XiGo Note 121 Surface Area From NMR and Particle Size
Diunggah oleh
prakush01975225403Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
XiGo Note 121 Surface Area From NMR and Particle Size
Diunggah oleh
prakush01975225403Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Surface Area Determination from Particle Size and NMR
XiGo Nanotools 116 Research Drive, Bethlehem, PA 18015
(732) 762-2787 fax: (610) 465-8631 www.xigonanotools.com
Page | 1
In principle, a surface area value can be calculated from particle size data; there
are a variety of techniques that can give an approximate particle size distribution (PSD.
Unfortunately, the PSD of many materials are broad and irregular. Three common
descriptors are the mean, mode and median (d
50
). These values can differ markedly as the
PSD broadens. Which, then, is the most appropriate single value to calculate surface area?
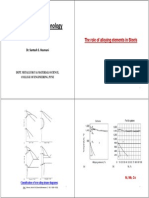
Figure 1 shows the PSD for a sample of a 2vol% aqueous suspension of a micro fine TiO
2
.
The particle size is fairly uniformly distributed about the modal value (70nm) where the
majority of the particles reside but the suspension contains a tail of agglomerates that
skews the mean and median sizes. Table 1 lists the surface area values calculated from the
three sizes. They are noticeably different.
Many real-world particles are far from round or uniform. Light scattering devices
determine an equivalent spherical diameter (ESD) - the diameter of a sphere that would
give the same result as the actual particle. Different techniques can yield very different ESD
for the same particle; the more asymmetric the particle, the larger the difference in ESD.
Any surface area value calculated from PSD data is, at best, only a crude approximation.
In contrast to PSD devices, when calculating wetted surface area values from NMR
relaxation data, there are no assumptions made regarding either particle size or shape. The
Acorn Area can work with virtually any particle in any liquid at any concentration and
since measurements typically take less than 5 minutes this makes it ideal for QC
measurements.
Measuring the correct wetted surface area of active pharmaceutical ingredient
(API) is vital because API surface area directly impacts not only bioavailability but also the
rate of dissolution (Noyes-Whitney equation). There is also a growing body of evidence
that, for any type of nanoparticle, it is the surface area and not particle size that is the
defining metric controlling toxicological interaction. Figure 2 illustrates the difficulty where
the PSD is bimodal. Here 10% of the API (the fraction at ca 200nm) accounts for 90% of
the wetted surface area. Table 2 compares the wetted surface areas of six Lots of the
same API that had passed QC by laser diffraction particle size measurements. The
reproducibility of the NMR measurements was ca 1%. Lot#1 is clearly different (smaller
SA).
A
p
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
N
o
t
e
1
2
1
TABLE 1
Particle Size Surface Area
(nm) (m
2
/g)
91 (mean) 16
82 (median, d
50
) 18
70 (mode) 21
Mean PSD (LD): 2.4m
Estimated SA: 2m
2
/g
Measured SA (NMR): 24m
2
/g
TABLE 2
Lot# 1 2 3 4 5 6
SA (NMR) 4.4 5.3 5.6 5.4 5.2 5.4
Figure 1
Figure 2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- How Effective Can optical-CT 3D Dosimetry Be WithoDokumen5 halamanHow Effective Can optical-CT 3D Dosimetry Be Withobright nvachirawitBelum ada peringkat
- How To Measure Molecular Weight (Same Methode, Other Paper)Dokumen6 halamanHow To Measure Molecular Weight (Same Methode, Other Paper)Julien HalnautBelum ada peringkat
- XiGo Note 103 Silica Surface Area With The Acorn AreaDokumen4 halamanXiGo Note 103 Silica Surface Area With The Acorn Areaprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- 5.isca RJRS 2012 356Dokumen4 halaman5.isca RJRS 2012 356prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Stereological Correction of Liberation DistributionsDokumen8 halamanStereological Correction of Liberation DistributionsHARIMETLYBelum ada peringkat
