Treatment of Hypertension: Antihypertensive Agents
Diunggah oleh
Hanif Gandoh0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan4 halamantable of hypelipidimia drugs
Judul Asli
Tables
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Initable of hypelipidimia drugs
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan4 halamanTreatment of Hypertension: Antihypertensive Agents
Diunggah oleh
Hanif Gandohtable of hypelipidimia drugs
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
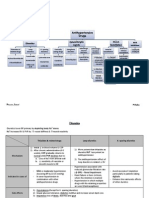
Treatment of Hypertension
Diuretics e.g. hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide
M.O.A cause sodium and water loss decrease blood volume decrease C.O lower B.P
Uses Mild to moderate hyper tension
Antihypertensive Agents
Diuretics ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin
Receptor
blockers
Ca channel
blockers
Vasodilators
Drugs acting on
sympathetic
system
ACE inhibitors e.g. captopril, enalapril, ramipril
M.O.A Vasodilatation by
- Inhibiting ACE
- Inactivating Bradyknin
- aldosterone production
Pharmacokinetics - GIT absorption after oral dose
- Prodrugs converted to active metabolite in liver (Enalaprilat is the active metabolite of enalapril given by I.V in ER)
- Long t1/2 (given once daily)
Uses - Renovascular hypertension (hypertension results from excess rennin production)
- hypertension in patients with chronic renal disease, ischemic heart disease, diabetes
- heart failure
Adverse effects - Acute renal failure (patient with renal artery stenosis)
- Hyperkalemia (patient with renal insufficiency or diabetes)
- Severe hypotension (hypovolemic patients)
- Dry cough, wheezing, Angioneurotic edema in nose, throat, tongue and larynx
(caused by inhibition of bradykinin metabolism, which accumulate in bronchial mucosa)
- Dysgeusia, skin rash, fever, Proteinuria, neutropenia (just in Captopril because it contains sulfhydryl grp.)
Contraindication - During the second and third trimesters of pregnancy
- Renal artery stenosis
Drug interaction - potassium-sparing diuretics
- NSAIDs (impair their hypotensive effects by blocking bradykinin-mediated vasodilatation)
Angiotensin receptor blockers e.g. Losartan, Valsartan
M.O.A - Selective block of AT1 receptors (no effects on Bradykinin)
- complete inhibition of angiotensin (they inhibit the process from the beginning)
Pharmacokinetics - Orally
- Long t1/2 (given once daily)
- Losartan is a potent active metabolite
- Valsartan doesnt have an active metabolite
- Dont cross BBB
Uses As ACEI
Adverse Effects AS ACEI except:
- Dry cough, wheezing, Angioneurotic edema (they dont affect Bradykinin metabolism)
Ca
channel blockers Dihydropyridine group
(Nifedipine, Nicardipine)
Verapamil Diltiazem
Main effects act mainly on smooth muscle and used as
vasodilators
act more on the myocardium and used
as antiarrhythmic drug
intermediate effect
M.O.A Block Ca influx resulting into: - Peripheral vasodilatation
- Decrease cardiac contractility
Pharmacokinetics - Orally (1/2 to 2hrs onset of action) and I.V.(1-3min onset of action)
- Absorbed in GIT
- Highly bound to plasma proteins (nifedipine and Verapamil >90%) , (Diltiazem <70-80%)
- verapamil and diltiazem have active metabolites
- nifedipine doesnt have active metabolites
Uses - Treatment of chronic hypertension with oral preparation
- I.V. Nicardipine used in hypertensive emergency
Adverse Effects - Headache , Flushing , Hypotension
- Peripheral edema (ankle edema)
- Tachycardia
- Headache , Flushing , Hypotension
- Peripheral edema (ankle edema)
- Bradycardia (Cardiac depression A-V
block)
- Constipation
- Headache , Flushing , Hypotension
- Peripheral edema (ankle edema)
- Bradycardia (Cardiac depression
A-V block)
Vasodilators Hdralazine Minoxidil Diazoxide Sodium nitropruside
Site of action
Arteriodilator Arteriodilator Arteriodilator Arterio & venodilator
M.O.A Direct Opening of K channels in
smooth ms. membranes by
minoxidil sulfate
(active metabolite)
Opening of K channels
Release of nitric oxide ( NO)
Route of admin.
