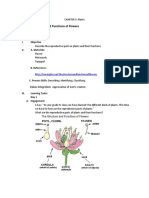
SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry A SBP
Diunggah oleh
allthecrappystuffJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry A SBP
Diunggah oleh
allthecrappystuffHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
BAHAGIAN PENGURUSAN SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH
DAN SEKOLAH KECEMERLANGAN
KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA
CHEMISTRY
TRIAL-EXAM
SPM 2012
MARKING SCHEME
PAPER 1
PAPER 2
PAPER 3
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
2
SKEMA KERTAS 1
PENTAKSIRAN DIAGNOSTIK AKADEMIK
SBP 2012
CHEMISTRY 4541/1
1 A 26 C
2 A 27 D
3 C 28 C
4 A 29 D
5 A 30 B
6 D 31 B
7 B 32 C
8 A 33 A
9 B 34 C
10 A 35 C
11 B 36 D
12 A 37 A
13 D 38 B
14 C 39 B
15 D 40 D
16 A 41 D
17 B 42 D
18 D 43 A
19 C 44 B
20 B 45 C
21 C 46 B
22 D 47 C
23 D 48 B
24 B 49 D
25 A 50 C
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
3
MARKING SCHEME
CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 SECTION A (4541/2)
Question Mark scheme Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
1(a) A: Detergents
B: Soap
r : sodium salt
1
1
2
1(b)(i) magnesium ion // or calcium ion
r : Mg
2+
, Ca
2+
1
2
1(b)(ii) Soaps are biodegradable 1
1(c) Analgesics
Psychotherapeutic
r: wrong spelling
1
1
2
1(d)(i) Sugar
Aspartame
1
1
3
1(d)(ii) To add / restore the colour of food // To enhance its visual
appeal / appearance// more attractive
1
TOTAL 9
Question Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
2(a)(i)
Magnesium
r:Mg
1
2
2(a)(ii) Has 3 shell occupied with electrons 1
2 (b)
1. Proton number of chlorine is higher than magnesium // the
number of proton of chlorine atom higher than magnesium atom
// total positive charged in nucleus higher than magnesium
2. The attractive force between the nucleus and the electrons in
chlorine atom stronger than magnesium atom // nuclei attraction
towards electrons stronger.
1
1
2
2(c) Light bulb // in welding process 1 1
2 (d) Argon 1 1
2(e)(i)
3 Cl
2 (g)
+ 2 Fe
(s)
2 FeCl
3(s)
1
1
2(e)(ii) Mass iron (III) chloride = 0.05 x 161 // 8.05 g 1 1
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
4
2(e)(ii)
1
1
Total 9
Question Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
3(a)(i) 6 1
4
3(a)(ii) To estimate the age of fossils and artifacts 1
3(a)(iii) C-12 // C-13
1
3(a)(iv) 7 / 6 1
3(b)(i) A: covalent
r: covalent bond
B: ionic
r: ionic bond
1
1
6
3(b)(ii) 2.8.8.1 1
3(b)(iii) High melting point and boiling point // conduct electricity in
molten or aqueous solution // soluble in water // insoluble in
organic solvent.
[Any one]
1
3(c)(iv) 2K + Cl
2
2KCl
1. Formula of reactants and products correct
2. Balance the chemical equation
1
1
TOTAL 10
13
C
6
12
C
6
Or
Hot iron wool
Wul besi panas
Heat
Panaskan
Chlorine gas
Gas klorin
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
5
Question Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
4(a)(i)
Pipette
r: wrong spelling
1
3
4(a)(ii)
Phenolphthalein // methyl orange
r: wrong spelling
1
4(a)(iii)
Phenolphthalein : pink to colourless //
methyl orange : yellow to orange
1
4(b)(i)
2KOH + H
2
SO
4
K
2
SO
4
+ 2H
2
O
Formula of reactants and products correct
Balance the chemical equation
1
1
2
4(b)(ii)
1. Mol of KOH = (1.0)(25) / 1000
= 0.025 mol
2. Molarity of H
2
SO
4
= (0.0125)(1000) / 10
= 1.25 mol dm
-3
//
Molarity of H
2
SO
4
= 0.0125 /0.01 = 1.25 mol dm
-3
Or
b
a
V M
V M
b b
a a
; Molarity of H
2
SO
4
=
10
) 25 ( 1
2
1
x
= 1.25 mol dm
-3
r: wrong unit or without unit
1
1
2
4(c)(i)
Hydrogen ion
r: H
+
(symbol ion)
1
3
4(c)(ii)
1. no water
2. contain of molecule // no hydrogen ion, H
+
1
1
TOTAL 10
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
6
Question Mark scheme Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
5(a) Chemical formula that shows the simplest whole number ratio of
atom of each element in the compound.
