Bio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - Notes
Diunggah oleh
Camille Andrea RositaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - Notes
Diunggah oleh
Camille Andrea RositaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
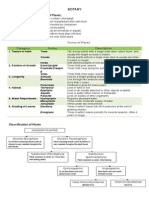
Bio 101 Lab EXERCISE 1 General Morphology of Vascular Plant Groups Vascular tissues Possessed by all vascular plants
s Function as transport system Composed of xylem and phloem Life History of Vascular Plants Sporophyte o Diploid stage o Dominant generation Gametophyte o Haploid stage o Reduced or is dependent on the sporophyte in many vascular plants o Female gametophyte embryo sac o Male gametophyte pollen grain PTERIDOPHYTES Lower vascular plants Seedless plants Phylum Lycophyta and Phylum Pterophyta Phylum Lycophyta Lycophytes I.e., Lycopodium, Selaginella Lycopodium Club Moss True roots, stems, and leaves Roots and stem of most sporophytes are dichotomously branched o But, other have monopodial branching Having one main axis from which lateral branches arise Presence of rhizomes o Produces adventitious roots Leaves: Microphyllous Sporophylls (leaves containing sporangia) are sometimes aggregated into strobili Spore type: Homosporous Selaginella Blue green fern Some species are erect, some shrubby Leaves: o Spirally arranged o Small leaves may be ovate, lanceolate or orbicircular
Rhizophores present o Prop-like structures originating from the stem at points of branching o Bear roots at distal ends o Spore type: Heterosporous
Phylum Pterophyta Psilophytes I.e., Psilotum, Tmesipteris Psilotum An epiphyte on tree ferns, coconut trees, or at the base of tree trunks Plant body consists of a basal branched rhizome system and an upright green aerial portion that is freely and dichotomously branched Leaves: enations; Prophyll Sporangia found in groups (=synangia) With underground rhizome, covered with rhizoids, to anchor the plant and has an absorptive surface Stem used for photosynthesis Sphenophytes I.e., Equisetum Equisetum Axis subdivided into definite nodes and internodes o Aerial stem appears to be jointed o Leaves: Megaphyllous Found at nodes Whorls of non-green leaves Roots emerge from the nodes of the underground rhizome Reproductive structure: Strobili (terminal cones) o Consists of sporangiophore, which bears sporangia Cell wall contains silica Ferns Spore-bearing plants Sporophyte is differentiated into: o True leaves (frond) o Stem o Roots Leaves: Megaphyll o Exhibit circinnate vernation Serves as protection for the young leaf Rhizome is often very short
Fern gametophyte: Prothallus Scale frond (basal frond) o Used to trap organic matter o Used for attachment
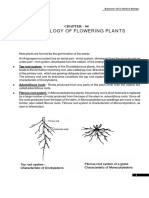
1. Microphyll Leaves without leaf gaps 2. Megaphyll Have leaf gaps 3. Sporophyll Leaves that contain spores/sporangia 4. Prophyll 5. Sporangiophores Stalks that bear sporangia EXERCISE 2 Organs, Development, and Modifictations Embryonic Parts Cotyledon o Modified leaves Embryonic Axis o Attached to the cotyledons o Divided into two regions: Epicotyl Hypocotyl o Plumule = miniature leaves + epicotyl o Radicle Embryonic root Found at the tip of hypocotyl Germination Types Epigeal Germination o Cotyledon rises from the ground o Hypocotyl elongates Hypogeal Germination o Cotyledon remains in the ground o Epicotyl elongates Additional Monocot Embryonic Parts Coleoptile o Sheath that protects emerging shoot Coleorhiza o Sheath that protects emerging root ORGAN MODIFICATION When the organ performs a different function from its usual function Root Function: Absorption and anchorage Types: o Tap root From the embryonic root o Adventitious root Non-embryonic root
