MCC Design for Three Motors Under 40 Characters
Diunggah oleh
Farhan SaadatJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MCC Design for Three Motors Under 40 Characters
Diunggah oleh
Farhan SaadatHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
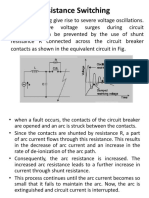
Design of motor control center ( MCC )
Introduction
In this report we will design (mcc) for three motor with different ratings,
First: define motor control center: it contains three parts:
Fuse
Contactor
Over load relay
So we should select ratings of three parts for each motor as shown in fig (1) (which
will design)
Fig (1)
Fuse:
!he construction of fuse as shown in fig (2)
!he main function of these units is to open the
Circuit in which they are inserted "y melting of
Fusi"le elements and to interrupt the current when
It e#ceeds a given value for a sufficient length of time
Finally, it should "e pointed out that fuses protect the motor
$gainst over currents roughly five times greater than motor
%ated current and those they must "e com"ined with additional
&rotection devices
Fuse rating is determined according to:
rated current In'
the Id(In ratio (Id ) starting current)' Fig (2)
Starting time
Thermal overload:
Is widely used on "oth the fractional and integral horsepower manual starters
for protection of motors from sustained electrical over currents that could result from
overloading of the driven machine or from e#cessively low line voltage
Overload protection for an electric motor is necessary to prevent "urnout and to
ensure ma#imum operating life *lectric motors will, if permitted, operate at an output of
more than rated capacity Conditions of motor overload may "e caused "y an overload on
driven machinery, "y low line voltage, e#cessive voltage un"alance, or "y an open line in
a poly phase system, which results in single+phase operation ,nder any condition of
overload, a motor draws e#cessive current that causes overheating Since motor winding
insulation deteriorates when su"-ected to overheating, there are esta"lished limits on
motor operating temperatures
!o protect a motor from overheating, overload relays are employed on a motor
control to limit the amount of current drawn !his is overload protection, or running
protection In situations where the motor must operate in high am"ient temperature
condition, manufacturers have optional higher temperature rated models !he I***
standard 11. esta"lishes a temperature classification for insulation systems' the
temperature classification indicates the ma#imum (hot+spot) temperature at which the
insulation system can "e operated for normal e#pected service life
O"viously, the higher the rating, the higher the cost
!he ideal overload protection for a motor is an element with current+sensing
properties very similar to the heating curve of the motor which would act to open the
motor circuit when full+load current is e#ceeded !he operation of the protective device
should "e such that the motor is allowed to carry harmless over+loads "ut is /uic0ly
removed from the line when an overload has persisted too long as shown in fig (1)
Fig (3)
Contactors:
2agnetic contactors are electromagnetically operated switches that provide a
safe and convenient means for connecting and interrupting "ranch circuits !he principal
difference "etween a contactor and a motor starter is that the contactor does not contain
overload relays Contactors are used in com"ination with pilot control devices to switch
lighting and heating loads and to control $C motors in those cases where overload
protection is provided separately
Some e#amples of contactor in mar0et:
3ow we provide some ta"les a"out ratings of motor, fuses, over load relay4contactor
Table (1)
Table (2)
Some figures on (mcc):
51 &hase, 67(87 9:
52ain is 877 $mp, ;<7 =olt 2a#
59ori:ontal >us: 877, =ertical >us: 877