1 1
5(b)(i) Mass of Mg = 2.4 g
Mass of O = 1.6 g
1
6
5(b)(ii) Mole of Mg = 2.4 / 24 = 0.1
Mol of O = 1.6 / 16 = 0.1
Mg : O = 1 : 1
1
1
5(b)(iii) MgO 1
5(b)(iv) to allow oxygen enter the crucible 1
5(b)(v) Repeat the process heating, cooling and weighing until a
constant mass is obtained.
1
5(c)
Apparatus set-up correct and functional
Labeled : magnesium ribbon, heat
1
1
2
5(d)(i) Zinc oxide // aluminium oxide
r: formula
1
2
5(d)(ii) Silver is less reactive / not reactive metal 1
TOTAL 11
Magnesium
ribbon
Heat
crucible
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
7
Question Mark scheme
Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
6(a) Hydrogenation 1
5
6(b) C
4
H
8 +
H
2
C
4
H
10
1
6(c)(i)
Mole of butene = 2.8 /56 = 0.05 mol
1
6(c)(ii) P1. 1 mol of butene burns in oxygen gas produce 4 mol of
carbon dioxide.
Therefore 0.05 mol of butene burns in oxygen gas produce 0.2
mol of carbon dioxide //
C
4
H
8
: CO
2
1 : 4
0.05 : 0.2
P2. volume of CO
2
= 0.2 x 24 = 4.8 dm
3
1
1
6(d) P1: 2 cm
3
of but-2-ene and 2 cm
3
of butane gas are filled in two
different test tubes.
P2 : 2 -3 drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
is added to both test tubes.
P3: But-2-ene decolourises purple acidified KMnO
4
Purple acidified KMnO
4
in butane remains unchange.
Or
P1: 2 cm
3
of but-2-ene and 2 cm
3
of butane gas are filled in two
different test tubes.
P2 : 2-3 drops of bromine water is added to both test tubes.
P3: But-2-ene decolourises brown bromine water.
Brown bromine water in butane remains unchange.
1
1
1
Or
1
1
1
3
6(e)(i) A: unvulcanised rubber
B: vulcanised rubber
1
1
3
6(e)(ii) Rubber type B/ vulcanised rubber is more elastic than rubber
type A/ unvulcanised rubber
1
TOTAL 11
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
8
SECTION B
Question Mark scheme
Mark
Mark
7 (a)
(i) Ascending order : Cu, Y,X, W
(ii)
P1 : Positive terminal : Cu
P2 : Potential difference : 1.3V
P3: Copper is less electropositive // X is more electropositive
correct value and unit
1
1
1
1
4
7 ( b) (i)
Experiment I : Pb
2+
, Cl
-
Experiment II: H
+
. OH
-
, Cl
r: lead(II) ion, chloride ion
Hydrogen ion, hydroxide ion, chloride ion
1
1
2
7(b)(ii)
Experiment 1 Experiment II
Product at anode:
Chlorine gas
Products at cathode:
Oxygen gas
Reason:
P1: Cl
-
is discharged
P2: the only
anion presence
and discharged at anode
Reason:
P1:OH
-
is selected to be
discharged
P2:the position of OH
-
is lower
than Cl
-
in electrochemical series
.Half equation:
2Cl
-
Cl
2
+ 2e
P1:Correct formula of
reactant and product :
P2: Balance equation
. Half equation:
4OH
-
2 H
2
O + O
2
+ 4e
P1: Correct formula of reactant
and product
P2: Balance equation
1 + 1
1 + 1
1 + 1
1 + 1
1 + 1
10
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
9
7(c)
P1: Positive terminal: R
P2: Negative terminal:Cu
P3: Suitable metal for R : Silver
P4: Suitable solution for R : Silver nitate solution
1
1
1
1
4
Total 20
Question Mark scheme Mark Mark
8(a)
P1. Smaller size has larger total surface area.
P2. Absorb heat faster.
P3. Bigger size has smaller total surface area.
P4. Absorb heat slower
1
1
1
1
4
(b)(i)
Copper(II) sulphate
1 1
(b)(ii)
1. Experiment I
Rate of reaction = 40/2 = 20 cm
3
min
-1
2. Experiment II
Rate of reaction = 60/2 = 30 cm
3
min
-1
1
1
2
(b)(iii)
P1. Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher than
Experiment I.
