field component of what value? ( 0 = 4 107 Tm/A, 0 = 8.85 1012 C2/Nm2 and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 0.50 1015 N/C b. 2.00 105 N/C c. 2.20 104 N/C d. 45 N/C 68. An electromagnetic wave with a peak magnetic field component of 1.5 107 T carries what average power per unit area? (0 = 4 107 Tm/A, 0 = 8.85 1012 C2/Nm2 and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 12 W/m2 b. 2.7 W/m2 c. 3.0 W/m2 d. 1.3 W/m2 69. A radio wave transmits 1.2 W/m 2 average power per unit area. What is the peak value of the associated magnetic field? (0 = 4 107 Tm/A and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 1.0 107 T b. 8.4 103 T c. 1.2 T d. 30 T 70. How is the direction of propagation of an electromagnetic wave oriented relative to the associated E and B fields? a. parallel to both E and B b. perpendicular to both E and B c. parallel to E , perpendicular to B d. parallel to B , perpendicular to E
116
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 71. What is the maximum value of the electric field E at 1.0 m from a 100-W light bulb radiating in all directions? (0 = 4 107 Tm/A, c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 77 V/m b. 2 000 V/m c. 4 000 V/m d. 6 000 V/m 72. Determine the amount of energy carried in l.0 m of a 3.5-mW He-Ne laser beam if the cross-sectional area of the beam is 5.0 106 m2. a. 0.012 J b. 4.1 108 J c. 1.2 1011 J d. 1.0 J 73. The Earth is 1.49 1011 m from the Sun. If the solar radiation at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is 1 340 W/m2, what is the total power output of the Sun? a. 7.48 1027 W b. 2.34 1030 W c. 6.62 1026 W d. 3.74 1026 W 74. If the radiant energy from the Sun comes in as a plane EM wave of intensity 1 340 W/m 2, calculate the peak values of E and B. (0 = 4 107 Tm/A) a. 330 V/m, 3.0 104 T b. 1 010 V/m, 3.35 106 T c. 330 V/m, 3.35 106 T d. 1 010 V/m, 3.0 104 T 75. Peak values for a neodymium-glass laser are 600 J for 1 nanosecond . If the cross-section of the laser beam is 1 cm2, what are the maximum values of E and B? (0 = 4 107 Tm/A, c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 2 109 V/m, 2 T b. 4 108 V/m, 7 T c. 2 109 V/m, 7 T d. 4 108 V/m, 2 T 76. A solar cell has a light-gathering area of 10 cm2 and produces 0.20 A at 0.80 V (dc) when illuminated with sunlight of intensity 1 000 W/m2. What is the efficiency of the solar cell? a. 16% b. 7% c. 23% d. 4%
117
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 21.12 The Spectrum of Electromagnetic Waves 77. In order of increasing frequency, which of the following is correct? a. visible, radio, ultraviolet and x-ray b. infrared, visible, ultraviolet and gamma c. visible, gamma, ultraviolet and x-ray d. infrared, x-ray, visible and gamma 78. A radar pulse returns 3.0 104 seconds after it is sent out, having been reflected by an object. What is the distance between the radar antenna and the object? ( c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 9.0 104 m b. 4.5 104 m c. 6.0 104 m d. 1.0 104 m 79. In order to keep its food hot, a restaurant will place it under which type of lamp? a. infrared b. visible light c. ultraviolet d. x-ray 80. Glass panes are opaque to a certain type of radiation, which passes through quartz. What type of radiation is it? This radiation is important in ozone layer reactions. a. microwave b. gamma c. x-ray d. ultraviolet 81. A radio wave signal, which transmits at a frequency of 7.20 MHz, has what wavelength? ( c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 41.7 m b. 4.17 m c. 28.8 m d. 2.4 102 m 82. A radar pulse sent out to an airplane at a distance of 20.0 km will return as an echo to the source in what time interval? (c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 33.3 106 s b. 66.7 106 s c. 133 106 s d. 0.033 3 106 s
118
