INFLAMMATION REGULATION
Diunggah oleh
madison614040 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
379 tayangan13 halamanDefense reactions cause tissue injury during conditions of inflammation. Inflammation diminishes at the completion of the healing process. Chemical mediators like histamines and prostaglandins trigger inflammation in response to trauma, toxins, or microbes. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects and are used to treat inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and pain. NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes and thereby inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.
Deskripsi Asli:
Study for Last Test pharmacology for nursing
Judul Asli
Study for Last Test pharmacology
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniDefense reactions cause tissue injury during conditions of inflammation. Inflammation diminishes at the completion of the healing process. Chemical mediators like histamines and prostaglandins trigger inflammation in response to trauma, toxins, or microbes. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects and are used to treat inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and pain. NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes and thereby inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
379 tayangan13 halamanINFLAMMATION REGULATION
Diunggah oleh
madison61404Defense reactions cause tissue injury during conditions of inflammation. Inflammation diminishes at the completion of the healing process. Chemical mediators like histamines and prostaglandins trigger inflammation in response to trauma, toxins, or microbes. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects and are used to treat inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and pain. NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes and thereby inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 13
Terms Definitions
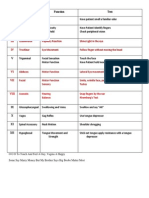
During which conditions does defense
reactions cause tissue injury?
Rheumatoid arthritis & asthma
What point of the healing process does
inflammation diiminish?
Completion
What can cause inflammation? Trauma, toxic chemicals, & microbial agents
Name some chemical mediators that trigger
inflammation?
Histamines, lipids like prostaglandins & small/ large peptides,
interleukin-1, & bradykinin
When does rheumatoid arthritis occur? When WBCs attack the synovium and initiate an inflammatory
attack
What drugs have analgesic, anti-inflammatory
& antipyretic effects on the body are used for
inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions?
NSAIDs
COX-2 Inhibitors are used to treat what? Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis & pain
What drug inhibits prostaglandin synthesis in
the CNS & has antipyretic & analgesic
properties?
Acetaminophen
What condition is a metabolic disorder
characterized by high level of uric acid in the
blood?
Gout
Acute gouty attacks are treated with what? Indomethacin, NSAIDs, glucocorticoids & prophylactic therapy
What agents are used in treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis & have been shown to
slow the course of the disease?
Disease-Modifying Anti Rheumatic
Name some NSAIDs? Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, nabumetone, Naproxen,
Oxaprozin, Celecoxib, Meloxicam & Sumatriptan
What's the only NSAID that irreversibly inhibits
COX-1 & 2?
Aspirin
Which drug is used to treat migrain headaches
that is a serotonin agonist?
Sumatriptan
NSAIDs inhibit which set of enzymes that
catalyze the first step in prostanoid
biosynthesis?
Cycloxygenase
Prostaglandins are synthesized from what
through the cycloxygenase pathway?
Arachidonic acid
Prostaglandin F2a, leukotrienes and
thromboxanes activate what?
Phosphatidyl inositol metabolism, causing increase in Ca2+
Adverse effects of aspirin and salicylic acid
derivatives?
Inc gastric secretion, reduced platelet aggregation, Na+ & H2O
retention, which causes edema & hyperkalemia
What types of drugs have the same effects as
aspirin but with less intense GI effects?
Propionic acid derivates like ibuprofen, fenoprofen
What NSAIDS are typically not used to reduce
fever?
Acetic acid derivatives like etodolac, & incomethacin
Adverse effects of NSAIDs? GI effects like n & v, ulcers, skin irritations, Na+ & H2O retention
leading to edema & hyperkalemia, interstitial nephritis (except
aspirin), prolonged bleeding times
Which NSAID can cause MI and CVA but has
less GI irritation than aspirin?
Celecoxib (COX-2 inhibitor)
Safest NSAID? Naproxen
Which has low cost and long history of safety? Aspirin
Which NSAID is very potent & can cause CNS
disturbances?
Indomethacin
Old DMARDs? Methotreate, hydroxychloroquine
Newer DMARDs? TNF- inhibitors, leflunomide, &anakinra
What's Reye's syndrome? Acute encephalopathy, fat depositions in liver & other visceral
organs
What drugs treat gout? Allupiinol, probenecid, & colchine
Which anti-gout drug inhibits xanthine
oxidase activity?
