Vmware Technical Interview Q & A
Diunggah oleh
ashokkumarmdu0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
127 tayangan27 halamanVmware Technical Interview Q & A
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
RTF, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniVmware Technical Interview Q & A
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai RTF, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
127 tayangan27 halamanVmware Technical Interview Q & A
Diunggah oleh
ashokkumarmduVmware Technical Interview Q & A
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai RTF, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 27
Interview Question for VMware Administrator.
1. Difference between ESX server and ESXI Server
ESX Server - Contains Service Console OS, comes all the enterrise level futures li!e "A,VMotion,#$S which
%ives hi%hest suort for the Virtuali&ation. 'ow the current version of ESX server is (.)
ESXi Server * #oesn+t contain service console OS, comes in a ,-M. foot rint. 'ow a da/s the same will 0e
comin% shied with Servers. 1ou can store it on a microchi or a us0 drive and /ou can install it easil/. It
doesn+t suort an/ enterrise futures li!e VMotion, "A, #$S etc.
2. What are the three port groups present in ESX server networking
2. Virtual Machine 3ort 4rou - 5sed for Virtual Machine 'etwor!
-. Service Console 3ort 4rou - 5sed for Service Console Communications
,. VM6ernel 3ort 4rou - 5sed for VMotion, iSCSI, '7S Communications
3. What are the types of communications which requires an IP address for sure
Service Console and VM6ernel 8VMotion and iSCSI9, these communications does not haen without an I3
address 8:hether it is a sin%le or dedicated9
!. In the ESX Server "icensing features #$otion %icense is showing as &ot used' why
Even thou%h the license 0o; is selected, it shows as <=icense 'ot 5sed< until, /ou ena0le the VMotion otion
for secific vSwitch.
( .What are the core services of #)
VM rovisionin%, >as! Schedulin% and Event =o%%in%
*. )an we do v$otion +etween two datacenters If possi+"e how it wi"" +e
1es we can do vMotion 0etween two datacenters, 0ut the mandator/ re?uirement is the VM should 0e owered
off.
,. What is #) agent -nd what service it is corresponded to What are the minimum req.s for #) agent
insta""ation
VC a%ent is an a%ent installed on ESX server which ena0les communication 0etween VC and ESX server.
>he daemon associated with it is called vmware-hostd , and the service which corresonds to it is called as
m%mt-VMware, in the event of VC a%ent failure @ust restart the service 0/ t/in% the followin% command at the
service console
" service mgmt-VMware restart "
VC a%ent installed on the ESX server when we add it to the VC, so at the time of installation if /ou are %ettin%
an error li!e < VC A%ent service failed to install <, chec! the AOt si&e whether it is sufficient or not.
/. What are the fi"es that make a #irtua" $achine
.vm; - Virtual Machine Confi%uration 7ile
.nvram - Virtual Machine .IOS
.vmd! - Virtual Machine #is! file
.vsw - Virtual Machine Swa 7ile
.vmsd - Virtual Machine Snashot #ata0ase
.vmsn - Virtual Machine Snashot file
.vmss - Virtual Machine Susended State file
.vmware.lo% - Current =o% 7ile
.vmware-B.lo% - Old =o% file
0. What are the devices that can +e added whi"e the virtua" $achine running
In VI ,.C we can add "ard #is! and 'ICDs while the machine runnin%.
In vShere (.) we can add Memor/ and 3rocessor alon% with "## and 'ICDs while the machine runnin%
12. What is a temp"ate
:e can convert a VM into >emlate, and it cannot 0e owered on once it+s chan%ed to temlate. >his is used
to ?uic! rovisionin% of VMDs.
11. What are the common issues with snapshots What stops from taking a snapshot and how to fi3
it
If /ou confi%ure the VM with Maed =5'Ds, then the snashot failed. If it is maed as virtual then we can
ta!e a snashot of it.
If /ou confi%ure the VM with Maed =5'Ds as h/sical, /ou need to remove it to ta!e a snashot.
12. What4s is #irtua" )enter
VCenter 5sed to Mana%e ESXI servers in a clustered environment, Centrali&ed Administration of multile
ESXI server clusters.
13. What is a #&I) and vSwitch
A V'IC is a virtual nic which is added when we create a virtual machine. It+s a software 0ased nic 8virtuali&ed
nic9 which ena0les the communication 0etween vm+s or 0etween a vm or vSwitch.
A vSwitch is nothin% 0ut the h/sical nic which is installed on the ESX server. >he same h/sical nic shared to
all the virtual machines hosted on that articular ESX server. So it is actin% as a Switch in this scenario. :e
can connectAconfi%ure 2)2E virtual machines to use a h/sical nic, in other words we can create a virtual
switch that contain 2)2E orts. 'o h/sical switch rovides these man/ orts in real time. And in other case,
we can create the vSwitch without an/ h/sical nic also. It+s urel/ software 0ased vSwitch 8the same is used
0etween VM2 and VM-
1!. What is v$otion 5ow it 5appen
Movin% a virtual machine from an ESX host to another while it is runnin%. 1ou will %et a ver/ minimum
downtime for the virtual machine with this if ever/thin% confi%ured roerl/. If /ou want to do some
maintenance tas!s on one ESX server in the cluster, /ou can vMotion all the virtual machines runnin% on it to
other ESX server which has the enou%h resources availa0le.
1(. What is #$ware 67S 86istri+uted 7esource Schedu"er9
VMware #$S 8#istri0uted $esource Scheduler9 is a utilit/ that balances computing workloads with availa0le
resources in a virtuali&ed environment. >he utilit/ can 0e confi%ured for manual or automatic control.
1*. What is :au"t ;o"erance
7ault >olerance 87>9 is a new feature in vShere that ta!es VMware+s "i%h Availa0ilit/ technolo%/ to the ne;t
level 0/ rovidin% continuous rotection for a virtual machine 8VM9 in case of a host failure. It is 0ased on the
$ecord and $ela/ technolo%/ that was introduced with VMware :or!station that lets /ou record a VM+s
activit/ and later la/ it 0ac!.
1,. What is 5igh -vai"a+i"ity
VMware vShere "i%h Availa0ilit/ 8"A9 rovides eas/-to-use, cost effective hi%h availa0ilit/ for alications
runnin% in virtual machines. In the event of h/sical server failure, affected virtual machines are automaticall/
restarted on other roduction servers with sare caacit/. In the case of oeratin% s/stem failure, vShere "A
restarts the affected virtual machine on the same h/sical server.
1/. What is )"one
A clone is a co/ of an e;istin% virtual machine. >he e;istin% virtual machine is called the arent of the clone.
:hen the clonin% oeration is comlete, the clone is a searate virtual machine F thou%h it ma/ share virtual
dis!s with the arent virtual machine.
10. What is Storage # $otion
Stora%e vMotion is a comonent of VMware vShere that allows the live mi%ration of a runnin% virtual
machineDs 8VM9 file s/stem from one stora%e s/stem to another, with no downtime for the VM or service
disrution for end users. >his mi%ration occurs while maintainin% data inte%rit/.
22. What is %<& 8%ogica" unique &um+er9
A lo%ical unit num0er 8=5'9 is a uni?ue identifier used to desi%nate individual or collections of hard dis!
devices for address 0/ a rotocol associated with a SCSI, iSCSI, 7i0re Channel 87C9 or similar interface. =5's
are central to the mana%ement of 0loc! stora%e arra/s shared over a stora%e area networ! 8SA'9.
21. What is Storage -rea &etwork
A stora%e area networ! 8SA'9 is a hi%h-seed secial-urose networ! 8or su0 networ!9 that interconnects
different !inds of data stora%e devices with associated data servers on 0ehalf of a lar%er networ! of users.
22. What is &etwork -rea Storage
'etwor!-attached stora%e 8'AS9 is a dedicated hard dis! stora%e device that is set u with its own networ!
address and rovides file-0ased data stora%e services to other devices on the networ!.
23. What is S7$ 8site 7ecovery $anager9
VMware vCenterG Site $ecover/ Mana%er ma!es disaster recover/ raid, relia0le and mana%ea0le, so that
or%ani&ations can meet their recover/ o0@ectives. Site Recovery Manager delivers centralied management
of recovery plans and automates t!e recovery process. It turns comle; aer run 0oo!s associated with
traditional disaster recover/ into an inte%rated element of virtual infrastructure mana%ement, allowin%
or%ani&ations to imrove recover/ lan testin% dramaticall/.
"#. $!at is #$ware vSphere standard virtua" switch
The VMware vSphere standard switch (vSwitch) is your basic "network virtualization" switch Most o! the
!eatures were re"uired to connect the virtual machines to the virtual host and physical #$% cards so that they
all have network connectivity
2(. What is VMware vSphere distributed virtual switch
VSphere distributed virtual switch (also called a vDS, or vNetwork Distributed Switch), you must have a
license for vSphere Enterprise plus Edition. rom there, you can take advanta!e of the followin! features"
# $entrali%ed confi!uration for all network switch ports, across the entire virtual infrastructure.
# Ethernet port, $D&, and Net flow statistics that !o with a virtual machine as it moves from one ES' Server
to another due to V(otion.
# Network policies that !o with a virtual machine durin! V(otion.
# )* rate limitin!.
# &rivate V+,Ns.
# Support for third-party switches (with the only option today bein! the $isco Ne*us .///-V).
2*. What is hot p"ug in
VMware vSphere&s hot-add '(M and hot-plug %)* !unctions allow you to add additional virtual hardware to
running virtual machines The bene!it o! being able to do this is the ability to provide more resources to your
machines without bringing servers down to add the additional resources Simply put+ this is additional capacity
without downtime
2,. What is 5ost Profi"e
Host Profiles is a VMware vCenter feature that is available on hosts licensed with ,nterprise )lus, and it allows you to
take an ESX or ESXis configuration rofile and aly it to other hosts! "ts a #uick and easy way to relicate
configurations for hosts in a cluster, and also to $onitor a hosts co$liance with the selected host rofile!
28. What are the minimum hardwares require to install ESXI 5.1 server?
Supported server platform
7or a list of suorted latforms, see the VMware Comati0ilit/ 4uide at httHAAwww.vmware.comAresourcesAcomati0ilit/
%#&bit 'rocessor
# ESXi C.2 will install and run onl/ on servers with E(-0it ;IE C35s.
# ESXi C.2 re?uires a host machine with at least two cores.
# ESXi C.2 suorts onl/ =A"7 and SA"7 C35 instructions.
# ESXi C.2 re?uires the 'XAX# 0it to 0e ena0led for the C35 in the .IOS.
# ESXi C.2 suorts a 0road ran%e of ;E( multicore rocessors. 7or a comlete list of suorted rocessors, see
the VMware comati0ilit/ %uide at httHAAwww.vmware.comAresourcesAcomati0ilit/.