GYMNOSPERMS Seed bearing plants Literally means naked seed Refers to a character in which the ovules are borne in an exposed position on the sporophylls Phylum Cycadophyta Reproductive structures: o Megasporophylls Contain ovules or seeds o Microsporophylls Contains pollen Dioecious! Generally unbranced leaves Sporophyte body: o Corona (large leaves) o Caudex (trunk) Leaves: o Compound o Also exhibits circinnate vernation I.e., Cycas revoluta Phylum Coniferophyta Single mains stem with spreading side branches Staminate (male) and Pistillate (female) cones I.e., Pinus Phylum Gnetophyta Connecting link between the gymnosperms and angiosperms Angiospermic features: o Compound nature of microsporangiate and megasporangiate strobili Resembles the inflorescence of angiosperms o Presence of vessels in the xylem o Broad, angiosperm-like blades Pinnate-reticulate venation Leaves: Simple I.e., Gnetum DEFINITION OF TERMS
Can be from stem, leaves, or fruits Function Storage Storage Storage Storage Storage Support
Water Hyacinth Katakataka Doa Aurora Bougainvillea Banana Tendrils Pitcher Plant Asparagus Cycas
Root Modifications Specimen Modification Radish Enlarged tap (Labanos) root Carrot Enlarged tap root Turnip Enlarged tap root Sweet Potato Enlarged (Kamote) adventitious root Ube Enlarged adventitious root Pandan Prop roots (adventitious) Orchid Velamen
leaves Bublous petiole; Stolon Meristematic leaf margin Bracts Bracts Psuedostem; corm Leaves and stem Modified leaf apex Cladode Cataphylls
Buoyancy; reproduction Reproduction Attract pollinators Attract pollinators Support Additional nutrition Photosynthetic stem Protection
Nara Mangrove
Prevents water loss; sometimes used for photosynthesis Root Nodule Nitrogen fixation Pneumatophores Gas exchange
EXERCISE 3 PLASTIDS Leucoplasts Do not contain pigments Around the nucleus White in color (semi-transparent) Amyloplast Stores starch grains o Initially produced in chloroplasts o Have hilum Can be concentric or eccentric Stain potato (Solanum tuberosum) cells with IKI Elaioplasts Stores fat globules Chloroplasts Contains chlorophyll Also contains other pigments Chromoplast Chlorophyll is masked by other dominant pigments Carotenoid orange Xanthophyll yellow Anthocyanin Stored in vacuoles
Stem Function: Support and conduction Leaf Function: Photosynthesis and transpiration Function Storage Storage Storage Reproduction Water retention; photosynthesis Storage
Leaf and Stem Modifications Specimen Modification Potato Tuber (stem) Gabi Corm (stem Tubo Thickened stem (stem); pseudostem Grass Stolon (stem) Agoho Cladode (stem) Ginger Onion Sanseviera Cactus Rhizome (stem) Bulb (stem and leaf) Rhizome; fleshy leaf Phylloclade; cladode/spiny leaves
Aloe vera
No function; storage Storage and photosynthesis; water retention and protection Rhizome; fleshy Storage
o Largest organelle in plant cells Synthesized in cytoplasm
Tannin Phenolic substances capable of complexing with proteins Protect plants from herbivory Used to dye leather Prevents plants from dehydration and rotting Stored in vacuoles Synthesized in tannosomes Crystals Raphides o Found in Colocasia esculenta (gabi) Styloids o Much larger than raphides o Tooth-pick like o Supports air spaces o Found in Eichhornia crassipes Prism o Found in Cystolith found in Lithocyts o Composed of calcium carbonate o Found in epidermal cells o Found in Ficus elastic Druse o Found in Dieffenbacchia
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyDokumen62 halamanLecture 1 - Introduction To Plant AnatomyRalph AlbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewwe 2 NDDokumen72 halamanReviewwe 2 NDYnah BambalanBelum ada peringkat
- PteridophyteDokumen5 halamanPteridophyteAakash YadavBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyDokumen84 halamanAnatomygiaBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom PlantaeDokumen17 halamanKingdom PlantaeHenry LimBelum ada peringkat
- Chap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDokumen10 halamanChap - 05 Morphology of Flowering PlantsgprasadatvuBelum ada peringkat
- Botany 101Dokumen7 halamanBotany 101Gladdin ChloeBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom PlantaeDokumen4 halamanKingdom PlantaeWahyudin MuktiBelum ada peringkat
