Ineffective Renal Tissue Perfusion
Diunggah oleh
Hendra TanjungDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ineffective Renal Tissue Perfusion
Diunggah oleh
Hendra TanjungHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ineffective Renal Tissue Perfusion
Definition: Decrease in oxygen resulting in the failure to nourish the tissues at the capillary
level
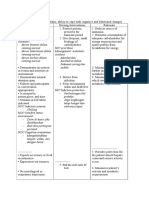
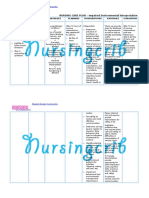
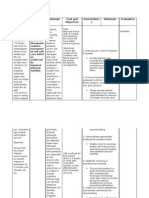
Ineffective Renal Tissue Perfusion Related to Decreased Renal Blood Flow
Defining Characteristics
Anuria or oliguria
Decreased urinary creatinine clearance
Increased serum creatinine
Increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
Electrolyte abnormalities: potassium, sodium
Increased MAP, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP), pulmonary artery
diastolic (PAD) pressure, central venous pressure (CVP) secondary to fluid overload
Sinus tachycardia
Metabolic acidosis
Crackles on lung auscultation
Engorged neck veins
Fluid weight gain
Pitting edema
Mental status changes
Anemia
1626
Outcome Criteria
CO is >4.0 L /min.
CI is >2.2 L /min/m2.
MAP, PAOP, PAD, and CVP are within normal limits for patient.
Electrolytes are within normal range.
Serum creatinine and BUN are within normal range.
Normal acid-base balance.
Level of consciousness is normal.
Lungs are clear on auscultation.
Urinary output is within normal limits, or patient is stable on dialysis.
Hemoglobin and hematocrit values are stable.
Nursing Interventions and Rationale
1. Monitor intake and output, urine output, and patient weight.
2. Collaborate with physician regarding the administration of crystalloids, colloids, blood, gand blood
products to increase circulating volume and maintain MAP >70 mm Hg.
3. Collaborate with physician regarding the administration of inotropes to enhance myocardial
contractility and increase CI to >2.5 L /min.
4. Collaborate with physician regarding the administration of diuretics to the oliguric patient to flush
out cellular debris and increase urine output.
5. Minimize the patient's exposure to nephrotoxic drugs to decrease damage to kidneys.
6. Monitor blood levels of drugs cleared by kidneys to avoid accumulation.
7. Monitor patient for signs of electrolyte imbalance due to impaired electrolyte regulation.
8. Maintain surveillance for signs and symptoms of fluid overload.
9. Monitor patient's clinical status and response to dialysis therapy to ensure the patient is receiving
safe and effective dialytic therapy.
Definition : at risk for a decrease in blood circulation to the kidney that many compromise health
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Risk For Acute Confusion 1-4Dokumen2 halamanRisk For Acute Confusion 1-4DewiRestiNazullyQiran100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- NCMH Newspaper ReadingDokumen1 halamanNCMH Newspaper ReadingRye AnchBelum ada peringkat
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDokumen1 halamanCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCPDokumen4 halamanNCPDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- NCP - ConstipationDokumen3 halamanNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanBelum ada peringkat
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDokumen4 halamanNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Diagnosis: Acute ConfusionDokumen4 halamanNursing Diagnosis: Acute Confusionasmika danaBelum ada peringkat
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Dokumen2 halamanIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- NCPDokumen3 halamanNCPJezza RequilmeBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDokumen2 halamanNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesBelum ada peringkat
- NCP 2Dokumen2 halamanNCP 2ampalBelum ada peringkat
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDokumen3 halamanRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- Acute Pain NCPDokumen1 halamanAcute Pain NCPJed AvesBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen2 halamanIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDokumen5 halamanNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP For Pain - Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen5 halamanNCP For Pain - Rheumatoid Arthritisveorjan100% (1)
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDokumen2 halamanProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawBelum ada peringkat