R(M
# -4. $AM minimum
# 3rovide at least I4. of $AM to ta!e full advanta%e of ESXi C.2 features and run virtual machines in t/ical
roduction environments.
)ardware *irtualiation Support
# >o suort E(-0it virtual machines, suort for hardware virtuali&ation 8Intel V>-; or AM# $VI9 must 0e ena0led on
;E( C35s.
# >o determine whether /our server has E(-0it VMware suort, download the C35 Identification 5tilit/ from
vmware.com.
# 'etwor! Adaters
# One or more 4i%a0it or 2) 4. Ethernet controllers. 7or a list of suorted networ! adater models, see the
VMware Comati0ilit/ 4uide at httHAAwww.vmware.comAresourcesAcomati0ilit/.
20. What is a #$ware too"
VMware Tools is a suite o! utilities that enhances the per!ormance o! the virtual machine&s guest operating
system and improves management o! the virtual machine -ithout VMware Tools installed in your guest
operating system+ guest per!ormance lacks important !unctionality
32. What is vSphere
VMware $nc is a so!tware company that develops many suite o! so!tware products specially !or
providing various virtualization solutions There are many cloud products+ datacenter products+ and
desktop products and so on
vSphere is a so!tware suite that comes under datacenter product vSphere is like Microso!t .!!ice
suite which has many so!tware/s like MS .!!ice+ MS ,0cel+ and MS (ccess and so on 1ike Microso!t
.!!ice vsphere is also a so!tware suite that has many so!tware/s like v%enter+ ,S2i+ vSphere client
and so on So the combination o! all these so!tware/s is vSphere vSphere is not a particular so!tware
that you can install and use+ 3it is 4ust a package name which contains sub components5
1. What are the changes made in configuration fi"es whi"e taking a snapshot of the running virtua"
machine
The snapshot !eature is most use!ul when you want to preserve the state o! the virtual machine so you can
return to the same state repeatedly To simply save the current state o! your virtual machine+ then pick up work
later with the virtual machine in the same state it was when you stopped+ suspend the virtual machine
2. What is Sing"e Sign on in v Sphere (.1
(ns6 vSphere 78 introduces the v%enter Single Sign .n service as part o! the v%enter Server management
in!rastructure This change a!!ects v%enter Server installation+ upgrading+ and operation (uthentication by
v%enter Single Sign-.n makes the VMware cloud in!rastructure plat!orm more secure by allowing the vSphere
so!tware components to communicate with each other through a secure token e0change mechanism+ instead
o! re"uiring each component to authenticate a user separately with a directory service like (ctive 9irectory
: What are the different +etween ESXI !.1 = ESXI (.1
Capailit! ESX ESXi
"rouleshootin#
per$ormed via Service Console ESXi Shell
%ctive &irector
%uthentication Enabled Enabled
Se%ure S!slo# 'ot Suorted Suorted
&ana#ement
'etwor( Service Console "nterface VM(ernel "nterface
)u$bo *ra$es Suorted Suorted
Hardware Montioring
+ rd Party agents installed in Service
console Via C"M Providers
,oot fro$ S%' Suorted in ESX Suorted in ESXi
Software atches and
udates
'eeded as s$ilar to linu- oeration
syste$
*ew acthes because of s$all
footrint and $ore secure
vShere web %ccess .nly e-eri$ental
*ull $anagenet caability via
vSPhere web client
)o%(ed *own &ode 'ot resent
Present ! /ockdown $ode
revents re$ote users to login
to the host
Scrited "nstalltion Suorted Suorted
vM% Suort 0es 0es
Ma1or %d$inistration
co$$and2line
Co$$and es-cfg2 es-cli
+apid deplo!ment via
,uto *eplo! 'ot suorted Suorted
Custom Ima#e
%reation 'ot suorted Suorted
VMkernel 'etwork
3sed for
vMotion,*ault 4olarance,Stoarge
Connectivity
Manage$ent 'etwork ,
vMotion, *ault 4olarance,
Stoarge Connectivity, "SCS"
ort binding
!. What are the procedures to do physica" 2 virtua" migrations what are the port required to do the
same 7efer >( or 7efer pdf fi"e
(. What is the difference +etween &;:S = #$:S partition 7efer >3
*.If my v )enter is down so what impact happen in my #irtua" environment
(ns 6 #othing will when v center down and Virtual environment run !ine
,. 6ifference +etween c"one = snapshot
, clone is a copy of a virtual machine. , template is a master copy of a virtual machine that can be used to
create many clones.
0hen you clone a virtual machine, you create a copy of the entire virtual machine, includin! its settin!s, any
confi!ured virtual devices, installed software, and other contents of the virtual machine1s disks. 2ou also have
the option to use !uest operatin! system customi%ation to chan!e some of the properties of the clone, such as
the computer name and networkin! settin!s.
$lonin! a virtual machine can save time if you are deployin! many similar virtual machines. 2ou can create,
confi!ure, and install software on a sin!le virtual machine, and then clone it multiple times, rather than creatin!
and confi!urin! each virtual machine individually.
, template is a master copy of a virtual machine that can be used to create and provision virtual machines.
3emplates cannot be powered on or edited, and are more difficult to alter than ordinary virtual machine. ,
template offers a more secure way of preservin! a virtual machine confi!uration that you want to deploy many
times.
, snapshot preserves the state and data of a virtual machine at a specific point in time.
# 3he state includes the virtual machine4s power state (for e*ample, powered-on, powered-off, suspended).
# 3he data includes all of the files that make up the virtual machine. 3his includes disks, memory, and other devices, such as
virtual network interface cards.
/.What are the causes facing the issue to do the virtua" 2 virtua" migration and how trou+"eshoot this.
7efer ? >/ #2#
; $! my v %enter goes down so what is the procedure to create the new v %enter and how i can con!igure all
the previous settings done on old v %enter same apply to new v center
12. What is Server hardening 7efer >* or refer 3"3 fi"e
88 -ho we can update client windows patches !rom -S*S server procedure to con!igure the -S*S server
!rom client site what are the change should be made on registry and how -S*S works
8< -hat are the de!erence between windows <==> ? windows <=8<@
13. What is ;hin provisioning and thick provisioning.
(6 Thin provisioningA8B is a mechanism that applies to large-scale centralized computer disk storage systems+
S(#s+ and storage virtualization systems Thin provisioning allows space to be easily allocated to servers+ on a
4ust-enough and 4ust-in-time basis 7ef >1 +e"ow
1!. What are the prerequisite to do #irtua" 2 #irtua" migration ports required to do the same 7efer >/
1(.What are the new features imp"ement in v Sphere (.1 7efer ? >0
8C %urrent setup o! your site ( e0plain) which Server+ storage+ ,S2$ version+ VM+ 9ata backup+ VM backup
has been used in company
8D 9ay to day activities per!orming (4ob role ? 'esponsibilities) at the client side
1/. What is update manager >, or 7efer P6:
8; Eow we can update the ,S2$ versions what are the steps should be taken to do the up gradation
Q2. :hatDs the difference 0etween thic!-rovisioned and thin-rovisioned dis!s in ESX (.)J
Versions of ESX rior to (.) were onl/ caa0le of creatin% thic!-rovisioned dis!s. #is!s in this format are created
with the entire si&e of the dis! re-allocated on h/sical stora%e at the time the dis! is created. >his re-allocation
means that creatin% a 2))4. virtual dis! actuall/ consumes 2))4. of h/sical dis! sace on /our drives.
Q. "ow can I convert a thin-rovisioned dis! to thic!, or a thic!-rovisioned dis! to thin, in ESX (.)J
Allocatin% h/sical sace to virtual dis!s can 0e a resource intensive oeration. >he internal rocess that carves out
dis! sace on /our h/sical dis! drives could have an imact on the erformance of other virtual machines 8VMs9.
>hus, re-allocation rovided a wa/ to ensure that this resource-intensive oeration occurred all at once, onl/ when
new dis!s were rovisioned.
Comare this 0ehavior to thin-rovisioned dis!s. :ith a thin-rovisioned dis!, the amount of h/sical dis! stora%e
used 0/ a virtual dis! is e?ual to the amount of actual data on that dis!. If /ou create a 2))4. dis! 0ut onl/ use
-)4. of that dis!, the actual dis! consumtion on /our h/sical drives will 0e -)4..
>here are two downsides to thin rovisionin%. 7irst, each e;ansion of the re?uires a small amount of e;tra
resources to accomlish. >his activit/ can have a sli%ht imact on dis! erformance, articularl/ when man/ VMs
share the same #atastore. Second, administrators must a/ careful attention to dis! consumtion. .ecause ever/
dis! <0elieves< that it has more sace availa0le than it actuall/ has, the situation 0ecomes ossi0le where a well-
meanin% VM consumes all /our h/sical stora%e. >he result of fillin% u /our dis!s in this manner can 0e ainful at
0est.
>oda/+s imrovements to dis!s, SA's, and dis! rovisionin% have reduced the erformance imact of thin
rovisionin%. >hus, usin% thin-rovisioned dis!s can dramaticall/ reduce /our wasted dis! sace. "owever, /ou
must 0e e;cetionall/ careful to never fill that dis! sace to caacit/. Monitorin% dis! sace usa%e and havin% e;tra
dis!s on hand in an emer%enc/ are vitall/ imortant.
3his article provides steps to chan!e the provisionin! of a virtual disk from thick to thin, or from thin to thick.
3he procedure uses the vSphere $lient and v$enter Server to perform this task.
Resolution
Note" 5efore followin! these procedures, V(ware hi!hly recommends that you have a valid backup of the
virtual machine and enou!h space to convert the virtual machine1s disk(s) from thin to thick.
3o chan!e the provisionin! of a virtual machine base disk from thin to thick from the Datastore 5rowser"
.. &ower off the virtual machine.
6. 7n vSphere $lient, ri!ht-click the virtual machine in the inventory.
8. $lick Edit Settings to display the Virtual Machine Properties dialo! bo*.
9. $lick the Hardware tab and select the appropriate hard disk in the Hardware list.
