1.pecutan Elektromagnet
Diunggah oleh
Anna Latifah CammryJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1.pecutan Elektromagnet
Diunggah oleh
Anna Latifah CammryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
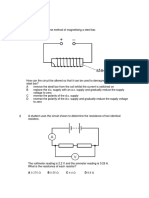
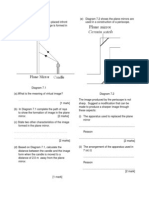
NAME: LAtih Tubi 1: Electromagnetic Induction 1. Diagram 2.
1 shows a bar magnet before and when is pushed into a solenoid.
(a) Name the science phenomenon involved in Diagram 2.1? [1 marks] (b) State the
[1 marks] (c) Diagram 2.2 shows a magnet bar is pulling away from inside a solenoid.On Diagram 2.2 (i) mark the direction of the current flow in the circuit [2 marks] (ii) by using an arrow mark the compass direction on the compass above [1 marks]
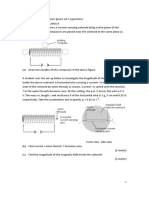
2. Diagram 8.1 and 8.2 show electrical motor used to lift up pails of cement to top floor on construction building.
(a) What is meant by catapult field? ......................................................................................................................................... [1 marks] (b) (i) In the space below, draw the pattern of catapult field of Diagram 8.1. [2 marks]
(ii) State the direction of rotation of the motor as shown in Diagram 8.1. ......... [1 marks] (c) Based on diagram 8.1 and 8.2 , (i) which motor is more suitable to be used by the construction workers to lift up the pails of cement? ................................................................................................................................................. [1 marks] (ii) Explain your answer in c(i). ................................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................................. [2 marks] (d) If the d.c power supply became weak, the construction workers have to use the a.c. supply. Explain the modifications that need to be done on the motor, so that the workers will be able to use it. . [2 marks] (e) The input power of the motor is 2000W. If the motor can lift up 10 kg cement to the height of 12 m in 1.4 s. Calculate the effiency of the motor.
[3 marks] 3. Diagram 3.1 shows a bar magnet being pushed into a solenoid at a speed of 2ms-1.
Diagram 3.1 (a) State the physical quantity that is represented by the deflection of the galvanometer. .[1 mark] (b) (i) State two differences that can be observed from diagram 3.1(a) and diagram 3.2(b). ..................................................................................................................................... .[2 marks] (ii) Based on your answer in 3(b)(i), explain why these differences occur? .................................................................................................................................... .[2 marks] (c) Name the physics law involved in 3 (b) (ii). .[1 marks]
4. (a) Diagram 6.1 shows a bar magnet being moved towards a solenoid. P and Q are the poles of the bar magnet. The direction of induced current produced and the poles of the solenoid are as shown in the diagram.
State the polarity of the poles of the bar magnet. P: Q: (b)The magnet is then moved away from the solenoid. This is as shown in diagram 6.2
[2 marks]
Magnet bar move away from solenoid Diagram 6.2
(i) Draw the direction of induced current,I and needle of galvanometer in diagram 6.2. [2 marks] (ii) State Lenzs Law .[1 marks] (iii) State two ways to increase the magnitude of the induced current 1 2.[2 marks] (d) Diagram 6.3 shows an experimental set-up to study several materials to be used as the core of an electromagnet.
(i) State the type of power supply that is suitable for this experiment ...[1 marks] (ii) Give one reason to justify your answer in (d)(i) ...[1 marks]
5. (a) State Flemings left hand rule.
[2 marks]
(b) From the aspect of the component and the working principle, state the difference between a D.C motor and an A.C dynamo. [3 marks] (c)
The magnetic flux, the current and the number of coils used in both the motors are the same. Compare the shape of the magnet used in the 2 motors.Compare the efficiency of the 2 motors. Correlate the shape of the magnet used with the efficiency and deduce a relevant physics concept. [5 marks] (d) James buys a new bigger fishing boat. When he transfers the motor from his previous fishing boat to the new boat, he finds that the power of the motor is low. But he has no more money to buy a new motor. He decides to modify the old motor by using new magnetic coil and replaced the permanent magnet with a electromagnet. Based on the 2 ideas of James, suggest modifications can be done by him to upgrade the power of the old motor. [10 marks]
6. Diagram 10.1 shows a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field and the direction of current flow is as shown.
