Chapter 5 (Part 3)
Diunggah oleh
simayyilmaz0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan20 halamanHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan20 halamanChapter 5 (Part 3)
Diunggah oleh
simayyilmazHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 20
Chapter 5 (part 3)
Enzyme Kinetics (cont.)
Michaelis-Menton
E + S ES E + P
V
max
K
m
K
cat
K
cat
/K
m
k
1
k
-1
k
cat
Vo = Vmax [S]
Km + [S]
V
max
K
m
k
cat
k
cat
/K
m
How do you get values for V
max
, K
m
and k
cat
?
Can determine K
m
and V
max
experimentally
Km can be determined without an absolutely
pure enzyme
K
cat
values can be determined if V
max
is known
and the absolute concentration of enzyme is
known (V
max
= k
cat
[E
total
]
Lineweaver-Burke Plots
(double reciprocal plots)
Plot 1/[S] vs 1/V
o
L-B equation for straight
line
X-intercept = -1/Km
Y-intercept = 1/Vmax
Easier to extrapolate
values w/ straight line vs
hyperbolic curve
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
V
o
[S]
[S] Vo
0.5 0.075
0.75 0.09
2 0.152
4 0.196
6 0.21
8 0.214
10 0.23
V max
Km
Km ~ 1.3 mM
Vmax ~ 0.25
[S] Vo
2.000 13.333
1.333 11.111
0.500 6.579
0.250 5.102
0.167 4.762
0.125 4.673
0.100 4.348
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B 0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2
V
o
[S]
-1/Km = -0.8
Km = 1.23 mM
1/Vmax = 4.0
Vmax = 0.25
Enzyme Inhibition
Inhibitor substance that binds to an enzyme and interferes
with its activity
Can prevent formation of ES complex or prevent ES
breakdown to E + P.
Irreversible and Reversible Inhibitors
Irreversible inhibitor binds to enzyme through covalent
bonds (binds irreversibly)
Reversible Inhibitors bind through non-covalent interactions
(disassociates from enzyme)
Why important?
Reversible Inhibitors
E + S <-> ES -> E + P
E + I <-> EI
Ki = [E][I]/[EI]
Competitive
Uncompetitive
Non-competitive
Types of Reversible Enzyme
Inhibitors
Competitive Inhibitor (CI)
CI binds free enzyme
Competes with substrate for enzyme binding.
Raises Km without effecting Vmax
Can relieve inhibition with more S
Competitive Inhibitors look like substrate
NH
2
C
O
HO
NH
2
S
O
H2N
O
Sulfanilamide PABA
PABA precursor to folic acid in bacteria
O
2
C-CH
2
-CH
2
-CO
2
-------> O
2
C-CH=CH-CO
2
succinate fumarate
Succinate dehydrogenase
O
2
C-CH
2
-CO
2
Malonate
Uncompetitive Inhibitor (UI)
UI binds ES complex
Prevents ES from proceeding to E + P or back to E + S.
Lowers Km & Vmax, but ratio of Km/Vmax remains the
same
Occurs with multisubstrate enzymes
Non-competitive Inhibitor (NI)
NI can bind free E or ES complex
Lowers Vmax, but Km remains the same
NIs dont bind to S binding site therefore dont effect
Km
Alters conformation of enzyme to effect catalysis but not
substrate binding
Irreversible Inhibitors
H
3
C O P
O
S C
C
H
O
O CH
2
CH
3
C
O CH
2
CH
3
O
S
CH
3
CH
2
H C
CH
3
O
CH
3
P
F
O
O
C
CH
3
H
CH
3
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate
(nerve gas)
H
3
C O P
O
S
S
CH
3
NO
2
Organophosphates
Inhibit serine hydrolases
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
parathion
malathion
Viagra
Kinetics of Multisubstrate
Reactions
E + A + B <-> E + P + Q
Sequential Reactions
a) ordered
b) random
Ping-pong Reactions
Cleland Notation
Sequential Reactions
E EA (EAB) (EPQ) EQ E
A B P Q
A B
P Q
A B
E
EA
EB
(EAB)(EPQ)
P
Q
EQ
EP
E
Random
Ordered
Ping-Pong Reactions
E (EA)(FP) (F) (FB)(EQ) E
A B P Q
In Ping-Pong rxns first product released before
second substrate binds
When E binds A, E changes to F
When F binds B, F changes back to E
Lineweaver-Burke Plot of
Multisubstrate Reactions
Increasing
[B]
Increasing
[B]
Sequential Ping-Pong
1/Vo
1/[S]
1/Vo
1/[S]
Vmax doesnt change
Km changes
Both Vmax & Km change
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Buffer, Integrator, and Differentiator Op AmpsDokumen24 halamanBuffer, Integrator, and Differentiator Op AmpssimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Bchm2000 L8Dokumen24 halamanBchm2000 L8simayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- 4week Chapter 2Dokumen12 halaman4week Chapter 2simayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Microelectronic Circuits I: CH 2: Operational AmplifiersDokumen15 halamanMicroelectronic Circuits I: CH 2: Operational AmplifierssimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Notes Solutions Chapter 05 LargeDokumen127 halamanNotes Solutions Chapter 05 LargesimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Unified and Distributed Qos-Driven Cell Association Algorithms in Heterogeneous NetworksDokumen12 halamanUnified and Distributed Qos-Driven Cell Association Algorithms in Heterogeneous NetworkssimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- CH 3 DatalinkDokumen35 halamanCH 3 DatalinksimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Notes Solutions Chapter 05 LargeDokumen127 halamanNotes Solutions Chapter 05 LargesimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- STR 912 FaDokumen78 halamanSTR 912 FasimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Calculating Net Protein ChargeDokumen7 halamanCalculating Net Protein ChargesimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 (Part 2) : Protein Purification and AnalysisDokumen17 halamanChapter 3 (Part 2) : Protein Purification and AnalysissimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- 2-Dieu Che Tuong TuDokumen136 halaman2-Dieu Che Tuong TuAnhTưBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Ad Hoc Networks - RoutingDokumen8 halamanAd Hoc Networks - RoutingsimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rini