Note" 3he Disk &rovisionin! 3ype section on the ri!ht displays either 3hin &rovision or 3hick &rovision.
7f the disk provision type is 3hick, disk provisionin! has already taken place. 7n this case, the disk
provisionin! is 3hin.
:. $lick Cancel to e*it out of Virtual Machine Properties dialo! bo*.
;. $lick the Summary tab of the virtual machine.
<. =nder Resources, ri!ht-click the datastore where the virtual machine resides and click
Browse atastore.
>. Double-click the virtual machine folder to display the .vmdk file.
?. )i!ht-click the .vmdk file, and click !n"late. 3he !n"late option converts the disk to thick provisioned.
Notes"
# 7f the !n"late option is !rayed out, this may indicate that the virtual machine is not powered off or that it
is not thin provisioned.
# 3here should be no snapshots and the conversion is performed on the base disk.
3o convert a virtual machine base disk from thick to thin provisionin! by chan!in! the datastore and usin!
offline virtual machine mi!ration"
.. &ower off the virtual machine.
6. )i!ht-click the virtual machine, and click Migrate.
8. $lick Change datastore.
9. $lick Ne#t, and select a datastore that is not the same as the current datastore.
:. rom the dropdown, select the $hin Provision virtual disk format.
;. $lick Ne#t, then %inish.
Note& 3his process re@uires more than one datastore. 7f only a sin!le datastore e*ists, you can clone the virtual
machine to a destination machine with thin provisioned disks instead of mi!ratin!.
Q- H5nderstandin% Clones
A clone is a co/ of an e;istin% virtual machine. >he e;istin% virtual machine is called the arent of the clone. :hen
the clonin% oeration is comlete, the clone is a searate virtual machine F thou%h it ma/ share virtual dis!s with
the arent virtual machineH see 7ull and =in!ed Clones9.
KChan%es made to a clone do not affect the arent virtual machine. Chan%es made to the arent virtual machine do
not aear in a clone.
KA cloneDs MAC address and 55I# are different from those of the arent virtual machine.
If /ou want to save the current state of the virtual machine, so /ou can revert to that state in case /ou ma!e a
mista!e, ta!e a snashot. If /ou want to ma!e a co/ of a virtual machine for searate use, create a clone.
:h/ Ma!e a CloneJ
Installin% a %uest oeratin% s/stem and alications can 0e time consumin%. :ith clones, /ou can ma!e man/
coies of a virtual machine from a sin%le installation and confi%uration rocess.
Clones are useful when /ou must delo/ man/ identical virtual machines to a %rou. 7or e;amleH
KAn MIS deartment can clone a virtual machine for each emlo/ee, with a suite of reconfi%ured office
alications.
KA virtual machine can 0e confi%ured with a comlete develoment environment and then cloned reeatedl/ as a
0aseline confi%uration for software testin%.
KA teacher can clone a virtual machine for each student, with all the lessons and la0s re?uired for the term.
:ith clones /ou can convenientl/ ma!e comlete coies of a virtual machine, without 0rowsin% a host file s/stem or
worr/in% if /ou have located all the confi%uration files.
7ull and =in!ed Clones
>here are two t/es of cloneH
KA full clone is an indeendent co/ of a virtual machine that shares nothin% with the arent virtual machine after the
clonin% oeration. On%oin% oeration of a full clone is entirel/ searate from the arent virtual machine.
KA lin!ed clone is a co/ of a virtual machine that shares virtual dis!s with the arent virtual machine in an on%oin%
manner. >his conserves dis! sace, and allows multile virtual machines to use the same software installation.
7ull Clones H A full clone is an indeendent virtual machine, with no need to access the arent. 7ull clones do not
re?uire an on%oin% connection to the arent virtual machine. .ecause a full clone does not share virtual dis!s with
the arent virtual machine, full clones %enerall/ erform 0etter than lin!ed clones. "owever, full clones ta!e lon%er
to create than lin!ed clones. Creatin% a full clone can ta!e several minutes if the files involved are lar%e.
=in!ed Clones H A lin!ed clone is made from a snashot of the arent. 8See 5nderstandin% Snashots.9 All files
availa0le on the arent at the moment of the snashot continue to remain availa0le to the lin!ed clone. On%oin%
chan%es to the virtual dis! of the arent do not affect the lin!ed clone, and chan%es to the dis! of the lin!ed clone do
not affect the arent.
A lin!ed clone must have access to the arent. :ithout access to the arent, a lin!ed clone is disa0led. See =in!ed
Clones and Access to the 3arent Virtual Machine
=in!ed clones are created swiftl/, so /ou can easil/ create a uni?ue virtual machine for each tas! /ou have. 1ou can
also easil/ share a virtual machine with other users 0/ storin% the virtual machine on /our local networ!, where
other users can ?uic!l/ ma!e a lin!ed clone. >his facilitates colla0orationH for e;amle, a suort team can
reroduce a 0u% in a virtual machine, and an en%ineer can ?uic!l/ ma!e a lin!ed clone of that virtual machine to
wor! on the 0u%.
7ull Clones and Snashots of the 3arent
A full clone is a comlete and indeendent co/ of a virtual machine. "owever, the full clone dulicates onl/ the
state of the virtual machine at the instant of the clonin% oeration. >hus the full clone does not have access to an/
snashots that ma/ e;ist of the arent virtual machine.
Q, H 8 $nstalling an ,S2i to retrieve backup data thru VMFS is much !aster than installing -indows to
retrieve backup data thru #TFS
< $! all ,S2i hosts are down+ you will still need to setup a new ,S2i host anyway in order to run the
backup VMs
: %hances o! VMFS corruption - never e0perienced be!ore %hances o! #TFS corruption@ Guite
o!ten (t least an virus attack to delete !iles on an VMFS volume is highly unlikely
H Simulaneous connection (write) in a S(# volume is supported by VMFS but not #TFS which will
lead to corruption (Eaving < backup app writing to the same volume at the same time etc@)
Eaving said the above+ someone reminded me about the big di!!erence between using the storage !or
backup and replication For replication+ it will be VMFS instead o! #TFS Eowever+ since backup will
be compressed and dedup+ we will need Veeam to restore it+ or use e0tract utility provided Thus+
#TFS will provide direct access to restore the backup !rom any connected -indows computer or
even e0ecute the backup VMs to boot up immediately thru v)ower -ith VMFS+ we will add an
additional step o! mapping the VM9I !iles into a -indows VM etc to access it That&s the only
disadvantages $ can agreed upon+ apart !rom the <TJ limits
GH 6 -hat $s %aptured by the Snapshot@
The snapshot captures the entire state o! the virtual machine at the time you take the snapshot This
includes6
KThe state o! all the virtual machine&s disks
KThe contents o! the virtual machine&s memory
KThe virtual machine settings
G7 6 )<V
Introdu%tion to -&ware Converter
VMware %onverter is designed to do the !ollowing6
# convert local and remote physical servers with &@ 6@W&;I$E
# convert many )<V conversions at the same time with a centralized console
# convert third party VMs to VMware For e0ample- MS Virtual )%+ MS Virtual Server+ Lackup ,0ec
1iveState+ ? Jhost
# %lone and backup physical machines to virtual machines as part o! a 9' plan
VMware %onverter comes in two !lavors They are6
# VMware %onverter Starter (F',, ,dition)
# VMware %onverter ,nterprise
.! course not all !eature are supported on the !ree edition For a comparison chart between these two
editions+ see this link
%urrently+ VMware %onverter is only supported to convert -indows systems !rom physical to virtual
(!or speci!ic versions+ see the F(G) For speci!ic in!ormation on VMware %onverter+ see this data
sheet
#
*ownloadin# . Installin# -&ware Converter
To download VMware %onverter+ simply go to the download link on the product webpage This will
take you to the download site to download the VMware %onverter Starter edition %lick 9ownload
#ow (!ter !illing out the registration !orm and accepting the license agreement+ you will see
something like this6 ,ither 'un or Save the download .nce downloaded+ click 'un+ like
this6 Mou&ll be taken to the VMware %onverter $nstallation -izard+ like this6
#ow click #e0t+ accept the license agreement again+ take the de!ault installation
directory+ and take the Typical ('ecommended) installation method by clicking #e0t #e0t+ click
$nstall -hen installation completes+ you should see this %heck the checkbo0 !or 'un VMware
%onverter and click Finish Finally+ a!ter VMware %onverter starts+ you should see this
screen6 #ow that you have installed this amazing 8DMb program+ let&s !ind out what it
can do in part <
Summar!
$n summary+ VMware %onverter is a very cool application that can speed up your physical server
migration and assist in other ways such as disaster recovery -ith VMware %onverter being available
in the F',, Starter ,dition+ there is no reason not to try out VMware %onverter := and start
converting those physical machines to virtual machines todayN
/sin# -&ware Converter
-hen VMware %onverter starts+ you will be asked i! you want to enter a license (to use the ,nterprise
version) or move into Starter mode To go into Starter mode+ click )ontinue in Starter $ode
There are two purposes !or VMware %onverter6
8) $mport a Virtual Machine !rom a physical machine or other type o! virtual machine
<) %on!igure Virtual Machine to make an e0isting image bootable
$n our case+ we are going to demonstrate how you can import a hard drive !rom a physical machine
(while that machine is running)+ change the drivers on it to be VMware drivers+ and boot it in VMware
The !irst step o! this is importing the virtual machine
Importin# -irtual &a%hines
To $mport a virtual machine+ 4ust click on the Import $achine button the top le!t side o! the inter!ace
#e0t+ you&ll see the $mport dialog bo0 come up %lick &e3t twice Select the type o!
source to import !rom6 $n our case+ we selected physical computer but notice all the
di!!erent sources you can import virtual machines !rom Mou could import an e0isting virtual machine+
a physical machine that this program is running on+ or a remote machine over the network
-e !illed out the remote $) address and administrator usernameOpassword+ then clicked
&e3t The VM %onverter will connect to the remote machine over the network at this time Mou will get
the message that the VM %onverter agent needs to be installed on the remote machine
%lick Aes (!ter the agent install is done+ you will see a window that looks like this6
Eere you need to select the volumes you want to convert and i! you want them to be
resized $ chose to only convert the % drive and to reduce the size to the smallest size possible (!ter
doing that+ click &e3t
#e0t you will need to choose a destination+ click &e3t
-e will choose to put this physical machine on our standalone VMware Server (as that is all we have
installed)
%lick &e3t
#ow you will need to speci!y a name !or this virtual server and a shared !older that is accessible to
both virtual machines To do this+ $ created a !older called %6PSharedVM and opened it up to !ull
control !or everyone (see below)
(!ter you !ill out the new name and the share+ click &e3t.