(a) Based on diagram 10.1, (i) draw the resultant magnetic field when the current carrying conductor is placed in the permanent magnetic field. (ii) show the direction of the force on the current carrying conductor. (iii) in which direction - K, L, M and N will the conductor move? [5 marks] (b) Diagram 10.2 shows the position of a copper wire PQ when the switch is off. Diagram 10.3 and Diagram 10.4 show the positions of a copper wire PQ when the switch is on in various strength of magnetic field.
Based on Diagram 10.2, Diagram 10.3 and Diagram 10.4, (i) what happens to the copper wire PQ when the switch is turned on? (ii) compare the distance between the copper wire PQ and the plastic holder in Diagram 10.3 and Diagram 10.4. (iii) compare the strength of magnadur magnets in Diagram 10.3 and Diagram 10.4. (iv) relate the distance between the copper wire PQ and the plastic holder with the strength of the magnets. (v) hence, relate the force produced in the copper wire PQ with the the strength of magnets. [5 mark ]
(c) Diagram 10.5 shows the basic structure of a moving coil ammeter. Suggest modifications that can be made to the meter so that it has the following characteristics: (i) Uniform scale. (ii) High sensitivity. (iii) The pointer is easily returned to zero when there is no current flow. [10 marks ]
(d) Diagram 10.4 shows a moving coil ammeter
Explain how you would design a moving coil ammeter that can function better. In your explanation, emphasize the following aspects: (i) the sensitivity of the ammeter, (ii) the shape of the permanent magnet, (iii) the shape of the core, (iv) the type of the core material, (v) the type of the ammeter scale. [ 10 marks]
SKEMA JAWAPAN Modul Latih Tubi 1 Electromagnetic Induction
No 1(a) (b) c) Answer Electromagnetic induction North 1 1 Marks
2(a)
Catapult field is resultant magnetic field / combination/interactions of the magnetic field due to the current in the conductor and external magnetic field
b(i) 2
b(ii) c(i) c (ii)
Counter-clockwise Motor in diagram 8.2 -More number of coils in diagram 8.2 will increases the current flow. -Larger current flow will result in a large force , easy to carry the pail of cement Modification: Replace the split ring commutator with two slip ring Explanation Change dc to ac supply
1 1
2 Each slip ring is always contact with the same carbon brush, so when the direction of the current changes , the direction of the current in the coil dont change (e) Effiency of the motor Effiency of the motor = 42% TOTAL 3 (a) (b)(i) (b)(ii)
(c) Electromotive force // e.m.f.//induced current i- number of turns : 3.1 (a) < 3.1(b) ii-deflection of galvanometer : 3.1(a) < 3.1(b) - Rate of change of flux increase - Induce emf increases Faradays Law
x 100% x 100%
12 1 2 2 TOTAL 1 6 2
4(a)
P: North Q:South
(b)(i) 2
(b)(ii) (b)(iii)
(d)(i) (d)(ii)
The direction of the induced current in a solenoid is such that its magnetic effeft always opposes the change producing it. - stronger magnet -increase number of turn of the solenoid -increase the speed of movement Direct current Magnitude and direction of current will remain constant TOTAL
1 2 1 1 9
5 (a)
-When the first finger, second finger and the thumb are extended with an angle of90O to each other; -The first finger shows the direction of the magnetic field, the secondfinger show the current and then the thumb show the direction of force generated. D.C Motor Need power supply Consist a pair of split ring commutator Transform electrical energy into mechanical energy A.C Dynamo Need no power supply Consist a pair of slip ring commutator Transform mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(Sabah 2009) 2
(b)
The direction of forces Direction of current determine using FLeftHR determine using FRightHR - Planar surface magnet in figure (a) and concave surface magnet in figure (b) -Figure (b) has higher efficiency compare than figure (a) - Concave surface magnet produce radial magnetic field. - The direction of force generated always act along the tangent of a circle. This produces smooth rotation and waste no energy - Radial magnetic flux always alters the direction of force generated to ensure smooth rotation.