- Powder CharacterizationDokumen21 halamanPowder CharacterizationecternalBelum ada peringkat
- ACRS2015 Paper-ID 136Dokumen8 halamanACRS2015 Paper-ID 136Duong HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 HunterDokumen21 halamanChapter 3 HunterOsama AnatyBelum ada peringkat
- Light ScatteringDokumen3 halamanLight ScatteringAngel Quijano ArmengolBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Plasmon Resonance: K. Scott Phillips and Quan Jason ChengDokumen12 halamanSurface Plasmon Resonance: K. Scott Phillips and Quan Jason ChengTin Tức Mỗi NgàyBelum ada peringkat
- CHE572 Chapter 2 Particle Size Characterization PDFDokumen18 halamanCHE572 Chapter 2 Particle Size Characterization PDFMuhd FahmiBelum ada peringkat
- DTS Nano Series Training Course Size DayDokumen98 halamanDTS Nano Series Training Course Size DayDerya KöseBelum ada peringkat
- Shape and Size of Microfine Aggregates: X-Ray Microcomputed Tomography vs. Laser DiffractionDokumen11 halamanShape and Size of Microfine Aggregates: X-Ray Microcomputed Tomography vs. Laser DiffractionSiddhesh Kamat MhamaiBelum ada peringkat
- Settlement of Shallow Foundations On Sand - A Database StudyDokumen18 halamanSettlement of Shallow Foundations On Sand - A Database StudySidali RafaBelum ada peringkat
- Tracer Particles and Seeding For Particle Image Velocimetry: A MellingDokumen11 halamanTracer Particles and Seeding For Particle Image Velocimetry: A MellingFSBollBelum ada peringkat
- 64 Measurement of Particle Size Distribution in Suspension Polymerization Using in Situ Laser BackscatteringDokumen9 halaman64 Measurement of Particle Size Distribution in Suspension Polymerization Using in Situ Laser BackscatteringGufran AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Water Body Extraction From Multi Spectral Image byDokumen6 halamanWater Body Extraction From Multi Spectral Image byMaxim MaximBelum ada peringkat
- Density Log Dexter Tanabe 20000241Dokumen15 halamanDensity Log Dexter Tanabe 20000241Dexter TanabeBelum ada peringkat
- Density Logging FinalDokumen8 halamanDensity Logging FinalAvighyan ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- BET Analysis Book MethodsDokumen38 halamanBET Analysis Book MethodsZirrus GlassBelum ada peringkat
- Crossmark: Materials Science & Engineering ADokumen10 halamanCrossmark: Materials Science & Engineering ASofiane TaaneBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensor Development A. BackgroundDokumen11 halamanSurface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensor Development A. BackgroundBui Trung TuyenBelum ada peringkat
- Micromeritics IDokumen11 halamanMicromeritics ISirisha MBelum ada peringkat
- Estimating The Cut (Ds0) Sizeof Classifiers Without Product Particle-SizemeasurementDokumen10 halamanEstimating The Cut (Ds0) Sizeof Classifiers Without Product Particle-SizemeasurementbehnamBelum ada peringkat
- Geoquimica Traduccion 1Dokumen11 halamanGeoquimica Traduccion 1carlos ramosBelum ada peringkat
- Articulo A Guide To Characterizing Particle Size and Shape PDFDokumen11 halamanArticulo A Guide To Characterizing Particle Size and Shape PDFNestor QvinteroBelum ada peringkat
- Tamaño de Particula D10d50d90Dokumen5 halamanTamaño de Particula D10d50d90vivianareynosoBelum ada peringkat
- Publications: Water Resources ResearchDokumen16 halamanPublications: Water Resources ResearchMarvin Ubaldo SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids Using An Interferometric MethodDokumen6 halamanDetermination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids Using An Interferometric Methodahmad hasabiBelum ada peringkat
- SCHA1201Dokumen94 halamanSCHA1201Saptanshu SamalBelum ada peringkat
- ESPECTROSCOPIA 3 INDokumen19 halamanESPECTROSCOPIA 3 INErika ApazaBelum ada peringkat
- AbstractDokumen10 halamanAbstractKakarot BnBelum ada peringkat
- Crystallite Size Analysis of Supported Platinum Catalysts by XRDDokumen2 halamanCrystallite Size Analysis of Supported Platinum Catalysts by XRDAhmed Gamal AshourBelum ada peringkat