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 83. The human eye is sensitive to light with wavelength down to 390 nm. What is the frequency of radiation at this wavelength? (1 nm = 109 m and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 1.8 108 Hz b. 8.5 108 Hz c. 1.1 1011 Hz d. 7.7 1014 Hz 84. An ultraviolet light wave has a wavelength of 300 nm and speed of 2.1 108 m/s through a transparent medium. What is the frequency of this wave in the medium? (1 nm = 10 9 m and c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 6.3 102 Hz b. 9.0 102 Hz c. 7.0 1014 Hz d. 10 1014 Hz 85. Microwave radiation is useful in which of the following? a. sending phone messages b. cooking food c. aircraft navigation d. All of the above are valid choices. 86. Temperature variation of different parts of a persons body can be detected by analyzing the emission pattern of which type of electromagnetic radiation? a. microwave b. infrared c. ultraviolet d. x-rays 87. Of the various types of electromagnetic radiation, which is the most penetrating through all forms of matter? a. infrared b. gamma c. visible light d. ultraviolet 88. What value of inductance should be used in a series circuit with a capacitor of 1.8 103 F when designed to radiate a wavelength of 35 m? ( c = 3.00 108 m/s) a. 3.8 mH b. 2.6 102 mH c. 3.8 103 mH d. 1.9 104 mH
119
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 89. As an electromagnetic wave travels through free space, its speed can be increased by: a. increasing its frequency. b. increasing its energy only. c. increasing both its energy and momentum. d. None of the above will increase its speed. 90. An object that is giving off only infrared electromagnetic waves is giving off heat through: a. convection. b. conduction. c. radiation. d. visible light. 91. The electromagnetic radiation that causes tanning: a. can produce cancer. b. rarely passes through glass windows. c. is absorbed by ozone. d. is all of the above. 92. What is the wavelength of 100-MHz television EM waves? ( c = 3 108 m/s) a. 0.3 cm b. 3 m c. 9 km d. 10 m 93. Find the frequency of x-rays of wavelength 1010 m. (c = 3 108 m/s) a. 3 1018 Hz b. 3 1016 Hz c. 6 109 Hz d. 3 108 Hz 21.13 The Doppler Effect for Electromagnetic Waves 94. In the Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves, which of the following gives the greatest shift in frequency? a. the source moving toward the non-moving observer at speed v b. the observer moving toward the non-moving source at speed v c. the source moving toward the approaching observer, both at speed v/2 d. All of the above give the same shift.
120
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 95. The Doppler shift for electromagnetic radiation from distant galaxies moving away from the observer is called a: a. red shift. b. blue shift. c. black shift. d. vacuum shift. 96. An observer is moving in space toward a distant star at 100 km/s while the star is moving toward the observer at 200 km/s; the relative velocity being 300 km/s of approach. What relative change in frequency of the light from the star as seen by the observer? (The speed of light in space is 3.00 105 km/s). a. 0.10% increase b. 0.10% decrease c. 0.067% increase d. 0.033% decrease
121
Chapter 21, Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
CHAPTER 21 - ANSWERS
# C1. C2. C3. C4. C5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Ans D B A C C C A B A B B D C B A C C D B B D A A D A B D A D C B D A A Difficulty 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 3 2 3 ` # 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. Ans D B B A C D A D B A D C D B D D B A B D C B B C C B D C C C A C C D Difficulty 2 2 3 2 2 2 1 2 2 3 3 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 # 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. Ans A B C D B A B A C D B C A B B A D A C D C D B B D D C D B A D A A Difficulty 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 3 2 2 3 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
122
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- AC Circuits Fundamentals QuizDokumen4 halamanAC Circuits Fundamentals QuizCris Diane G. DatingginooBelum ada peringkat
- AC EXERCISE KEY POINTSDokumen3 halamanAC EXERCISE KEY POINTSsumitBelum ada peringkat