Aspect Increase the number of turn of the coil Increase the length of the coil Using thicker copper wire Increase current Placed concave iron core at both side of cylinder core(replaced permanent magnet) Using concave surface soft iron
Modification - Increase the total force generated - Increase strength of electromagnet - Increase the total force generated - Increase strength of electromagnet Reduce resistance to increase current - Increase the total force generated - Increase strength of electromagnet Save cost 10
Produce radial magnetic field to ensure smooth rotation. Total 20
Selangor 2009
5 Correct diagram permanent field, electromagnet field and combined field (ii) Show the direction and label the force (iii) N (i) PQ moves away from the holder/ to the right/outwards (ii) PQ moves further in Diagram 10.4 compare than diagram 10.3 (iii) the strength of magnadur magnet in 10.4 is larger compare than diagram 10.3 (iv) the larger the strength of magnadur magnet the longer the distance between cooper wire PQ and plastic holder (v) the stronger the magnet the larger the force produced (i) d) Modification use stronger magnet (for sensitivity) use curve magnets / concave use cylindrical core Explanation -stronger magnetic field / --larger rotation produce radial magnetic field / to get a linear scale -to supply uniform magnetic field - Produces uniform interaction between permanent magnetic field and the magnetic field produce by the copper coil -easy to magnetize and demagnetize -to concentrate the magnetic field The produced uniform reading Produces uniform magnetic field Will increasing the degree of deflection // accuracy When theres no current flow, spring will return to its original position Can detect small change in force Mrsm 2010 7 (a) The production of induced current or induced e.m.f. without using the power supplies but using the relative motion between a conductor or a magnet The number of conductor wires in diagram 10.2 is higher compare than diagram 10.1 The deflection of galvanometer pointer in diagram 10.2 is higher compare than diagram 10.1 The higher the number of conductor, the higher the rate of cutting of magnetic flux The higher the rate of cutting of magnetic flux the higher the induced current Faraday law The (magnadur) magnets produce a magnetic field rotate the coil in clock wise//anticlockwise direction 1
use soft iron core
10
use linear scale LAIN2 Use radial magnet Increasing the number of turns of coil Attach hair springs
Small mass/longer of pointer
(b)
(c)
d)
the coil cut across the magnetic field/changing in magnetic flux current is induced in the coil the commuator change the direction in the coil so that the direction of current in external circuit always the same. Aspect Explanation Lower thickness of the Easy to vibrate diaphragm(thinner) Strong strength of material for Not easily to damage/break the diaphragm Higher/more number of turn Increase the magnetic field of coil line Increase the diameter of the Reduced resistance coil wire Stronger the magnetic field Increase the magnetic field line
10
(b) 1st : the angle of deflection of the pointer in 10.2 is bigger 2nd : the distance of the copper rod in 10.2 is further 3rd : power supply in 10.2 is greater then 10.1 111 (c) (i) (ii) The bigger the force the further the distance The bigger the current the larger the force 11 (d) 1st : current flows from Z to Y and fromWto X in half cycle 2nd : magnetic field form around the copper strips 3rd : current flows in opposite directions in the half cycle 4th : the copper strips moves outwards// repel 1111 1st : use stronger magnet 2nd : stronger magnetic field / larger rotation 3rd : use curve magnets / concave 4th : produce radial magnetic field / to get a linear scale 5th : use cylindrical core 6th : to supply uniform magnetic field
7th : use soft iron core 8th : to concentrate the magnetic field 9th : use linear scale 10th : the angle of rotation is linear
What is meant by Electromagnetic Induction The production of induced current or induced e.m.f. without using the power supplies but using the relative motion between a conductor or a magnet 10 c)
The (magnadur) magnets produce a magnetic field rotate the coil in clock wise//anticlockwise direction the coil cut across the magnetic field/changing in magnetic flux current is induced in the coil the commuator change the direction in the coil so that the direction of current in external circuit always the same.
