Review of Tenses
Diunggah oleh
Georgia KleoudiDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Review of Tenses
Diunggah oleh
Georgia KleoudiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
`1
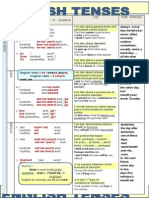
REVIEW OF TENSES
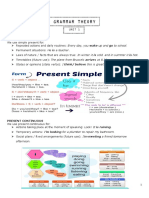
Present Simple
general truth
habitual action
timetables
stative verbs
Present Continuous
action in progress
temporary action
plan for the near future
criticism about habitual behavior (forever, always, constantly)
Present Perfect Simple
An action that happened in the past with no specific time given, but that affects the
present.
COMPARE:
Tom has broken his leg.
(no specific time given=Present Perfect Simple)
Tom broke his leg last month.
(specific time given=Past Simple
action that began in the present and continues up to the present (for, since)
With time periods that havent finished
(with this week/this month/this year etc.)
I have been busy this week.
Your English has improved this month.
Sales have improved this year.
with the expressions:
This is /It is the 1
st
-2
nd
time that- This is/ It is the worst-best..that
Whats the difference :
a) Ian has been to Italy.
b) Ian has gone to Italy.
c) Ian has been in Italy for two years.
In (a): Ian went and returned.
In (b):Ian went and not yet returned.
In (c): Ian lives there/is still there. We also mention the duration using for.
`2
Present Perfect Continuous
action that began in the present and continues up to the present with emphasis on
duration (for, since)
action that has finished with visible results in the present
STUDY CAREFULLY
When. + Past simple?
How long...+ present perfect ?
How long ago..+ Past simple
A) When/How long ago did it start raining?
B)It started raining an hour ago/at 1oclock.
A)How long has it been raining?
B)It has been raining for an hour/since 1 oclock.
Past Simple
action that took place at a definite time in the past
actions that happened in the past one after another
to describe past habits and past situations (like used to but would only for past habits)
Past Continuous
action in progress at a specific time in the past
incomplete actions taking place at the same time in the past
action in progress interrupted by another action( simple past)
Past Perfect Simple
action that happened before another action
Past Perfect Continuous
action that started before another action in the past and was still in progress at the time of the
2
nd
action
action that had finished in the past with visible results in the past
`3
STUDY CAREFULLY
By the time/when/before + Past simple, Past Perfect (Simple/Continuous)
By the time /when we got there, he had already left.
I had checked my passport before I left for the airport.
This tribe had died out centuries before.
By the time/when he arrived, the band had been playing for 2 hours.
Raymond had been smoking for 10 years before he finally gave up.
By + + Past Perfect (Simple/Continuous)
We arrived at the party late. By then, the band had already started playing.
They had eaten by noon.
By 2002, he had been teaching for 20 years.
After, as soon as +Past Perfect, Past Simple
I got up after/as soon as I had eaten.
It was the first/second time
It was the first time that I had travelled abroad.
It was + superlative (+ever)
It was the best book I had ever read.
For, since, all day/night/week/year
They had been running in the marathon since 10 oclock/for 3 hours/all day.
COMPARE
She is tired because she has been studying for 5 hours.
She was tired because she had been studying for 5 hours.
`4
FUTURE SIMPLE
a decision made at the moment of speaking
predictions or personal opinions about the future ( perhaps, probably, think, believe,expect)
requests, offers, warnings, promises, threats
FUTURE CONTINUOUS
actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future
future actions which have already been planned or are part of a routine
a polite request about someones plans, especially if we want to ask a favor
BE GOING TO
predictions based on evidence
plans or decisions that have already been made
FUTURE PERFECT SIMPLE
for an action which will have been completed before a specific point of time in the future
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS
to show the duration of an action up to a certain point of time in the future.
STYDY CAREFULLY
We dont use will after before, after, when, while, till/until, by the time, once(=), as soon
as(=),as long as(=), the moment that. Instead of future we use present tenses.
By the time + Present Simple, Future Perfect (Simple or Continuous)
By the time he arrives, the train will have left.
John will have been studying for six years by the time he graduates.
By + + Future Perfect (Simple/Continuous)
By 2002, he will have been teaching for 20 years.
By 10.00 the train will have left.
COMPARE
The meeting will have finished by 6.
The meeting wont have finished by 6.