- Circuits 2Dokumen3 halamanCircuits 2lesterPECE100% (5)
- Q&A 2 AC Fundamental, Resonance, Transient CKT Q&ADokumen20 halamanQ&A 2 AC Fundamental, Resonance, Transient CKT Q&Asaravanan chennanBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial - 4: Practice ProblemsDokumen4 halamanTutorial - 4: Practice ProblemsParthaMoulikBelum ada peringkat
- AC Circuit 1 (Single-Phase)Dokumen2 halamanAC Circuit 1 (Single-Phase)marlon desaculaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple ChoiceDokumen4 halamanPractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple Choiceapi-127299018Belum ada peringkat
- Multiple choice questions on AC circuits and phasorsDokumen4 halamanMultiple choice questions on AC circuits and phasorsKate Rose Santos0% (1)
- Ac Final Exam QuestionnaireDokumen4 halamanAc Final Exam QuestionnaireKate Rose SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Review Questions Review QuestionsDokumen31 halamanReview Questions Review QuestionssrinivasBelum ada peringkat
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDokumen19 halamanPhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 7Dokumen30 halamanCH 7terasaini77Belum ada peringkat
- Class Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDokumen41 halamanClass Xii - CH-7 Alternating Current (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270sBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Circuits Ii Direction: Read Each Item Carefully and Chose The BEST Answer From The Given Choices. Write YourDokumen4 halamanElectrical Circuits Ii Direction: Read Each Item Carefully and Chose The BEST Answer From The Given Choices. Write YourJeterine AriasBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Dokumen12 halamanFinal Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Ahyad Arif Abdul Rahman100% (2)
- Physics II Problems PDFDokumen1 halamanPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSBelum ada peringkat
- Compilations of Problems in Gibilisco 2Dokumen5 halamanCompilations of Problems in Gibilisco 2Michael ObcemeaBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer Questions in AC Systems: N Order To Tune A Parallel Resonant Circuit To A Lower Frequency, The Capacitance MustDokumen4 halamanReviewer Questions in AC Systems: N Order To Tune A Parallel Resonant Circuit To A Lower Frequency, The Capacitance MustRonald James DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Physics II Problems PDFDokumen1 halamanPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits MCQs and SolutionsDokumen7 halamanPractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits MCQs and SolutionsGrace ShykolBelum ada peringkat
- Element 3 AdditionalDokumen2 halamanElement 3 Additionalpochid843Belum ada peringkat
- Alternating CurrentDokumen4 halamanAlternating CurrentVallery Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 6454 Topper 21 129 510 4 141 Alternating Current Up201612091917 1481291232 6512Dokumen49 halaman6454 Topper 21 129 510 4 141 Alternating Current Up201612091917 1481291232 6512nrulz8503Belum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Dokumen10 halamanFinal Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2RaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Gibilisco Chapter Test (Chap 9-18)Dokumen9 halamanGibilisco Chapter Test (Chap 9-18)Iahhel FactoranBelum ada peringkat
- Acckt Single PhaseDokumen6 halamanAcckt Single Phaseken peligrinoBelum ada peringkat
- Scoe - Bee - Unit 3 MCQDokumen5 halamanScoe - Bee - Unit 3 MCQnakul kamatkarBelum ada peringkat
- Module - Ac CircuitsDokumen6 halamanModule - Ac CircuitsFalgun GeraBelum ada peringkat
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test BankDokumen13 halamanWolfson Eup3 Ch28 Test Bankifghelpdesk0% (1)
- Acces Point - Ee Refresher 4Dokumen13 halamanAcces Point - Ee Refresher 4christinesarah0925Belum ada peringkat
- Principles of ElectricityDokumen6 halamanPrinciples of ElectricityAlfredo CondeBelum ada peringkat
