Combinational Logic - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Diunggah oleh
Suneelkrishna Rallabhandi0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan3 halamanCombinational logic is a type of digital logic implemented by Boolean circuits. The output is a pure function of the present input only. Sequential logic has memory while combinational logic does not.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniCombinational logic is a type of digital logic implemented by Boolean circuits. The output is a pure function of the present input only. Sequential logic has memory while combinational logic does not.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan3 halamanCombinational Logic - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Diunggah oleh
Suneelkrishna RallabhandiCombinational logic is a type of digital logic implemented by Boolean circuits. The output is a pure function of the present input only. Sequential logic has memory while combinational logic does not.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Combinational logic
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Not to be confused with combinatory logic, a topic in mathematical logic.
In digital circuit theory, combinational logic (sometimes also referred to as time-independent logic
[1]
) is a
type of digital logic which is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present
input only. This is in contrast to sequential logic, in which the output depends not only on the present input but
also on the history of the input. In other words, sequential logic has memory while combinational logic does not.
Combinational logic is used in computer circuits to performBoolean algebra on input signals and on stored data.
Practical computer circuits normally contain a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. For example, the
part of an arithmetic logic unit, or ALU, that does mathematical calculations is constructed using combinational
logic. Other circuits used in computers, such as half adders, full adders, half subtractors, full subtractors,
multiplexers, demultiplexers, encoders and decoders are also made by using combinational logic.
An alternate term is combinatorial logic,
[2]
though this usage may be considered controversial.
[3]
Contents
1 Representation
2 Logic formula minimization
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Representation
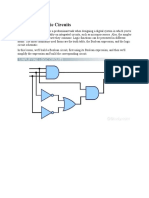
Combinational logic is used to build circuits that produce specified outputs from certain inputs. The construction
of combinational logic is generally done using one of two methods: a sum of products, or a product of sums. A
sum of products can be visualized in a truth table, as in this example:
Result Logical equivalent
F F F F
F F T F
F T F F
F T T F
T F F T
T F T F
T T F F
T T T T
Combinational logic - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combinational_logic
1 of 3 5/16/2014 10:42 PM
Using sum of products, all logical statements which yield true results are summed, giving the result:
Using Boolean algebra, the result simplifies to the following equivalent of the truth table:
Logic formula minimization
Minimization (simplification) of combinational logic formulas is done using the following rules:
With the use of minimization (sometimes called logic optimization), a simplified logical function or circuit may
be arrived upon, and the logic combinational circuit becomes smaller, and easier to analyse, use, or build.
See also
Sequential logic
Asynchronous logic
FPGA
Formal verification
References
^ C.J. Savant, Jr.; Martin Roden; Gordon Carpenter. "Electronic Design: Circuits and Systems". 1991. ISBN
0-8053-0285-9 p. 682
1.
^ Clive Maxfield. "FPGAs: World Class Designs" (http://books.google.com/books?id=kQuOKBSOz5QC&
pg=PA70&dq=%22combinatorial+logic%22&hl=en&sa=X&ei=vBSdULe_LMPHqQGploDoCg&
2.
Combinational logic - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combinational_logic
2 of 3 5/16/2014 10:42 PM
ved=0CEQQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=%22combinatorial%20logic%22&f=false). p. 70. 2009. ISBN 1856176215
^ Cliff Cummings. "Common Mistakes In Technical Texts" (http://www.sunburst-design.com/papers
/Technical_Text_Mistakes.pdf). 2009.
3.
