Final Exam Review Psychology
Diunggah oleh
Jacob HustonHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Final Exam Review Psychology
Diunggah oleh
Jacob HustonHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Final Exam Review
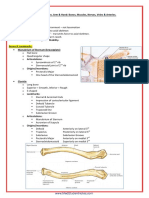
Major parts of neurons (covered in lecture) Cell body- materials needed by the neuron are made here Axon terminal Synapse- terminal point of axon branch, which releases neurotransmitters Dendrtie- projection that picks up impulses from other neurons Node- gap between myelin sheath and axon, which helps conduction of nerve impulses Axon- nerve fiber projecting from the cell body that carries nerve impulses Myelin sheath- fatty coat that insulates the axons of some nerve cells, speeding transmission of impulses Glial cells- support cells in nervous system that play roles in the formation of myelin and blood-brain barrier, respond to injury, and remove debris Blood-brain barrier- glial cells forming a fatty coating that prevents certain substances from entering the brain Myelin Sheath- glial cell-wrappers around axons that act as insulators of the neurons signal. Acetylcholine- neurotransmitter used to control activity, including movements, memory, attention, and dreaming Dopamine- neurotransmitter that plays a key role in movement and reward Norepinephrine- norepinephrine also underlies the fight-or-flight response, directly increasing heart rate, triggering the release of glucose from energy stores, and increasing blood flow to skeletal muscle. It increases the brain's oxygen supply Serotonin- It is a well-known contributor to feelings of well-being, therefore it is also known as a happiness hormone. GABA- inhibits neuron dampening neural activity Endorphins- chemicals in brain that play a role in pain reduction EEG- recording brain electrical activity at the surface of the skull, CT- scanning technique using multiple x-rays for a 3-D image, MRI- magnetic fields to visualize brain structure, PET- uptake of glucose, fMRI- magnetic fields to visualize brain activity, TMS- magnetic fields to enhance or interrupt brain function, and MEG- brain activity using magnotomers Lens- changes curvature to keep images in focus, Cornea- focus light on the retina, Iriscolored area containing muscles that control the pupil, Pupil- opening in the center of the iris that lets in light, Retina- light converted into nerve impulses, Fovea- part of eye where light rays are most sharply focused, Optic Nerve- impulses from retina to brain Eardrum- vibrates to sound waves Ear canal- conducts sound waves to the eardrum Cochlear nerve- transmits nerve impulses from inner ear to brain Vestibule- position/ semicircular canal- balance sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami, and fat Stage 1- light sleep; Stage 2- slower waves, sleep spindles, k complexes; Stage 3/4- deep sleep, delta waves; Stage 5- REM sleep, high brain activity. o Insomnia- most common/having trouble falling asleep/waking in the night/trouble returning to sleep, narcolepsy- rapid/sudden onset of sleep, sleep apnea- blockage of airway during sleep, nightmares- bad dreams, night terrors- screaming/yelling/ confused child while in deep sleep, sleepwalking- walking while fully asleep.
