Me203 hw1 Fall13
Diunggah oleh
Ammar KhanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Me203 hw1 Fall13
Diunggah oleh
Ammar KhanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ME 203 Thermodynamics-1 Homework 1
Problems
1.
Due Date: 14.11.2013
2.
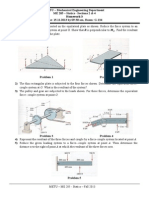
Warm air is contained in a piston-cylinder assembly oriented horizontally as shown in figure. The air cools slowly from an initial volume of 0.0032 m3 to a final volume of 0.0017 m3. During the process, the spring exerts a force that varies linearly from an initial value of 900 N to a final value of zero. The atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa, and the area of the piston face is 0.018 m2. Friction between the piston and the cylinder wall can be neglected. For the air in the piston-cylinder assembly, determine the initial and final pressures, each in kPa and atm.* Felix Baumgartner, a 43 year old skydiver and stunt performer, jumped from 39045 m to break highest manned balloon flight and fastest speed of free fall on October 14, 2012. He started his fall from 2nd layer of atmosphere,stratosphere and reached a maximum speed of 325.8 m/s at 49 seconds and maintained this speed for 11 seconds. Afterwards, the daredevil possibly entered troposphere, first layer of atmosphere and started to decelerate but continued his free fall for another 3 minutes and 19 seconds. a) Consider Felix as a closed system and show him explicitly on a figure.How long would it take to reach the same maximum speed if we ignored the effect of air resistance (i.e.there were no heat loss to the surrounding due to friction)? What would be the amount of free fall when he just reached maximum speed and at the end of first minute? (Assumption: gravitial accelaration is constant and 9.81m/s) b) What was the heat loss though due to viscous dissipation(friction) during acceleration period if accelaration of Felix is assumed as constant? What was the amount of free fall when he just reached maximum speed and at the end of first minute? What is the heat loss during acceleration period and steady speed period? (Assumption: The mass of Felix is 85 kg, acceleration of Felix is linear and there is no work on boundaries.) c) (optional) Find more detailed data about the jump and perform same analysis to get more accurate results of heat loss and free fall distance. Oxygen (O2) gas within piston cylinder assembly undergoes an expansion from a volume V1=0.012 m3 to a volume V2=0.034m3 . The polytropic relation between pressure and volume is p=AV-1 + B where A=0.05 bar and B=3.1 bar. For O2, determine initial and final pressures and net work.* Figure below shows a gas contained in a vertical pistoncylinder assembly. A vertical shaft whose cross-sectional area is 0.8 cm2 is attached to the top of the piston. The total mass of the piston and shaft is 30 kg. While the gas is slowly heated, the internal energy of the gas increases by 0.15 kJ, the potential energy of the pistonshaft combination increases by 0.25 kJ, and a force of 1334 N is exerted on the shaft as shown in the figure. The piston and cylinder are poor conductors, and friction between them is negligible. The local atmospheric pressure is 1 bar and g=9.81 m/s2. Show system boundaries and determine, (a) the work done by the shaft-piston combination, (b) the work done by system in displacing the atmosphere, and (c) the heat transfer to the gas, all in kJ.*
3.
4.
*Adapted fron Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, Moran and Shapiro.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Problem Set 1 - Aeng4Dokumen1 halamanProblem Set 1 - Aeng4Jhunnel MaganesBelum ada peringkat
- BasicsDokumen1 halamanBasicsRishi Raj100% (1)
- Problems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirDokumen3 halamanProblems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirKynn VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) Group A & BDokumen11 halamanTutorial Sheet (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) Group A & BVISHAL GUPTABelum ada peringkat
- PRINT AndersonDokumen7 halamanPRINT AndersonCed Sison100% (1)
- II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsDokumen8 halamanII B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec - 2015 ThermodynamicsAshok DaraBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 ProblemsDokumen3 halamanModule 1 ProblemsShane PatulotBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment1 MEL140 - 2013 PDFDokumen3 halamanAssignment1 MEL140 - 2013 PDFSanaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen15 halamanPhysicssandrosteklegebre100% (1)