Allopurinol
Which anti-gout drug decreases the
reabsorption of uric acid?
Probenecid
Which anti-gout drug is anti-inflammatory
that decreases leukocyte activity?
Colchine
NSAIDs inhibit the synthesis of what
compound?
Prostaglandin
When are prostaglandins released? Allergic & inflammatory process
What can cause platelet aggregation & smooth
muscle contraction?
TXA2 (thromboxane A2)
What prostaglandins increase intracellular
Ca2+?
PGE2, PGF2a, leukotrienes thromboxane A2
Actions of prostaglandins? Vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, vessel permeability, enhance
pain effects of bradykinin, directly cause pain, induce fever,
increase or decrease cAMP
Actions of histamines? Increases gap junction space, cause tissue congestion, swelling,
bronchoconstriction, causes sneezing, watery eyes, itching, cause
pressure & pain
Actions of thromboxanes? Cause platelet aggregation, vasoconstriction, smooth muscle
contraction, enhance function of inflammatory cells, increase
intracellular Ca2+
Actions of leukotrienes? Inc vessel permeability, platelet aggregation, stimulate
neutrophils, increase intracellular calcium, causes
bronchoconstriction
What sensitizes nerves to the action of
bradykinin & histamine & causes pain, fever &
inflammation?
PGE2
What system is not inhibited by NSAIDs but is
inhibited by colchine?
Lipooxygenase
Which joint disorder involves bone ends
rubbing together?
Osteoarthritis
Which joint disorder involves swollen inflamed
synovial membrane?
Rheumatoid arthritis
Arachidonic acid leads to the production of 5-lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenases (COX-1, and COX-2)
what two enzymes?
What activates the production of
Phospholipase A2, which leads to the
production of arachidonic acid?
Bradykinin & angiotensin
What inhibits the production of Phospholipase
A2, which leads to the production of
arachidonic acid?
Corticosteroids
What increases protective mucous? PGE2
What is the immediate precursor of
leukotrienes?
5-HETE
Prostaglandins leads to physiological
responses?
Platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, and allergic
reactions
What happens to after prostaglandins bind to
G proteins?
Formation of diacylglycerol & IP3 is enhanced
Uses of aspirin? Prevent heart attacks, arthritis, headache, other pains, & body
aches
How proinflammatory cytokines lead to RA? Cause inc cellular filtration into endothelium, inc production &
release of proteolytic enzymes leading to degradation of
cartilage/joint space narrowing, inc osteoclast activity -> bone
erosion, demineralization
What happens during initiation of
pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Synovitis?
Vascular injury causes influx of immune cells & plasma causing
synoviocyte hyperplasia
What happens during immune response of
pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Synovitis?
Cellular reactivation & proliferation of cytokines e.g Tumor
Necrotic factor & interleukines. Neutrophils attracted and activated
What happens during inflammation of
pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Synovitis?
Phagocytosis of immune complex and release of prostaglandins
and lysosomal enzymes occur
What happens during destruction of
pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Synovitis?
Collegenase (destroys cartilage); and prostaglandins secreted by
synoviocytes
What triggers release of COX-2? Oxidative stress, injury, ischemia, seizures & neurodegenerative
diseases
Name a selective COX-2 inhibitor? Celecoxib
COX-2 inhibitors are NOT used for what? Analgesia, like headache, or to decrease platelet aggregation
What COX inhibitors cause no gastric damage? COX-2 inhibitors
What happens the acetyl group on aspirin? It irreversibly (covalently) inhibits cyclooxygenase. Acetylated
cyclooxygenase
What decreases synthesis of mucous? PGE2 & PGF2alpha
How does the antipyretic action of aspirin
work?
It causes peripheral vasodilation, therefore, heat dissipation,
increases respiration, high doses hyperventilation
Side effects of aspirin? Increased gastric acid secretion, decreases mucous protection,
therefore causes epigastric distress, ulceration and hemorrhage
What increases platelet aggregation? TXA2
What decreases platelet aggregation? PGI2
How does aspirin cause anticoagulation? It decreases TXA2
How can aspirin cause edema & hyperkalemia? It decreases renal flow & increases retention of Na+ & H2O by
affecting the actions of PGE2 & PGI2, which maintains renal blood
flow
Side effect of acetaminophen at high doses? Hepatoxicity
How does aspirin affect the synthesis of PGE2
and PGI2?