Michael Predko and Myke Predko, Digital electronics demystified, McGraw-Hill, 2004. ISBN
0-07-144141-7
External links
Combinational Logic & Systems Tutorial Guide (http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/Projects/Labview
/combindex.html) by D. Belton, R. Bigwood.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Combinational_logic&oldid=599288240"
Categories: Logic in computer science Digital electronics
This page was last modified on 12 March 2014 at 14:08.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may
apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered
trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Combinational logic - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combinational_logic
3 of 3 5/16/2014 10:42 PM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Combinational CircuasdasditDokumen2 halamanCombinational CircuasdasditAnthony OlanBelum ada peringkat
- LDST AssignentDokumen2 halamanLDST AssignentRajesh RamwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4: Combinational Logic GatesDokumen15 halamanGroup 4: Combinational Logic GatesRofelyn EnteroBelum ada peringkat
- Ecadd Long ReportDokumen13 halamanEcadd Long ReportSirenjeevi RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Technics: Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology InstituteDokumen30 halamanDigital Technics: Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology InstituteRichardJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Organization & Architechture CB320Dokumen25 halamanComputer Organization & Architechture CB320Alex JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Group Assignment (Beng 1113)Dokumen15 halamanGroup Assignment (Beng 1113)Faris AzminBelum ada peringkat
- V3i9 0363 PDFDokumen9 halamanV3i9 0363 PDFRasa Uchiha SankarBelum ada peringkat
- Report Title: Combinational Logic Prepared byDokumen10 halamanReport Title: Combinational Logic Prepared byAbdullah KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Logic Design IntroductionDokumen2 halamanFundamentals of Logic Design IntroductionRamo ZBelum ada peringkat
- Corrections AesDokumen21 halamanCorrections AesDivya SriBelum ada peringkat
- A Quick Guide To Reversible Logic 6-1Dokumen20 halamanA Quick Guide To Reversible Logic 6-1Mochamad NursidiqBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Integrated Circuit: IntroductionDokumen5 halamanDigital Integrated Circuit: IntroductionPolkam SrinidhiBelum ada peringkat
- Simplifying Logic CircuitsDokumen3 halamanSimplifying Logic Circuitskavindu AmeshBelum ada peringkat
- Ewdts08-41 - Copy - 1Dokumen3 halamanEwdts08-41 - Copy - 1Prateek MudgilBelum ada peringkat
- COA CH 1Dokumen33 halamanCOA CH 1DesyilalBelum ada peringkat
- Multiplexer-Based Design of Adders/Subtractors and Logic Gates For Low Power VLSI ApplicationsDokumen8 halamanMultiplexer-Based Design of Adders/Subtractors and Logic Gates For Low Power VLSI ApplicationssunilBelum ada peringkat
- A 32 BIT MAC Unit Design Using Vedic MultiplierDokumen6 halamanA 32 BIT MAC Unit Design Using Vedic MultiplierdycsteiznBelum ada peringkat
- Morris ManoDokumen59 halamanMorris ManoRohit Mann75% (4)
- Plate No. 1 Application of Sequential Circuit Queueing SystemDokumen5 halamanPlate No. 1 Application of Sequential Circuit Queueing SystemejlorsBelum ada peringkat
- Week10 Module10Dokumen8 halamanWeek10 Module10buscainojed078Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 LG & BADokumen27 halamanChapter 3 LG & BATolesa ShoreBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation and Programming of Software For Minimizing The Costs of Digital CircuitsDokumen7 halamanImplementation and Programming of Software For Minimizing The Costs of Digital CircuitsHermomBelum ada peringkat
- SADGUNmajortheory MiniDokumen52 halamanSADGUNmajortheory MiniKotagiri AravindBelum ada peringkat
- SADGUNmajortheoryDokumen51 halamanSADGUNmajortheoryKotagiri AravindBelum ada peringkat
- Gate-Level Synthesis of Boolean Functions Using Binary Multiplexers and Genetic ProgrammingDokumen8 halamanGate-Level Synthesis of Boolean Functions Using Binary Multiplexers and Genetic Programmingbabypaul4321Belum ada peringkat
- Logic Synthesis - WikipediaDokumen4 halamanLogic Synthesis - WikipediasukhoiBelum ada peringkat
- Logic Design NotesDokumen193 halamanLogic Design NotesAnup Konnur100% (1)
- Espresso Heuristic Logic MinimizerDokumen4 halamanEspresso Heuristic Logic MinimizerAnshul PawaskarBelum ada peringkat
- Logic CircuitsDokumen8 halamanLogic Circuitsfewpew LumanglasBelum ada peringkat
- Logic Gate: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen10 halamanLogic Gate: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHazim SanusiBelum ada peringkat