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDokumen3 halamanCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosBelum ada peringkat
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDokumen3 halamanDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloBelum ada peringkat
- NCP EsrdDokumen9 halamanNCP EsrdMarisol Dizon100% (1)
- NCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDokumen9 halamanNCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKarel LuBelum ada peringkat
- NCP HemothoraxDokumen3 halamanNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Self Care DeficitDokumen3 halamanSelf Care DeficitAddie Labitad100% (2)
- Diarrhea Care PlanDokumen2 halamanDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Belum ada peringkat
- NCP 2Dokumen2 halamanNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- A Nursing Care Plan VaDokumen3 halamanA Nursing Care Plan VaArianne Paola QuindoyBelum ada peringkat
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Dokumen4 halamanAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen2 halamanIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Belum ada peringkat
- 14 Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlansDokumen5 halaman14 Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlansNickesha Mckenzie75% (4)
- Risk For FallsDokumen1 halamanRisk For FallsEugene UCBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Self EsteemDokumen3 halamanNCP Self EsteemAlfadz AsakilBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Epidural HemDokumen32 halamanNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- NCP LymphedemaDokumen1 halamanNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDokumen3 halamanNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Belum ada peringkat
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokumen6 halamanImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokumen3 halamanNCP Activity Intolerancekeiii_21Belum ada peringkat
- 217 RF Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionDokumen8 halaman217 RF Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunctionapi-271775750Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDokumen4 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen1 halamanIneffective Tissue PerfusionEm Castillo50% (2)
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and InjuryDokumen4 halamanAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and Injuryprickybiik50% (2)
- NCP AneurysmDokumen4 halamanNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP - EdemaDokumen1 halamanNCP - Edemavipncpusers100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDokumen3 halamanRisk For InfectioncamziiiBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For UtiDokumen3 halamanNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- 5 NCPDokumen3 halaman5 NCPAllord Lacanilao Bungay0% (1)
- Impaired Physical Mobility NCPDokumen3 halamanImpaired Physical Mobility NCPYan ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For CTTDokumen1 halamanNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimBelum ada peringkat
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen5 halamanRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Impaired Skin DMDokumen3 halamanImpaired Skin DMimnotdatsunny100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen2 halamanAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroBelum ada peringkat
- MSN PresentationDokumen36 halamanMSN Presentationsanangamba akhamBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Renal FailureDokumen15 halamanAcute Renal FailureFilip DadićBelum ada peringkat
- Hepatorenal Syndrome: Anusha Gupta Department of GastroenterologyDokumen45 halamanHepatorenal Syndrome: Anusha Gupta Department of Gastroenterologyvishal padwaleBelum ada peringkat
- CKD Case PresentationDokumen25 halamanCKD Case PresentationMohamed Anwer NaleefBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Failure: DR Uzma BanoDokumen29 halamanRenal Failure: DR Uzma BanoUzma BanoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management: Nursing Management: Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen22 halamanNursing Management: Nursing Management: Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasedian rachmat saputroBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of CKDDokumen7 halamanIntroduction of CKDAndrelyn Balangui LumingisBelum ada peringkat