5Short Circuit %ating: 1? @
5*nclosure: 3ema 1
59as (;) Aestinghouse Si:e 1 Starters with
solid state overloads
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Experiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationDokumen10 halamanExperiment 8 Synchronous Generator Line SynchronizationMd Rodi Bidin100% (1)
- Siemens 3TF ContactorsDokumen15 halamanSiemens 3TF ContactorsDavid tangkelangiBelum ada peringkat
- Testing of RelaysDokumen9 halamanTesting of RelaysAnimesh JainBelum ada peringkat
- Rating of The Circuit BreakersDokumen19 halamanRating of The Circuit BreakersRoopa ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Ductor TestingDokumen4 halamanDuctor Testingmgharrier100% (1)
- Electrical Machines: DC Generator and MotorDokumen114 halamanElectrical Machines: DC Generator and MotorJanardan ShivashankarBelum ada peringkat
- Ac Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?Dokumen13 halamanAc Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?miguel itson100% (1)
- Figure 1 - Motor Control CabinetDokumen6 halamanFigure 1 - Motor Control CabinetJosé Vicente González VivasBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Gear1Dokumen35 halamanSwitch Gear1Subhasish MahapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Relay Testing Flowchart Valence Electrical Training Services PDFDokumen2 halamanDigital Relay Testing Flowchart Valence Electrical Training Services PDFbisas_rishiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 19 - Electrical Single Line DiagramDokumen45 halamanModule 19 - Electrical Single Line DiagramDipayan DasBelum ada peringkat
- LEC # 08 Distribution System Voltage RegulationDokumen61 halamanLEC # 08 Distribution System Voltage RegulationSaddam jatt786Belum ada peringkat
- Eep-Testing and Commissioning of MetalClad SwitchgearDokumen3 halamanEep-Testing and Commissioning of MetalClad Switchgearabdulyunus_amirBelum ada peringkat
- ABB Low Voltage Motor Control Center SpecificationDokumen17 halamanABB Low Voltage Motor Control Center SpecificationSimbu ArasanBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical MachinesDokumen66 halamanElectrical MachinesHrushi KesanBelum ada peringkat
- Schunk Carbon-Brush Brush PressureDokumen8 halamanSchunk Carbon-Brush Brush PressurePrittam Kumar JenaBelum ada peringkat
- TMEIC Industrial Motors Overview Brochure Letter-HiResDokumen12 halamanTMEIC Industrial Motors Overview Brochure Letter-HiResWallerson AbreuBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Selection of Substation EquipmentDokumen40 halamanDesign and Selection of Substation EquipmentHasan AlmatroodBelum ada peringkat
- Practical File of PLC and SCADADokumen17 halamanPractical File of PLC and SCADAvara prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Working Principle of Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)Dokumen4 halamanWorking Principle of Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)Thandayudhapani VeeraputhiranBelum ada peringkat
- MV VFD SpecDokumen17 halamanMV VFD Specronfrend100% (1)
- Voltage Sag PresentationDokumen26 halamanVoltage Sag Presentationpmandwani4687Belum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractDokumen5 halamanExperiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractKkBelum ada peringkat
- Load EqualisationDokumen4 halamanLoad EqualisationLaxmikant BagaleBelum ada peringkat
- MCS IiDokumen1 halamanMCS Iicyyguy3kBelum ada peringkat
- Group 20 presents principles of star-delta motor startingDokumen22 halamanGroup 20 presents principles of star-delta motor startingRiya Priyadarshni80% (5)
- Course Outline: 1. Introduction To WECC 2. Fundamentals of ElectricityDokumen51 halamanCourse Outline: 1. Introduction To WECC 2. Fundamentals of ElectricityWoldemariam WorkuBelum ada peringkat