The meeting wont have finished until 6. ( 6)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- LRN June 2018 Level C2 Past PaperDokumen21 halamanLRN June 2018 Level C2 Past PaperGeorgia Kleoudi53% (17)
- Irregular Verbs List (Portuguese Translation)Dokumen2 halamanIrregular Verbs List (Portuguese Translation)acgome94% (17)
- LRN Level B2 June 2016 Exam Paper With SpeakingDokumen19 halamanLRN Level B2 June 2016 Exam Paper With SpeakingGeorgia Kleoudi67% (3)
- LRN Level B2 January 2016 Exam PaperDokumen14 halamanLRN Level B2 January 2016 Exam PaperGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- TEFL Module 1 QuizDokumen5 halamanTEFL Module 1 QuizProfe Roca100% (1)
- Pre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2Dokumen44 halamanPre Chapter Tenses - 2021-2daniel madrigalBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDokumen23 halamanPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousKathrin Wolf100% (1)
- Final DemoDokumen10 halamanFinal DemoEmKey GCBelum ada peringkat
- Form 5 Chapter 3 - The World of SportDokumen31 halamanForm 5 Chapter 3 - The World of SportsyilaBelum ada peringkat
- Fiche Cours AnglaisDokumen9 halamanFiche Cours Anglaisliman boukar BoukarBelum ada peringkat
- Present Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsDokumen7 halamanPresent Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsYanina ChaileBelum ada peringkat
- EP 2 Discussion HandoutDokumen5 halamanEP 2 Discussion HandoutJoshua Matanguihan CapitanBelum ada peringkat
- Verb Tense Review: The Importance of TimeDokumen32 halamanVerb Tense Review: The Importance of Timebaba ioana100% (1)
- On Course B1 Summary. Unit 1Dokumen2 halamanOn Course B1 Summary. Unit 1Isabel BelloBelum ada peringkat
- Tenses ReviewDokumen38 halamanTenses Reviewmasro apriwanBelum ada peringkat
- PRESENT PERFECT PresentationDokumen20 halamanPRESENT PERFECT PresentationMateriales InglesBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect ContinuousDokumen17 halamanPresent Perfect Continuousfaizan001Belum ada peringkat
- General RevisionDokumen7 halamanGeneral RevisionfatimroxaBelum ada peringkat
- Remaining TensesDokumen4 halamanRemaining Tensessaigbogun099Belum ada peringkat
- Past Simple TenseDokumen36 halamanPast Simple TenseRosary QuilingBelum ada peringkat
- Errors Based On TensesDokumen56 halamanErrors Based On TensesSan DeepBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect - Past PerfectDokumen16 halamanPresent Perfect - Past PerfectBárbara Rodríguez GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- 6 TensesDokumen51 halaman6 TensesSyedWajahatAli100% (1)
- Verbs!: Verb Forms Review of TensesDokumen33 halamanVerbs!: Verb Forms Review of TensesradityaBelum ada peringkat
- Dory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesDokumen20 halamanDory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesHuyền Trinh NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect ContinuousDokumen15 halamanPresent Perfect ContinuousMario A. RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- English Verb TensesDokumen5 halamanEnglish Verb TensesNabil El makoudyBelum ada peringkat
- What Is TenseDokumen6 halamanWhat Is TenserazaabbBelum ada peringkat
- Present Simple: Driving at The MomentDokumen5 halamanPresent Simple: Driving at The MomentIulian SirbuBelum ada peringkat
- Pioneer C1Dokumen15 halamanPioneer C1ahomaBelum ada peringkat
- There Are 12 Tenses in EnglishDokumen6 halamanThere Are 12 Tenses in EnglishyrynukaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Present: Simple, Perfect, and Progressive/continuousDokumen3 halamanPresent: Simple, Perfect, and Progressive/continuouscyrine khbouBelum ada peringkat
- TENSESDokumen17 halamanTENSESJonathan AmadeusBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen35 halamanTensesMarianBelum ada peringkat
- English Test Simple Present and Present ProgressiveDokumen17 halamanEnglish Test Simple Present and Present Progressivecontes_alinaBelum ada peringkat
- Life 6. Unit 2Dokumen18 halamanLife 6. Unit 2Diana moraBelum ada peringkat
- Best English Grammar Notes by Top IAS CoDokumen54 halamanBest English Grammar Notes by Top IAS Coana mBelum ada peringkat