Activation-synthesis- theory that dreams reflect inputs from brain activation originating in the pons, which the forebrain then attempts to weave into a story. o Sociocognitive- hypnosis based on peoples attitudes, beliefs, and expectations. Dissociation theory- hypnosis based on separation between personality functions that are usually integrated. o Depressants- Decreases activity of the central nervous system. Alcohol. o Stimulants- drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system, heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure. Tobacco- reduces stress, tension, and anxiety. o Opiate narcotics- drugs that reduce pain and induce sleep. Morphine. o Psychedelic- Alters perception, mood, thoughts. Marijuana, LSD. Latent learning- learning that isnt directly observable. Observational learning (Bandura)- learning by watching others. Children learn to act aggressively by watching aggressive role models. Insight learning- all of the sudden learning of something through an aha moment. Explicit/declarative (Semantic-knowledge of facts about the world, Episodicevents of life) Implicit (Procedural- memory of how to do things, Priming- ability to identify a stimulus more easily and quickly after weve encountered a similar stimuli.) Phonemes- categories of sound our vocal apparatus produces. Morphemes- smallest meaningful units of speech. Imitation account- children lean language through imitation. Nativist account- children are born knowing how language works. Social-pragmatics account- children infer what words and sentences mean from context and social interactions. General cognitive processing account- language learning is result of general skills that children apply across a variety of activities. 4 stages of cognitive development- sensorimotor- no thought beyond immediate physical experiences, preoperational- able to think beyond the here and now, but unable to perform mental transformations, concrete- able to perform mental transformations bun only on concrete physical objects, formal operationshypothetical and abstract reasoning. Attachment styles o Secure- after moms departure upset but greets return with joy, secure base. o Insecure avoidant- indifference to moms departure and little reaction with return. o Insecure anxious-panics with departure and mixed reaction on return. o Disorganized- inconsistent and confused responses with moms departure and return. o Dual Process Model (Central and Peripheral Route)- Central route processes are those that require a great deal of thought, and therefore are likely to predominate under conditions that promote high elaboration. Peripheral route processes, on the other hand, do not involve elaboration of the message through extensive cognitive processing of the merits of the actual argument presented.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Stages of Memory: Sensory Memory Short-Term StorageDokumen1 halamanStages of Memory: Sensory Memory Short-Term StorageJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 1 PsychologyDokumen6 halamanExam 1 PsychologyJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Sturd I VantDokumen3 halamanSturd I VantJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Edu 2009 Fall Exam C TableDokumen17 halamanEdu 2009 Fall Exam C Tableasri_bharudinBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 2 Review PsychologyDokumen10 halamanExam 2 Review PsychologyJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Psych Exam 3Dokumen10 halamanPsych Exam 3Jacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Math 523 - Winter 2013 Cross Reference Between Textbook EditionsDokumen1 halamanMath 523 - Winter 2013 Cross Reference Between Textbook EditionsJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Don't Step On The MDokumen1 halamanDon't Step On The MJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Book IX Ovid NotesDokumen2 halamanBook IX Ovid NotesJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Stats 531 Quick NotesDokumen2 halamanStats 531 Quick NotesJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Book XV Ovid NotesDokumen3 halamanBook XV Ovid NotesJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Book IX Ovid NotesDokumen2 halamanBook IX Ovid NotesJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Book VIII Ovid NotesDokumen2 halamanBook VIII Ovid NotesJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- SOA Exam ScheduleDokumen1 halamanSOA Exam ScheduleJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 First Discussion Reading ResponseDokumen1 halamanWeek 2 First Discussion Reading ResponseJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- STATS 406 SyllabusDokumen2 halamanSTATS 406 SyllabusJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4, Discussion 1 Reading ResponseDokumen1 halamanWeek 4, Discussion 1 Reading ResponseJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4 Discussion 2 Reading ResponseDokumen1 halamanWeek 4 Discussion 2 Reading ResponseJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- #Include