- Harmonic Treatment in Industrial Power SystemDokumen41 halamanHarmonic Treatment in Industrial Power SystemAmirBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Switchgear and Motor Control Centre GuideDokumen11 halamanElectrical Switchgear and Motor Control Centre GuideAde PramonoBelum ada peringkat
- Allen-Bradley PLC System DocumentationDokumen61 halamanAllen-Bradley PLC System DocumentationMuhammad Zaka100% (2)
- Basics of Motor Control CentersDokumen72 halamanBasics of Motor Control CentersRaihanKhan100% (1)
- Resistance GroundingDokumen4 halamanResistance Groundingjawad_13Belum ada peringkat
- AC Adjustable Speed DriveDokumen5 halamanAC Adjustable Speed DriveVENKATESAN RBelum ada peringkat
- How Does Your Capacitor Work?: PanelsDokumen4 halamanHow Does Your Capacitor Work?: PanelsNavneet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Print Reading TrainingDokumen0 halamanElectrical Print Reading TrainingEddy Fernando Queca CadizBelum ada peringkat
- HIPASE-E 001-AB-310 Application Board ExcitationDokumen3 halamanHIPASE-E 001-AB-310 Application Board ExcitationChi PhamBelum ada peringkat
- Induction Motor TestingDokumen14 halamanInduction Motor Testingrajan100% (3)
- Sabre 3008 WebDokumen70 halamanSabre 3008 Webjchs2880Belum ada peringkat
- 123-145kV GIS CatalogueDokumen8 halaman123-145kV GIS Cataloguembloex100% (1)
- MCB vs MCCB vs ELCB vs RCCB: What's the DifferenceDokumen5 halamanMCB vs MCCB vs ELCB vs RCCB: What's the Differencecurazaq100% (1)
- Siemens STEP Series Basics of Switchboards PDFDokumen60 halamanSiemens STEP Series Basics of Switchboards PDFHussamBelum ada peringkat
- HV SWITCHGEAR CONSTRUCTION AND DRAWING INDEXDokumen28 halamanHV SWITCHGEAR CONSTRUCTION AND DRAWING INDEXmentong100% (2)
- Calculate Size of Contactor, Fuse, C.B, Over Load Relay of DOL StarterDokumen5 halamanCalculate Size of Contactor, Fuse, C.B, Over Load Relay of DOL Startererson1981Belum ada peringkat
- VFD Design GuideDokumen7 halamanVFD Design GuideKhaldoon AlnashiBelum ada peringkat
- Control of MachinesDokumen355 halamanControl of Machineswado11Belum ada peringkat
- Technical Seminar On VFDDokumen17 halamanTechnical Seminar On VFDRadhika Priyadarshini100% (7)
- Working Principle of An AlternatorDokumen31 halamanWorking Principle of An AlternatorDerrick Reyes0% (1)
- Nicc802 Padmount Transformer BrochureDokumen8 halamanNicc802 Padmount Transformer Brochureparas99Belum ada peringkat
- APFC Panel DesigningDokumen16 halamanAPFC Panel Designingyrmn200% (1)
- Switch YardDokumen28 halamanSwitch YardPrashant BajpaiBelum ada peringkat
- DC Machine FundamentalsDokumen13 halamanDC Machine FundamentalsJamesDelmanBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Control CenterDokumen8 halamanMotor Control CenterdinoBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Motor Winding Project ReportDokumen14 halamanElectric Motor Winding Project Reportajaybm1Belum ada peringkat
- Grid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power SystemsDari EverandGrid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power SystemsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- Electromagnetic Foundations of Electrical EngineeringDari EverandElectromagnetic Foundations of Electrical EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Education Commission: Sector H-9, Islamabad Phone: 051-111119432 Fax: 051-111119432 Email: Info - Ana@hec - Gov.pkDokumen3 halamanHigher Education Commission: Sector H-9, Islamabad Phone: 051-111119432 Fax: 051-111119432 Email: Info - Ana@hec - Gov.pkFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Tafsir Al Ikhlas 1Dokumen10 halamanTafsir Al Ikhlas 1yanadewaBelum ada peringkat