- Verbal Tenses2nd Bat 2Dokumen52 halamanVerbal Tenses2nd Bat 2nazhaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present: The Simple Future Is A Verb Tense That's Used To Talk About Things That Haven't Happened YetDokumen9 halamanSimple Present: The Simple Future Is A Verb Tense That's Used To Talk About Things That Haven't Happened YetMega TrianaBelum ada peringkat
- TENSESDokumen6 halamanTENSESThilagavathy ThirugnanasambandamBelum ada peringkat
- Copia de Copia de TENSESDokumen20 halamanCopia de Copia de TENSESjazminBelum ada peringkat
- Past:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDokumen12 halamanPast:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousAhmed Abd El HafeezBelum ada peringkat
- GrammarDokumen5 halamanGrammarAngelo BattagliaBelum ada peringkat
- Glossary 5Dokumen50 halamanGlossary 5camila piranBelum ada peringkat
- Present PerfectDokumen18 halamanPresent PerfectYeimy LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Trabalho de Campo de Ingles-História - 2023 - Turma GDokumen11 halamanTrabalho de Campo de Ingles-História - 2023 - Turma Gfrenqui MussaBelum ada peringkat
- Tense ReviewDokumen41 halamanTense ReviewMarga Molins SotorresBelum ada peringkat
- Present PerfectDokumen38 halamanPresent PerfectTina JoseanuBelum ada peringkat
- PresentperfectDokumen12 halamanPresentperfectapi-252190418Belum ada peringkat
- Times EnglishDokumen6 halamanTimes EnglishAngelina HarabagiuBelum ada peringkat
- All Tenses ChartDokumen4 halamanAll Tenses ChartKaren Andrade100% (2)
- Present Perfect Tense: Compiled by Ermawati ZN, M. PDDokumen10 halamanPresent Perfect Tense: Compiled by Ermawati ZN, M. PDYoga KazamaBelum ada peringkat
- 16 TensesDokumen6 halaman16 TensesLizi BitadzeBelum ada peringkat
- Support de Cours Lp1-CD-cDokumen67 halamanSupport de Cours Lp1-CD-cKouadio franck KouassiBelum ada peringkat
- Present TenseDokumen18 halamanPresent TenseDarina ShabetyaBelum ada peringkat
- Test Romana EnglezaDokumen97 halamanTest Romana EnglezaRaluca CiupeBelum ada peringkat
- The Tense SystemDokumen7 halamanThe Tense SystemMohammed ShahabBelum ada peringkat
- Simple TenseDokumen13 halamanSimple TenseChad HayesBelum ada peringkat
- Timpuri Verbale Engleza RezumatDokumen5 halamanTimpuri Verbale Engleza RezumatBogdan StefanBelum ada peringkat
- VerbsDokumen48 halamanVerbsRyla TangahuBelum ada peringkat
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDokumen17 halamanPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousLiliana RaduBelum ada peringkat
- шпаргалка tensesDokumen7 halamanшпаргалка tensesГригорий ВоронBelum ada peringkat
- HND Year 2 Common Texts NewDokumen64 halamanHND Year 2 Common Texts Newbsonleader5Belum ada peringkat
- Composition Notes Friendly Letter B1 and B2 Esolnet HellasDokumen9 halamanComposition Notes Friendly Letter B1 and B2 Esolnet HellasGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Review Test Unit 1Dokumen3 halamanReview Test Unit 1Georgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Derivative Chart: Noun Adjective Verb Adverb Meaning HeadDokumen2 halamanDerivative Chart: Noun Adjective Verb Adverb Meaning HeadGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Need To and Have ToDokumen3 halamanNeed To and Have ToGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- b2 Oral Candidate Prompts Dec 08Dokumen7 halamanb2 Oral Candidate Prompts Dec 08Georgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Grammar LexixallyDokumen4 halamanTeaching Grammar LexixallyGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- 2master Phrasal VerbsDokumen26 halaman2master Phrasal VerbsGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Answer SheetDokumen2 halamanAnswer SheetGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Letter PuzzlesDokumen27 halamanLetter PuzzlesGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- First Lesson With An AdultDokumen1 halamanFirst Lesson With An AdultGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- LRN Informational BrochureDokumen5 halamanLRN Informational BrochureGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Talking About The Future: A) Future Continuous FormDokumen2 halamanTalking About The Future: A) Future Continuous FormGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Need To and Have ToDokumen3 halamanNeed To and Have ToGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- The Plasticity of Categories ColorDokumen34 halamanThe Plasticity of Categories ColorGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Final Test: C' Senior Class: Part 1. Vocabulary and GrammarDokumen4 halamanFinal Test: C' Senior Class: Part 1. Vocabulary and GrammarGeorgia KleoudiBelum ada peringkat