- Fpga Control Motor AsincronDokumen7 halamanFpga Control Motor AsincronVasileSpireaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computer ArchitectureDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Computer ArchitectureLwanga Charles Chas100% (1)
- Studies On BLDC Motor For Position Control Using PID-Fuzzy-Neural Network and Anti-Windup ControllersDokumen6 halamanStudies On BLDC Motor For Position Control Using PID-Fuzzy-Neural Network and Anti-Windup ControllershesaBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Circuit Simulation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen4 halamanElectronic Circuit Simulation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaetherhuntBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation and Code Generation of Digital Circuits and System Using MATLAB & SIMULINKDokumen16 halamanImplementation and Code Generation of Digital Circuits and System Using MATLAB & SIMULINKVLSISD36 Edwin DominicBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation and Code Generation of Digital Circuits and System Using MATLAB & SIMULINKDokumen16 halamanImplementation and Code Generation of Digital Circuits and System Using MATLAB & SIMULINKhamim ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Base Computer Based Measuring TechniquesDokumen104 halamanBase Computer Based Measuring TechniquesmakayaboBelum ada peringkat
- Flip-Flop Grouping in Data-Driven Clock Gating: Varghese James A, Divya S, Seena GeorgeDokumen9 halamanFlip-Flop Grouping in Data-Driven Clock Gating: Varghese James A, Divya S, Seena GeorgeDigvijay ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Design of Digital Synthetic Gene Circuits: Mario A. Marchisio, Jo RG StellingDokumen14 halamanAutomatic Design of Digital Synthetic Gene Circuits: Mario A. Marchisio, Jo RG StellingShampa SenBelum ada peringkat
- Adrija Ray Maths Report 2023 FinalDokumen12 halamanAdrija Ray Maths Report 2023 FinalAdrija RayBelum ada peringkat
- Current-Mode Digital Gates and CircuitsDokumen4 halamanCurrent-Mode Digital Gates and CircuitsqwertypointBelum ada peringkat
- VTU LD Lab ManualDokumen5 halamanVTU LD Lab ManualManjesh ShettyBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar (Reversible Logic Circuit) Indranil NandyDokumen50 halamanSeminar (Reversible Logic Circuit) Indranil NandyIndranil Nandy100% (7)
- Lab 3 - Logisim Sequence CircuitDokumen37 halamanLab 3 - Logisim Sequence CircuitMinh Nhật TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- csc213 AssignmentDokumen8 halamancsc213 Assignmentstevefocus01Belum ada peringkat
- 4 Gate Level Design of A Digital ClockDokumen7 halaman4 Gate Level Design of A Digital Clocklktee92Belum ada peringkat
- AdrijaRay Maths 4th Sem ReportDokumen12 halamanAdrijaRay Maths 4th Sem ReportAdrija RayBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE Conference OpenPLCDokumen6 halamanIEEE Conference OpenPLCThiago AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- Thippesh (P L C)Dokumen7 halamanThippesh (P L C)Manik KandanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8Dokumen20 halamanLecture 8Mohd Al AsadiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Introduction: CSI161 Introduction To Computing (Lecture 4.2) Digital LogicDokumen37 halamanChapter 1 Introduction: CSI161 Introduction To Computing (Lecture 4.2) Digital LogicOffie MphaleBelum ada peringkat
- Field-Programmable Gatearrays:: Herbert Grünbacher Einer W. Hartenstein (Eds.)Dokumen11 halamanField-Programmable Gatearrays:: Herbert Grünbacher Einer W. Hartenstein (Eds.)PrabakaranBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome - Based EducationDokumen26 halamanElectronics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome - Based EducationRachel Yam 3nidad100% (1)
- Robo 2Dokumen4 halamanRobo 2Fernando PlazaBelum ada peringkat
- Boolean Algebra and Digital LogicDokumen15 halamanBoolean Algebra and Digital LogicCarlo TenorioBelum ada peringkat
- Combinational Logic Circuit PDFDokumen2 halamanCombinational Logic Circuit PDFChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Verilog Implementation of Reversible Logic GateDokumen7 halamanVerilog Implementation of Reversible Logic GateDhamini GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Geethanjali College of Engineering and TechnologyDokumen2 halamanGeethanjali College of Engineering and TechnologySuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Lump Pot 76 OhmDokumen3 halamanLump Pot 76 OhmSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Wharton1972 PDFDokumen4 halamanWharton1972 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Smith Chart From Black Magic DesignDokumen1 halamanSmith Chart From Black Magic DesignkgrhoadsBelum ada peringkat
- How Does A Smith Chart Work?Dokumen12 halamanHow Does A Smith Chart Work?ani18100% (5)