- Shahid Mehmood S/O Abdul Rehman Khan Harpalkay: Web Generated BillDokumen1 halamanShahid Mehmood S/O Abdul Rehman Khan Harpalkay: Web Generated BillFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- English Catalougue DhakDokumen66 halamanEnglish Catalougue DhakFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- The PMP Exam: Quick Reference Guide, Sixth Edition (Test Prep Series) The PMP Exam: Quick Reference Guide, Sixth Edition (Test Prep Series)Dokumen1 halamanThe PMP Exam: Quick Reference Guide, Sixth Edition (Test Prep Series) The PMP Exam: Quick Reference Guide, Sixth Edition (Test Prep Series)Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Ali Naqvi 2016 New Updated CVDokumen3 halamanAli Naqvi 2016 New Updated CVFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Practices of the Holy Night of Bara'ahDokumen3 halamanPractices of the Holy Night of Bara'ahFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- 1253 Adeelshah - 14@yahoo - Com ADEEL HAIDERDokumen3 halaman1253 Adeelshah - 14@yahoo - Com ADEEL HAIDERFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- bm9ybWFsdGVzdHJlcG9ydA AspxDokumen3 halamanbm9ybWFsdGVzdHJlcG9ydA AspxFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Application DossierDokumen10 halamanApplication DossierFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Defence Housing Authority Multan Employment Application FormDokumen2 halamanDefence Housing Authority Multan Employment Application FormFarhan Saadat0% (1)
- 26 08 13Dokumen26 halaman26 08 13Shankar PerumalBelum ada peringkat
- 54370Dokumen19 halaman54370Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Agenda of Electrical Qualification and Other Issues at Lahore Meeting (21, 22 July-2016)Dokumen3 halamanAgenda of Electrical Qualification and Other Issues at Lahore Meeting (21, 22 July-2016)Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Gantry Crane ElectricalDokumen46 halamanGantry Crane ElectricalFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- (Luminaries For Street Lighting)Dokumen8 halaman(Luminaries For Street Lighting)Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- 7 8 PDFDokumen1 halaman7 8 PDFFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- (LV Dist. Board)Dokumen6 halaman(LV Dist. Board)Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Site Instruction Regarding Electrical ConduitsDokumen2 halamanSite Instruction Regarding Electrical ConduitsFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- (Standby DG Set& AMF Panel) (Jun-12)Dokumen23 halaman(Standby DG Set& AMF Panel) (Jun-12)Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Install Cable TraysDokumen5 halamanInstall Cable TraysFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Letter Farhan SaadatDokumen1 halamanCover Letter Farhan SaadatFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Tarbela DamDokumen4 halamanTarbela Damadeelkhan4340% (1)
- Deferral of Studies (Freezing) Form: Form Bsc-4 University of Engineering and Technology LahoreDokumen1 halamanDeferral of Studies (Freezing) Form: Form Bsc-4 University of Engineering and Technology LahoreFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- 54370Dokumen19 halaman54370Farhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Generation, Transmission and Distribution Prof. D. P. Kothari Center For Energy Studies Indian Institute of Technology, DelhiDokumen20 halamanPower System Generation, Transmission and Distribution Prof. D. P. Kothari Center For Energy Studies Indian Institute of Technology, DelhiFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- S T NS T N: Parks & Horticulture Authority (PHA) FaisalabadDokumen4 halamanS T NS T N: Parks & Horticulture Authority (PHA) FaisalabadFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- BA GeneralDokumen1 halamanBA GeneralFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- StatisticsDokumen1 halamanStatisticsMuhammad UsamaBelum ada peringkat
- 85 Diagram of Tunnel Boring MachineDokumen1 halaman85 Diagram of Tunnel Boring MachineFarhan SaadatBelum ada peringkat