It decreases their synthesis
How do NSAIDs affect prostaglandin synthesis? They inhibit prostaglandins that inhibit vasoconstrictors
Examples of vasoconstrictors? Angiotensin II, Catecholamines, & Vasopressin
What results from aspirin overdose? Vasomotor collapse, coma & dehydration
High dose of aspirin causes what? Anti-inflammation, tinnitus, & central hyperventilation
How much aspirin is needed to decrease
myocardial infarctions?
150-300mg/day
How much aspirin is considered low dose? 600 mg/day
What's considered high dose of aspirin? 4000 mg/day
Low dose aspirin follows what kind of
elimination kinetics?
1st order
High dose aspirin follows what kind of
elimination kinetics?
Zero order
1/2 life of low dose (600 mg) aspirin? 3 hrs
1/2 life of high dose (4000 mg) aspirin? 15 hrs
Salicylates interact with what drugs to cause a
reduced rate of aspirin absorption?
Antacids
Salicylates interact with what drugs to cause
hemorrhage?
Heparin or anticoagulants
Acetaminophen's action are more prominent
where?
The CNS
In what patients is acetaminophen used to as
substitute for aspirin?
Patients who have gastric complaints and need antpyretic &
analgesic
Side effects of therapeutic doses
acetaminophen?
Skin rash, minor allergic rxns, minor alterations in leukocyte
count, renal tubular necrosis, & hypoglycemic coma
What used in case of acetaminophen overdose? N-acetylcysteine
What causes Reye's syndrome? Aspirin
Does acetaminophen cause Reye's syndrome? No
Which drug has no anti-inflammatory action? Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen has little effect in what region
of the body?
Peripherally
What is contraindicated in gout and why? Aspirin becauses it competes with uric acid
Colchine decreases the release of what
enzymes?
Lipoxygenase, & leukotrienes and other mediators inflammation
Allopurinol inhibit what enzyme? Xanthine oxidase
Colchine decreases the mobility of what? Neutrophils
How does colchine affect cell division of
granulocytes?
It binds to mitotic spindles and decreases cell division
How does colchine affect mobility of
neutrophils?
It causes depolymerization of microtubular proteins and it binds to
tubulin
What disorder results from high levels of uric
acid in the blood?
Gout
How does uric acid cause tissue damage? Granolocytes phagocytize the urate crystals which causes oxygen
metabolites and lactate in synovial tissues
What can aggravate gouty attacks? Purines, excessive alcohol consumption, a rich diet or kidney
disease
What's used to treat acute gout attacks? NSAIDs besides aspirin, indomethacin,
What causes chronic gout? Genetics resulting in increase in the rate of purine synthesis, renal
deficiency, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, or excessive production or
uric acid associated with cancer chemotherapy
Treatment of chronic gout ? Uricosuric drugs that increase excretion of uric acid, & use of
allopurinol
Examples of uricosuric agents? Probenacid & Sulfinpyrazone
What promotes renal clearance of uric acid by
inhibiting the urate-anion exchanger in the
proximal tubule?
Uricosuric agents
What disrupts mobility of granulocytes, and
inhibits the synthesis and release of the
leukotrienes?
Colchine
What is effective in the treatment of primary
hyperuricemia of gout & hyperuricemia
secondary to other conditions?
Allopurinol
What gout treatment has the side effect of
nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
myopathy, neutropenia, aplastic anemia &
alopecia?
Colchine
What gout treatment has the side effect of skin
rashes in ~ 3 % of patients along with nausea &
diarrhea?
Allopurinol
Adverse effect of chronic NSAID use? Analgesic nephropathy
What can causes susceptibility to acute renal
insufficiency?
