HSDPA & PS Rate Maintenance Based On UMAT
Diunggah oleh
Bsskkd Kkd0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
100 tayangan10 halamanThis document discusses troubleshooting abnormal HSDPA rates in UMTS networks. It provides guidance on using RNC L2 statistics, CDT tracking, and flow control algorithms to determine if issues are related to the IU interface, RNC, IUB interface, or UE. Specific indicators like RLC buffer occupancy, assigned rate, throughput, and retransmission rate are examined. Potential causes include lack of data over IU, low rates issued by RNC, IUB packet loss, and UE window size reductions. Flow control modes are compared to isolate problems.
Deskripsi Asli:
HSDPA & PS Rate Maintenance Based on UMAT
Judul Asli
HSDPA & PS Rate Maintenance Based on UMAT
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses troubleshooting abnormal HSDPA rates in UMTS networks. It provides guidance on using RNC L2 statistics, CDT tracking, and flow control algorithms to determine if issues are related to the IU interface, RNC, IUB interface, or UE. Specific indicators like RLC buffer occupancy, assigned rate, throughput, and retransmission rate are examined. Potential causes include lack of data over IU, low rates issued by RNC, IUB packet loss, and UE window size reductions. Flow control modes are compared to isolate problems.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
100 tayangan10 halamanHSDPA & PS Rate Maintenance Based On UMAT
Diunggah oleh
Bsskkd KkdThis document discusses troubleshooting abnormal HSDPA rates in UMTS networks. It provides guidance on using RNC L2 statistics, CDT tracking, and flow control algorithms to determine if issues are related to the IU interface, RNC, IUB interface, or UE. Specific indicators like RLC buffer occupancy, assigned rate, throughput, and retransmission rate are examined. Potential causes include lack of data over IU, low rates issued by RNC, IUB packet loss, and UE window size reductions. Flow control modes are compared to isolate problems.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 10
HSDPA UMTS Rate maintenance
Based on UMAT V0.20
www.finetopix.com
mon3em .
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
It is all based on the logical relation between RLC_Buffer, Assigned rate by RNC, & the
allocated bandwidth for the services, & from this three relations you can clearly anticipate
which & where is your problem.
RNC CDT L2 statistics
Track Set
To start the CDT at the RNC LMT, the proposed parameters configurations are as follows:
CDT L2 statistics tracking configuration
Ensure that the abnormal rate & the problematic beheaviour has occurred, process for one minute or around it
& stop the CDT tracking.
Rate View:
L2 is the RNC L2 statistics reflect the true situation, what directly reflect the rate changes in the
statistics is RB.ulDlPduNum (L2 PDU sent down the number), and RB.usDlRetranRate (L2
downlink retransmission rate), RB.ulDlNasPktThroughput (L2 downlink throughput of data
received) as below illustration
statistics, the rate case View.
Determine the approximate cause of problems
A number of reasons can lead to abnormal rate,
For the downlink rate analysis of the different interfaces you have to determine whether the problem is IU, RNC
or IUB.
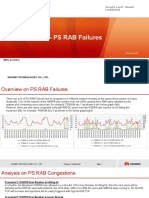
The following judgments are based on UMAT for "HSDPA throughput curves
Open the CDT, the straight on the toolbar
Then click the icon
Right click on the graph to see the legend :
RLC BO: Rlc buffer with green color
Allocated HSDPA bandwidth with blue color
RB rate issued by RNC with red color
Retransmission rate in black color
When the problem is in IU interface or the application layer (such as TCP), the amount of data sent to RNC
through IU is inadequate & the rate will naturally be not ideal & RLC BO will fluctuate
RLC BO full circumstances of the curve (VDF test)
Green curve in the figure is RLC BO case,
RLC BO key is to have or not (0 or non-0), if the RLC BO Has a non-0 value, it means that those data can be
sent to RNC
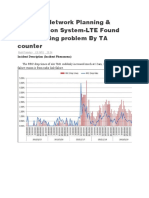
The following is an RLC BO abnormality curve:
Figure 2-1 RLC BO shortfall curve
In this graph, four-fifths of the beginning part, RLC BO (green curve) is basically 0, indicating that during this
period (because of the low rate of downlink), lack of IU.
The last part of fifth, RLC BO increased significantly, when the rate of abnormalities is decreased.
When problem is functionally related
The rate of abnormal performance in the data is:
1) RLC BO has data,
2) RB issued a rate lower than the allocated HSDPA bandwidth by NodeB .