Oral Oral Rapid intravenous
Intravenous infusion
Uses 1.Moderate -severe hypertension
(In combination with diuretic &
-blockers)
2.Hypertensive pregnant woman
1.Moderate -severe
hypertension
(In combination with diuretic &
-blockers)
2. baldness
1.Hypertensive emergency
(In combination with diuretic &
-blockers)
2. Hypoglycemia due to
insulinoma
1.Hypertensive emergency
(In combination with diuretic &
-blockers)
2.Severe heart failure
Adverse Effects Hypotension, reflex tachycardia, palpitation, angina, salt and water retention ( edema)
Severe hypotension
*more in original slides*
Specific adverse
effects
- lupus erythematosus like
syndrome
- Hypertrichosis
(excessive growth of hair)
*Contraindicated in females
- Inhibit insulin release from
cells of the pancreas causing
hyperglycemia
*Contraindicated in diabetics
- Methemoglobin during
infusion
- Cyanide toxicity
- Thiocyanate toxicity
Drugs acting on
sympathetic system
-blockers -blockers Centrally Acting Adrenergic Drugs
2 agonist
e.g. Propranolol, atenolol prazosin Clonidine - methyl dopa
M.O.A They lower blood pressure by :
- decreasing C.O.
- inhibiting the release of renin
- Block - receptors in
arterioles and venules
- Decrease both afterload
& preload
- diminishes central
adrenergic outflow
- doesnt decrease renal
blood flow
- converted to methyl NE
centrally to diminish the
adrenergic outflow
- Decrease peripheral
resistance
Uses - mild to moderate
hypertension.
- In severe cases used in
combination with other drugs
- hypertension
complicated by renal
disease
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Medico Legal Aspects of DeathDokumen206 halamanMedico Legal Aspects of Deathrosana f.rodriguez83% (12)
- Antihypertensive Agents GuideDokumen3 halamanAntihypertensive Agents GuideCharles BayogBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac MedicationsDokumen9 halamanCardiac Medicationsnovikane100% (1)
- Muscular System WebquestDokumen7 halamanMuscular System WebquestJxcari50% (2)
- Principles of Occlusion: Key TermsDokumen35 halamanPrinciples of Occlusion: Key TermsStef AleBelum ada peringkat
- BugSpeaks Sample ReportDokumen27 halamanBugSpeaks Sample ReportAnonymous 76wOMTpBelum ada peringkat
- ABX Pentra 60-C Plus Analyzer - Service ManualDokumen314 halamanABX Pentra 60-C Plus Analyzer - Service ManualJose Rolando Orellana Rodriguez100% (2)
- The Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomyDokumen18 halamanThe Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomymeseniaBelum ada peringkat
- 10-11 Treatment of HypertensionDokumen11 halaman10-11 Treatment of HypertensionHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiotonic DrugsDokumen67 halamanCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDokumen61 halamanCardiovascular PharmacologyTeeOne920% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyDokumen24 halamanPharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyshyamkattiBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Hypertensive 20191211Dokumen35 halamanAnti Hypertensive 20191211helloitsmenadBelum ada peringkat
- Ishac M2 Cardio Antihypertensives 2010Dokumen16 halamanIshac M2 Cardio Antihypertensives 2010Franchesca LugoBelum ada peringkat
- Angina Pharmacology YeahDokumen16 halamanAngina Pharmacology YeahMuhammad AfifuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive Drugs.Dokumen35 halamanAntihypertensive Drugs.Abdul WahabBelum ada peringkat
- A.10. What Is The Mechanism of Action of Antihypertensive Drugs?Dokumen2 halamanA.10. What Is The Mechanism of Action of Antihypertensive Drugs?Albert Tesoro Silang Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- ACE InhibitorsDokumen26 halamanACE Inhibitorsali mohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive Agents 2ndDokumen40 halamanAntihypertensive Agents 2ndalikhan52612Belum ada peringkat
- 6.1. AntihipertensiDokumen52 halaman6.1. AntihipertensiDada DoniBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive DrugsDokumen7 halamanAntihypertensive Drugshamadadodo7Belum ada peringkat
- Congestive Heart Failure: CardiacDokumen36 halamanCongestive Heart Failure: CardiacHUZAIFA YAMAANBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology 3 - Management of Heart FailureDokumen59 halamanPharmacology 3 - Management of Heart Failurealbatros000Belum ada peringkat
- Study Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionDokumen39 halamanStudy Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionAlejandro Daniel Landa MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- CVD and HTNDokumen60 halamanCVD and HTNZsazsa100% (1)
- CVS PharmacologyDokumen60 halamanCVS PharmacologyGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 24-25 - Antihypertensive AgentsDokumen30 halamanLecture 24-25 - Antihypertensive AgentsJedoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio Lab MedsDokumen11 halamanCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesBelum ada peringkat
- HypertensionDokumen54 halamanHypertensionBadri KarkiBelum ada peringkat