#ow+ take the de!ault to allow the disk space to grow (that is really up to you)
%lick &e3t
Take the de!ault network options and click &e3t Take the de!ault on customizations and click &e3t
Mou are now ready to import the virtual machineN
%lick &e3t
$onitoring = #erifying the Import
The import will now begin Eere is what it looks like6
$n my case+ because $ chose to trans!er a physical machine over the 1(# (with one device using
wireless)+ it took me < hours and C minute to trans!er the complete >JL image -hen it was done+
here were the results6
GC
This guide covers the !ollowing components o! vSphere
Virtual
Machines
,S2i hosts
Virtual
#etwork
v%enter
Server+
plus its
database
and clients
v%enter
*pdate
Manager
,verything
else is out
o! scope
and hence
#.T
covered by
the guide
This
includes
v%enter
Virtual
(ppliance
vSphere
Manageme
nt
(ssistant
(vM()
any other
add-on
component
6escripti
on of
fie"ds
,ach
guideline is
uni"uely
identi!ied
by the
concatenat
ion o!
)roduct-
Version-
%omponen
t-$9 Some
e0amples6
vSphere-
5.0-esxi-
apply-
patches
vSphere-
5.0-vm-
prevent-
device-
interaction
-edit
vSphere-
5.0-
vnetwork-
reject-
mac-
change-
dvportgrou
p
vSphere-
5.0-
vcenter-
isolated-
vum-proxy
-hen
re!erring to
guidelines
within a
single
version+
the
)roduct-
Version
may be
omitted
and the
component
-$9 used
by itsel!+
eg
esxi-apply-
patches
The )ro!ile
!ield
indicates
the relative
increase in
security
provided
by the
guidelines
Some
guidelines
describe
an issue
with more
than one
de!ense+
and these
will be
associated
with more
than one
pro!ile
Profi"e 3?
guidelines
that should
be
implement
ed in all
environme
nts
Profi"e 2?
guidelines
that should
be
implement
ed !or
more
sensitive
environme
nts+ eg
those
handling
more
sensitive
data+ those
sub4ect to
stricter
complianc
e rules+
etc
Profi"e 1?
guidelines
that only
be
implement
ed in the
highest
security
environme
nts+ eg
top-secret
governmen
t or
military+
e0tremely
sensitive
data+ etc
%ontrol
Type
indicates
how the
guideline is
implement
ed
Parameter
? ( system-
level
parameter
should be
set to a
particular
value+
either
speci!ied in
the
guideline
or else
site-
speci!ic
)onfigura
tion? (
certain
hardware
andOor
so!tware
con!igurati
on or
combinatio
n o!
settings
should be
used
@peration
a"?
$ndicates
an ongoing
check+
either
monitoring
!or certain
actions or
conditions+
or else
veri!ying
the use o!
proper
procedures
(ssessment )rocedure6 describes how to validate whether or not the guideline is being !ollowed The remediation procedure is generally not described+ but in some cases the remediation steps are available in
an e0ternal re!erence
The
!ollowing
!ields are
!illed in
where
applicable
or
determinat
e
)onfigura
tion
Parameter
)onfigura
tion :i"e
6esired
#a"ue
Is 6esired
#a"ue the
6efau"t
&egative
:unctiona
" Impact
indicates i!
this
guideline
has any
side
e!!ects that
reduce or
prevent
normal
!unctionalit
y
-here
possible+
%1$
commands
!or
assessme
nt and
remediatio
n are
provided
The
commands
are
provided
!or the
vSphere
%1$ (v%1$)+
,S2i Shell+
and
)ower%1$
'e!erence
to the ()$
which
relates to a
guideline is
also
provided i!
possible
For the
,S2i
guidelines+
a special
column
indicates
whether or
not the
guidelines
can be
con!igured
using Eost
)ro!iles
GD
*pdate Manager
Simpli!y VMware vSphere management by automating patches and updates vSphere *pdate
Manager makes it easy to manage tracking and patching o! vSphere hosts
Ieep machines up to date and in compliance
'educe risks o! patching
,liminate vSphere downtime related to host patching
Ieep Machines *p-to-date and in %ompliance
(utomate patch management and eliminate manual tracking and patching o! vSphere hosts and
virtual machines vSphere *pdate Manager compares the state o! vSphere hosts with baselines+ then
updates and patches to en!orce compliance to mandated patch standards
Jain visibility into patch status across the virtual in!rastructure with a patch compliance dashboard
Stage and schedule patching !or remote sites
9eploy o!!line bundles o! patches downloaded directly !rom vendor websites
'educe the 'isks o! )atching
Store snapshots !or a user-de!ined period so administrators can roll back the virtual machine i!
necessary
Securely patch o!!line virtual machines without e0posing them to the network+ reducing the risk o!
non-compliant virtual machines
Make sure the most current version o! a patch is applied with automatic noti!ication services
,liminate vSphere 9owntime 'elated to )atching
vSphere *pdate Manager works in con4unction with vSphere 9istributed 'esource Scheduler (9'S)
to provide non-disruptive host patching when remediating a cluster vSphere *pdate Manager works
with vSphere 9'S to put hosts in maintenance mode one by one and migrates virtual machines live
to other hosts while patching
(utomatically migrate virtual machines to other hosts during patching Migrate virtual machines back
a!ter patching
G> V<V
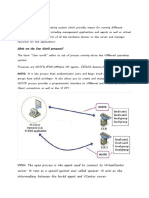
Eow to $mport a Virtual Machine into ,S2i )art 86 )<V Migration+ $ described cold and hot migrations+
the di!!erence between physical-to-virtual ()<V) and virtual-to-virtual (V<V) migrations+ and how to
per!orm a )<V migration using VMware v%enter %onverter $n the second hal! o! this two-part series+
$/ll e0plain how to import an e0isting virtual machine (VM) into an ,S2O,S2i Server
VMware v%enter %onverter supports several di!!erent kinds o! virtual machines $t can import into
,S2O,S2i virtual machines created in a VMware application or in a competing product $t/s important
to note+ however+ that not all virtualization products use the same virtualization method when running
guest machines VMware -orkstation+ VMware )layer+ VMware Server+ VMware Fusion+ )arallels
9esktop+ Microso!t Virtual )% and Microso!t Virtual Server Q all o! which are compatible with v%enter
%onverter Q use hosted virtualizationVMware ,S2O,S2i Server and Microso!t Eyper-V Server+ on
the other hand+ use bare-metal virtualization to run VMs The !ormer group o! so!tware runs on top o!
an e0isting operating system+ while the latter group runs on top o! the host hardware
These di!!erences mean little once v%enter %onverter has completed the conversion process+ but
virtual machines created in hosted virtualization so!tware re"uire di!!erent migration steps !rom virtual
machines created in bare-metal virtualization plat!orms
Rust about all V<V migrations are cold migrations+ which re"uire that the source system be powered
o!! during the conversion process $t is+ however+ possible to per!orm a hot migration o! a virtual
machine using the hot migration method as described in Eow to $mport a Virtual Machine into ,S2i6
)art 8 (!ter installing v%enter %onverter Standalone to the virtual machine+ launch the %onversion
wizard Select 3)owered-.n Machine5 !rom the drop-down menu+ click 31ocal Machine+5 and then
!ollow the same steps as described in the section )<V6 Eot Migration
.ne thing to keep in mind be!ore per!orming a hot migration+ however+ is that+ in some instances+
v%enter Server can inter!ere with the migration process $! the source system is inside a 9istributed
'esource Schedule (9'S) cluster that v%enter Server controls+ 9'S )ower Management (9)M) will
turn o!! the ,S2O,S2i host that v%enter %onverter is working with %hange 9)M to Manual via the
cluster/s Settings screen be!ore per!orming the hot migration .nce the migration is complete+ revert
)ower Management to its previous con!iguration
(lthough hot migrations have their purpose+ they/re only needed when a virtual machine is too
important to be taken o!!line $n all other instances+ you should per!orm a cold migration The !ollowing
steps detail the o!!line conversion process
-2-0 Cold &i#ration
1. )ower down the source machine be!ore proceeding Select 3%onvert Machine5 !rom the toolbar to
launch the %onversion wizard
See steps 2a and 2+ to import a VM !rom a hosted virtualization plat!ormS See steps 3a and 3+ to
import a VM !rom a bare-metal virtualization plat!orm
2a. Hosted Virtualization %hoose 3VMware -orkstation or .ther VMware Virtual Machine5 or
3Lackup $mage or Third-)arty Virtual Machine5 !rom the Source Type drop-down menu+ depending on
which plat!orm the source machine is using
2+. Hosted Virtualization ,nter the !ull !ile or network path linking to the virtual machine Supported
third-party plat!orms include Microso!t Virtual )% and Microso!t Virtual Server (vmc)+ and )arallels
9esktop (pvs) *se vm0 !or virtual machines created in VMware #ote that i! you/re importing a VM
!rom Microso!t Virtual )%+ you should remove the Virtual )% (dditions !rom the machine+ as they can
inter!ere with the conversion process
,nter the login credentials !or the server i! accessing a network share+ and then click 3#e0t5 Skip to
step !.