- Pset1 - T1-T3Dokumen3 halamanPset1 - T1-T3ChocomalteeChocomalteeBelum ada peringkat
- HomeworkaDokumen1 halamanHomeworkaSafa Eren PEPEÇBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2Dokumen46 halamanCH 2جلال بولادBelum ada peringkat
- Tut 3Dokumen4 halamanTut 3SamarthBelum ada peringkat
- GATE ThermodynamicsDokumen84 halamanGATE ThermodynamicsRajesh Verma75% (4)
- Isentropic Process-Nozzle, Diffuser - Unit 1Dokumen92 halamanIsentropic Process-Nozzle, Diffuser - Unit 1siddharth GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 (7th Edition)Dokumen6 halamanChapter 3 (7th Edition)zaqbasalmau100% (1)
- CH 1Dokumen7 halamanCH 1Asad IslamBelum ada peringkat
- T1 Ug 90Dokumen6 halamanT1 Ug 90germangsilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen44 halamanChapter 1John Jairo Ortiz Martinez91% (11)
- First Law of Thermodynamics 1580126216698243765e2ed008943f7Dokumen3 halamanFirst Law of Thermodynamics 1580126216698243765e2ed008943f7Atul YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamic Question BankDokumen10 halamanThermodynamic Question BankRaj PratyushBelum ada peringkat
- 2013Dokumen31 halaman2013Narayanan SrinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Sample ProblemDokumen2 halamanThermodynamics Sample ProblemRonelle Royce MarisBelum ada peringkat
- FEEG1003 Problem Sheet 3Dokumen2 halamanFEEG1003 Problem Sheet 3ellyBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet 1Dokumen2 halamanTutorial Sheet 1Syed YousufuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Mine Ventilation Notes For Beginners PDFDokumen16 halamanMine Ventilation Notes For Beginners PDFalwcastillo100% (2)
- Problem Set (10 Questions) of First-Second Law of ThermodynamicsDokumen4 halamanProblem Set (10 Questions) of First-Second Law of Thermodynamicscoolcool2167Belum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 1Dokumen1 halamanProblem Set 1kensusantoBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 2 TermodinamicaDokumen2 halamanTarea 2 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Old Question Papers 2008 2012Dokumen25 halamanOld Question Papers 2008 2012monu991Belum ada peringkat
- TT P1Dokumen4 halamanTT P1Juan Manuel Uceda PérezBelum ada peringkat
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDokumen37 halamanMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Takehome ActivityDokumen5 halamanTakehome ActivityEdmond Yurag LLusalaBelum ada peringkat
- Homework #2Dokumen3 halamanHomework #2LUISROBelum ada peringkat
- 340 Assignment 1Dokumen2 halaman340 Assignment 1Vandyck Mensah EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Steam Table: Mollier ChartDokumen8 halamanSteam Table: Mollier ChartabdcivilBelum ada peringkat
- IES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1991Dokumen7 halamanIES CONV Mechanical Engineering 1991GURURAJ CBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Tutorial - QuestionsDokumen11 halamanThermodynamics Tutorial - Questionsdinalamin195Belum ada peringkat
- HW 4 3.12Dokumen33 halamanHW 4 3.12Anonymous U3DpVvqVWx0% (3)
- Me 333Dokumen2 halamanMe 333Sandeep Prabakaran100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsDokumen1 halamanTutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsKaustubh Mallik100% (1)
- P 303 AnsDokumen4 halamanP 303 AnsDiptoBelum ada peringkat
- 16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 6Dokumen6 halaman16.050 Thermal Energy: Page 1 of 6ZeroRecoBelum ada peringkat
- ENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Dokumen6 halamanENGIN 3502 Assignment 2 Sem 1 2023Manel SashikalaBelum ada peringkat
- All HW 303 Fall 17Dokumen138 halamanAll HW 303 Fall 17Muhammad MehadiBelum ada peringkat
- UniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Dokumen9 halamanUniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Dominador RomuloBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 2 VannessDokumen8 halamanCHAPTER 2 VannessMekeilah AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2071 PDFDokumen24 halamanTutorial 2071 PDFPrabin Acharya100% (1)
- Homework #2 PDFDokumen3 halamanHomework #2 PDFNataly Yisel ArizaBelum ada peringkat
- Jul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4Dokumen1 halamanJul-Nov 2015: ME-1101 Thermodynamics Tutorial - 4mechmuthu1Belum ada peringkat
- D C & E E H81ETD/CHEE1016 E T: Xample HeetDokumen2 halamanD C & E E H81ETD/CHEE1016 E T: Xample HeetPrakkash RajantheranBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 ThermoDokumen1 halamanAssignment 1 ThermoAbhijit NathBelum ada peringkat