- Alternating CurrentDokumen6 halamanAlternating CurrentGagan .SBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Board Exam ElexDokumen10 halamanPre Board Exam Elexart16marasiganBelum ada peringkat
- Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 7Dokumen9 halamanNcert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 7getthef.ckfromshivashishBelum ada peringkat
- Ee ProbsDokumen3 halamanEe ProbsChristine Baldemoro Alforte75% (4)
- More Board Exam Questions on Power Electronics ReviewerDokumen9 halamanMore Board Exam Questions on Power Electronics ReviewerKristiqn KolevBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical Engineering Problem Sheet 2Dokumen5 halamanBasic Electrical Engineering Problem Sheet 2ud54Belum ada peringkat
- EASA Module 3i MCQ (114 Questions)Dokumen46 halamanEASA Module 3i MCQ (114 Questions)Junaid YounusBelum ada peringkat
- Physics II Problems PDFDokumen1 halamanPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSBelum ada peringkat
- Alternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01Dokumen5 halamanAlternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01daksh singhBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics RefresherDokumen2 halamanElectronics RefresherPaolo Steven PolintanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen2 halamanChapter 7Monisha RBelum ada peringkat
- AISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Dokumen4 halamanAISSCE ASGNMT CHapter 7 Class 12Sajid KhanBelum ada peringkat
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokumen8 halamanThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical circuit quiz with answersDokumen7 halamanElectrical circuit quiz with answersivygrace gabestpaelmaoBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Ac XiiDokumen4 halamanWorksheet Ac XiiYug GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- AC CIRCUITS QUIZDokumen2 halamanAC CIRCUITS QUIZNaqash RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- AC Fundamentals Part 1Dokumen8 halamanAC Fundamentals Part 1KhatelynBelum ada peringkat
- Mock Electrical Engineer ExamDokumen21 halamanMock Electrical Engineer ExamJohn MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Ang Gwapo Ko Naman Shettt Pahingi NG Reviwer1122Dokumen21 halamanAng Gwapo Ko Naman Shettt Pahingi NG Reviwer1122John MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Refresher Electronics1Dokumen27 halamanRefresher Electronics1Lanbert FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Alternating Emf and CurrentDokumen4 halamanAlternating Emf and Currentpraveen godaraBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Sample Problems 06Dokumen5 halamanElectronics Sample Problems 06Genesis PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Kiet BeeDokumen4 halamanKiet BeeGAURAV GUPTABelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 PDFDokumen2 halamanTutorial 1 PDFSYAFIQAH ISMAIL100% (1)
- QuizzesDokumen3 halamanQuizzesFrizz CruzBelum ada peringkat
- EE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsDokumen4 halamanEE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsAmit DipankarBelum ada peringkat
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Dari EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Dari EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Belum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics NotesDokumen100 halamanPediatrics Notessanflash100% (1)
- Peds NotesDokumen101 halamanPeds Notesrvar839100% (1)
- RenalDokumen4 halamanRenalanonymousBelum ada peringkat
- Acland TestisDokumen1 halamanAcland TestisanonymousBelum ada peringkat
- Selected ProblemsDokumen45 halamanSelected ProblemsanonymousBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Atoms, MoleculesDokumen27 halamanChapter 2 Atoms, Moleculesanonymous0% (1)
- CH 02 TestDokumen15 halamanCH 02 TestanonymousBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Chemical FoundationsDokumen28 halamanChapter 1 Chemical Foundationsanonymous100% (1)