3a. !are-"etal Virtualization Select 3VMware $n!rastructure Virtual Machine5 or 3Eyper-V Server5
!rom the drop-down menu on the Source System screen $! v%enter %onverter is not installed to
Eyper-V Server+ a prompt will appear re"uesting permission to install the application to the system
%on!irm the installation o! the so!tware to proceed with the conversion
,nter the server address and login credentials !or the ,S2O,S2i or Eyper-V Server %lick 3#e0t5 to go
to the Source Machine screen
3+. !are-"etal Virtualization Search through the inventory to locate the source system $! you/re
accessing ,S2O,S2i through v%enter Server+ choose 3Eosts and %lusters5 or 3VMs and Templates+5
depending on where the source machine is housed Select the virtual machine to import into the
,S2O,S2i Server+ and then click 3#e0t5
!. Select 3VMware $n!rastructure Virtual Machine5 !rom the Select 9estination Type drop-down menu
,nter the address+ user name+ and password !or ,S2O,S2i Server into the re"uired !ields %lick
3#e0t5 to go to the 9estination Virtual Machine screen
(. ,nter a new name !or the destination machine or use the de!ault name Select a destination
location !or the VM i! managing ,S2O,S2i through v%enter Server %lick 3#e0t5 to go to the
9estination 1ocation screen
*. Select a host+ resource pool+ or cluster to accommodate the virtual machineS select a datastore
where the !iles associated with the virtual machine should be stored (optional)S and then select the
virtual hardware version !rom the drop-down menu (optional) *se Version H !or machines running
,S2O,S2i :0+ Version D !or machines running ,S2O,S2i H0+ and Version > !or machines running
,S2O,S2i 70 %lick 3#e0t5 to go to the .ptions screen
,. %lick 3,dit5 to make changes to a hardware device $! you/re importing a virtual machine based on
the Microso!t -indows operating system+ select 3(dvanced5 !rom the middle pane to view the )ost-
%onversion tab *ncheck 3'emove System 'estore %heckpoints on 9estination5 %heck
3'econ!igure 9estination Virtual Machine5 to personalize the .S (eg+ create a uni"ue name and
password+ enter a new product license+ or change the workgroup or domain settings) %lick 3#e0t5
a!ter making the desired changes
> 'eview your selections on the Summary screenS then click 3Finish5 to begin importing the VM
>0
VMware vSphere 78 is a minor update+ not a new vSphere version+ but admins are discovering
plenty o! !eatures and patches in vSphere 78
ThisVMware&s vSphere 78 is a minor version update in name+ but with changes to data backup+
replication and the de!ault inter!ace+ vSphere 78 !eatures have garnered a lot o! interest
-hether you&ve already upgraded and want to get more !rom your virtual in!rastructure or want to
know what to e0pect !rom vSphere 78+ this guide will introduce !eatures like the de!ault -eb client+
replication+ VMware&s controversial single sign-on $9 authentication and more (long with the
!eatures& specs+ learn about the patches VMware issued !or vSphere 78+ which some admins say
came out without proper testing
Table o! contents6
Single sign-on6 $s it the hero or villain o! vSphere 78@
9o you still need Site 'ecovery Manager@
Joodbye+ -indows client Eello+ -eb clientN
VMware 9ata 'ecovery goes into retirement
1icensing evolves with SMLs in mind
Single sign-on6 $s it the hero or villain o! vSphere 78@
VMware single sign-on (SS.) made its debut as a much-reviled vSphere 78 !eature SS. uses a
standalone server as an authentication broker between administrators and various VMware products
$t won notoriety "uickly !or its bugs+ and VMware issued patches 'egardless o! this stumble+ SS. is
integral to vSphere+ changing the way VMware administrators manage directories VMware now
o!!ers authentication against the corporate directory with a centralized mechanism !or VMware
applications to use
1earn how vSphere 78 SS. breaks your dependence on Microso!t (ctive 9irector and v%enter
(re you e0periencing these problems with VMware SS.@
Some claim VMware pushed 78 out too soon+ leading to SS. and SS1 patches
9o you still need Site 'ecovery Manager@
Many VMware admins want to replicate virtual machines (VMs)+ mirroring them to another location in
case the primary storage !ails Le!ore vSphere 78+ this meant buying VMware Site 'ecovery
Manager (S'M) or a third-party tool VSphere 78 !eatures a limited version o! replication -- vSphere
'eplication -- that&s missing some o! S'M&s !eatures VSphere 'eplication needed its own patch to !i0
two issues6 one with installation and the other with recovering VMs at a secondary site
Shared-nothing live migration+ which is a related !eature o! vSphere 78+ is part o! VMware&s roadmap
!or S'M and 'eplication Shared-nothing live migration will play a role in S'M&s integration with
v%loud 9irector and disaster recovery to cloud service providers $n the <=8: vSphere update+ look
!or more !eatures around policy-based disaster recovery and integration between vSphere 9ata
'ecovery+ VMware Eigh (vailability and S'M
Mou might be able to use vSphere 'eplication instead o! S'M
Jet to know VMware&s shared-nothing live migration
Fi0 replication problems with the vSphere 78 patch
Joodbye+ -indows client Eello+ -eb clientN
Jet used to working with the -eb client VMware made its -eb client the de!ault inter!ace !or
vSphere in 78+ and !eatures new to vSphere 78 will not be available in the -indows-based client
VMware boasts that in the 78 update it improved the -eb client&s scalability and disaster recovery
capabilities
#o more white screens o! death when you use the vSphere -eb client
VMware 9ata 'ecovery goes into retirement
-hen $T pros complained about backup limitations in VMware 9ata 'ecovery (V9')+ the company
released vSphere 9ata )rotection (V9)) with version 78 V9) communicates with VMware vStorage
()$ !or 9ata )rotection V9) eliminated V9'+ but hasn&t eliminated all o! the limitations o! its
!orerunner $t does back up only changed blocks+ reducing backup time signi!icantly
1icensing evolves with SMLs in mind
,nough with the technical !eatures VMware shed its virtual '(M (v'(M) licensing scheme with the
release o! vSphere 78+ going back to physical %)*-based licensing The change o! heart especially
bene!its small and medium-sized businesses (SMLs)+ which can now license an enterprise-class
vSphere installation
>12 7equired ports for vcenter
>he VMware vCenter Server s/stem must 0e a0le to send data to ever/ mana%ed host and receive data from ever/
vShere Client. >o ena0le mi%ration and rovisionin% activities 0etween mana%ed hosts, the source and destination hosts
must 0e a0le to receive data from each other.
VMware uses desi%nated orts for communication. Additionall/, the mana%ed hosts monitor desi%nated orts for data from
the vCenter Server s/stem. If a firewall e;ists 0etween an/ of these elements and :indows firewall service is in use, the
installer oens the orts durin% the installation. 7or custom firewalls, /ou must manuall/ oen the re?uired orts. If /ou
have a firewall 0etween two mana%ed hosts and /ou want to erform source or tar%et activities, such as mi%ration or
clonin%, /ou must confi%ure a means for the mana%ed hosts to receive data.
+oteH In Microsoft :indows Server -))I, a firewall is ena0led 0/ default. >his ta0le outlines the orts re?uired for
communication 0etween comonentsH
'or
t
Description
I) vCenter Server re?uires ort I) for direct ">>3 connections. 3ort I) redirects re?uests to ">>3S
ort ((,. >his redirection is useful if /ou accidentall/ use http://server/ instead of
https://server/ .
+oteH Microsoft Internet Information Services 8IIS9 also use ort I).
,IL >his ort must 0e oen on the local and all remote instances of vCenter Server. >his is the =#A3
ort num0er for the #irector/ Services for the vCenter Server %rou. >he vCenter Server s/stem
needs to 0ind to ort ,IL, even if /ou are not @oinin% this vCenter Server instance to a =in!ed
Mode %rou. If another service is runnin% on this ort, it mi%ht 0e refera0le to remove it or chan%e
its ort to a different ort. 1ou can run the =#A3 service on an/ ort from 2)-C throu%h ECC,C.
If this instance is servin% as the Microsoft :indows Active #irector/, chan%e the ort num0er from
,IL to an availa0le ort from 2)-C throu%h ECC,C.
((, >he default ort that the vCenter Server s/stem uses to listen for connections from the vShere
Client. >o ena0le the vCenter Server s/stem to receive data from the vShere Client, oen ort
((, in the firewall.
>he vCenter Server s/stem also uses ort ((, to monitor data transfer from S#6 clients.
If /ou use another ort num0er for ">>3S, /ou must use ip-address:port when /ou lo% in to
the vCenter Server s/stem.
E,E 7or vCenter Server =in!ed Mode, this is the SS= ort of the local instance. If another service is
runnin% on this ort, it mi%ht 0e refera0le to remove it or chan%e its ort to a different ort. 1ou
can run the SS= service on an/ ort from 2)-C throu%h ECC,C.
L)- >he default ort that the vCenter Server s/stem uses to send data to mana%ed hosts. Mana%ed
hosts also send a re%ular heart0eat over 5#3 ort L)- to the vCenter Server s/stem. >his ort
must not 0e 0loc!ed 0/ firewalls 0etween the server and the hosts or 0etween hosts.
L), 3ort L), must not 0e 0loc!ed 0etween the vShere Client and the hosts. >he vShere Client uses
this orts to disla/ virtual machine consoles
I)I
)
:e0 Services ">>3. 5sed for the VMware VirtualCenter Mana%ement :e0 Services.
I((
,
:e0 Services ">>3S. 5sed for the VMware VirtualCenter Mana%ement :e0 Services.
2))
I)
vCenter Inventor/ Service ">>3.
2)(
(,
vCenter Inventor/ Service ">>3S.
2)2
)L
vCenter Inventor/ Service Service Mana%ement.
2)2
22
vCenter Inventor/ Service =in!ed Mode Communication.
E))
LL
:e0 Service chan%e service notification ort.
It is necessary to know different terminology used wit! *Mware, list of t!ose terminology are mentioned as below
ESXi - Es;i is a thin, em0edded version of the ESX server that does not have a service console. It moves the Server
6ernels to a dedicated hardware device.
IS- image - A C# or #V# ima%e that can 0e downloaded and 0urnt on a C#-$OM or #V#-$OM or, mounted as a
loo0ac! device.
.luster - A server %rou in the virtual environment. Clusters ena0le a hi%h-availa0ilit/ solution. A cluster is a collection of
ESX Server hosts and associated virtual machines that share resources and a mana%ement interface.
)./ 0!ardware compatibility list1 - >he definitive list of hardware that VMware suorts.
)ost - A comuter that uses virtuali&ation software to run virtual machines. Also called the host machine or host comuter.
>he h/sical comuter on which the virtuali&ation 8or other9 software is installed.
2uest -perating System - An oeratin% s/stem that runs on a virtual machine.
*Mware *.enter - A virtual infrastructure mana%ement roduct that mana%es and rovide valua0le services for virtual
machines and underl/in% virtuali&ation latforms from a central, secure location.
*Mware vSp!ere client - An interface that allows to connect an/ windows 3C remotel/ to a vCenter Server or ESXAESXi.
S(+ 0storage area network1 - A lar%e-caacit/ networ! of stora%e devices that can 0e shared amon% multile VMware
ESX server hosts. A SA' is re?uired for VMotion.
Root user - >he sueruser who has full administrative rivile%es to lo% in to an ESX Server host. >he root user can
maniulate ermissions, create users and %rous, and wor! with events.