The following is a lack of performance of the UE, UE L2 led the initiative to inform the RNC to
reduce the receive window, which affects the RNC issued a rate of speed caused by exception:
UE rate issue
The green for the RLC BO, red for the RNC issued data, blue for the HSDPA bandwidth allocation situation.
From this figure we can see, RLC BO (green) has been very full, HSDPA bandwidth allocation (blue) is also
adequate, while the RNC issued a rate (red) has been maintained at a very low position.
IUB Interface problems:
IUB interface issues, NodeB problem, UU interface problems, the
IUB interface to determine what the problem principle is: RNC issued rate and the volatility of HSDPA
bandwidth allocation agreement. The following is an Iub packet loss rate caused by fluctuations:
IUB packet loss rate caused by fluctuations
It can be seen from the figure, HSDPA bandwidth allocation (blue) has been cyclically fluctuated ,
while the RNC issued a rate (red) which showed with similar fluctuations in bandwidth allocation.
The following is a NodeB HSDPA Path of the lack of SCR configuration caused by the low rate of
cases:
IUB rate caused by fluctuations in bandwidth allocation
Retransmission case
IUB RLC retransmission, Right in the throughput of the map, select the legend, hook in the "downlink RLC
retransmission rate, " this indicator:
IUB retransmission index configuration
retransmission rate
Retransmission rate of less than 1% is generally considered to be received at this time
retransmission rate curve is coincident with the axis, like the figure above the
retransmission rate often reaches 30% of the cases,
IUB flow control mode:
Another distinction between Iub problem or empty-case an important means is by changing
the NodeB by configuring the flow control algorithm switch (command: SET
HSDPAFLOWCTRLPARA, parameters: SWITCH), at different flow control algorithms
under the action of View NodeB allocation of HSDPA bandwidth,
NodeB currently supports three different flow control algorithms
NodeB list of supported flow control algorithm
No Chinese Name English Name Features
1 AUTO_ADJUST_FLOW_CTRL
Consider the packet loss
and delay IUB,
Consider the available
bandwidth IUB
Consider the empty case
2 SIMPLE_FLOW_CTRL
Consider the available
bandwidth IUB
Consider the empty case
3 NO_FLOW_CTRL
Consider the empty case
As the three flow control algorithm in bandwidth allocation, consider the factors characteristic of a ladder, by
comparing the different flow control mode bandwidth allocation between HSDPA, changes in bandwidth
allocation is most likely to handle the problem occurred.
If the L2 retransmission rate, is continue relatively in simple & auto-adjust :
* If the adaptive flow control and simple flow control of the HSDPA bandwidth allocation are resulted in very
different trend, the retransmission is due to the existence of IUB loss.
* If the adaptive flow control and simple flow control of the HSDPA bandwidth allocation results are consistent,
the reasons for retransmission most likely UU mouth.
If the L2 retransmission rate, continue in the three algorithms:
* If the three kinds of flow control mode are resulted similar (there are exceptions), current problem is mainly
lies in the air interface.
* If no-flow-control has better result, and the remaining two have exceptions, the current problem mainly lies in
the IUB transmission configuration.
* If auto-adjust flow control is only abnormal, this is possibly due to existence IUB-order packets which cause
NodeB FP negative positives, or trigger a larger delay jitter at adaptive bandwidth adjustment of flow control.
IUB interface,
There are two main IUB interface checks:
1) HSDPA Path RCR configured correctly.
2) IUB involved in the transmission device configuration is correct.
If the NodeB is the V18 version of the software, you can also download it via NodeB LMT's "HSDPA MONITOR"
to observe the distribution of the bandwidth of the situation at this time in NodeB:
HSDPA monitoring of start position
The following is a list of monitoring results:
Figure 3-1 HSDPA in the form of monitoring
The results include five columns of data, meaning that five were:
1. Total Bandwidth (bps) port the total available bandwidth is calculated as: IUB port physical port
bandwidth
2. R99 Allocated Bandwidth (bps) on the physical port bandwidth R99,
3. Hsdpa Remain Bandwidth (bps) HSDPA available bandwidth is calculated as: min (HSDPA RT Path
allocation of bandwidth + HSDPA NRT bandwidth allocation,
4. Hsdpa Allocated Bandwidth (bps): refers to the HSDPA on the distribution of all the DSP bandwidth.
5. Hsdpa Used Bandwidth (bps): refers to all DSP operations on the actual use of HSDPA bandwidth.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Belum ada peringkat
- 3G.LTE Network Capacity ManagementDokumen62 halaman3G.LTE Network Capacity Managementmyosos100% (3)
- WcdmaDokumen102 halamanWcdmaعبدالرحمن دقداق91% (11)
- AnalysisReport - PS - RAB - Failure V2Dokumen6 halamanAnalysisReport - PS - RAB - Failure V2gramesh08Belum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDari EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- LTE PDSCH ThroughputDokumen16 halamanLTE PDSCH ThroughputElego13thBelum ada peringkat
- Iub TroubleshootingDokumen36 halamanIub TroubleshootingToni MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Umts Possible CauseDokumen25 halamanUmts Possible Causemanish_chaturvedi_19Belum ada peringkat
- 3G Netact OptimizationDokumen34 halaman3G Netact OptimizationÖzgür ÖzcanBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsDari EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsBelum ada peringkat
- ZTE DRBC (ZTE Dynamic Radio Bearer Control Algorithm)Dokumen45 halamanZTE DRBC (ZTE Dynamic Radio Bearer Control Algorithm)Faise Jan100% (3)
- 3G Interview QuestionsDokumen51 halaman3G Interview Questionspayam12Belum ada peringkat
- Cisco Platinum CCNA & CCNP Lab Kit - CertificationKitsDokumen16 halamanCisco Platinum CCNA & CCNP Lab Kit - CertificationKitssiete100% (1)
- 3g Optimization v2 PDFDokumen50 halaman3g Optimization v2 PDFPutri Dorotea TouorBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco XE IOS Upgrade ProcessDokumen86 halamanCisco XE IOS Upgrade ProcessDeepakBelum ada peringkat
- 3G Huawei RAN Resource Monitoring and ManagementDokumen53 halaman3G Huawei RAN Resource Monitoring and ManagementgiorginoBelum ada peringkat
- Downtilts To Improve SINR and Reduce OvershootingDokumen5 halamanDowntilts To Improve SINR and Reduce OvershootingEltayeb Abdalla HamodaBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Closed Loop Power Control On The UL RSSIDokumen12 halamanEffect of Closed Loop Power Control On The UL RSSIaadi1_2_3Belum ada peringkat
- LTE Reference Study For InterviewDokumen32 halamanLTE Reference Study For Interviewusmanghani8257Belum ada peringkat
- 3G Key OptimDokumen105 halaman3G Key OptimAndre100% (1)
- Worst Cells - CE UL Congestion in HuaweiDokumen4 halamanWorst Cells - CE UL Congestion in HuaweijaffarshineBelum ada peringkat
- QADokumen3 halamanQARead2018Belum ada peringkat
- Performance Optimization 3G LUCKNOWDokumen24 halamanPerformance Optimization 3G LUCKNOWSunil Gupta75% (4)
- Umts Radio Network KpiDokumen49 halamanUmts Radio Network KpisirnateBelum ada peringkat
- RRC Setup Report v1Dokumen23 halamanRRC Setup Report v1Furqan AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Decrease in PS Drop PDFDokumen3 halamanDecrease in PS Drop PDFAki DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- PCHR Drop CauseDokumen29 halamanPCHR Drop CauseMohamed SherifBelum ada peringkat
- 3G OptimisationDokumen9 halaman3G OptimisationhaddadlamariBelum ada peringkat
- 3G Huawei Capacity Optimization ProcessDokumen45 halaman3G Huawei Capacity Optimization ProcessAndres Gaytan100% (2)
- Practical Guide to LTE-A, VoLTE and IoT: Paving the way towards 5GDari EverandPractical Guide to LTE-A, VoLTE and IoT: Paving the way towards 5GBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Power Congestion and Code CongestionDokumen15 halamanWhat Is Power Congestion and Code CongestionAgus Andriyas100% (3)
- Iub TroubleshootingDokumen36 halamanIub TroubleshootingNicholas Wilson100% (6)
- 3G OPTIMIZATION - v2Dokumen50 halaman3G OPTIMIZATION - v2Muhammad Ilham100% (1)