- DS100-30C Centurion Brush SealsDokumen2 halamanDS100-30C Centurion Brush SealsTanveer AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Rivet Handbook: Blind Rivets GuideDokumen15 halamanRivet Handbook: Blind Rivets GuidenextreaderBelum ada peringkat
- 2600 SeriesDokumen94 halaman2600 SeriesFabio Peres de LimaBelum ada peringkat
- 1000080496-PIB 无负荷状态下齿轮箱噪声Dokumen2 halaman1000080496-PIB 无负荷状态下齿轮箱噪声xlzyydf2015Belum ada peringkat
- Eaton Price List 2017 PDFDokumen13 halamanEaton Price List 2017 PDFAli MuntazirBelum ada peringkat
- 5) MastDokumen24 halaman5) Mastعلي اثمار ناهي سباهيBelum ada peringkat
- 4.heater TreaterDokumen53 halaman4.heater TreaterMohamed Elabbasy100% (1)
- BALLUFF-KT Mechanik Gesamt enDokumen135 halamanBALLUFF-KT Mechanik Gesamt enJarosław Polske ZbawBelum ada peringkat
- Massey-Ferguson-298-Tractor de Llantas-Parts-ManualDokumen22 halamanMassey-Ferguson-298-Tractor de Llantas-Parts-ManualELKIN MAURICIO RAMIREZ PEREZBelum ada peringkat
- Case Ih SM-MaxxumDokumen3.970 halamanCase Ih SM-Maxxumcostelchelariu100% (10)
- Piping FundamentalsDokumen54 halamanPiping FundamentalsAveen100% (1)
- Borehole Geomechanics and Well DesignDokumen6 halamanBorehole Geomechanics and Well DesignMourad B. WassefBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic ABS Specification: I. Product ProfileDokumen12 halamanHydraulic ABS Specification: I. Product ProfileMarlon MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- SME Unit 3Dokumen28 halamanSME Unit 3Shreyas MBelum ada peringkat
- PC130 Part Cat NewDokumen312 halamanPC130 Part Cat NewsatyaBelum ada peringkat
- SantopreneT TPV Extrusion Guide and Technical SolutionsDokumen28 halamanSantopreneT TPV Extrusion Guide and Technical SolutionsAristo OnanBelum ada peringkat
- Impo1 9Dokumen20 halamanImpo1 9mouhcine maouhoubBelum ada peringkat
- C17D5Dokumen3 halamanC17D5nuqBelum ada peringkat
- Parts Manual E45 Compact Excavator: S/N AG3G11001 & Above S/N AHHC11001 & AboveDokumen459 halamanParts Manual E45 Compact Excavator: S/N AG3G11001 & Above S/N AHHC11001 & AboveZawminhtun100% (2)
- Karim Ahmed Fahmy 200330237 Lab 6 Investigation of The Variation in Refrigerator Coefficient of Performance For Various Evaporating TemperaturesDokumen4 halamanKarim Ahmed Fahmy 200330237 Lab 6 Investigation of The Variation in Refrigerator Coefficient of Performance For Various Evaporating TemperaturesKristin OlsonBelum ada peringkat
- No-Nonsense Classical Mechanics - SchwichtenbergDokumen392 halamanNo-Nonsense Classical Mechanics - SchwichtenbergbuddlightbeerlogBelum ada peringkat
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of High Compute Density Data Centers To Assure System Inlet Air SpecificationsDokumen9 halamanComputational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of High Compute Density Data Centers To Assure System Inlet Air SpecificationsalkmindBelum ada peringkat
- Bernoulli S PrincipleDokumen13 halamanBernoulli S PrincipleElla ZainuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Wall Hung Electric BoilerDokumen2 halamanWall Hung Electric BoilerDaxom NavidensBelum ada peringkat
- Workshop 4: Burning Velocity Model For Partially-Premixed CombustionDokumen30 halamanWorkshop 4: Burning Velocity Model For Partially-Premixed CombustionIjaz FazilBelum ada peringkat
- H-Type Instruction ManualDokumen90 halamanH-Type Instruction ManualcraponzelBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen9 halamanPDFchandra sonarBelum ada peringkat
- Aws C7.2-98Dokumen116 halamanAws C7.2-98venkatesh100% (2)
- Design of Water Tank PDFDokumen31 halamanDesign of Water Tank PDFabdulqader100% (2)
- ST1098 Allison Transmission Fluid and Filter Service RecommendationsDokumen6 halamanST1098 Allison Transmission Fluid and Filter Service RecommendationsJohn Gray100% (1)