*irtual Mac!ine - A virtual machine is a software comuter that, li!e a h/sical comuter, runs an oeratin% s/stem and
alications. Multile virtual machines can oerate on the same host s/stem concurrentl/.
*M3S - A clustered file s/stem that stores virtual dis!s and other files that are used 0/ virtual machines.
Service console - >he modified =inu; !ernel that serves as the mana%ement interface to the ESX server.
*Mkernel - A !ernel that controls the server hardware and schedules virtual machine comutations and IAO oerations.
*Motion F the caa0ilit/ to move a runnin% virtual machine from one ESX host to another and faster than some other
editions.
Storage *Motion F the caa0ilit/ to move a runnin% virtual machine from one stora%e device to another
DRS F #istri0uted $esource Scheduler F automatic load 0alancin% of an ESX cluster usin% VMotion
)( F "i%h Availa0ilit/ F In case of hardware failure in a cluster, the virtual servers will automaticall/ restart on another
host in the cluster.
$!at4s +ew in vSp!ere #.1
:ith this release, the VMware virtual datacenter oeratin% s/stem continues to transform ;IE I> infrastructure into the most efficient,
shared, on-demand utilit/, with 0uilt-in availa0ilit/, scala0ilit/, and securit/ services for all alications and simle, roactive automated
mana%ement. >he new and enhanced features in vShere (.2 are listed 0elow.
# Installation and #elo/ment
# Stora%e
# 'etwor!
# Availa0ilit/
# Mana%ement
# 3latform Enhancements
# 3artner Ecos/stem
Installation and Deployment
# *Mware ESX. VMware vShere (.2 and its su0se?uent udate and atch releases are the last releases to include 0oth ESX
and ESXi h/ervisor architectures. 7uture ma@or releases of VMware vShere will include onl/ the VMware ESXi architecture.
o VMware recommends that customers start transitionin% to the ESXi architecture when delo/in% VMware vShere
(.2.
o VMware will continue to rovide technical suort for VMware ESX accordin% to the VMware vShere suort olic/.
o >o learn more a0out the ESXi architecture and how to mi%rate from ESX to ESXi, %o to the VMware ESX to ESXi
5%rade Center.
# Scripted Install for ESXi. Scrited installation of ESXi to local and remote dis!s allows raid delo/ment of ESXi to man/
machines. 1ou can start the scrited installation with a C#-$OM drive or over the networ! 0/ usin% 3XE 0ootin%. 1ou cannot
use scrited installation to install ESXi to a 5S. device. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation 4uide, the ESXi
Installa0le and vCenter Server Setu 4uide, and the ESXi Em0edded and vCenter Server Setu 4uide.
# vSp!ere .lient Removal from ESX5ESXi 6uilds. 7or ESX and ESXi, the vShere Client is availa0le for download from the
VMware :e0 site. It is no lon%er ac!a%ed with 0uilds of ESX and ESXi. After installin% ESX and ESXi, users are directed to
the download a%e on the VMware :e0 site to %et the comati0le vShere Client for that release. >he vShere Client is still
ac!a%ed with 0uilds of vCenter Server. See the ESX and vCenter Server Installation 4uide, the ESXi Installa0le and vCenter
Server Setu 4uide, and the ESXi Em0edded and vCenter Server Setu 4uide.
Storage
# 6oot from S(+. vShere (.2 ena0les ESXi 0oot from SA' 8.7'9. iSCSI, 7CoE, and 7i0re Channel 0oot are suorted. $efer
to the "ardware Comati0ilit/ 4uide for the latest list of 'ICs and Conver%ed Adaters that are suorted with iSCSI 0oot.
See the iSCSI SA' Confi%uration 4uide and the 7i0re Channel SA' Confi%uration 4uide.
# )ardware (cceleration wit! vStorage ('Is for (rray Integration 0*((I1. ESX can offload secific stora%e oerations to
comliant stora%e hardware. :ith stora%e hardware assistance, ESX erforms these oerations faster and consumes less
C35, memor/, and stora%e fa0ric 0andwidth. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# Storage 'erformance Statistics. vShere (.2 offers enhanced visi0ilit/ into stora%e throu%hut and latenc/ of hosts and
virtual machines, and aids in trou0leshootin% stora%e erformance issues. '7S statistics are now availa0le in vCenter Server
erformance charts, as well as es;to. 'ew VM#6 and datastore statistics are included. All statistics are availa0le throu%h the
vShere S#6. See the vShere #atacenter Administration 4uide.
# Storage I5- .ontrol. >his feature rovides ?ualit/-of-service caa0ilities for stora%e IAO in the form of IAO shares and limits
that are enforced across all virtual machines accessin% a datastore, re%ardless of which host the/ are runnin% on. 5sin%
Stora%e IAO Control, vShere administrators can ensure that the most imortant virtual machines %et ade?uate IAO resources
even in times of con%estion. See the vShere $esource Mana%ement 4uide.
# iS.SI )ardware -ffloads. vShere (.2 ena0les 2)40 iSCSI hardware offloads 8.roadcom CMM229 and 240 iSCSI hardware
offloads 8.roadcom CM)L9. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide, the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide, and the iSCSI SA' Confi%uration
4uide.
# +3S 'erformance En!ancements. 'etwor!in% erformance for '7S has 0een otimi&ed to imrove throu%hut and reduce
C35 usa%e. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
+etwork
# +etwork I5- .ontrol. >raffic-mana%ement controls allow fle;i0le artitionin% of h/sical 'IC 0andwidth 0etween different
traffic t/es, includin% virtual machine, vMotion, 7>, and I3 stora%e traffic 8v'etwor! #istri0uted Switch onl/9. See the ESX
Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# I'v% En!ancements. I3vE in ESX suorts Internet 3rotocol Securit/ 8I3sec9 with manual !e/in%. See the ESX Confi%uration
4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# /oad&6ased 7eaming. vShere (.2 allows d/namic ad@ustment of the teamin% al%orithm so that the load is alwa/s 0alanced
across a team of h/sical adaters on a v'etwor! #istri0uted Switch. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi
Confi%uration 4uide.
# E1888 v+I. En!ancements. E2))) v'IC suorts @um0o frames in vShere (.2. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide and the
ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
(vailability
# $indows 3ailover .lustering wit! *Mware )(. Clustered Virtual Machines that utili&e :indows 7ailover
Clusterin%AMicrosoft Cluster Service are now full/ suorted in con@unction with VMware "A. See Setu for 7ailover Clusterin%
and Microsoft Cluster Service.
# *Mware )( Scalability Improvements. VMware "A has the same limits for virtual machines er host, hosts er cluster, and
virtual machines er cluster as vShere. See Confi%uration Ma;imums for VMware vShere (.2 for details a0out the
limitations for this release.
# *Mware )( )ealt!c!eck and -perational Status. >he VMware "A dash0oard in the vShere Client rovides a new
detailed window called Cluster Oerational Status. >his window disla/s more information a0out the current VMware "A
oerational status, includin% the secific status and errors for each host in the VMware "A cluster. See the vShere Availa0ilit/
4uide.
# *Mware 3ault 7olerance 0371 En!ancements. vShere (.2 introduces an 7>-secific versionin%-control mechanism that
allows the 3rimar/ and Secondar/ VMs to run on 7>-comati0le hosts at different 0ut comati0le atch levels. vShere (.2
differentiates 0etween events that are lo%%ed for a 3rimar/ VM and those that are lo%%ed for its Secondar/ VM, and reorts
wh/ a host mi%ht not suort 7>. In addition, /ou can disa0le VMware "A when 7>-ena0led virtual machines are delo/ed in a
cluster, allowin% for cluster maintenance oerations without turnin% off 7>. See the vShere Availa0ilit/ 4uide.
# DRS Interoperability for *Mware )( and 3ault 7olerance 0371. 7>-ena0led virtual machines can ta!e advanta%e of #$S
functionalit/ for load 0alancin% and initial lacement. In addition, VMware "A and #$S are ti%htl/ inte%rated, which allows
VMware "A to restart virtual machines in more situations. See the vShere Availa0ilit/ 4uide.
# En!anced +etwork /ogging 'erformance. 7ault >olerance 87>9 networ! lo%%in% erformance allows imroved throu%hut
and reduced C35 usa%e. In addition, /ou can use vm;net, v'ICs in 7>-ena0led virtual machines. See the vShere Availa0ilit/
4uide.
# .oncurrent *Mware Data Recovery Sessions. vShere (.2 rovides the a0ilit/ to concurrentl/ mana%e multile VMware
#ata $ecover/ aliances. See the VMware #ata $ecover/ Administration 4uide.
# vStorage ('Is for Data 'rotection 0*(D'1 En!ancements. VA#3 now offers VSS ?uiescin% suort for :indows Server
-))I and :indows Server -))I $- servers. >his ena0les alication-consistent 0ac!u and restore oerations for :indows
Server -))I and :indows Server -))I $- alications.
Management
# v./I En!ancements. vC=I adds otions for SCSI, VAAI, networ!, and virtual machine control, includin% the a0ilit/ to
terminate an unresonsive virtual machine. In addition, vShere (.2 rovides controls that allow /ou to lo% vC=I activit/. See
the vShere Command-=ine Interface Installation and Scritin% 4uide and the vShere Command-=ine Interface $eference.
# /ockdown Mode En!ancements. VMware ESXi (.2 loc!down mode allows the administrator to ti%htl/ restrict access to the
ESXi #irect Console 5ser Interface 8#C5I9 and >ech Suort Mode 8>SM9. :hen loc!down mode is ena0led, #C5I access is
restricted to the root user, while access to >ech Suort Mode is comletel/ disa0led for all users. :ith loc!down mode
ena0led, access to the host for mana%ement or monitorin% usin% CIM is ossi0le onl/ throu%h vCenter Server. #irect access to
the host usin% the vShere Client is not ermitted. See the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# (ccess *irtual Mac!ine Serial 'orts -ver t!e +etwork. 1ou can redirect virtual machine serial orts over a standard
networ! lin! in vShere (.2. >his ena0les solutions such as third-art/ virtual serial ort concentrators for virtual machine
serial console mana%ement or monitorin%. See the vShere Virtual Machine Administration 4uide.
# v.enter .onverter )yper&* Import. vCenter Converter allows users to oint to a "/er-V machine. Converter disla/s the
virtual machines runnin% on the "/er-V s/stem, and users can select a owered-off virtual machine to imort to a VMware
destination. See the vCenter Converter Installation and Administration 4uide.