The number of conductor wires in diagram 10.2 is higher compare than diagram 10.1 The deflection of galvanometer pointer in diagram 10.2 is higher compare than diagram 10.1 The higher the number of conductor, the higher the rate of cutting of magnetic flux The higher the rate of cutting of magnetic flux the higher the induced current Faraday law
Aspect Lower thickness of the diaphragm(thinner) Strong strength of material Higher/more number of turn
explanation Easy to vibrate Not easily to damage/break Increase the
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cutter Wheel - H1140Dokumen4 halamanCutter Wheel - H1140Sebastián Fernando Canul Mendez100% (2)
- ABB 3HAC050988 AM Arc and Arc Sensor RW 6-En PDFDokumen238 halamanABB 3HAC050988 AM Arc and Arc Sensor RW 6-En PDForefat1Belum ada peringkat
- 2014 CXC Elec Paper 2Dokumen15 halaman2014 CXC Elec Paper 2api-255989257Belum ada peringkat
- CH 10Dokumen125 halamanCH 10Lisset Soraya Huamán QuispeBelum ada peringkat
- Template EbcrDokumen7 halamanTemplate EbcrNoraBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Field Strength of CoilDokumen16 halamanMagnetic Field Strength of CoilDewan Olin ChotepadaeBelum ada peringkat
- MRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)Dokumen10 halamanMRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)ChewLee TanBelum ada peringkat
- 9 TransformerDokumen7 halaman9 TransformerMThana BalanBelum ada peringkat
- SPM 2003Dokumen18 halamanSPM 2003faisalsmkpnBelum ada peringkat
- ElectromagnetismDokumen3 halamanElectromagnetismpinkyoya86Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial TRANSFORMERkem Cuti 2011Dokumen7 halamanTutorial TRANSFORMERkem Cuti 2011Mohamad Rizal MukhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Final ThirdDokumen3 halamanEnergy Final ThirdDr. Ghassan Nihad JawadBelum ada peringkat
- Icse X Magnetism Question BankDokumen7 halamanIcse X Magnetism Question BankanimeshtechnosBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism PDFDokumen7 halamanMagnetism and Electromagnetism PDFEng Bahanza100% (1)
- Form 5Dokumen13 halamanForm 5Vanusha AzzrielBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnet DemagnetizationDokumen11 halamanElectromagnet DemagnetizationSyazlina SamsudinBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 P2Dokumen20 halamanChapter 7 P2Amelia SuidBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism and MotorsDokumen7 halamanElectromagnetism and Motorsi don't have enough money for chicken nuggetsBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic InductionDokumen18 halamanElectromagnetic InductionAsish ThampiBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)Dokumen10 halamanMagnetism To Transformer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)6C09 FUNG CHI LAMBelum ada peringkat
- Section BDokumen8 halamanSection BDewan Olin ChotepadaeBelum ada peringkat
- MCTE 2331 Electrical Machines ExamDokumen7 halamanMCTE 2331 Electrical Machines ExamAmir ALQedraBelum ada peringkat
- FZK k2 BHGN BDokumen8 halamanFZK k2 BHGN BAdyfairos NayahBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Effect of Current ExerciseDokumen12 halamanMagnetic Effect of Current Exercisemaatla monkgeBelum ada peringkat
- IT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)Dokumen10 halamanIT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)rospazitaBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic InductionDokumen5 halamanElectromagnetic InductionfaisalsmkpnBelum ada peringkat
- Physics PP2Dokumen15 halamanPhysics PP2yiegori2006Belum ada peringkat
- Perfec Score MelakaDokumen8 halamanPerfec Score MelakacikgusuriyatiBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10 A Physics Assignment - MagnetismDokumen8 halamanGrade 10 A Physics Assignment - MagnetismRoselyn TrixieBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8: Electromagnetism.: Answer All QuestionDokumen7 halamanChapter 8: Electromagnetism.: Answer All Questioncikgu salehBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Final SecondDokumen2 halamanEnergy Final SecondDr. Ghassan Nihad JawadBelum ada peringkat
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (Oic)Dokumen1 halamanIslamic University of Technology (Iut) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (Oic)Ashik AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic EffectsDokumen12 halamanElectromagnetic EffectsJeft AshlaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter: Electromagnetism: ChecklistDokumen20 halamanChapter: Electromagnetism: ChecklistCart Kartika50% (2)
- Chapter 7 P2Dokumen20 halamanChapter 7 P2siewkiemBelum ada peringkat
- Section A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDokumen15 halamanSection A (45 Marks) Answer All Questions in The Spaces ProvidedtopcatBelum ada peringkat