Int Main (Std::cout "Hello, World." )Dokumen1 halaman#Include Int Main (Std::cout "Hello, World." )Jacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- SOA Exam ScheduleDokumen1 halamanSOA Exam ScheduleJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 Second Discussion Reading ResponseDokumen1 halamanWeek 2 Second Discussion Reading ResponseJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Propositions: For by With ThroughDokumen1 halamanPropositions: For by With ThroughJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- Newsletter TemplateDokumen3 halamanNewsletter TemplateJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- MemosDokumen2 halamanMemosJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- InsuranceDokumen12 halamanInsuranceJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- New WorkDokumen9 halamanNew WorkJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- ExpdesignDokumen80 halamanExpdesignJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- 487 547 1 PB PDFDokumen46 halaman487 547 1 PB PDFJacob HustonBelum ada peringkat
- RegressionDokumen15 halamanRegressionHussain GolwalaBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- 5z-12-Shania Lee Digestive System ReportDokumen6 halaman5z-12-Shania Lee Digestive System Reportapi-254080761Belum ada peringkat
- Napfa Resource Book For Pe Teachers 20140506Dokumen25 halamanNapfa Resource Book For Pe Teachers 20140506api-259265137100% (1)
- Cardiac Surgery Basic KnowledgeDokumen28 halamanCardiac Surgery Basic KnowledgeGinwong100% (1)
- Science 8 Fourth 4 DaysDokumen4 halamanScience 8 Fourth 4 DaysAshley Lopez100% (5)
- Pathology Questions Mcqs in WordDokumen109 halamanPathology Questions Mcqs in WordP D SpencerBelum ada peringkat
- SepsisDokumen19 halamanSepsisapi-308355800Belum ada peringkat
- Answer: CHAPTER 1 Stimuli and ResponsesDokumen8 halamanAnswer: CHAPTER 1 Stimuli and Responses林柄洲Belum ada peringkat
- Epistasis PracticeDokumen1 halamanEpistasis PracticeChristian MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Cells TestDokumen3 halamanCells TestSabita SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CPR 10Dokumen3 halamanCPR 10melodia gandezaBelum ada peringkat
- Keys To Effective Low Level Light Therapy & CellumaDokumen4 halamanKeys To Effective Low Level Light Therapy & CellumaPilarBelum ada peringkat
- Urologic Principles and Practice 2nd EditionDokumen692 halamanUrologic Principles and Practice 2nd EditionRonuve RonuveBelum ada peringkat
- Hip MusclesDokumen31 halamanHip MusclesvinaymanBelum ada peringkat
- Primitive Streak Notochord FormationDokumen41 halamanPrimitive Streak Notochord FormationCsongiBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic GlomerulonephritisDokumen6 halamanChronic GlomerulonephritisIsak ShatikaBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDokumen2 halamanGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- I. Clinical Summary A. General Data ProfileDokumen8 halamanI. Clinical Summary A. General Data ProfileDayan CabrigaBelum ada peringkat
- The Brain Has A Body Adaptive Behavior Emerges From Interactions of Nervous System, Body and Environment by Hillel J. Chiel and Randall D. Beer 1997Dokumen5 halamanThe Brain Has A Body Adaptive Behavior Emerges From Interactions of Nervous System, Body and Environment by Hillel J. Chiel and Randall D. Beer 1997AmiraBelum ada peringkat
- DU MSC Zoology 2021 Entrance Paper PDFDokumen15 halamanDU MSC Zoology 2021 Entrance Paper PDFSuchismita BanerjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study VithoulkasDokumen11 halamanCase Study VithoulkasTatiana Savciuc75% (4)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen7 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionCaressie BiscoBelum ada peringkat
- Object and Space PerceptionDokumen10 halamanObject and Space PerceptionadriricaldeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 039Dokumen40 halamanChapter 039Chandra MuraliBelum ada peringkat
- A&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Dokumen42 halamanA&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaBelum ada peringkat
- Stomatitis: An Overview: Protecting The Oral Cavity During Cancer TreatmentDokumen4 halamanStomatitis: An Overview: Protecting The Oral Cavity During Cancer TreatmentLenna IkawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Haematology 2018 Reading ListDokumen2 halamanHaematology 2018 Reading ListnooneBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Acid BaseDokumen4 halamanApproach To Acid BaseJose Carlos Guerrero AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- Threshold and RecruitmentDokumen16 halamanThreshold and RecruitmentShamaine Anne SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Qatar - Blueprint and Reference (Dec 2016)Dokumen7 halamanQatar - Blueprint and Reference (Dec 2016)Jashim Jumli IIBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Approaches ElbowDokumen68 halamanSurgical Approaches ElbowPrakash AyyaduraiBelum ada peringkat