- Analysis and Design Principles of Microwave Antennas: Instructor Name: Amitabha Bhattacharya Institute: IIT KharagpurDokumen2 halamanAnalysis and Design Principles of Microwave Antennas: Instructor Name: Amitabha Bhattacharya Institute: IIT KharagpurSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDokumen3 halamanAntennas and Wave PropagationArockia RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetics Field Theory 69 Important MCQDokumen12 halamanElectromagnetics Field Theory 69 Important MCQANIL SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Performance Analysis of 41 Corporate Feed Circular Polarized Rectangular Micro Strip Patch Antenna Using Hfss IJERTV3IS090767 PDFDokumen6 halamanDesign and Performance Analysis of 41 Corporate Feed Circular Polarized Rectangular Micro Strip Patch Antenna Using Hfss IJERTV3IS090767 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- The Study of A New Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna PDFDokumen4 halamanThe Study of A New Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Plane Waves Part I - 2 PDFDokumen13 halamanPlane Waves Part I - 2 PDFAnkur SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Transmit Measured Data XXX Receive Measured Data Receive No. IDokumen3 halamanTransmit Measured Data XXX Receive Measured Data Receive No. ISuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Impedance Matching Techniques.: Module 2: Transmission Lines Lecture 15: Impedance Matching Using Transmission LineDokumen6 halamanImpedance Matching Techniques.: Module 2: Transmission Lines Lecture 15: Impedance Matching Using Transmission LineAnonymous yz5MQGtBelum ada peringkat
- An Ultra-Broadband 3-dB Power Divider: Fanghai Xu Gaofeng Guo en Li Ju WuDokumen4 halamanAn Ultra-Broadband 3-dB Power Divider: Fanghai Xu Gaofeng Guo en Li Ju WuSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- An Ultra-Broadband 3-dB Power Divider: Fanghai Xu Gaofeng Guo en Li Ju WuDokumen4 halamanAn Ultra-Broadband 3-dB Power Divider: Fanghai Xu Gaofeng Guo en Li Ju WuSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Wharton1972 PDFDokumen4 halamanWharton1972 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- The Study of A New Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna PDFDokumen4 halamanThe Study of A New Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Snpview: Free S-Parameter Web ViewerDokumen14 halamanSnpview: Free S-Parameter Web ViewerSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Yagi Uda Antenna Using HFSS Software.Dokumen10 halamanDesign of Yagi Uda Antenna Using HFSS Software.Suneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Yagi Antenna AnujDokumen25 halamanYagi Antenna AnujclearhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Novel Low Cost 1-To-4 Microstrip Wilkinson Power DividerDokumen4 halamanNovel Low Cost 1-To-4 Microstrip Wilkinson Power DividerSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Propagation GateDokumen12 halamanWave Propagation GateSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Wharton1972 PDFDokumen4 halamanWharton1972 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- FM Transmission and Reception Rider 1949 PDFDokumen402 halamanFM Transmission and Reception Rider 1949 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Learn Sanskrit - Lesson 5Dokumen16 halamanLearn Sanskrit - Lesson 5Swanand Raikar100% (1)
- Basics of Vedic AstrologyDokumen18 halamanBasics of Vedic Astrologyclaudiota100% (1)
- Lump Pot 76 OhmDokumen3 halamanLump Pot 76 OhmSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Newman1985 PDFDokumen7 halamanNewman1985 PDFSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Vedic AstrologyDokumen18 halamanBasics of Vedic Astrologyclaudiota100% (1)
- Hfss ProjectsDokumen7 halamanHfss ProjectsSuneelkrishna RallabhandiBelum ada peringkat
- Semantics of Programming Languages: Lecture Notes OnDokumen97 halamanSemantics of Programming Languages: Lecture Notes OnciucchiBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Assig 2021Dokumen41 halamanLab Assig 2021Rafshan ImbisaatBelum ada peringkat
- Recursion: Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1/25Dokumen25 halamanRecursion: Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 1/25Tryer0% (1)
- PPL Lab ManualDokumen12 halamanPPL Lab ManualRaghu Vamsi PotukuchiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes in Discrete MathematicsDokumen220 halamanLecture Notes in Discrete Mathematicsjpaulino100% (4)
- (Ernest, Paul) The Philosophy of Mathematics Educa (BookFi)Dokumen344 halaman(Ernest, Paul) The Philosophy of Mathematics Educa (BookFi)Aisyah AdelinaBelum ada peringkat
- CDDokumen8 halamanCDPrasad BobyBelum ada peringkat
- Symbolic Logic 1Dokumen22 halamanSymbolic Logic 1Malik Shahzeb KhanBelum ada peringkat
- MATH UNIT 2 GRADE 3 LESSON 29 Sinugbuanong BinisayaDokumen74 halamanMATH UNIT 2 GRADE 3 LESSON 29 Sinugbuanong BinisayaLucrecia Tanoy100% (6)