- C79000-G8976-1466 ROS v5.5 RSG909R ConfigurationManualDokumen432 halamanC79000-G8976-1466 ROS v5.5 RSG909R ConfigurationManualSever SudakovBelum ada peringkat
- Iub InvestigationDokumen32 halamanIub Investigationifyjoslyn100% (1)
- Outer-Loop Power Control in A Live UMTS Network: Measurement, Analysis and ImprovementsDokumen5 halamanOuter-Loop Power Control in A Live UMTS Network: Measurement, Analysis and ImprovementsOnur KoyuncuBelum ada peringkat
- LTE Channel Coding and Link AdaptationDokumen14 halamanLTE Channel Coding and Link AdaptationsugadoorBelum ada peringkat
- LTE FDD Network - KPI Case StudyDokumen39 halamanLTE FDD Network - KPI Case StudySK Basak BDBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Error: Reference Source Not FoundDokumen3 halamanChapter Error: Reference Source Not FoundKàrthîkéyàn PérîyàsàmyBelum ada peringkat
- Blocking 3G VMS VersionDokumen15 halamanBlocking 3G VMS VersionCao Văn TuấnBelum ada peringkat
- 3G Optimizatio1Dokumen5 halaman3G Optimizatio1Satish JadavBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1.1 RNC ResourcesDokumen4 halaman1.1.1 RNC ResourcesJohn StewartBelum ada peringkat
- C WINDOWS TEMP Plugtmp-29 Plugin-Sprp501Dokumen31 halamanC WINDOWS TEMP Plugtmp-29 Plugin-Sprp501Ekwere Wilfred UdohBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1.2 Nodeb ResourcesDokumen2 halaman1.1.2 Nodeb ResourcesJohn StewartBelum ada peringkat
- RRC Setup Report v1Dokumen23 halamanRRC Setup Report v1Amrinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei Training GuideDokumen5 halamanHuawei Training GuidediporufaiBelum ada peringkat
- Single Site Acceptance AnalysisDokumen29 halamanSingle Site Acceptance Analysissalaheddin_mahasnehBelum ada peringkat
- HSDPA License and Uplink CE Congestion Analysis: Prepared byDokumen14 halamanHSDPA License and Uplink CE Congestion Analysis: Prepared byjabooscribdBelum ada peringkat
- RNO Analysis Mate V1Dokumen119 halamanRNO Analysis Mate V1Manik KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- 3G IUB ParametersDokumen3 halaman3G IUB ParametersMohan OletiBelum ada peringkat
- Optimisation Procedures Which Can Be ADokumen3 halamanOptimisation Procedures Which Can Be AKàrthîkéyàn PérîyàsàmyBelum ada peringkat
- 4 WCDMA Load Control Algorithm and Parameters RAN10Dokumen166 halaman4 WCDMA Load Control Algorithm and Parameters RAN10MkathuriBelum ada peringkat
- General Description of Dynamic Channel Configuration Control - DCCC - AlgorithmDokumen10 halamanGeneral Description of Dynamic Channel Configuration Control - DCCC - Algorithmdiefenbaker13Belum ada peringkat
- RRC Setup ReleaseDokumen11 halamanRRC Setup ReleaseHữu Việt TạBelum ada peringkat
- RAN 3G Interfaces+ProtocolsDokumen15 halamanRAN 3G Interfaces+Protocolsnavvicky082079Belum ada peringkat
- HSUPA Parameter HuaweiDokumen17 halamanHSUPA Parameter HuaweiemilsonacruzBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Network ControllerDokumen2 halamanRadio Network ControllerBaneeishaque0% (1)
- HSUPA (5) - Principles of HSUPA Link Budget and Network Estimation-20070329-A-1.0Dokumen51 halamanHSUPA (5) - Principles of HSUPA Link Budget and Network Estimation-20070329-A-1.0watever22100% (1)
- Performance Study of The GSM Circuit-Switched Data Channel Research ProjectDokumen25 halamanPerformance Study of The GSM Circuit-Switched Data Channel Research ProjectnngoweBelum ada peringkat
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONDari EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONBelum ada peringkat
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDari EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingBelum ada peringkat
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDari EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksBelum ada peringkat