P2. Substance X used in Experiment II is a catalyst.
P3. Catalyst provided an alternative path with requires a
lower
activation energy.
P4. More particles are able to achieve lower activation
energy.
P5. Frequency of effective collisions between zinc atoms and
hydrogen ions are higher.
1
1
1
1
1
5
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
10
(b)(iv)
1. Label of axes and unit
2. Correct curve and label
1
1
2
(v)
1. Correct formula of reactants and product
2. Balanced equation
Zn + 2H
+
Zn
2+
+ H
2
1
1
2
(vi)
1. Rate of reaction using sulphuric acid is higher.
2. Volume of hydrogen gas released is doubled.
3. Sulphuric acid is a diprotic acid.
4. Concentration of hydrogen ions in sulphuric acid is double
than that in hydrochloric acid.
1
1
1
1
4
Total 20
Volume of
gas / cm
3
Time / min
Exp II
Exp I
2
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
11
Question Mark scheme
Mark
Mark
9(a) P1: Magnesium atom undergoes oxidation
P2: oxidation number increases from 0 to 2+
P3: Copper (II) ion undergoes reduction
P4: oxidation number decreases from +2 to 0
P5: The reaction involving oxidation and reduction
1
1
1
1
1
MAX
4
(b)
Experiment I
L can reduce copper(II) oxide// L can react with copper(II) oxide
L is more reactive than copper.
Experiment II
M can reduce copper(II) oxide//M can react with copper(II)
oxide
M is more reactive than copper.
Experiment III
M cannot reduce L oxide // M cannot react with L oxide.
M is less reactive than L//L is more reactive than M.
The arrangement in order of increasing reactivity toward oxygen is Cu,
M and L.
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
5
1
6
(c)
Procedure :
P1. Pour 2 cm
3
of potassium bromide solution into a test tube.
P2. Add 2 cm
3
of chlorine water to the test tube and shake the mixture.
P3. Add 2 cm
3
of 1,1,1 trichloroethane to the test tube and shake the
mixture.
P4. Record the observation
P5. Repeat steps 1-4 using another halogens and halide solution.
.
1
1
1
1
1
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
12
Result :
Chlorine water Bromine water Iodine water
Potassium
chloride
X X
Potassium
bromide
X
Potassium
iodide
Ionic equation:
1. Cl
2
+ 2Br
-
2Cl
-
+ Br
2
2. Cl
2
+ 2I
-
2Cl
-
+ I
2
3. Br
2
+ 2I
-
2Br
-
+ I
2
1
1
1
1
1
10
20
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
13
Question Mark scheme
Mark
Mark
10(a)
Precipitation / double decomposition reaction
Barium nitrate solution/barium chloride solution
[Any sulphate solution]
Example: sodium sulphate, potasium sulphate, sulphuric
acid
Reject : Lead(II) sulphate, calcium sulphate
Ba
2+
+ SO
4
2
BaSO
4
1
1
1
1
4
10(b)(i)
Cation : Iron(II) ion / Fe
2+
Anion: Chloride ion / Cl
1
1
2
10(b)(ii)
Test for NO
3
P1: Add 2 cm
3
of dilute sulphuric acid into the test tube follow
by 2 cm
3
of iron(II) sulphate solution.
P2: Add a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid
P3: carefully and slowly along the side of slanting test tube
into the mixture.
P2: A brown ring is formed.
1
1
1
1
4
10(c)
Procedure:
P1. Add zinc nitrate solution to sodium carbonate solution
in a beaker.
P2. Stir the mixture.
P3. Filter the white precipitate/solid zinc carbonate formed.
P4. Add zinc carbonate to sulphuric acid in a beaker until
some zinc carbonate solid no longer dissolve.
P5. Filter the mixture.
P6. Transfer the filtrate to a evaporating dish.
P7. Heat the filtrate(zinc sulphate solution) until saturated//
Heat the filtrate to about one-third (1/3) of its initial
volume
P8. Allow the saturated solution to cool at room temperature.
P9. Filter the crystals formed.