NSAIDs
2nd most unwanted effects of NSAIDs? Skin reactions like urticaria and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
How do gold salts treat gout? They inhibit phagocytosis and lysosomal enzymes
What drug is used for arthritis? Infliximab
What drug is used for migraine headache? Sumatriptan
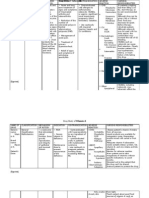
Terms Definitions
COPD = chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease
1. Emphysema 2. Asthma 3. Bronchiectasis 4. chronic bronchitis
**COPD = IRREVERSIBLE airway obstruction
Emphysema alveolar destruction with airspace enlargement & Airway collapse
drugs used: Bronchodilator: theophyline
Adrenergic Agonist -combivent
- a combination of a B adrenergic agonist + an anticholinergic = a
bronchodilatory for the treatment of COPD
Atrovent the drug of choice for long term management of COPD
causes - Xerostomia
Asthma most common respiratory disease
- REVERSIBLE airway obstruction
- reduced expiratory airflow
- clinical signs: wheezing, shortness of breath
Asthma is triggered by allergens
exercise
stress
pollution
2nd hand smoke
infections
Asthma medications 1. corticosteroids
- nasonex & flovent HFA & nasacort
2. mast cell stabilizers
-cromelyn - Intal
3. anticholinergics
-comnivent
4. beta agonists
-albuterol
5. xanthines
-theophylline
6. leukotriene receptor agonists
-Singulair
Use of Singulair prevent of asthma; is NOT used for an asthma attack.
- psychiatric problems have been reported: agitation, suicide,
depression, insomnia & irritability
Dental concerns of asthma
medications:
pulmonary hypertension
minimize stress
extra steriods
What do you do to prevent Acute
respiratory failure from asthma?
avoid aspirin & NSAIDS and erythromycin
keep emergency equipment available
Etiology: giving oxygen w/ nitrous oxide or CNS depressant
Bronchodilators 1. adrenergic agonists
2. xanthines
3. anticholinergic drugs
**Bronchodilators is REVERSIBLE airway obstruction
Adrenergic agonists Ex: proventil HFA/PRO AIR HFA
(bronchodilators) -albuterol
uses: txt of asthma and COPD
Advair Diskus A combination of a B adrenergic agonist + a corticosteroid =
improves pulmonary function.
Pharmacological effect of
Adrenergic agonists
drugs stimulate B2 receptor in the lungs...relaxing the smooth muscles
Adverse effects of Adrenergic
agonists
nervousness, tachycardia and insomnia
Xanthines (bronchodilators) uses: chronic asthma & COPD
-MAJOR drug - caffeine, theophylline
Bronchodilators in reversible airway obstruction
What is the pharmacological effect
of Xanthines?
Bronchodilation
What are the adverse effects of
Xanthines?
CNS stimulant
Insomnia
Nervousness
Diuresis (increased secretion of urine)
What is a drug interaction of
Xanthines?
Erythromycin can increase the serum levels of Theophylline and
toxicity may result
What is the 3rd Bronchodilator? Anticholinergics
It is an Ihalation agent for COPD clients & asthmatics who cannot
tolerate adrenergic agonists
What are the side effects of
anticholinergic drugs?
They are minimal but include dry mouth
What is cromolyn sodium or Intal
used for and it's pharmacological
effect?
It's only effect is to PREVENT asthma...it has NO bronchodilator
action.
It's pharm. effect is that it prevents release of histamine from
sensitized mast cells.
What is the least toxic of all Asthma
meds?
Intal (cromolyn sodium).
It's advantage is safety & available in metered doses
What are corticosteroid nasal
sprays used for?
They are used to treat asthmatics who are refractory to (others don't
work) asrenergic agonists. CANNOT be used for an asthma attack
What is the pharmacological effect
of corticosteroid nasal sprays?
It's an ANTIINFLAMMATORY nasal spray to increase pulmonary
function by a decrease in wheezing, tightness & coughing
What are some examples of
corticosteroids?
Nasacort (triamcinolone)
Flovent HFA inhaler (fluticasone)
Nasonex (no sig. effects of dental treatment)
What are some adverse effects of
corticosteroids?
Adrenal suppression
Poor wound healing
Immunosuppression
What are clients who use oral
corticosteriod inhalers advised to
do?
Rinse their mouth after using the inhaler to minimize the chance of
candidiasis.
What are two nasal decongestants
or agents for respiratory conditions?
Sudafed
Allegra D
What are the effects and uses of Constrict respiratory mucosa & stimulate B adrenergic receptors
nasal decongestants? causing bronchial relaxation.