- Pteridophytes NephrolepisDokumen14 halamanPteridophytes NephrolepisBảo NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Pteridophyta Wulan FixDokumen83 halamanPteridophyta Wulan FixWulanAnggraeniBelum ada peringkat
- Botany Lecture - Chapter 6Dokumen51 halamanBotany Lecture - Chapter 6cherokeeBelum ada peringkat
- Affinities Among Petrido PhylaDokumen6 halamanAffinities Among Petrido PhylaAbdul BasitBelum ada peringkat
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDokumen8 halamanMorphology of Flowering PlantsJigyansa DashBelum ada peringkat
- Crop 1Dokumen6 halamanCrop 1Cynel DelaBelum ada peringkat
- Bryophytes PDFDokumen7 halamanBryophytes PDFPoohooBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom PlantaeDokumen8 halamanKingdom PlantaeDavidBelum ada peringkat
- Review NotesDokumen4 halamanReview NoteshonnyremotoBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Anatomy FixDokumen48 halamanPlant Anatomy FixAprilia ReniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDokumen4 halamanChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsRahul SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics of Various PlantsDokumen8 halamanCharacteristics of Various PlantsSakshi TewariBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFDokumen113 halamanLecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFLance CarandangBelum ada peringkat
- Plant KingdomDokumen2 halamanPlant KingdomAnimated TamashaBelum ada peringkat
- Pteridophyta Classification: 1. Pteridophytes Are Considered As The First Plants To Be Evolved On LandDokumen7 halamanPteridophyta Classification: 1. Pteridophytes Are Considered As The First Plants To Be Evolved On LandAashankBelum ada peringkat
- EuphyllophytesDokumen4 halamanEuphyllophytesAnonymous nCUMLsDLD1Belum ada peringkat
- Gametophyte or ProthallusDokumen31 halamanGametophyte or Prothallusjha.crexa11Belum ada peringkat
- Kingdom Plantae 2023Dokumen28 halamanKingdom Plantae 2023Shawn Xed De La VictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- BOTANY 201 Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo TomasDokumen28 halamanBOTANY 201 Laboratory Department of Biological Sciences College of Science University of Santo TomasRicky Justin NgoBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V SharkDokumen4 halamanBio Study Guide:: 1 Essay Pig V SharkHeidi RechenbergBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Anatomy & Physiology: Ayendago Emmanuel AtiahDokumen132 halamanPlant Anatomy & Physiology: Ayendago Emmanuel AtiahBelko Mark MubarakBelum ada peringkat
- UP Diliman - Geol 130 Plants ReportDokumen94 halamanUP Diliman - Geol 130 Plants ReportMac ServitoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 Land Plants IDokumen12 halamanLab 4 Land Plants ILa Shawn SpencerBelum ada peringkat
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDokumen34 halamanAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 - Plants - (Students)Dokumen41 halamanUnit 5 - Plants - (Students)ajtorresbritoBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDokumen35 halamanPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoBelum ada peringkat
- Angiosperm: Seed Plants. Produce Reproductive Structures Called and - Angiosperms Are Also Known AsDokumen11 halamanAngiosperm: Seed Plants. Produce Reproductive Structures Called and - Angiosperms Are Also Known AsazuitazoolkiflieBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Dokumen66 halamanPlant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Magy Tabisaura GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Ch5p1thero30082022024424 0Dokumen22 halamanCh5p1thero30082022024424 0Rohit Kumar MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDokumen26 halamanMorphology of Flowering PlantsfidhavfathimaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of PlantsDokumen2 halamanTypes of PlantsArt Justin SahagunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDokumen16 halamanChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsYashiBelum ada peringkat
- Pteridophyta Basic CharacteristicsDokumen4 halamanPteridophyta Basic CharacteristicsLata Rajendra VaishBelum ada peringkat