P10. Dry the crystals by pressing it between two sheets of
filter papers.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
Total 20
http://www.chngtuition.blogspot.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Biology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity NotesDokumen1 halamanBiology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity Notesdebbycley70% (10)
- SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa SelangorDokumen49 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa SelangorzerosakuraBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa PerakDokumen65 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa PerakJohn NgooBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMISTRY Kertas 1 PDFDokumen28 halamanCHEMISTRY Kertas 1 PDFBooyahyah123Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDokumen4 halamanChemistry Form 4 Definition ListallthecrappystuffBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa PenangDokumen83 halamanSPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa PenangLee ChungBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Set 2 Essay BDokumen10 halamanBio Set 2 Essay BSyakirin Nur ImanBelum ada peringkat
- Perfect Score Bio 2011 Q SPMDokumen76 halamanPerfect Score Bio 2011 Q SPMDelima AdanBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Chandini ThesisDokumen71 halamanChandini Thesismallesh D trigarBelum ada peringkat
- Sterilization Validation GuideDokumen10 halamanSterilization Validation GuideVenkata Rama50% (2)
- Forty-Five Years of Split-Brain Research and Still Going StrongDokumen7 halamanForty-Five Years of Split-Brain Research and Still Going StrongJuan Ignacio GelosBelum ada peringkat
- Article in Press: Process Safety and Environmental ProtectionDokumen12 halamanArticle in Press: Process Safety and Environmental ProtectionAbeer El ShahawyBelum ada peringkat
- Zo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaDokumen20 halamanZo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaAbhishek Singh ChandelBelum ada peringkat
- 2019PSNLLB43642-648Syahdietal 1 PDFDokumen15 halaman2019PSNLLB43642-648Syahdietal 1 PDFAlina Vitali TabarceaBelum ada peringkat
- Expression and ExtractionDokumen34 halamanExpression and ExtractionNaveenBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Dokumen100 halamanMicrobiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Arief NorddinBelum ada peringkat
- Cystic Fibrosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers May 2015Dokumen20 halamanCystic Fibrosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers May 2015Tapan AnkleshwariaBelum ada peringkat
- Agroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaDokumen7 halamanAgroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaArjuna SeneviratneBelum ada peringkat
- 09 Chapter 5Dokumen48 halaman09 Chapter 5Swagath NBelum ada peringkat
- Formulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediDokumen2 halamanFormulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediKevin ThenediBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Biology IntroductionDokumen21 halamanIGCSE Biology IntroductionSilya ZhaoBelum ada peringkat
- Excretory System of FrogDokumen3 halamanExcretory System of FrogSree Lekshmi V SBelum ada peringkat
- Agricultural Science Class 3 QuestionsDokumen3 halamanAgricultural Science Class 3 QuestionsEmmanuel DominicBelum ada peringkat
- Antioxidant Assays: 1. DPPH Assay (2, 2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl)Dokumen4 halamanAntioxidant Assays: 1. DPPH Assay (2, 2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl)Krishnaswamy VkdBelum ada peringkat
- 6 135Dokumen6 halaman6 135Ashok LenkaBelum ada peringkat
- Non Linear PharmacokineticsDokumen33 halamanNon Linear PharmacokineticsClaudBelum ada peringkat
- AlbuminaDokumen4 halamanAlbuminaSuprovet LabotatorioBelum ada peringkat
- QTPPDokumen3 halamanQTPPRajesh Bhapkar100% (1)
- Dr. Ishaq KhanDokumen1 halamanDr. Ishaq Khanfatima malikBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of Lipid Profile Among Patients With Seborrheic DermatitisDokumen7 halamanAssessment of Lipid Profile Among Patients With Seborrheic DermatitisAinun Aii NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacological AntagonismDokumen4 halamanPharmacological AntagonismMuhammad MasroorBelum ada peringkat
- Termamyl 120LDokumen8 halamanTermamyl 120Lnothing2902Belum ada peringkat
- Haematology and TransfusionDokumen3 halamanHaematology and TransfusionDinusha RajapakseBelum ada peringkat
- Hardy-Weinberg Principle WebquestDokumen6 halamanHardy-Weinberg Principle Webquestapi-232072092Belum ada peringkat
- Case Report 1676563639Dokumen6 halamanCase Report 1676563639noah jemedafeBelum ada peringkat
- S5LT 11f 6Dokumen8 halamanS5LT 11f 6Kristine Joy PitaBelum ada peringkat
- Major Reasons for Deforestation in Malaysia including Oil Palm PlantationsDokumen2 halamanMajor Reasons for Deforestation in Malaysia including Oil Palm PlantationsJenny LaiBelum ada peringkat
- CR (Acac) ExptDokumen4 halamanCR (Acac) Exptdsw27Belum ada peringkat