Meningitis
Diunggah oleh
mango91286Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Meningitis
Diunggah oleh
mango91286Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
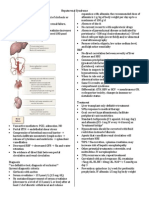
Bacterial meningitis: Causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis Mortality: 25% in community acquired acute bacterial meningitis o Associated
d with: >60 years old, obtunded mental status on admission, onset of seizures within 24 hours of admission Complications: cognitive impairment, hearing loss, seizures, hydrocephalus, visual deficits Classic triad of fever, nuchal rigidity, altered mental status: in less than half of patients 95% of patients had at least 2 of: headache, fever, nuchal rigidity, altered mental status Headache is most common Other symptoms: nausea, vomiting, photophobia, rash (meningococcal) Kernigs sign and Brudzinskis sign not considered useful diagnostically (5% sensitive, 95% specific) Nuchal rigidity: 30% sensitive, 68% specific Clinical features not consistent Causes 4.0 mmol/L or more is consistent with bacterial meningitis instead of aseptic postsurgical meningitis Latex agglutination: detects capsular polysaccharides of bacterial pathogens. For patients with negative CSF Gram stain from previous antibiotic use. High false positive rates. PCR: 100% sensitive, 98.2% specific. Expensive, not widely available Other studies: CSF VDRL, CSF PCR for enteroviruses and herpesvirus, CSF fungal stain, CSF mycobacterial stain Treatment If negative CSF Gram stains and cultures + high clinical suspicion chose treatment based on host presentation o
Diagnosis CSF: Gram stain and culture, cell count, glucose, protein o CT in patients with: immunocompromise, papilledema, focal neurological deficits, CSF shunts, history of hydrocephalus, and/or trauma to prevent brain herniation (secondary to intracranial masses) Two sets of blood cultures before initiation of antibiotics Blood lactic acid if recent neurosurgical procedure
Penicillin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) <0.1 mg/mL penicillin G, ampicillin Penicillin MIC 0.1-1 mg/mL third generation cephalosporin (ceftriaxone), cefepime, meropenem Penicillin MIC >2.0 mg/mL vancomycin + third generation cephalosporin Ceftriaxone MIC > 2mg/mL add rifampin Pneumococcal meningitis: dexamethasome (0.15 mg/kg every 6 hours) for the first 2-4 days. Only before and during first antibiotic dose. Decreases risk of adverse outcomes. Meningococcal meningitis: respiratory isolation first 24 hours, prophylaxis for close contacts. If patient does not improve in 48 hours, repeat LP. However, neck stiffness may persist up to 7 days. Length of antiobiotic regimen: 7 days for N meningitides and H influenzae, 10-14 days for S pneumonia, 14-21 days for S agalactiae, 21 days for L monocytogenes or aerobic Gram negative bacilli
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- SubtitleDokumen30 halamanSubtitlemango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Factors Associated With Success and Failure of Weaning Children From Prolonged Enteral Nutrition - A Retrospective Cohort StudyDokumen6 halamanFactors Associated With Success and Failure of Weaning Children From Prolonged Enteral Nutrition - A Retrospective Cohort Studymango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Probiotics in GI DisordersDokumen35 halamanProbiotics in GI Disordersmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Cisapride Use in Pediatric Patients With Intestinal Failure and Its Impact On Progression of Enteral NutritionDokumen6 halamanCisapride Use in Pediatric Patients With Intestinal Failure and Its Impact On Progression of Enteral Nutritionmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Cannabis in GI and Liver DiseaseDokumen19 halamanCannabis in GI and Liver Diseasemango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Epidemiologyand Pathophysiologyof Gastroparesis: Baha Moshiree,, Michael Potter,, Nicholas J. TalleyDokumen14 halamanEpidemiologyand Pathophysiologyof Gastroparesis: Baha Moshiree,, Michael Potter,, Nicholas J. Talleymango91286Belum ada peringkat
- When SupplyDokumen2 halamanWhen Supplymango91286Belum ada peringkat
- FHDokumen1 halamanFHmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Constipation and Bowel RegimensDokumen17 halamanConstipation and Bowel Regimensmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Hepatorenal SyndromeDokumen1 halamanHepatorenal Syndromemango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Past Journal Club QuestionsDokumen3 halamanPast Journal Club Questionsmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- NBME PercentilesDokumen1 halamanNBME Percentilesmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Medical Care For Immigrant ChildrenDokumen36 halamanMedical Care For Immigrant Childrenmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingDokumen1 halamanLower Gastrointestinal Bleedingmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Conrad Fischer MCQsDokumen328 halamanConrad Fischer MCQsPopescu Tina100% (1)