- Penentuan Ukuran Kristal XRD Dan TemDokumen9 halamanPenentuan Ukuran Kristal XRD Dan TemNi Putu Dian PuspithaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Text - A Guide To Characterizing Particle Size and Shape - 23AGO2020Dokumen11 halaman1 - Text - A Guide To Characterizing Particle Size and Shape - 23AGO2020Estefanía Gómez RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- J 2011 Ultramicroscopy Psds Local ThresholdingDokumen6 halamanJ 2011 Ultramicroscopy Psds Local Thresholdingwaseemkhan49Belum ada peringkat
- Particle Size Regression Correction For NIR Spectrum (Tamanho de Particula, MI 2013)Dokumen8 halamanParticle Size Regression Correction For NIR Spectrum (Tamanho de Particula, MI 2013)Mikaelle DutraBelum ada peringkat
- Optics & Laser Technology: Wei Liu, Xianming Sun, Jin ShenDokumen5 halamanOptics & Laser Technology: Wei Liu, Xianming Sun, Jin ShenJonalyn CaliwagBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative Metodology For Gold Nanoparticles Diameter Characterization Using PCA Technique and UV-VIS SpectrophotometryDokumen6 halamanAlternative Metodology For Gold Nanoparticles Diameter Characterization Using PCA Technique and UV-VIS Spectrophotometryzain malikBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of 3D Pore-Scale Flow in Index-Matched Porous MediaDokumen8 halamanMeasurement of 3D Pore-Scale Flow in Index-Matched Porous MediaBen MunroBelum ada peringkat
- XiGo Note 101 Powder Surface Area Comparison BET and Acorn AreaDokumen4 halamanXiGo Note 101 Powder Surface Area Comparison BET and Acorn Areaprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- 2012 082 PDFDokumen15 halaman2012 082 PDFAliniski123Belum ada peringkat
- Ac 049428 XDokumen12 halamanAc 049428 XAlessandro Xalexalex RanalliBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Behavior of An Altered Reservoir Limestone: Multi-Scale and Core Analysis ApproachesDokumen12 halamanMechanical Behavior of An Altered Reservoir Limestone: Multi-Scale and Core Analysis ApproachesRosa K Chang HBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement: C. Ararat-Ibarguen, R.A. Pérez, M. IribarrenDokumen10 halamanMeasurement: C. Ararat-Ibarguen, R.A. Pérez, M. IribarrenALEJANDRA FONTALVO STUDENTBelum ada peringkat
- RTM ASSIGNMENT 2: WATER EQUIVALENCE OF LIF TLDSDokumen12 halamanRTM ASSIGNMENT 2: WATER EQUIVALENCE OF LIF TLDSOtieno MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Next Network of Excellence in Training: Lecture Notes For "Litho-Density Logs"Dokumen11 halamanNext Network of Excellence in Training: Lecture Notes For "Litho-Density Logs"carlosBelum ada peringkat
- Abbe Refractometer: 1 ObjectiveDokumen9 halamanAbbe Refractometer: 1 ObjectiveMuhammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring paper roughness using speckle analysisDokumen6 halamanMeasuring paper roughness using speckle analysisapino14Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 01 Particle Size Analyzer (Full Report)Dokumen6 halamanLab 01 Particle Size Analyzer (Full Report)Yi Ling GohBelum ada peringkat
- T192898 - AvanceCore App Note - DOSYDokumen8 halamanT192898 - AvanceCore App Note - DOSYLaiza Bruzadelle LoureiroBelum ada peringkat
- Unfolding Particle Size Distributions of Tea Grades: Ft. 43, & A), A Printed in CeylonDokumen11 halamanUnfolding Particle Size Distributions of Tea Grades: Ft. 43, & A), A Printed in Ceylonharish kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Review OPT442Dokumen3 halamanReview OPT442Arnab Barman RayBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Optical Spectrum For Hematite Nanofluid Longpass Tunable FilterDokumen5 halamanAnalysis of Optical Spectrum For Hematite Nanofluid Longpass Tunable FilterAJER JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Far-Field Plasmonic Resonance Enhanced Nano-Particle Image Velocimetry Within A Micro ChannelDokumen16 halamanFar-Field Plasmonic Resonance Enhanced Nano-Particle Image Velocimetry Within A Micro ChannelABelum ada peringkat