# En!ancements to )ost 'rofiles. 1ou can use "ost 3rofiles to roll out administrator assword chan%es in vShere (.2.
Enhancements also include imroved Cisco 'e;us 2)))V suort and 3CI device orderin% confi%uration. See the ESX
Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# 9nattended (ut!entication in vSp!ere Management (ssistant 0vM(1. vMA (.2 offers imroved authentication caa0ilit/,
includin% inte%ration with Active #irector/ and commands to confi%ure the connection. See VMware vShere Mana%ement
Assistant.
# 9pdated Deployment Environment in vSp!ere Management (ssistant 0vM(1. >he udated delo/ment environment in
vMA (.2 is full/ comati0le with vMA (.). A si%nificant chan%e is the transition from $"E= to CentOS. See VMware vShere
Mana%ement Assistant.
# v.enter -rc!estrator %#&bit Support. vCenter Orchestrator (.2 rovides a client and server for E(-0it installations, with an
otional ,--0it client. >he erformance of the Orchestrator server on E(-0it installations is %reatl/ enhanced, as comared to
runnin% the server on a ,--0it machine. See the vCenter Orchestrator Installation and Confi%uration 4uide.
# Improved Support for )andling Recalled 'atc!es in v.enter 9pdate Manager. 5date Mana%er (.2 immediatel/ sends
critical notifications a0out recalled ESX and related atches. In addition, 5date Mana%er revents /ou from installin% a
recalled atch that /ou mi%ht have alread/ downloaded. >his feature also hels /ou identif/ hosts where recalled atches
mi%ht alread/ 0e installed. See the vCenter 5date Mana%er Installation and Administration 4uide.
# /icense Reporting Manager. >he =icense $eortin% Mana%er rovides a centrali&ed interface for all license !e/s for vShere
(.2 roducts in a virtual I> infrastructure and their resective usa%e. 1ou can view and %enerate reorts on license !e/s and
usa%e for different time eriods with the =icense $eortin% Mana%er. A historical record of the utili&ation er license !e/ is
maintained in the vCenter Server data0ase. See the vShere #atacenter Administration 4uide.
# 'ower Management Improvements. ESX (.2 ta!es advanta%e of dee slee states to further reduce ower consumtion
durin% idle eriods. >he vShere Client has a simle user interface that allows /ou to choose one of four host ower
mana%ement olicies. In addition, /ou can view the histor/ of host ower consumtion and ower ca information on the
vShere Client 3erformance ta0 on newer latforms with inte%rated ower meters. See the vShere #atacenter Administration
4uide.
'latform En!ancements
# 'erformance and Scalability Improvements. vShere (.2 includes numerous enhancements that increase erformance and
scala0ilit/.
o vCenter Server (.2 can suort three times more virtual machines and hosts er s/stem, as well as more concurrent
instances of the vShere Client and a lar%er num0er of virtual machines er cluster than vCenter Server (.). >he
scala0ilit/ limits of =in!ed Mode, vMotion, and v'etwor! #istri0uted Switch have also increased.
o 'ew otimi&ations have 0een imlemented for AM#-V and Intel V>-; architectures, while memor/ utili&ation
efficienc/ has 0een imroved still further usin% Memor/ Comression. Stora%e enhancements have led to si%nificant
erformance imrovements in '7S environments. V#I oerations, virtual machine rovisionin% and ower
oerations, and vMotion have enhanced erformance as well.
See Confi%uration Ma;imums for VMware vShere (.2.
# Reduced -ver!ead Memory. vShere (.2 reduces the amount of overhead memor/ re?uired, eseciall/ when runnin% lar%e
virtual machines on s/stems with C35s that rovide hardware MM5 suort 8AM# $VI or Intel E3>9.
# DRS *irtual Mac!ine )ost (ffinity Rules. #$S rovides the a0ilit/ to set constraints that restrict lacement of a virtual
machine to a su0set of hosts in a cluster. >his feature is useful for enforcin% host-0ased ISV licensin% models, as well as
!eein% sets of virtual machines on different rac!s or 0lade s/stems for availa0ilit/ reasons. See the vShere $esource
Mana%ement 4uide.
# Memory .ompression. Comressed memor/ is a new level of the memor/ hierarch/, 0etween $AM and dis!. Slower than
memor/, 0ut much faster than dis!, comressed memor/ imroves the erformance of virtual machines when memor/ is
under contention, 0ecause less virtual memor/ is swaed to dis!. See the vShere $esource Mana%ement 4uide.
# vMotion En!ancements. In vShere (.2, vMotion enhancements si%nificantl/ reduce the overall time for host evacuations,
with suort for more simultaneous virtual machine mi%rations and faster individual virtual machine mi%rations. >he result is a
erformance imrovement of u to I; for an individual virtual machine mi%ration, and suort for four to ei%ht simultaneous
vMotion mi%rations er host, deendin% on the vMotion networ! adater 8240E or 2)40E resectivel/9. See the vShere
#atacenter Administration 4uide.
# ESX5ESXi (ctive Directory Integration. Inte%ration with Microsoft Active #irector/ allows seamless user authentication for
ESXAESXi. 1ou can maintain users and %rous in Active #irector/ for centrali&ed user mana%ement and /ou can assi%n
rivile%es to users or %rous on ESXAESXi hosts. In vShere (.2, inte%ration with Active #irector/ allows /ou to roll out
ermission rules to hosts 0/ usin% "ost 3rofiles. See the ESX Confi%uration 4uide and the ESXi Confi%uration 4uide.
# .onfiguring 9S6 Device 'asst!roug! from an ESX5ESXi )ost to a *irtual Mac!ine. 1ou can confi%ure a virtual machine
to use 5S. devices that are connected to an ESXAESXi host where the virtual machine is runnin%. >he connection is
maintained even if /ou mi%rate the virtual machine usin% vMotion. See the vShere Virtual Machine Administration 4uide.
# Improvements in En!anced vMotion .ompatibility. vShere (.2 includes an AM# Oteron 4en. , 8no ,#'owNG9 EVC
mode that reares clusters for vMotion comati0ilit/ with future AM# rocessors. EVC also rovides numerous usa0ilit/
imrovements, includin% the disla/ of EVC modes for virtual machines, more timel/ error detection, 0etter error messa%es,
and the reduced need to restart virtual machines. See the vShere #atacenter Administration 4uide.
'artner Ecosystem
# v.enter 9pdate Manager Support for 'rovisioning, 'atc!ing, and 9pgrading EM.:s ESX 'ower'at! Module. vCenter
5date Mana%er can rovision, atch, and u%rade third-art/ modules that /ou can install on ESX, such as EMCDs
3ower3ath multiathin% software. 5sin% the caa0ilit/ of 5date Mana%er to set olicies usin% the .aseline construct and the
comrehensive Comliance #ash0oard, /ou can simlif/ rovisionin%, atchin%, and u%rade of the 3ower3ath module at
scale. See the vCenter 5date Mana%er Installation and Administration 4uide.
# 9ser&configurable +umber of *irtual .'9s per *irtual Socket. 1ou can confi%ure virtual machines to have multile virtual
C35s reside in a sin%le virtual soc!et, with each virtual C35 aearin% to the %uest oeratin% s/stem as a sin%le core.
3reviousl/, virtual machines were restricted to havin% onl/ one virtual C35 er virtual soc!et. See the vShere Virtual Machine
Administration 4uide.