- PART 1: MCQ (10 Marks) : Instruction Encircle The BEST Answer NB: Do Not Cancel Any AnswerDokumen2 halamanPART 1: MCQ (10 Marks) : Instruction Encircle The BEST Answer NB: Do Not Cancel Any AnswerRomeo MougnolBelum ada peringkat
- Force of Magnetic Field StructureDokumen3 halamanForce of Magnetic Field StructureCikgu AriefBelum ada peringkat
- 2011-2021 Electromagnetism Questions - ANSKEYDokumen3 halaman2011-2021 Electromagnetism Questions - ANSKEYharshitorgodBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Motor question-EXEXDokumen2 halamanElectric Motor question-EXEXJessicaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise: Transformer & Lenz' LawDokumen1 halamanExercise: Transformer & Lenz' LawWAN NOOR AZILAH BT WAN UMAR MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 3 - ElectromagnetismDokumen35 halamanPhysics Module Form 5 Chapter 3 - Electromagnetismrenu0% (1)
- Chapter 8 P2Dokumen28 halamanChapter 8 P2Arivalzakan MuthusamyBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises ElectromagnetDokumen6 halamanExercises ElectromagnetSyahida SyasyaBelum ada peringkat
- R 161214112017Dokumen2 halamanR 161214112017srinivasallam1986_87Belum ada peringkat
- T127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical EngineeringDokumen6 halamanT127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical Engineeringharish babu aluruBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 Electromagnetism RevisionDokumen27 halamanYear 11 Electromagnetism RevisionLawrenceOnthugaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen5 halamanPhysicsPrakriti ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Skor A+ Fizik JPNS 2014 - Elektromagnet - SkemaDokumen6 halamanModul Skor A+ Fizik JPNS 2014 - Elektromagnet - SkemaCikita IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- DC Machines2Dokumen97 halamanDC Machines2Carlos VásquezBelum ada peringkat
- UCE Physics 2013 Paper 2Dokumen4 halamanUCE Physics 2013 Paper 2Shy DudeBelum ada peringkat
- Eletronic and RadioactiveDokumen16 halamanEletronic and RadioactiveShiu Ping WongBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICS FORM 3 PP2 Teacher - Co - .Ke End Term 2Dokumen9 halamanPHYSICS FORM 3 PP2 Teacher - Co - .Ke End Term 2James GichariBelum ada peringkat
- Capacitor plates separation effect on voltmeter readingDokumen4 halamanCapacitor plates separation effect on voltmeter readingRanveerBelum ada peringkat
- Measurements 006Dokumen6 halamanMeasurements 006Hemed hafidhBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 8 DC Machines IDokumen18 halamanTopic 8 DC Machines IThairu MuiruriBelum ada peringkat
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IDokumen5 halamanWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IniharikaBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDokumen9 halamanMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet-Magnetism&EM (2001 To 2017) - Final PDFDokumen4 halamanWorksheet-Magnetism&EM (2001 To 2017) - Final PDFHem HemBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokumen2 halamanGujarat Technological Universityjijo123408Belum ada peringkat
- EEE Chapter 2 PDFDokumen37 halamanEEE Chapter 2 PDFKrishna ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Pcc-Ee 303Dokumen2 halamanPcc-Ee 303Amlan SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Penilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (4)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Motto 2 TulipDokumen1 halamanMotto 2 TulipAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- 5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionDokumen51 halaman5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Cartaorganisasipp 2015Dokumen2 halamanCartaorganisasipp 2015Anna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- 5 278218652765913090 PDFDokumen39 halaman5 278218652765913090 PDFcikguwanismktsl-1Belum ada peringkat
- Nama Putera 1 BaktiDokumen1 halamanNama Putera 1 BaktiAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Ting 1 Bijak 2013Dokumen15 halamanTing 1 Bijak 2013Anna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010 Kertas 2 Set 3 PDFDokumen18 halamanSoalan Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010 Kertas 2 Set 3 PDFAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- F5C3-Electromagnetism PpsDokumen21 halamanF5C3-Electromagnetism PpsAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Nama Putera 1 BaktiDokumen1 halamanNama Putera 1 BaktiAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Documents - Tips Modul Kimia Tingkatan 4Dokumen50 halamanDocuments - Tips Modul Kimia Tingkatan 4Anna Latifah Cammry33% (3)
- Sekolah Berasrama PenuhDokumen55 halamanSekolah Berasrama PenuhPrince AceBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis Soalan Fizik Kertas 2 BHG A Trial SPM 2010Dokumen3 halamanAnalisis Soalan Fizik Kertas 2 BHG A Trial SPM 2010Norhazami HashimBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Trial Paper 2013 - Maths - Sekolah Berasrama Penuh - Part 2Dokumen34 halamanSPM Trial Paper 2013 - Maths - Sekolah Berasrama Penuh - Part 2uzai88Belum ada peringkat