Final PosterDokumen1 halamanRini Final PostersimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- ManetDokumen106 halamanManetarulrajiv1Belum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Chap3 Prob 1Dokumen10 halamanChap3 Prob 1simayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Fourier SeriesDokumen74 halamanFourier SeriesBurhan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Rini Final PosterDokumen1 halamanRini Final PostersimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Adhoc WirelessDokumen23 halamanAdhoc WirelessJyothi PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Introduction WCNDokumen30 halamanIntroduction WCNShaami AtmBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Chapter4 PDFDokumen36 halamanChapter4 PDFsimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- MIT16 36s09 Lec06 PDFDokumen15 halamanMIT16 36s09 Lec06 PDFsimayyilmazBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Determinants: 2.1 Determinants by Cofactor ExpansionDokumen23 halamanChapter 2: Determinants: 2.1 Determinants by Cofactor Expansionsimayyilmaz100% (1)
- TilesDokumen84 halamanTilesgagan raoBelum ada peringkat
- 1.principles of Chemistry, E. ElectrolysisDokumen7 halaman1.principles of Chemistry, E. ElectrolysisDr.AndrewMatovuBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Investigation of Organic CompundsDokumen6 halamanComparative Investigation of Organic CompundsKizer Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Experimental Lab Report 2Dokumen11 halamanExperimental Lab Report 2api-307749075Belum ada peringkat
- Effect of Heat Treatment On Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviours of 18ni-300 Maraging Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser MeltingDokumen11 halamanEffect of Heat Treatment On Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviours of 18ni-300 Maraging Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser MeltingHasan TaşBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Drilling Fluid Technology: Performances and Environmental ConsiderationsDokumen32 halamanDrilling Fluid Technology: Performances and Environmental ConsiderationsAli EttehadiBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Induced AccelerationDokumen6 halamanWave Induced AccelerationAnonymous g5FCwMRBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrochemical Trace Analysis FOR Metals and Metalloids: Wilson & Wilson's Comprehensive Analytical ChemistryDokumen13 halamanSpectrochemical Trace Analysis FOR Metals and Metalloids: Wilson & Wilson's Comprehensive Analytical ChemistryPedroLHernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyDokumen8 halamanLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- Design of Portal Frames - NotesDokumen32 halamanDesign of Portal Frames - NotesAdi Andriescu0% (1)
- CTO FullDokumen98 halamanCTO FullRamesh Babu100% (1)
- 120:360 - Biochemistry Fall 2015 Sample Questions For Exam 1Dokumen5 halaman120:360 - Biochemistry Fall 2015 Sample Questions For Exam 1BluedevBelum ada peringkat
- Asme SB466Dokumen9 halamanAsme SB466Stéphane LevasseurBelum ada peringkat
- ISA - 75.01.01.2012 - Flow Capacity - Sizing Equations For Fluid FlowDokumen70 halamanISA - 75.01.01.2012 - Flow Capacity - Sizing Equations For Fluid FlowCarlos Ramos100% (1)
- TPXData SheetDokumen4 halamanTPXData Sheetrameshkarthik810Belum ada peringkat
- Philippine National StandardsDokumen30 halamanPhilippine National StandardsJonathan Pascua CamachoBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Protein MaterialDokumen61 halamanProtein MaterialAlyssa NesianandaBelum ada peringkat
- Reactive DyesDokumen24 halamanReactive DyesrehanabbaciBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Brick - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen2 halamanFire Brick - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediareaktorenergiBelum ada peringkat
- Yeast Pop. LabDokumen3 halamanYeast Pop. Labtanu96tp5952Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal Expansion Settings in GleebleDokumen4 halamanThermal Expansion Settings in GleeblePranav TripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Materials: Mechanism in MetalsDokumen38 halamanEngineering Materials: Mechanism in Metalssamurai7_77Belum ada peringkat
- Chromatographyvolume 1Dokumen99 halamanChromatographyvolume 1JOSE R. LEALBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Casting Procedures For Fixed Partial DentureDokumen76 halaman3 - Casting Procedures For Fixed Partial Dentureyabhatia100% (1)
- Carbon Carbon CompositeDokumen22 halamanCarbon Carbon Compositeyogeshkmr01100% (1)
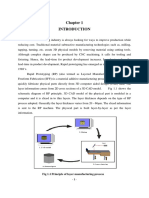
- Fig 1.1 Principle of Layer Manufacturing ProcessDokumen39 halamanFig 1.1 Principle of Layer Manufacturing ProcessgauravBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Precipitation + Solid-Aqueous EquilibriaDokumen26 halamanMetal Precipitation + Solid-Aqueous EquilibriaDotan NutodBelum ada peringkat
- Exp-Function Method For Nonlinear Wave Equations: Ji-Huan He, Xu-Hong WuDokumen9 halamanExp-Function Method For Nonlinear Wave Equations: Ji-Huan He, Xu-Hong Wufalcon_vamBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1-DMC 101-Basic ConceptsDokumen11 halamanChapter 1-DMC 101-Basic ConceptsArivalagan RevichandranBelum ada peringkat
- Characterization of Iron Oxide Thin Film Prepared by The Sol-Gel MethodDokumen2 halamanCharacterization of Iron Oxide Thin Film Prepared by The Sol-Gel MethodBryan Anders AguilarBelum ada peringkat