- AsterPropagationModel FinalDokumen23 halamanAsterPropagationModel FinalBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- 01 - Introduction To UMTSDokumen42 halaman01 - Introduction To UMTSBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- Mentum Planet 5.7.0 Patch 10-ReleaseNoticeDokumen4 halamanMentum Planet 5.7.0 Patch 10-ReleaseNoticeBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- Mentum Planet 5.7.0 Patch 10-ReleaseNoticeDokumen4 halamanMentum Planet 5.7.0 Patch 10-ReleaseNoticeBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- Ts 125321v110500pDokumen212 halamanTs 125321v110500pBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- 2GVS3G Drive Test With Tems: Lexcorp SolutionsDokumen11 halaman2GVS3G Drive Test With Tems: Lexcorp SolutionsBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- WCDMA RNP Cell Primary Scrambling Code Planning GuidanceDokumen31 halamanWCDMA RNP Cell Primary Scrambling Code Planning GuidanceSubrata Sen100% (1)
- 3g Node B On Ip MediaDokumen79 halaman3g Node B On Ip MediaBsskkd KkdBelum ada peringkat
- Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA)Dokumen38 halamanUnlicensed Mobile Access (UMA)hackep1Belum ada peringkat
- Question 2.Dokumen15 halamanQuestion 2.Brian OtugehBelum ada peringkat
- Ec2352 Computer Networks Question Bank CNDokumen4 halamanEc2352 Computer Networks Question Bank CNMuhamed HajaBelum ada peringkat
- Setting Up A LAN NetworkDokumen7 halamanSetting Up A LAN NetworkdawsonBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Services Digital Network PowerpointDokumen23 halamanIntegrated Services Digital Network PowerpointElmarie RecorbaBelum ada peringkat
- LTE Call Flow PS Redirection To UTRAN V2015 0105 V1 0Dokumen94 halamanLTE Call Flow PS Redirection To UTRAN V2015 0105 V1 0Nattawat PhumpanyaratBelum ada peringkat
- #Shut Down Spanning Tree Protocol#: #Ring 1 Configuration#Dokumen3 halaman#Shut Down Spanning Tree Protocol#: #Ring 1 Configuration#MrKia HaBelum ada peringkat
- Recent TrendsDokumen28 halamanRecent Trendsashokyadav739Belum ada peringkat
- Networking Notes in HindiDokumen29 halamanNetworking Notes in Hindi2abijeet43% (7)
- 1-Gestión y Costos - UBA - BibliografíaDokumen424 halaman1-Gestión y Costos - UBA - BibliografíaMaria Fernanda SandezBelum ada peringkat
- TEMS Automatic 9.0 - RTU Product SheetDokumen2 halamanTEMS Automatic 9.0 - RTU Product Sheetkiran_rm2006Belum ada peringkat
- ExamUnion 200-125 CCNA v3.0 Exam Questions, 200-125 Practice TestDokumen8 halamanExamUnion 200-125 CCNA v3.0 Exam Questions, 200-125 Practice TestMorrisPorreca2016032100% (1)
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN II/II)Dokumen39 halamanPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN II/II)svkg93Belum ada peringkat
- Guia 3com Switch-4500G Configuration-GuideDokumen598 halamanGuia 3com Switch-4500G Configuration-GuideChritian EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Hspa BasicDokumen59 halaman03 Hspa BasicRaufrmzBelum ada peringkat
- Future LTE Public Safety Systems June2016Dokumen2 halamanFuture LTE Public Safety Systems June2016gameOverBelum ada peringkat
- Ethernet Frame Size-BW CalculationsDokumen3 halamanEthernet Frame Size-BW CalculationsBiswajit DasBelum ada peringkat
- H3C WA6320 New Generation Access PointDokumen14 halamanH3C WA6320 New Generation Access PointCarlos MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- AN4577Dokumen25 halamanAN4577Arunkumar PbBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual Igs-3044gp GC v1.3Dokumen99 halamanUser Manual Igs-3044gp GC v1.3oring2012Belum ada peringkat
- Register 6 - Iu Interface Control Plane SCCP and RANAPDokumen94 halamanRegister 6 - Iu Interface Control Plane SCCP and RANAPTrilok SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- RIP Routing FundamentalsDokumen3 halamanRIP Routing FundamentalsKarlBelum ada peringkat
- Pan Os Networking AdminDokumen354 halamanPan Os Networking Adminaravindsivan92Belum ada peringkat
- 3G-4G Parameters Configuration UnderstandingDokumen13 halaman3G-4G Parameters Configuration UnderstandingHaroon Fazal MeoBelum ada peringkat
- LTE RoamingDokumen4 halamanLTE RoamingSumber RejekiBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network UNIT 2Dokumen30 halamanComputer Network UNIT 2Nihal GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- BRKSEC-3172 Advanced IOS XR SecurityDokumen70 halamanBRKSEC-3172 Advanced IOS XR Securityreferenceref31Belum ada peringkat