- 3.linear Motion2Dokumen10 halaman3.linear Motion2jemwesleyBelum ada peringkat
- 2 TransisstorDokumen11 halaman2 TransisstorjemwesleyBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDokumen33 halaman1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- SPM Trial 2012 Physics Qa PenangDokumen103 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Physics Qa PenangAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Dokumen17 halamanPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiBelum ada peringkat
- 6 RadioactiveDokumen9 halaman6 RadioactiveAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDokumen33 halaman1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- 1.pecutan ElektromagnetDokumen11 halaman1.pecutan ElektromagnetAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDokumen33 halaman1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- SPM Trial 2012 Physics A MRSMDokumen13 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Physics A MRSMAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 1Dokumen1 halamanAnswer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 1Cikgu FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- 3.linear Motion2Dokumen10 halaman3.linear Motion2jemwesleyBelum ada peringkat
- 1.pecutan ElektromagnetDokumen11 halaman1.pecutan ElektromagnetAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Dokumen17 halamanPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Trial 2012 Physics A MRSMDokumen13 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Physics A MRSMAnna Latifah CammryBelum ada peringkat
- PAT FORM 4 Perak Math 2011 Paper 1Dokumen17 halamanPAT FORM 4 Perak Math 2011 Paper 1Husna FadzilBelum ada peringkat
- 37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsDokumen7 halaman37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsSatyendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Knowing Annelida: Earthworms, Leeches and Marine WormsDokumen4 halamanKnowing Annelida: Earthworms, Leeches and Marine WormsCherry Mae AdlawonBelum ada peringkat
- Porta by AmbarrukmoDokumen4 halamanPorta by AmbarrukmoRika AyuBelum ada peringkat
- CSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDokumen48 halamanCSC-1321 Gateway User Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineKislan MislaBelum ada peringkat
- HS-2172 Vs HS-5500 Test ComparisonDokumen1 halamanHS-2172 Vs HS-5500 Test ComparisonRicardo VillarBelum ada peringkat
- Very Low Altitude Drag-Free Satellites: R D UpdatesDokumen5 halamanVery Low Altitude Drag-Free Satellites: R D Updatesraa2010Belum ada peringkat
- Lect 17 Amp Freq RespDokumen22 halamanLect 17 Amp Freq RespBent777Belum ada peringkat
- Tyfo SDokumen2 halamanTyfo SAndi AsBelum ada peringkat
- Cumulative List of Notices to MarinersDokumen2 halamanCumulative List of Notices to MarinersResian Garalde Bisco100% (2)
- Gene Regulation: Made By: Diana Alhazzaa Massah AlhazzaaDokumen17 halamanGene Regulation: Made By: Diana Alhazzaa Massah AlhazzaaAmora HZzBelum ada peringkat
- Ampersand MenuDokumen5 halamanAmpersand MenuJozefBelum ada peringkat
- Tennis BiomechanicsDokumen14 halamanTennis BiomechanicsΒασίλης Παπατσάς100% (1)
- Dimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutDokumen11 halamanDimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutRizqi RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 123Dokumen13 halamanPresentation 123Harishitha ManivannanBelum ada peringkat
- Ub40 LyricsDokumen76 halamanUb40 LyricsJose Lucio Flores SantosBelum ada peringkat
- L C R Circuit Series and Parallel1Dokumen6 halamanL C R Circuit Series and Parallel1krishcvrBelum ada peringkat
- Is Revalida ExamDokumen11 halamanIs Revalida ExamRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.Belum ada peringkat
- Revised fire drill performance standardsDokumen47 halamanRevised fire drill performance standardsKartikeya GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Lectura Isaac NewtonDokumen2 halamanLectura Isaac NewtonCESAR MAURICIO RODRIGUEZBelum ada peringkat
- Causes of DyspneaDokumen9 halamanCauses of DyspneaHanis Afiqah Violet MeowBelum ada peringkat
- المحاضرة الرابعة المقرر انظمة اتصالات 2Dokumen31 halamanالمحاضرة الرابعة المقرر انظمة اتصالات 2ibrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Fairs in Punjab 2021-22Dokumen9 halamanFairs in Punjab 2021-22Suchintan SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Module 37 Nur 145Dokumen38 halamanModule 37 Nur 145Marga WreatheBelum ada peringkat
- Wirkungen FlechtenstoffeDokumen21 halamanWirkungen FlechtenstoffeLogge UliBelum ada peringkat
- 5s OfficeDokumen10 halaman5s OfficeTechie InblueBelum ada peringkat
- Desiderata: by Max EhrmannDokumen6 halamanDesiderata: by Max EhrmannTanay AshwathBelum ada peringkat