Reduce nasal stuffiness.
What is an adverse effect of a nasal
decongestants?
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine which could interact
with epinephrine to cause a pressor response. (use epi with caution)
What is an expectorant? They are drugs that promote the REMOVAL & RELEASE of mucus
from the respiratory passages
EX. Mucinex DM
Why is Mucinex different from
Mucinex DM
The Mucinex DM has dextromethorphan added to control the cough
What is a Mucolytics? A drug that DESTROYS OR DISSOLVES mucus.
What is an antitussives? An agent which prevents or inhibits coughing like Delsym.
Opiods are most effective BUT are addicting
What is the mechanism of action of
antitussives?
They are chemically related to mrophine but lacking in narcotic
properties except for overdose. It controls the cough by depressing the
medullary cough center.
What is a drug used for smoking
cessation?
Chantix (varenicline)
a patial nicotine agonist due to stimulating dopamine activity to a
lesser degree than actual nicotine.
Xerostomia is noted
Terms Definitions
What are the contraindications for
taking Birth Control Pills?
Pregnancy
Breast feeding if under 6 weeks
postpartum
HTN 160/100
Vascular disease
Heavy smoking over 35
History of DVT, pulmonary embolism, stroke (Multi- Cardio risk
factors)
Endometrial cancer
Ischemic, heart valve defect
Breast cancer less than 5 years ago
Liver tumors
Cirrohosis
Active viral hepatitis
Diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy
Diabetes more than 20 years duration (BCP's increase glucose)
Mono-phasic pills Most common
Fixed ratio of estrogen and progestin throughout cycle
1 tab daily at the same time
21 and 28 tablets
7 placebo counters
Bi-phasic pills Fixed estrogen
Progesterone varies which mimics the normal cycle
Mini-pills Progestin only birth control pill
Alters cervical mucus altering the endometrium to inhibit
implantation
Designed to reduce circulatroy side effects
Increased risk pregnancy and BREAD THRU bleeding
If pill taken more than 3 hours late - need back - up contraception
for 48 hours.
All 28 pills are active.
Extended cycle BCP's 4 periods a year
May have break through bleeding
Always SUNDAY start
e.g. Seasonale (Ethinyl Estradiol / Levonorgestrel)
Seasonique
Continuous dose Lybrel - taken continuously without interruption for withdrawl
menses
FDA Pregnancy Category A Studies show no fetal risk
FDA Pregnancy Category B No fetal risk in animal studies
No risk assumed in humans
FDA Pregnancy Category C Fetal risk in animal studies
weight risk vs. benefit
FDA Pregnancy Category D Proven fetal risk
weigh risk vs. benefit if life-threatening
FDA Pregnancy Category X Proven fetal risk
Risk more than benefit - AVOID in pregnancy
Teratogenic effects of drugs Teratogen:
Substance that causes developmental abnormalities
Exposure may result in death of embryo or minor cellular damage
without congenital birth defects.
Results in malformations
exerts effects at a particular stage of fetal development
depends on dose
Teratogen = Smoking Includes intrauterine growth restriction
Still birth - primary and secondary smoke
Teratogen - Alcohol Miscarriage
Neurocognitive delay in child
Teratogen drugs ACE Inhibitors
Tetrocyclins
Warfarin
Androgens - male hormones
How to oral contraceptive exert their
therapeutic effects?
1. Suppress pituitary secretion of FSH and LF
2. Creates changes in the endometrium to make it less favorable for
implantation of fertilized ovum
3. Changes in quantity and viscosity of cervical mucous to make it
hostile to sperm.
Why are extended BCP's used? The active pill days or hormones in the pills are extended.
Inert pills reduced which shortens the period of withdrawl bleeding
for patient.
The shorter period of hormone free tablets increases the
contraceptives efficacy.
What are non - contraceptive benefits
of BCP's
Suppressed pain at ovulation - Mittelschmerz
Decreased dysmenorrhea
Lighter, shorter menstrual flow
Decreased iron deficiency anemia from decreased flow
Reduced risk of functional ovarian cysts
Protection against benign breast lesions
Reduced risk of pelvic inflammatory disease
Lower risk of ectoptic pregnancy
Decreased menstrual migraines
Decreased risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer.