- Acute CholecystitisDokumen1 halamanAcute Cholecystitismango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Congestive Heart FailureDokumen1 halamanCongestive Heart Failuremango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Acute CholecystitisDokumen1 halamanAcute Cholecystitismango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Micro Final CsDokumen13 halamanMicro Final Csmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Micro Exam 3 NotesDokumen7 halamanMicro Exam 3 Notesmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- PreTest Vignettes For 2CK, 8th EditionDokumen295 halamanPreTest Vignettes For 2CK, 8th Editionmango91286100% (7)
- NBME PercentilesDokumen1 halamanNBME Percentilesmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- CsDokumen11 halamanCsmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- BacteriaDokumen7 halamanBacteriamango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Answer SheetDokumen1 halamanAnswer Sheetmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Urinary IncontinenceDokumen0 halamanUrinary Incontinencemango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Abdominal PainDokumen78 halamanAbdominal Painmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- Student Objectives - ACOGDokumen164 halamanStudent Objectives - ACOGmango91286100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokumen0 halamanAbnormal Uterine Bleedingmango91286Belum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- John Jay Immunization FormDokumen3 halamanJohn Jay Immunization FormIsam BoukattayaBelum ada peringkat
- A Child With Fever and Hemorrhagic RashDokumen3 halamanA Child With Fever and Hemorrhagic RashCynthia GBelum ada peringkat
- Cuny Immunization Record FormDokumen2 halamanCuny Immunization Record Formmichael JacksonBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaDokumen8 halamanPathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaEugen TarnovschiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is MeningitisDokumen10 halamanWhat Is MeningitisJoshua Capa FrondaBelum ada peringkat
- Meningitis Diagnostics Use CasesDokumen15 halamanMeningitis Diagnostics Use Casesputriyulandari94Belum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Meningitis in Children Older Than One MonthDokumen23 halamanBacterial Meningitis in Children Older Than One MonthMario Mendoza TorresBelum ada peringkat
- GMU Immunization FormDokumen5 halamanGMU Immunization FormAurora Kitt McGowanBelum ada peringkat
- PHCP FinalsDokumen43 halamanPHCP FinalsEli ChuaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22: Young Adult Edelman: Health Promotion Throughout The Life Span, 8th EditionDokumen10 halamanChapter 22: Young Adult Edelman: Health Promotion Throughout The Life Span, 8th Editionmarvado10100% (1)
- Gram Negative Cocci-Sem 1.Dokumen21 halamanGram Negative Cocci-Sem 1.Charmaine Corpuz GranilBelum ada peringkat
- CodeDokumen88 halamanCodeGLADYSBelum ada peringkat
- Kolaeva NotesfsdffDokumen16 halamanKolaeva NotesfsdffsharenBelum ada peringkat
- WHO IVB 11.09 Eng PDFDokumen323 halamanWHO IVB 11.09 Eng PDFniaaseepBelum ada peringkat
- 11.17-Meningococcal Vaccine TRACK CHANGESDokumen12 halaman11.17-Meningococcal Vaccine TRACK CHANGESGaurav GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook: For Clinical Management of DengueDokumen124 halamanHandbook: For Clinical Management of DengueraattaiBelum ada peringkat
- Dermatology Videos by DR RihamDokumen31 halamanDermatology Videos by DR Rihamengr_shazzBelum ada peringkat
- Neurology MCQDokumen16 halamanNeurology MCQSudhakar Subramanian100% (1)
- MeningococcemiaDokumen5 halamanMeningococcemiaErhiecka BasaBelum ada peringkat
- Neisseria MeningitidisDokumen3 halamanNeisseria MeningitidishedstrongBelum ada peringkat
- VAERS Line List Report: Vax Type: HPV4 Status Date: 01-MAY-11 - 15-SEP-11 All Comb. w/ANDDokumen1.639 halamanVAERS Line List Report: Vax Type: HPV4 Status Date: 01-MAY-11 - 15-SEP-11 All Comb. w/ANDJudicial Watch, Inc.Belum ada peringkat
- Child With Non Blanching RashDokumen6 halamanChild With Non Blanching Rashtanya mathewBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial MeningitisDokumen30 halamanBacterial MeningitisFaris Alarshani100% (1)
- Screenshot 2021-06-04 at 23.19.29Dokumen72 halamanScreenshot 2021-06-04 at 23.19.29Amina Mohamed AbdikeirBelum ada peringkat
- Ishimine2013fiebre SignosDokumen26 halamanIshimine2013fiebre SignosAnirisulBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical SafetyDokumen11 halamanElectrical SafetyMoatasem AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Communicable DiseasesDokumen43 halamanCommunicable DiseasesjeshemaBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Negative CocciDokumen14 halamanGram Negative CocciRachel Marie M. GaniaBelum ada peringkat
- 100MCQsinTropicalMedicine (PDF Library)Dokumen76 halaman100MCQsinTropicalMedicine (PDF Library)Abdalla ShibailiBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Health Advisories, 2012 PDFDokumen170 halamanPhilippine Health Advisories, 2012 PDFRyan Michael OducadoBelum ada peringkat