- ProblemsDokumen35 halamanProblemsAhmed Adel IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- H. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)Dokumen20 halamanH. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)HectorCabzBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Problems-Ch 3Dokumen4 halamanTutorial Problems-Ch 3Aryan NayanBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 4 SolutionsDokumen7 halamanHomework 4 Solutionscalebgriffin31Belum ada peringkat
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Dari EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Belum ada peringkat
- Me 205 Fall 13 HW 3Dokumen1 halamanMe 205 Fall 13 HW 3Ammar Khan0% (1)
- Me203 hw2 Fall13Dokumen1 halamanMe203 hw2 Fall13Ammar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- ME 206 Homework 6Dokumen2 halamanME 206 Homework 6Ammar Khan0% (1)
- 10 Abrasive Machining ProcessesDokumen0 halaman10 Abrasive Machining ProcessesAmmar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Further Mechanics ExamZone AnswersDokumen2 halamanFurther Mechanics ExamZone AnswersAmmar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 124T026228H1Dokumen33 halaman124T026228H1LuisBelum ada peringkat
- Product Manual 04048 (Revision C) : SG GovernorDokumen54 halamanProduct Manual 04048 (Revision C) : SG GovernorMaximus Maxis100% (1)
- Service Experience 2009Dokumen19 halamanService Experience 2009Alexandru AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Manual TRC 1000 ACMDokumen49 halamanManual TRC 1000 ACMmicell dieselBelum ada peringkat
- WGDokumen89 halamanWGagiba100% (1)
- SSP 626 Audi Basics of Engine TechnologyDokumen124 halamanSSP 626 Audi Basics of Engine TechnologyNenko TenevBelum ada peringkat
- Bur 87634755NA - J.C.M. 1150K Tier 3 (ENG)Dokumen64 halamanBur 87634755NA - J.C.M. 1150K Tier 3 (ENG)Ricardo BilbaoBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogo Actuador BrayDokumen12 halamanCatalogo Actuador Braynacho richardBelum ada peringkat
- Parts List Hero HondaDokumen16 halamanParts List Hero HondaBhusarapu Srinivas77% (48)
- 1 - 安徽聚力 柱塞泵目录册Dokumen66 halaman1 - 安徽聚力 柱塞泵目录册WEI SHANGBelum ada peringkat
- TVS CorporateDirectory PDFDokumen45 halamanTVS CorporateDirectory PDFGp Mishra0% (1)
- ZF Ecosplit 12 Speed - 1325 - 751 - 101 - en 2009 PDFDokumen110 halamanZF Ecosplit 12 Speed - 1325 - 751 - 101 - en 2009 PDFfugega83% (6)
- Banana Jet - The Revolution of Jetfan DesignDokumen41 halamanBanana Jet - The Revolution of Jetfan DesignTobin Don100% (1)
- IM PAAE044212 13 InternalDokumen496 halamanIM PAAE044212 13 InternalJulia KusovaBelum ada peringkat
- Deutz TD2009 Workshop ManualDokumen312 halamanDeutz TD2009 Workshop ManualВенцислав Венев100% (4)
- Advanced Diesel With Blueperformance.: Technical Training - Product InformationDokumen128 halamanAdvanced Diesel With Blueperformance.: Technical Training - Product InformationIongornistuBelum ada peringkat
- Chasovoy Manual PhoenixDokumen84 halamanChasovoy Manual PhoenixJaya Manggala SaktiBelum ada peringkat
- Piaggio NRG - Power - PurejetDokumen248 halamanPiaggio NRG - Power - PurejetramiroBelum ada peringkat
- ZF ServocomDokumen49 halamanZF Servocomosama tariqBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Radial Piston PDFDokumen28 halamanMotor Radial Piston PDFSilvio RomanBelum ada peringkat
- 420.service.e Pupi Tp002 E3Dokumen34 halaman420.service.e Pupi Tp002 E3lcd22Belum ada peringkat
- Yan L70N Parts List PDFDokumen17 halamanYan L70N Parts List PDFSilver Silver100% (1)
- Service Bulletin RTA-62: 22.05.2003 Technical Information To All Owners / Operators of Sulzer RTA EnginesDokumen6 halamanService Bulletin RTA-62: 22.05.2003 Technical Information To All Owners / Operators of Sulzer RTA EnginesChristopher Garcia100% (2)
- DMS All Assignment & Exeracises (2019-2020)Dokumen6 halamanDMS All Assignment & Exeracises (2019-2020)Nikhil BhosaleBelum ada peringkat
- Datasheet Hatlapa Compressor VA100Dokumen2 halamanDatasheet Hatlapa Compressor VA100Carlos Andres MangaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen32 halamanUnit 1Rakeshkumarceg100% (1)
- Atlas Copco Hydraulic BreakersDokumen16 halamanAtlas Copco Hydraulic BreakersAkshay Yewle100% (1)
- 中国産機向S4S R96認証 (R96 3595-00 Approval)Dokumen15 halaman中国産機向S4S R96認証 (R96 3595-00 Approval)BASAK OZKANBelum ada peringkat
- 75-30 (Valve Assembly, Compressor Bleed)Dokumen20 halaman75-30 (Valve Assembly, Compressor Bleed)GP100% (1)
- S1000RR Technical DetailsDokumen32 halamanS1000RR Technical DetailsBintang TamagoBelum ada peringkat