- A. Pino 2009Dokumen9 halamanA. Pino 2009PedroBelum ada peringkat
- BC Sasonal Size DistributionDokumen7 halamanBC Sasonal Size Distributionrubens.pereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation of refractive index and temperature dispersion of ZnSe and SiDokumen5 halamanCalculation of refractive index and temperature dispersion of ZnSe and SiDidier Alejandro Patiño RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- AdditionalDokumen6 halamanAdditionalFaidah BazeronBelum ada peringkat
- Solid-State Water Electrolysis With An Alkaline MembraneDokumen4 halamanSolid-State Water Electrolysis With An Alkaline Membraneprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Industrial Electrolysis and Electrochemical Engg PDFDokumen3 halamanIndustrial Electrolysis and Electrochemical Engg PDFprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Extracts Thirukkural PDFDokumen20 halamanExtracts Thirukkural PDFprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- 076 PDFDokumen6 halaman076 PDFprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Water ElectrolysisDokumen18 halamanA Review On Water ElectrolysisSilvester KolicBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Water ElectrolysisDokumen18 halamanA Review On Water ElectrolysisSilvester KolicBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrophobic It y Hydro Phil I City and Si LanesDokumen10 halamanHydrophobic It y Hydro Phil I City and Si Lanesprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Single-Molecule Tracking of Polymer Surface Di Ffusion: Michael J. Skaug, Joshua N. Mabry, and Daniel K. SchwartzDokumen6 halamanSingle-Molecule Tracking of Polymer Surface Di Ffusion: Michael J. Skaug, Joshua N. Mabry, and Daniel K. Schwartzprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Dokumen5 halamanHydrogen Generation From Water Electrolysis-Possibilities of Energy Saving.Richard AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- DIAT HTT Lect 29 Not Yet CoveredDokumen10 halamanDIAT HTT Lect 29 Not Yet Coveredprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Rietveld Made Easy - OverviewDokumen3 halamanRietveld Made Easy - Overviewhp2020Belum ada peringkat
- UV-Vis Molecular Absorption Spectroscopy GuideDokumen33 halamanUV-Vis Molecular Absorption Spectroscopy GuideJulie AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Fluorescence Lifetime of Mn-Doped Znse Quantum Dots With Size DependenceDokumen3 halamanFluorescence Lifetime of Mn-Doped Znse Quantum Dots With Size Dependenceprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- List of ChemicalsDokumen1 halamanList of Chemicalsprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Band Gap Measurement in Compound SemiconductorsDokumen2 halamanBand Gap Measurement in Compound Semiconductorshantarto5844Belum ada peringkat
- D1210Dokumen40 halamanD1210prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Methods and Models of Quantum Dot SynthesisDokumen34 halamanChapter 3: Methods and Models of Quantum Dot Synthesisprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Bright and Water-Soluble Near Ir-Emitting Cdse/Cdte/Znse Type-Ii/Type-I Nanocrystals, Tuning The Efficiency and Stability by GrowthDokumen7 halamanBright and Water-Soluble Near Ir-Emitting Cdse/Cdte/Znse Type-Ii/Type-I Nanocrystals, Tuning The Efficiency and Stability by Growthprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Diat HTT Lect 25 To 27Dokumen12 halamanDiat HTT Lect 25 To 27prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Sol Gel Template Synthesis of Semiconductor Nanostructures: Brinda B. Lakshmi, Peter K. Dorhout, and Charles R. MartinDokumen6 halamanSol Gel Template Synthesis of Semiconductor Nanostructures: Brinda B. Lakshmi, Peter K. Dorhout, and Charles R. Martinprakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Diat HTT Lect 22 To 24Dokumen13 halamanDiat HTT Lect 22 To 24prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Diat HTT Lect-28Dokumen12 halamanDiat HTT Lect-28prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Diat HTT Lect 22 To 24Dokumen13 halamanDiat HTT Lect 22 To 24prakush01975225403Belum ada peringkat