- Law of Excluded Middle - WikipediaDokumen46 halamanLaw of Excluded Middle - WikipediaJayaveni JayaveniBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of AutomataDokumen22 halamanTheory of AutomataFatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Ai 2markDokumen15 halamanAi 2markrcgramBelum ada peringkat
- CFGDokumen58 halamanCFGAkshat SapraBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing The Random-Walk Algorithm For SAT: Helsinki University of TechnologyDokumen54 halamanAnalyzing The Random-Walk Algorithm For SAT: Helsinki University of TechnologypradeepdeceBelum ada peringkat
- Final Computer ProjectDokumen106 halamanFinal Computer ProjectJayesh TalrejaBelum ada peringkat
- TeachingPlan TheoryOfAutomata Fall 2020 DR Raheel 11102020 052419pmDokumen7 halamanTeachingPlan TheoryOfAutomata Fall 2020 DR Raheel 11102020 052419pmMohammad BilalBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Data Types in PythonDokumen18 halamanStandard Data Types in Pythonnitesh guptaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 08Dokumen31 halamanCH 08Kenny AdeBelum ada peringkat
- LP Assignment Report: Group 9 Akshit Sood Kartik Saboo Kshitij Madan Saurabh KhemukaDokumen9 halamanLP Assignment Report: Group 9 Akshit Sood Kartik Saboo Kshitij Madan Saurabh KhemukaAkshit SoodBelum ada peringkat
- GPPGDokumen56 halamanGPPGf1125706Belum ada peringkat
- Unit1Exam AnswersDokumen9 halamanUnit1Exam Answersfancy_maskBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Automata Chapter 4Dokumen24 halamanTheory of Automata Chapter 4Umer Asfandyar BalghariBelum ada peringkat
- Functional DependencyDokumen58 halamanFunctional DependencyKrishna VaitinadinBelum ada peringkat
- SDL Lab+Manual+2008+CourseDokumen59 halamanSDL Lab+Manual+2008+CourseArunKumar MogaparthiBelum ada peringkat
- DM PDFDokumen11 halamanDM PDFSumanth Ashwin ChowdariBelum ada peringkat
- CS8501 2marks Q ADokumen19 halamanCS8501 2marks Q AjayashreeBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Higher Education Add Maths Marking SchemeDokumen3 halamanSPM Higher Education Add Maths Marking SchemeChinWynn.comBelum ada peringkat
- Regular Expressions: Regular Expressions Are A Powerful Tool For Various Kinds of String ManipulationDokumen4 halamanRegular Expressions: Regular Expressions Are A Powerful Tool For Various Kinds of String ManipulationArya BhattBelum ada peringkat
- CFG SolutionsDokumen5 halamanCFG SolutionsJohn Le TourneuxBelum ada peringkat
- MCDokumen5 halamanMCnguyentruonghaiBelum ada peringkat
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDari EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and SciencePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDari EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDari EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniversePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDari EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1395)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Machinery of the Mind (An Interview)Dari EverandMachinery of the Mind (An Interview)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (28)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (410)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDari EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (20)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Higgs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceDari EverandHiggs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpacePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (30)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDari EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (60)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDari EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (49)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDari EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (54)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseDari EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniversePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (126)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (76)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDari EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (94)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxDari EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (27)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDari EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (500)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDari EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Mastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicDari EverandMastering Logical Fallacies: The Definitive Guide to Flawless Rhetoric and Bulletproof LogicPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (91)