- Module 1.3 - Applications of IntegrationDokumen4 halamanModule 1.3 - Applications of IntegrationJ KimBelum ada peringkat
- Holip 201207110500417645Dokumen105 halamanHolip 201207110500417645Jose Sanchez Palma100% (2)
- INTERNDokumen21 halamanINTERNSahil Shah100% (1)
- Thermon HPTDokumen2 halamanThermon HPTParag B HatwarBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Formulas and ConceptsDokumen9 halamanPhysics Formulas and ConceptsRedso LallBelum ada peringkat
- Air Filtration Technical ReferenceDokumen15 halamanAir Filtration Technical ReferenceMuhammad SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report Name-Shahil Kumar Singh REG NO - 19110126051 Roll No - 19eee43 Branch - Eee College - Bce BakhtiyarpurDokumen20 halamanProject Report Name-Shahil Kumar Singh REG NO - 19110126051 Roll No - 19eee43 Branch - Eee College - Bce BakhtiyarpurShahilsingh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Product Data Sheet: Acti 9 Idpna Vigi - Rcbo - 1P+N - 16A - C Curve - 4500A - 30ma - Type AcDokumen3 halamanProduct Data Sheet: Acti 9 Idpna Vigi - Rcbo - 1P+N - 16A - C Curve - 4500A - 30ma - Type AcFede MysynaBelum ada peringkat
- Y2 Module 2 Performing Mensuration and CalculationDokumen42 halamanY2 Module 2 Performing Mensuration and CalculationJasmine Gillado100% (1)
- anualCMOSMixed SignalCircuitDesign2ndEdJacobBaker PDFDokumen374 halamananualCMOSMixed SignalCircuitDesign2ndEdJacobBaker PDFMonideepika SBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0378779622008513 MainDokumen8 halaman1 s2.0 S0378779622008513 MainMansoor AsifBelum ada peringkat
- Kompresibilitas OkDokumen9 halamanKompresibilitas OkFeby RochmaniahBelum ada peringkat
- Capacitor Bank PDFDokumen2 halamanCapacitor Bank PDFsapnaadiyodiBelum ada peringkat
- Genset 550 Kva CatalogueDokumen4 halamanGenset 550 Kva CatalogueFirdasu CahyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Black Hole Physics PDFDokumen505 halamanIntroduction To Black Hole Physics PDFJuan Lombardero100% (5)
- Course: Applied Thermodynamics Course Code: 10ME43 Course Type: Core Sem: 4Dokumen3 halamanCourse: Applied Thermodynamics Course Code: 10ME43 Course Type: Core Sem: 4Prashanth JagadeeshBelum ada peringkat
- Sigma 2 and Sigma 2 T Series Operation and Maintenance ManualDokumen27 halamanSigma 2 and Sigma 2 T Series Operation and Maintenance ManualMedamriBelum ada peringkat
- Amber Gwh12ydDokumen99 halamanAmber Gwh12ydVasil GosevBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Analog Converters CAL30IG and CAL35IG Technical SpecificationsDokumen2 halamanUniversal Analog Converters CAL30IG and CAL35IG Technical SpecificationsMargaret DaughertyBelum ada peringkat
- HW1 Solution PDFDokumen6 halamanHW1 Solution PDFZuhair AliBelum ada peringkat
- SEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Components DocumentDokumen3 halamanSEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Components DocumentJohan ChaconBelum ada peringkat
- Irrigation System Running On Solar Power HAMMAD BHAIDokumen9 halamanIrrigation System Running On Solar Power HAMMAD BHAIRahulBelum ada peringkat
- Unit III (Part III)Dokumen14 halamanUnit III (Part III)YUSRA MERAJBelum ada peringkat
- The Plasma-Sheath Boundary Region - R.N.franklinDokumen13 halamanThe Plasma-Sheath Boundary Region - R.N.franklingkwltnaosBelum ada peringkat
- PAC E100S English Manual (20130502) SDokumen114 halamanPAC E100S English Manual (20130502) SAmílcar Duarte0% (1)
- 1.digital Thermometer Flexible Tip 2020Dokumen1 halaman1.digital Thermometer Flexible Tip 2020William GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
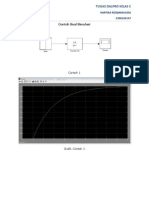
- Tugas Dalpro TikaDokumen6 halamanTugas Dalpro TikaKartika RizqimaulidaBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Assignment 3Dokumen4 halamanEnergy Assignment 3aukitBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetostriction MichelsonDokumen6 halamanMagnetostriction MichelsonOktafiani Nurita SariBelum ada peringkat
- pH/EC meter manualDokumen2 halamanpH/EC meter manualMuhammad Noman MehboobBelum ada peringkat