- Jadwal Kuliah Semester Genap 2023-2024 Prodi TI-SI-2Dokumen10 halamanJadwal Kuliah Semester Genap 2023-2024 Prodi TI-SI-2Hendra TanjungBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Perencanaan AuditDokumen26 halaman5 Perencanaan AuditHendra TanjungBelum ada peringkat
- Siti Fitriana F55118149Dokumen2 halamanSiti Fitriana F55118149Hendra TanjungBelum ada peringkat
- Call For Papers PDFDokumen1 halamanCall For Papers PDFYunisa Muhith WadiyartiBelum ada peringkat
- 1a Penelusuran+masalah Riset YesDokumen88 halaman1a Penelusuran+masalah Riset YesHendra TanjungBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Soal Midtest + Kunci JawabanDokumen28 halamanSoal Midtest + Kunci JawabanYuyun RasulongBelum ada peringkat
- Aroma TherapyDokumen89 halamanAroma TherapyHemanth Kumar G0% (1)
- Introduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorDokumen22 halamanIntroduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorSayyid Al ArizieBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Submission Form: Pgid Name of The MemberDokumen9 halamanAssignment Submission Form: Pgid Name of The MemberNamit GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Radiopharmaceutical Production: History of Cyclotrons The Early Years at BerkeleyDokumen31 halamanRadiopharmaceutical Production: History of Cyclotrons The Early Years at BerkeleyNguyễnKhươngDuyBelum ada peringkat
- American RunwayDokumen26 halamanAmerican RunwayGayathri SuriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Ccounting Basics and Interview Questions AnswersDokumen18 halamanCcounting Basics and Interview Questions AnswersAamir100% (1)
- Vrushalirhatwal (14 0)Dokumen5 halamanVrushalirhatwal (14 0)GuruRakshithBelum ada peringkat
- Storey Publishing Fall 2017 CatalogDokumen108 halamanStorey Publishing Fall 2017 CatalogStorey PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- Rediscovering The True Self Through TheDokumen20 halamanRediscovering The True Self Through TheManuel Ortiz100% (1)
- Visual Rhetoric Music Video Comparison Essay - Abby MckellopDokumen5 halamanVisual Rhetoric Music Video Comparison Essay - Abby Mckellopapi-597591424Belum ada peringkat
- Arsu and AzizoDokumen123 halamanArsu and AzizoZebu BlackBelum ada peringkat
- RF Design MCQ-1Dokumen16 halamanRF Design MCQ-1JeyavelBelum ada peringkat
- Filipino HousesDokumen4 halamanFilipino HousesjackBelum ada peringkat
- 7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanDokumen4 halaman7 - LESSON PLAN CULTURAL HERITAGE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY - Lesson PlanRute SobralBelum ada peringkat
- Asset Management PlanDokumen160 halamanAsset Management Planbkalatus1100% (1)
- Planet Maths 5th - Sample PagesDokumen30 halamanPlanet Maths 5th - Sample PagesEdTech Folens48% (29)
- Argumentative Essay Project DescriptionDokumen5 halamanArgumentative Essay Project DescriptionKaren Jh MoncayoBelum ada peringkat
- What Are RussiaDokumen3 halamanWhat Are RussiaMuhammad SufyanBelum ada peringkat
- Aìgas of Bhakti. at The End of The Last Chapter Uddhava Inquired AboutDokumen28 halamanAìgas of Bhakti. at The End of The Last Chapter Uddhava Inquired AboutDāmodar DasBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric AnaesthesiaDokumen24 halamanGeriatric Anaesthesiakarl abiaad100% (2)
- International Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)Dokumen22 halamanInternational Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)repositoryIPBBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges Faced by Freight Forwarders in Their Operations in Chennai City, Tamil NaduDokumen3 halamanChallenges Faced by Freight Forwarders in Their Operations in Chennai City, Tamil NaduNiraj KasbeBelum ada peringkat
- Corporation Law Case Digests Philippines Merger and ConsolidationDokumen7 halamanCorporation Law Case Digests Philippines Merger and ConsolidationAlpha BetaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Research ReportDokumen14 halamanFinal Research ReportAlojado Lamuel Jesu ABelum ada peringkat
- Amtek Auto Analysis AnuragDokumen4 halamanAmtek Auto Analysis AnuraganuragBelum ada peringkat
- International Human Rights LawDokumen21 halamanInternational Human Rights LawRea Nica GeronaBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure 8 VT 8Dokumen24 halamanBrochure 8 VT 8David GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Soap StudyDokumen25 halamanReport On Soap StudyAbhishek JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson I. Background InformationDokumen21 halamanLesson I. Background InformationsuidivoBelum ada peringkat