What are side effects of BCP's Nausea
Weight gain
Sore or swollen breasts
Spotting btw periods
lighter periods
mood changes
Adverse reactions to BCP's Adverse:
Abdominal Pain
Chest pain
severe headaches
Eye problems - blurred vision
Swelling and aching in legs and thighs.
Higher doses of estrogen increase the risk for thromboembolism,
stroke and MI
Low dose combo oral BCP's reduce the risk
Two arms of WHI study Estrogen and Progestin HT arm
Estrogen only - ET arm
Question - to see if either reduced incidence of heart, disease,
breast and colorectal cancer and fractures in post-menopausal
women - 16000 tested.
HT study findings Estrogen and Progestin _ HT
E nded after 5.2 years
Risks outweighed benefits
Increased risk of breast cancer
heart attack
stroke
blood clots
Decreased risk for
Colon cancer
spine and hip fractures
ET Study findings Estrogen only
Lasted 2 years
Did not prevent Cardio vascular disease
Increased risk of stroke
Did not affect breast cancer risk
Lowered risk for hip fracture
If had hysterectomy - can't take estrogen alone - increases chance
of endometrial cancer.
Conclusions of HT and ET study HT increased risk of breast cancer
Estrogen alone - DOES NOT increase risk
Hormone therapy SHOULD be prescribed for menopausal
symptoms
SHOULD NOT be prescribed for long term prevention of disease
such as CV (increases mortality with MI, stroke and DVT
Ostroporosis
Nursing implications for BCP's and
Drospirenone
Drospirenone is the only Progestin derived from Spironolactone
(not testosterone) structurally similar to progesterone
e.g. Yasmin, Yaz (monophasic - 24 days active)
Take serum K levels
Contraindications with Drospirenone Use increases serum potassium
Contraindicated with kidney, liver or adrenal insufficiency and use
of
NSAIDS
K+ sparing diuretics
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin II anatagonists
Heparin
ACHES A - Abdominal pain - blood clot in abdomen
C = Chest pain - sign of embolism
H - Headaches severe- dizziness, weakness, numbness, speech
difficulties
E - eye disorder - clot behind eye
S = severe leg pain or calf swelling = DVT
BCP's first time health education Risk Iron anemia
Thromboembolism goes up
No STD protection
PE, MI, CVA and retinol thrombosis is rare
To take the pill at the same time everyday and let them know about
side effects
Risk for uterine, ovarian and endometrial cancer goes UP
What are the indications for Anabolic
steroids
Testosterone derivative
INcreases strength and power
Creates euphoria and enhanced sexual performance
Side effects of anabolic steroids Dramatic increase in weight
Body size
changes in mood and behavior
Side effects - water retention
cardiovascular damage
cardiomyopathy
stroke
hepatic problems
lower HDL cholesterol - good fat
Physiologic and therapeutic uses of
drugs of Erectile Dysfunction
Medications
Viagra - selective reuptake inhibitor of cGMP in corpus cavernosa
(this helps relax smooth muscle which increases vasodilation and
increases blood flow)
Potentiates hypotensive effects of nitrates so is contraindicated with
use of other NITRATES
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Pharmacology Study Guide For NursingDokumen12 halamanPharmacology Study Guide For Nursingmadison61404100% (7)
- Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry AUDokumen109 halamanOrganic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry AUAshley DayagBelum ada peringkat
- Paracetamol Plant ProjectDokumen90 halamanParacetamol Plant ProjectEshan BhatBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Piascledine CT 5536Dokumen13 halamanPiascledine CT 5536Shahab EdalatianBelum ada peringkat
- Immune NotesDokumen8 halamanImmune Notesmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System NotesDokumen2 halamanEndocrine System Notesmadison614040% (1)
- Lab Values Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanLab Values Cheat Sheetmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 and 4 Nursing Care of Children For NursingDokumen3 halamanChapter 3 and 4 Nursing Care of Children For Nursingmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- Cranial NervesDokumen1 halamanCranial Nervesmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- Chart Summary of Medications Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDokumen1 halamanChart Summary of Medications Affecting The Autonomic Nervous Systemmadison61404100% (2)