- +1 Botany Capsule NotesDokumen27 halaman+1 Botany Capsule Notesarunankg3Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesDokumen5 halamanPlant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesRizka Apriliana KumalasariBelum ada peringkat
- Morphology of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanDokumen23 halamanMorphology of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot100% (1)
- MorphologyDokumen4 halamanMorphologytarunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Dokumen180 halamanChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLBelum ada peringkat
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDokumen79 halamanAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant Kingdom PDFDokumen5 halaman11 Biology Notes ch03 Plant Kingdom PDFakash guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Nonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsDokumen14 halamanNonvascular Plants and Seedless Vascular PlantsGalang AlphaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant KingdomDokumen4 halamanPlant Kingdomaditiyajhaab10Belum ada peringkat
- Practicle 6: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes: ObjectiveDokumen7 halamanPracticle 6: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes: ObjectiveMalik MonSafariBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21Dokumen46 halamanChapter 21Quices AyingBelum ada peringkat
- Morphology of Flowering Plants For PrintDokumen17 halamanMorphology of Flowering Plants For PrintOjobo Blessing100% (1)
- Bryophytes: Group 10 Ayon, Nera de Guzman, Reina Laure, Rhoda Shaina Reforba, Yasha JoyDokumen61 halamanBryophytes: Group 10 Ayon, Nera de Guzman, Reina Laure, Rhoda Shaina Reforba, Yasha JoyNera AyonBelum ada peringkat
- Supplementary Lecture NotesDokumen24 halamanSupplementary Lecture NotesAntonette OngBelum ada peringkat
- CropSci101 Module 3Dokumen11 halamanCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarDokumen14 halamanChapter 9:kingdom Palntae: Presented By: DR Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerBelum ada peringkat
- An Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledDokumen44 halamanAn Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledAlanie RakimBelum ada peringkat
- Blood ClottingDokumen1 halamanBlood ClottingCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- Penicillium Grew, The Streptomyces Were UnableDokumen3 halamanPenicillium Grew, The Streptomyces Were UnableCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Report 2 - Evening Spring FestivalDokumen2 halamanPerformance Report 2 - Evening Spring FestivalCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- Envi Sci - Alternative EnergyDokumen4 halamanEnvi Sci - Alternative EnergyCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- GraphsDokumen4 halamanGraphsCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- Bio ReviewerDokumen10 halamanBio ReviewerCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- My Time To Shine: Audience-Style: Theatre and PerformanceDokumen11 halamanMy Time To Shine: Audience-Style: Theatre and PerformanceCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- Flora Europaea FormDokumen1.342 halamanFlora Europaea FormCristina Cris100% (1)
- The Association For Tropical Biology and ConservationDokumen8 halamanThe Association For Tropical Biology and ConservationMaria Camila Garcia GiraldoBelum ada peringkat
- Zamias42022 46871 1 PBDokumen19 halamanZamias42022 46871 1 PBManuellaBelum ada peringkat
- A Short History About The Evolution of Gymnosperms: December 2016Dokumen15 halamanA Short History About The Evolution of Gymnosperms: December 2016JavierTarazonaBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesDokumen4 halamanBio 101 - Lab Exam 1 - NotesCamille Andrea RositaBelum ada peringkat
- 2023-24 Lab Manual Biology Class 11Dokumen125 halaman2023-24 Lab Manual Biology Class 11Nikhil Goel100% (1)
- Kelm302 PDFDokumen8 halamanKelm302 PDFRenuka kumariBelum ada peringkat