- Biletzki A - Is There A History of PragmaticsDokumen16 halamanBiletzki A - Is There A History of Pragmaticsdida13Belum ada peringkat
- Differences Between SpeechDokumen3 halamanDifferences Between Speechchew_93Belum ada peringkat
- Micro Test Crucial Words Page 223 - 224Dokumen2 halamanMicro Test Crucial Words Page 223 - 224Ludwin Salazar ValdiviaBelum ada peringkat
- mELANAU lANGUAGE PDFDokumen100 halamanmELANAU lANGUAGE PDFGenmanBelum ada peringkat
- Metodologi Studi IslamDokumen26 halamanMetodologi Studi IslamAyu Mareta MBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises Past Simple To Be PDFDokumen2 halamanExercises Past Simple To Be PDFGonzaloBelum ada peringkat
- Malay (Bahasa Melayu / ويلام ساهب) : ArabicDokumen4 halamanMalay (Bahasa Melayu / ويلام ساهب) : ArabicAzam-Savaşçı Anderson MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Proto-Vanga-Kozea (PVK) : A Constructed Proto-Language by Adam Emil SkoogDokumen6 halamanProto-Vanga-Kozea (PVK) : A Constructed Proto-Language by Adam Emil SkoogAdam Emil SkoogBelum ada peringkat
- Modal VerbsDokumen16 halamanModal VerbsSoyun AnnayewBelum ada peringkat
- Sentence TanglersDokumen17 halamanSentence TanglerssaturnitinerantBelum ada peringkat
- Mark Durie Malcolm Ross The Comparative Method Reviewed Regularity and Irregularity in Language Change PDFDokumen330 halamanMark Durie Malcolm Ross The Comparative Method Reviewed Regularity and Irregularity in Language Change PDFRubensMachinskiEduardoBelum ada peringkat
- High Flyer 2hDokumen6 halamanHigh Flyer 2hRamonaBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Using The Phrasal Verbs AboveDokumen1 halamanComplete Using The Phrasal Verbs AboveBuiducanh BuiBelum ada peringkat
- Swahili Term PaperDokumen10 halamanSwahili Term PapersaberchickenBelum ada peringkat
- Colors: Color Exampl e Color Words Native Korean Adjectives Sino-Korean Roots (Chinese)Dokumen3 halamanColors: Color Exampl e Color Words Native Korean Adjectives Sino-Korean Roots (Chinese)봄-Korean Language SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- MIC Speaking Handbook - 15.03.16 PDFDokumen21 halamanMIC Speaking Handbook - 15.03.16 PDFМилан СтарчевићBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Past TenseDokumen18 halamanSimple Past TenseNabila PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Hiragana and KatakanaDokumen19 halamanHiragana and Katakanawe_spidus_2006Belum ada peringkat
- KUIS A Subject-Verb AgreementDokumen3 halamanKUIS A Subject-Verb AgreementLidia HudiBelum ada peringkat
- Quantity-Sensitivity in Modern OTDokumen5 halamanQuantity-Sensitivity in Modern OTEric BakovicBelum ada peringkat
- Reported SpeechDokumen4 halamanReported SpeechCECILIA SASTREBelum ada peringkat
- Gold Exp B1 U4 Lang Test BDokumen2 halamanGold Exp B1 U4 Lang Test BRoxana Carolina Mendez ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- 1-6GrammarReview For Lessons 9-16Dokumen6 halaman1-6GrammarReview For Lessons 9-16Nur Azizah WidyaningsihBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Spoken and Written DiscourseDokumen19 halamanDifferences Between Spoken and Written DiscourseFaten AliBelum ada peringkat
- Dialogues For StartersDokumen6 halamanDialogues For StartersAnna RumyantzevaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 7 - Grupo 4Dokumen4 halamanActivity 7 - Grupo 4katherynBelum ada peringkat
- Topic Distribution For Straight Teaching Beed (Group 1) Name Subject Math Science English Filipino Aral. Pan. MapehDokumen8 halamanTopic Distribution For Straight Teaching Beed (Group 1) Name Subject Math Science English Filipino Aral. Pan. MapehMarilyn BadaBelum ada peringkat
- Review GrammarDokumen4 halamanReview GrammarLiberty Language CenterBelum ada peringkat
- Countries & Languages: 16 CluesDokumen2 halamanCountries & Languages: 16 CluesNguyen HalohaloBelum ada peringkat