# E;panded /ist of Supported 'rocessors. >he list of suorted rocessors has 0een e;anded for ESX (.2. >o determine
which rocessors are comati0le with this release, use the "ardware Comati0ilit/ 4uide. Amon% the suorted rocessors is
the Intel Xeon MC)) Series rocessor, code-named 'ehalem-EX 8u to I soc!ets9.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Vmware Interview Questions & Answers in 2016/2017: What Is A Vmkernel?Dokumen23 halamanVmware Interview Questions & Answers in 2016/2017: What Is A Vmkernel?Senthil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 30 Important Virtualization-VMware Interview Questions With AnswersDokumen5 halaman30 Important Virtualization-VMware Interview Questions With AnswersUmair AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 50 Basics GuideDokumen38 halamanVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 50 Basics Guideastro123321Belum ada peringkat
- VMWare Interview QuestionsDokumen6 halamanVMWare Interview QuestionsRavi Kumar PatnanaBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Interview QuestionsDokumen29 halamanVMware Interview QuestionsmunnyskBelum ada peringkat
- InteDokumen12 halamanIntemmmmaran4u100% (1)
- 100 Real Time Vmware Interview Questions and Answers 2017Dokumen38 halaman100 Real Time Vmware Interview Questions and Answers 2017rasik wankhedeBelum ada peringkat
- Virtualization FundamentalDokumen10 halamanVirtualization FundamentalJyoti Patel0% (1)
- VM Meterial1234Dokumen14 halamanVM Meterial1234Krishna ManoharBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDari EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedBelum ada peringkat
- Vmware Interview Questions PDFDokumen11 halamanVmware Interview Questions PDFPaul arceBelum ada peringkat
- VMWare Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen17 halamanVMWare Interview Questions and AnswersVidya BhilareBelum ada peringkat
- Virtualization Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen8 halamanVirtualization Interview Questions and AnswerssrisylamBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Vsphere BasicsDokumen28 halamanVMware Vsphere BasicsBellcini PrintBelum ada peringkat
- Linux Interview QuestionsDokumen51 halamanLinux Interview Questionsseenu933Belum ada peringkat
- Nutanix - Advanced-Setup-Guide-AOS-v51Dokumen29 halamanNutanix - Advanced-Setup-Guide-AOS-v51pkjk07Belum ada peringkat
- WITH ANS - Interview Qestions (ADP - CSC, Micro Land, TCS, IGate, Mi Infotech, MehendraSatyam)Dokumen12 halamanWITH ANS - Interview Qestions (ADP - CSC, Micro Land, TCS, IGate, Mi Infotech, MehendraSatyam)nagesh raoBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Interview Questions PDFDokumen77 halamanVMware Interview Questions PDFJadda GiriBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 NetworkingDokumen123 halamanModule 4 Networkinghafiz.atif100% (1)
- Windows Deployment Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandWindows Deployment Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Technical Interview QuestionsDokumen7 halamanVMware Technical Interview QuestionsRavi Chandra ChukkaBelum ada peringkat
- VCenter Management 5 5 VTSP Test Questions AnswersDokumen4 halamanVCenter Management 5 5 VTSP Test Questions AnswersWaru1150% (2)
- Top 10 Best Practices Vsphere BackupsDokumen13 halamanTop 10 Best Practices Vsphere BackupsCarlos MezaBelum ada peringkat
- 300+ (UPDATED) VMWARE Interview Questions and Answers 2020Dokumen25 halaman300+ (UPDATED) VMWARE Interview Questions and Answers 2020aasuxyzBelum ada peringkat
- Vsan 67 Administration GuideDokumen195 halamanVsan 67 Administration GuideLuis Fernando Lima DuarteBelum ada peringkat
- Vsphere Basic System AdministrationDokumen370 halamanVsphere Basic System AdministrationSandip KamlapureBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Insights Backup RecoveryDokumen12 halamanVMware Insights Backup RecoverymosqiBelum ada peringkat
- Xdoc - Tips Vmware Realtime Issues Question Amp AnswersDokumen20 halamanXdoc - Tips Vmware Realtime Issues Question Amp AnswersAnanth RengasamyBelum ada peringkat
- VSAN Stretched Cluster & 2 Node GuideDokumen148 halamanVSAN Stretched Cluster & 2 Node GuideMichele BrunelliBelum ada peringkat
- Using: 09 Feb 2023 Vrealize Operations 8.6Dokumen208 halamanUsing: 09 Feb 2023 Vrealize Operations 8.6aureltataruBelum ada peringkat
- Storage Implementation in VSphere 5Dokumen1.606 halamanStorage Implementation in VSphere 5SaifUlIslam100% (1)
- Creating Development Environments with Vagrant - Second EditionDari EverandCreating Development Environments with Vagrant - Second EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Building Cloud and Virtualization Infrastructure: A Hands-on Approach to Virtualization and Implementation of a Private Cloud Using Real-time Use-casesDari EverandBuilding Cloud and Virtualization Infrastructure: A Hands-on Approach to Virtualization and Implementation of a Private Cloud Using Real-time Use-casesBelum ada peringkat
- The Top 25 VMware ESXi CommandsDokumen8 halamanThe Top 25 VMware ESXi CommandspalkybdBelum ada peringkat
- Installing Vmware Esx and Esxi: Module Number 13-1Dokumen16 halamanInstalling Vmware Esx and Esxi: Module Number 13-1سعود المعشريBelum ada peringkat
- NSX For Vsphere Getting Started GuideDokumen43 halamanNSX For Vsphere Getting Started GuideAlexander FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Troubleshooting ESXiDokumen43 halamanTroubleshooting ESXithiag_2004Belum ada peringkat
- Linux Troubleshooting ScenariosDokumen9 halamanLinux Troubleshooting ScenariosSaji SyedBelum ada peringkat
- Implementing VMware Dynamic Environment Manager: Manage, Administer and Control VMware DEM, Dynamic Desktop, User Policies and Complete TroubleshootingDari EverandImplementing VMware Dynamic Environment Manager: Manage, Administer and Control VMware DEM, Dynamic Desktop, User Policies and Complete TroubleshootingBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Interview QuestionsDokumen9 halamanVMware Interview QuestionsSuman G100% (1)
- VMware ESXI PDFDokumen74 halamanVMware ESXI PDFVijayabhaskar ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- VMware L2 Interview QDokumen38 halamanVMware L2 Interview QVidya BhilareBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Intersight HandbookDokumen409 halamanCisco Intersight HandbookHsueh KevinBelum ada peringkat
- Azure LimitsDokumen519 halamanAzure Limitsashokkumarmdu100% (1)
- Vmware IMP Q & ADokumen24 halamanVmware IMP Q & AashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Citrix Important Interview-Q & ADokumen43 halamanCitrix Important Interview-Q & AashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Vmware IMP Q & ADokumen10 halamanVmware IMP Q & AashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Actual4Test: Actual4test - Actual Test Exam Dumps-Pass For IT ExamsDokumen11 halamanActual4Test: Actual4test - Actual Test Exam Dumps-Pass For IT ExamsashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- How Citrix Xenapp Works: Gunnalag Leave A Comment Go To CommentsDokumen4 halamanHow Citrix Xenapp Works: Gunnalag Leave A Comment Go To CommentsashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Citrix Interview Q & ADokumen46 halamanCitrix Interview Q & AashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Citrix KnowledgeDokumen2 halamanCitrix KnowledgeashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Citrix Web InterfaceDokumen5 halamanCitrix Web InterfaceashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Citrixports by Product 2013Dokumen10 halamanCitrixports by Product 2013Hai Nguyen KhuongBelum ada peringkat
- Powershell Creating ReportsDokumen23 halamanPowershell Creating ReportsashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Virtualization Interview Q & ADokumen16 halamanVirtualization Interview Q & AashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Vmware Interview QuestionDokumen15 halamanVmware Interview Questiontubaidada100% (1)
- IMPortant Techical Vminterview QuestionDokumen102 halamanIMPortant Techical Vminterview QuestionashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Vsphere5 Vcops InterviewDokumen38 halamanVsphere5 Vcops InterviewashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- Poweshell RemotingDokumen8 halamanPoweshell RemotingashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- VM Interview DocumentDokumen8 halamanVM Interview DocumentashokkumarmduBelum ada peringkat
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokumen15 halaman6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- VMware Interview Q ADokumen86 halamanVMware Interview Q ABharath KumarBelum ada peringkat
- VMware Management With PowerCLI 5.0Dokumen1 halamanVMware Management With PowerCLI 5.0MHuber42Belum ada peringkat
- VMware Interview Q ADokumen86 halamanVMware Interview Q ABharath KumarBelum ada peringkat
- VMWARE InterviewDokumen4 halamanVMWARE InterviewBaiju ManiBelum ada peringkat
- GCOM (Gated Community Management System) : AbstractDokumen1 halamanGCOM (Gated Community Management System) : AbstracthariraoBelum ada peringkat
- Hashicorp Certified Terraform Associate Practice Questions - AdvancedDokumen32 halamanHashicorp Certified Terraform Associate Practice Questions - AdvancedNARASIMHA CHARYBelum ada peringkat
- Lab - 5: Introduction To 8051 Microcontroller: 5.1 ObjectiveDokumen4 halamanLab - 5: Introduction To 8051 Microcontroller: 5.1 Objectivefarheen khosoBelum ada peringkat
- Mixed Signal Embedded ProgrammingDokumen268 halamanMixed Signal Embedded ProgrammingPavan Kumar100% (14)
- ClusterDokumen172 halamanClusterankit boxerBelum ada peringkat
- Viralnomics Final PDFDokumen146 halamanViralnomics Final PDFSkbio39100% (1)
- Installation Guide For Windows: Section 1 - Create An Account at Udaan Translation Web InterfaceDokumen15 halamanInstallation Guide For Windows: Section 1 - Create An Account at Udaan Translation Web Interfacekamarajme2006Belum ada peringkat
- Presentation For Apple M1 ChipDokumen16 halamanPresentation For Apple M1 ChipVilayat Ali100% (1)
- How To Configure Pricing Options For AX For RetailDokumen21 halamanHow To Configure Pricing Options For AX For RetailIslam Sultan100% (8)
- Application of Graph Theory in Web 2Dokumen9 halamanApplication of Graph Theory in Web 2Maria Benedetta VitalesBelum ada peringkat
- Cotter Joint CoferenceDokumen5 halamanCotter Joint CoferenceMuhammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- D20DT Frames Laboratorykk - Brief 2014-15Dokumen11 halamanD20DT Frames Laboratorykk - Brief 2014-15MaxBelum ada peringkat
- MVA Method Short Circuit CalculationDokumen17 halamanMVA Method Short Circuit CalculationbajricaBelum ada peringkat
- Cost of Sales AccountingDokumen147 halamanCost of Sales AccountingClaudio Cafarelli50% (2)
- Introduction To Plant SimulationlDokumen16 halamanIntroduction To Plant SimulationlLeon SakiBelum ada peringkat
- Its - An Interactive Translation SystemDokumen9 halamanIts - An Interactive Translation SystemMohammad AlanaziBelum ada peringkat
- Whats Is Mobile Rooting PDFDokumen3 halamanWhats Is Mobile Rooting PDFprakashBelum ada peringkat
- PRO II 8.0 Component and Thermophysical Properties - Reference ManualDokumen207 halamanPRO II 8.0 Component and Thermophysical Properties - Reference ManualLuis Carlos Ayllón EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- ASP LAB Manual Munotes - inDokumen102 halamanASP LAB Manual Munotes - inSanket KharatBelum ada peringkat
- How To Install WordPressDokumen11 halamanHow To Install WordPressmetaouiBelum ada peringkat
- Thinking Outside The SOX: 3 Simple Steps To Ensure "IPE" SOX ComplianceDokumen2 halamanThinking Outside The SOX: 3 Simple Steps To Ensure "IPE" SOX ComplianceShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Dcs PPT VijayDokumen14 halamanDcs PPT VijayvijaykumarselvamBelum ada peringkat
- BRKDCT 2615Dokumen124 halamanBRKDCT 2615fanvantanBelum ada peringkat
- List of Dealers Who Did Not Login On GST Portal and Filled Nill ReturnDokumen142 halamanList of Dealers Who Did Not Login On GST Portal and Filled Nill ReturnMayukh Singh0% (1)
- PLSQL 8 2 PracticeDokumen3 halamanPLSQL 8 2 PracticeRenaldi Adrian0% (1)
- Ee Draindumps 2024-Jan-18 by Alan 138q VceDokumen27 halamanEe Draindumps 2024-Jan-18 by Alan 138q Vcechamrajp1Belum ada peringkat
- ravaत किस्मत बदल देते हैं रावण संहिता के ये 10 तांत्रिक उपाय Patrika Hindi NewsDokumen12 halamanravaत किस्मत बदल देते हैं रावण संहिता के ये 10 तांत्रिक उपाय Patrika Hindi NewspuneetBelum ada peringkat
- The Linux Users' Guide (Beta-1) (Larry Greenfield)Dokumen175 halamanThe Linux Users' Guide (Beta-1) (Larry Greenfield)Moe B. UsBelum ada peringkat
- Value Engineering VA - VEDokumen146 halamanValue Engineering VA - VEactivedeen100% (1)
- Knowledge AdvisorDokumen461 halamanKnowledge Advisorbelinscaromeo0% (1)