- Antipsychotics Meds ListDokumen2 halamanAntipsychotics Meds Listmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- 214 Psychiatric QuestionsDokumen23 halaman214 Psychiatric Questionsmadison61404Belum ada peringkat
- Drug interaction checkerDokumen1 halamanDrug interaction checkermadison61404100% (3)
- Celecoxib drug guideDokumen10 halamanCelecoxib drug guidejessica_omegaBelum ada peringkat
- Invitro Dissolution and Assay of "Ibuprofen"Tablet.Dokumen59 halamanInvitro Dissolution and Assay of "Ibuprofen"Tablet.Md.Moniruzzaman100% (3)
- NSAIDs Guide - How Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs WorkDokumen3 halamanNSAIDs Guide - How Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs WorkKKN 11 UMY 2017Belum ada peringkat
- Mecanismo de Acción Del AcetaminofénDokumen9 halamanMecanismo de Acción Del AcetaminofénCero Excusas SA de C.VBelum ada peringkat
- Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Assays Confirm Bioactive Compounds in Ajwa Date FruitDokumen7 halamanAntioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Assays Confirm Bioactive Compounds in Ajwa Date Fruitrizla67100% (1)
- Pain Classification and Cancer Pain ManagementDokumen50 halamanPain Classification and Cancer Pain ManagementAli Aftab100% (1)
- What Is Schatzki Ring:: Ref: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 2005, 16 Edition, Page 1745Dokumen42 halamanWhat Is Schatzki Ring:: Ref: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 2005, 16 Edition, Page 1745Chadi MamloukBelum ada peringkat
- Toxi Lab Lecture Notes 6-15Dokumen7 halamanToxi Lab Lecture Notes 6-15Micah Lou CalambaBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Persistent Pain in Older Adults - Up to DateDokumen25 halamanTreatment of Persistent Pain in Older Adults - Up to DateMulya ImansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids and NSAIDsDokumen3 halamanPharmacology of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids and NSAIDsMirza HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen1 halamanDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJeyser T. GamutiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ketorolaco PDFDokumen8 halamanKetorolaco PDFCristhian Cuentas ObandoBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroproteccion Anticoagulacion y AntiagregaciónDokumen13 halamanGastroproteccion Anticoagulacion y AntiagregaciónYesica Villalba CerqueraBelum ada peringkat
- Histamine and H1 Antihistamines: Actions and UsesDokumen38 halamanHistamine and H1 Antihistamines: Actions and UsesIqra NasirBelum ada peringkat
- Bioactive Compounds From Medicinal Plants - Focus On Piper Species PDFDokumen16 halamanBioactive Compounds From Medicinal Plants - Focus On Piper Species PDFaguswrBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 Mcqs Pain ControlDokumen29 halaman2020 Mcqs Pain Controlareej alblowi100% (1)
- Laryngitis and PericarditisDokumen17 halamanLaryngitis and Pericarditis2B-4- TUNAC, Avvy Charlotte R.Belum ada peringkat
- 2033 Rheumatoid Arthritis 14-1 PDFDokumen48 halaman2033 Rheumatoid Arthritis 14-1 PDFAfif Al FatihBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Herpangina: Denta, Jurnal Kedokteran GigiDokumen5 halamanManagement of Herpangina: Denta, Jurnal Kedokteran GigirizadBelum ada peringkat
- Salicylic Acid Derivatives: Synthesis, Features and Usage As Therapeutic ToolsDokumen11 halamanSalicylic Acid Derivatives: Synthesis, Features and Usage As Therapeutic ToolsDostin JasserBelum ada peringkat
- Pain DrugDokumen15 halamanPain DrugSherlyta AlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDokumen4 halamanDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Teva PantoprazoleDokumen34 halamanTeva PantoprazoleqthermalBelum ada peringkat
- Coughs - and How To Treat ThemDokumen15 halamanCoughs - and How To Treat Themsimplybr95630% (1)
- Formulation Development and Compatibility Study of Dexketoprofen Injection Used in The Management of Post-Operative PainDokumen7 halamanFormulation Development and Compatibility Study of Dexketoprofen Injection Used in The Management of Post-Operative PainAdeeva MaulidaBelum ada peringkat
- Borda2018 PDFDokumen48 halamanBorda2018 PDFlarasBelum ada peringkat