- Meds #1 NotesDokumen4 halamanMeds #1 NotesAnh TrinhBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive Drugs ٠١١٦٥٨Dokumen10 halamanAntihypertensive Drugs ٠١١٦٥٨mohnad806mBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 antihypertensionSDSDokumen7 halamanLecture 1 antihypertensionSDSSara AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Farma - Antihipertensi Farmako NewDokumen18 halamanFarma - Antihipertensi Farmako NewLucky Arie SandiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDokumen175 halamanCardiovascular Pharmacologyaditi singhBelum ada peringkat
- HypertensionDokumen85 halamanHypertensionmelkamu AssefaBelum ada peringkat
- Semester 2 Drug ListDokumen7 halamanSemester 2 Drug ListNam_Pham_6481Belum ada peringkat
- Hypertension: Increase in Blood PressureDokumen29 halamanHypertension: Increase in Blood PressureKeesha Mae AnteBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Anginal Drugs ExplainedDokumen19 halamanAnti-Anginal Drugs ExplainedAnusha ZubairBelum ada peringkat
- Dept .Pharmacology and Toxicology COVAS, ParbhaniDokumen32 halamanDept .Pharmacology and Toxicology COVAS, ParbhanidahiphalehBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbaruDokumen45 halamanPharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbarulisaBelum ada peringkat
- Meds For HypertensionDokumen3 halamanMeds For HypertensionZonicsBelum ada peringkat
- CHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart FailureDokumen21 halamanCHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart Failuremohsen mirdamadiBelum ada peringkat
- Anti AnginaDokumen5 halamanAnti Anginalandita683Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Antihypertensive DrugsDokumen14 halaman1 Antihypertensive DrugsReda SoBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive & Antianginal DrugsDokumen5 halamanAntihypertensive & Antianginal Drugsdomememe1Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DDokumen40 halamanCardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DJose LunaBelum ada peringkat
- ANTIHIPERTENSI: Regulasi Tekanan Darah dan Terapi HipertensiDokumen36 halamanANTIHIPERTENSI: Regulasi Tekanan Darah dan Terapi HipertensiWulan Ulan DariBelum ada peringkat
- Anoosha Roll#21Dokumen19 halamanAnoosha Roll#21Anusha ZubairBelum ada peringkat
- Inhibitors of AngiotensinDokumen37 halamanInhibitors of AngiotensinBoyu GrtrBelum ada peringkat
- ANTI HYPERTENSIVE DRUGSDokumen7 halamanANTI HYPERTENSIVE DRUGSGabriella ChafrinaBelum ada peringkat
- 7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsDokumen10 halaman7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsHusniya MehamedBelum ada peringkat
- HTN JmiDokumen39 halamanHTN Jmink999999Belum ada peringkat
- Heart Talk (Ii) in Pandemic Of: COVID-19Dokumen27 halamanHeart Talk (Ii) in Pandemic Of: COVID-19Alles FirmansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 Study Guide PharmacologyDokumen23 halamanExam 3 Study Guide PharmacologymmonsonfBelum ada peringkat
- Vasodilators by Hiren PatelDokumen28 halamanVasodilators by Hiren PatelHiren_Patel_2427Belum ada peringkat
- 8D - HypertensionDokumen58 halaman8D - Hypertensionmashe1Belum ada peringkat
- CVPR Prototype Drugs TableDokumen27 halamanCVPR Prototype Drugs TablethommyvaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Dokumen163 halamanPharmacotherapy of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Aditya rathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs ClassificationDokumen24 halamanDrugs ClassificationManda HoBelum ada peringkat
- HP 200704 Pharmacological PDFDokumen5 halamanHP 200704 Pharmacological PDFIndira Damar PangestuBelum ada peringkat
- Pcol Lab MidtermDokumen26 halamanPcol Lab MidtermJoshua AysonBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Drugs For HypertensionDokumen62 halaman1 Drugs For HypertensionSaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation SyndromeDokumen3 halamanOvarian Hyperstimulation SyndromeHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- ImpetigoDokumen21 halamanImpetigoHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- GOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVDokumen53 halamanGOLD 2020 POCKET GUIDE Ver1.0 - FINAL WMVRupesh MohandasBelum ada peringkat
- Engaging Adolescent-Headss FrameworkDokumen28 halamanEngaging Adolescent-Headss FrameworkHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis HanifDokumen24 halamanPulmonary Tuberculosis HanifHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Case Discussion on Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDokumen43 halamanClinical Case Discussion on Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Ectopic Pregnancy OSCEDokumen4 halamanEctopic Pregnancy OSCEPatrick BayuBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormarlities On Physical Examination in A Patient With HepatosplenomegalyDokumen7 halamanAbnormarlities On Physical Examination in A Patient With HepatosplenomegalyHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Contraception - Updates: Mr. Wu Pin Ms. Nur SakinahDokumen66 halamanContraception - Updates: Mr. Wu Pin Ms. Nur SakinahHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation of Muscle WeaknessDokumen6 halamanInvestigation of Muscle WeaknessHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- OG Short CasesDokumen33 halamanOG Short CasesHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Benign and Malignant TumourDokumen5 halamanDifferences Between Benign and Malignant TumourHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- CCD InfertilityDokumen26 halamanCCD InfertilityHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- CCD - Ectopic Pregnancy HafyzDokumen29 halamanCCD - Ectopic Pregnancy HafyzHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- RETROPHARYNGEAL INFECTION CAUSES AND TREATMENTDokumen8 halamanRETROPHARYNGEAL INFECTION CAUSES AND TREATMENTHanif Gandoh100% (1)