- Manage Waste & Resources with WastivityDokumen21 halamanManage Waste & Resources with WastivitybhishmBelum ada peringkat
- BS en 10149-1 1996Dokumen16 halamanBS en 10149-1 1996ibson045001256100% (1)
- Design of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneDokumen7 halamanDesign of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneRonin ZxxBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of AnionsDokumen6 halamanAnalysis of Anionsjanrheb delapenaBelum ada peringkat
- Mod 2 BA PhysicsDokumen412 halamanMod 2 BA PhysicsBenitoKameloBelum ada peringkat
- Shell Thickness CalculationsDokumen2 halamanShell Thickness CalculationsskocogluBelum ada peringkat
- Solid Dosage Forms: Tablets: Abhay ML Verma (Pharmaceutics)Dokumen5 halamanSolid Dosage Forms: Tablets: Abhay ML Verma (Pharmaceutics)meet2abhayBelum ada peringkat
- Group Vii The HalogensDokumen58 halamanGroup Vii The HalogensYuanWei SiowBelum ada peringkat
- A Powerpoint Presentaion On Ready-Mix ConcreteDokumen22 halamanA Powerpoint Presentaion On Ready-Mix ConcreteGowriSenthilBelum ada peringkat
- CRC Handbook KivonatDokumen12 halamanCRC Handbook KivonatPresslly Gebol LopezBelum ada peringkat
- CoresDokumen5 halamanCoresJeremy MeyerBelum ada peringkat
- Basonetic 5030 MRF - Clutch PDFDokumen4 halamanBasonetic 5030 MRF - Clutch PDFsamsonit1Belum ada peringkat
- Water's Versatility as a Universal SolventDokumen7 halamanWater's Versatility as a Universal SolventTropz RenBelum ada peringkat
- Solubility and Solubilization: Mahendrasingh Ajitsingh Chavan M.Pharm I ST Year (Pharmaceutics) S.P.C.P. NagpurDokumen33 halamanSolubility and Solubilization: Mahendrasingh Ajitsingh Chavan M.Pharm I ST Year (Pharmaceutics) S.P.C.P. NagpurBolli SandeepBelum ada peringkat
- FRP Design Guide 06Dokumen28 halamanFRP Design Guide 06K Fink100% (5)
- BW Passivator+601 EN 2022 GL 341 PreviewDokumen2 halamanBW Passivator+601 EN 2022 GL 341 PreviewSuryana MamanBelum ada peringkat
- Making Materials Matter: Product CatalogueDokumen7 halamanMaking Materials Matter: Product Cataloguemustafasenbagci3693Belum ada peringkat
- Mandatory Appendix 41: EIH Support Plate DesignDokumen5 halamanMandatory Appendix 41: EIH Support Plate DesignHanafi BasriBelum ada peringkat
- Insulated Roof & Wall Panels Ks103 SSF Data Sheet: Microlambri Superlambri SmoothlambriDokumen5 halamanInsulated Roof & Wall Panels Ks103 SSF Data Sheet: Microlambri Superlambri SmoothlambriKhaled GamalBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Dental AmalgamDokumen64 halaman5 Dental AmalgamSmiley Josh100% (1)
- Bill of Material Sample For ResidentialDokumen4 halamanBill of Material Sample For ResidentialMyra Fe MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Rigid Pavement Design1Dokumen21 halamanRigid Pavement Design1s100% (1)
- BREF Glass Manufacturing Industry enDokumen323 halamanBREF Glass Manufacturing Industry enAleIBelum ada peringkat
- Sae Ams 2355K - 2011 PDFDokumen16 halamanSae Ams 2355K - 2011 PDFNav TalukdarBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Rolling Conditions On Ductile Fracture During PiercingDokumen6 halamanEffect of Rolling Conditions On Ductile Fracture During PiercingJJBelum ada peringkat
- Gunpowder, Explosion, and Explosive MaterialsDokumen23 halamanGunpowder, Explosion, and Explosive MaterialsEmelie TipayBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Flat Slab Using Equivalent Frame MethodDokumen41 halamanDesign of Flat Slab Using Equivalent Frame Methodabadittadesse100% (2)
- On Basics Bridge Engg SSBDokumen83 halamanOn Basics Bridge Engg SSBumeshBelum ada peringkat
- Underground Works GuideDokumen80 halamanUnderground Works GuidedanielamayavBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation Engineering-I Design of Shall PDFDokumen44 halamanFoundation Engineering-I Design of Shall PDFAhmed MohammedBelum ada peringkat