- CF Obstructive UropathyDokumen1 halamanCF Obstructive UropathyHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- BurnsDokumen9 halamanBurnsHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Health Information SystemsDokumen18 halamanHealth Information SystemsHanif Gandoh100% (2)
- Commed OSCE Tutorial For Dummies 2Dokumen7 halamanCommed OSCE Tutorial For Dummies 2Hanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- COLD CHAIN & VaccinationDokumen40 halamanCOLD CHAIN & VaccinationHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- FEVER HanifDokumen3 halamanFEVER HanifHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- NASA's Flying Laboratory Studies Impact of Air Pollution 2008on ArcticDokumen41 halamanNASA's Flying Laboratory Studies Impact of Air Pollution 2008on ArcticHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Table 1.23123Dokumen8 halamanMicrobiology Table 1.23123Hanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsDokumen31 halamanIntroduction To Beta Lactam AntibioticsVishaal BhatBelum ada peringkat
- PBL Peptic UlcerDokumen1 halamanPBL Peptic UlcerHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Rhytmn AbnormalitiesDokumen13 halamanCardiac Rhytmn AbnormalitiesHanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- Mock1 8thmarch CompDokumen36 halamanMock1 8thmarch Compdr_zafarBelum ada peringkat
- Diuretics Table (Pharma)Dokumen4 halamanDiuretics Table (Pharma)Hanif GandohBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Biology 2015 Paper 21Dokumen20 halamanIGCSE Biology 2015 Paper 21VeronicaAndrianBelum ada peringkat
- B.sc. Biotechnology - CcssDokumen61 halamanB.sc. Biotechnology - CcsssreyasbkBelum ada peringkat
- School: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Dokumen3 halamanSchool: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Jonalvin KEBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Meningitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen49 halamanUnderstanding Meningitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDrAbhilash RMBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanDokumen283 halamanClinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanAyman Yakout100% (4)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsDokumen81 halamanBiyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsAkshay chandrakarBelum ada peringkat
- Life ProcessesDokumen53 halamanLife Processessagar100% (1)
- Seed Maturation Process Explained in DetailDokumen22 halamanSeed Maturation Process Explained in DetailHitsugaya AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 2000 Paper I Marking SchemeDokumen4 halamanBiology 2000 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-2642329075% (4)
- Chapter 3Dokumen2 halamanChapter 3Rachel Marie M. Gania100% (1)
- Traumatic Brain Injury PresentationDokumen14 halamanTraumatic Brain Injury Presentationapi-413607178Belum ada peringkat
- Root Resorption: Challenge To The Endodontist: Acta Scientific Dental SciencesDokumen11 halamanRoot Resorption: Challenge To The Endodontist: Acta Scientific Dental SciencesMuhammadDeniRahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Histology Quiz - Scientific Term (AmCoFam)Dokumen22 halamanOral Histology Quiz - Scientific Term (AmCoFam)AmericanCornerFamily100% (5)
- ACE Biology O'level Book@2021Dokumen213 halamanACE Biology O'level Book@2021DuyBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 - Study GuideDokumen13 halamanCH 3 - Study Guide2688gieBelum ada peringkat
- Diagram Human Heart Kel 1Dokumen3 halamanDiagram Human Heart Kel 1Rahma SafitriBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Signaling Webquest: Part 1: Dropping SignalsDokumen3 halamanCell Signaling Webquest: Part 1: Dropping Signalsa60OBelum ada peringkat
- Funda Vital SignsDokumen63 halamanFunda Vital SignsElia Saph MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal heart sounds explainedDokumen3 halamanAbnormal heart sounds explainedmuhammad azizulhakimBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 The Integumentary SystemDokumen3 halamanUnit 1 The Integumentary SystemSharva BhasinBelum ada peringkat
- Cells and Tissues: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDokumen66 halamanCells and Tissues: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeNishith100% (4)
- Rab AlkesDokumen65 halamanRab AlkesHery Eko PrasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Funnotes VolumeDokumen108 halamanMedical Funnotes VolumeChinBelum ada peringkat
- Trimestral Exam First GradeDokumen3 halamanTrimestral Exam First Gradeemmanuel espinozaBelum ada peringkat