Tutorial: Physics Panel SMSSI
Diunggah oleh
MNYDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tutorial: Physics Panel SMSSI
Diunggah oleh
MNYHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Introduction To Physics
TUTORIAL
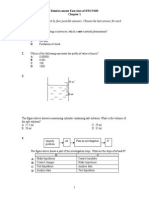
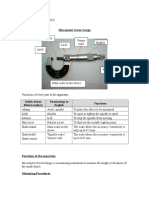
1. Fill in the empty boxes with the correct part.
2. Complete the table below :
Istilah dalam
Bahasa melayu
Terminology in
English
Functions
Rahang Anvil, spindle
Bidal o open or tighten the spindle to anvil
!e!"nci o stop the spindle #rom moving
$!r" racet Ratchet screw
$!ala "tama %ain scale on the
sleeve
$!ala bidal &
$!ala vernier
he scale where the acc"racy & sensitivity is "p to
'.'1 mm
Physics Panel SMSSI
1(
Introduction To Physics
). *hat is the "sed o# the micrometer screw ga"ge+
,. Complete the meas"ring proced"res o# msg+
1. -----.the thimble to --------the .aw / spindle 0
2. --------the ob.ect in between the anvil and spindle
). -------.the thimble again on the opposite direction to ---------..the ob.ect between the anvil and spindle..
,. *hen the ob.ect is --.., ---.. the ratchet screw "ntil yo" hear the #irst 1tic2 so"nd.
3. --------.the main scale by ---------.to the side position o# the thimble scale.
4. ------.the thimble scale by ---------..to the re#erence line on the main scale.
5. he #inal reading is obtained by -------------..the two readings above #rom both scales.
3. *hat are the steps to be ta!en in order to increase the acc"racy o# o"r meas"rement+
4. Can we "se the %icrometer $crew 6a"ge to meas"re the length o# the physics laboratory+ 7r
the height o# a tree+ 8# yes, why+ 8# no, why+
Multiple Choice Questions
5. A physical 9"antity o# meas"rement is said to be more precise i#
A. the :ero error is small
B. the average val"e is small
C. the relative deviation is small
;. the physical 9"antity o# meas"rement is small
(. *hich o# the #ollowing shows the same relationship o# a "nit +
A. 1 < = 1 !g m s
>1
B. 1 ? = 1 !g m
2
s
>2
C. 1 @a = 1 !g m
>1
s
>1
;. 1 * = 1 !g m
2
s
>1
A. *hich o# the #ollowing step m"st not be done when "sing a micrometer screw
ga"ge +
A. ;etermine the :ero error o# the micrometer screw ga"ge
Physics Panel SMSSI
1A
Introduction To Physics
B. %eas"re the ob.ect by tighten the spindle to anvil
C. Add "p the meas"ring reading with the :ero error
1'. )' milliseconds is e9"ivalent to
A. ) x 1'
>4
seconds
B. ) x 1'
>3
seconds
C. ) x 1'
>,
seconds
;. ) x 1'
>)
seconds
B. ) x 1'
>2
seconds
11. *hich o# the #ollowing pre#ix is not correct in representing its corresponding
symbol +
@re#ix $ymbol
A. %ega m
B. centi c
C. micro
;. pico p
12. Complete the table below :
Reading 1 2 ) , 3
Measurement 143.3 cm '.31) cm '.)35 cm 4.3) cm A3.2 cm
Ta!le "
Quantity Reading # cm Measuring instrument
;iameter o# a copper wire
;iameter o# a 23' ml bea!er
Ceight o# Abd"llah
Dength o# a table
hic!ness o# 1'' sheets o# paper
Ta!le $
Physics Panel SMSSI
2'
Introduction To Physics
hree meas"ring instr"ments : metre r"le , vernier calipers , and micrometer screw ga"ge , had been "sed by a st"dent to meas"re a #ew 9"antities .
able 1 shows a #ew readings o# the meas"rement .
/a0 Complete able 2 by matching the most possible reading and name the most possible meas"ring instr"ment which is "sed in the meas"rement .
/b0 $"ggest two methods to increase the acc"racy in the meas"rement o# the diameter o# a copper wire .
/c0 An aeroplane #light in a constant speed o# 52' !m per ho"r .
/i0 $tate the speed o# #light o# the aeroplane in m s
>1
.
/ii0 Cow #ar did the aeroplane #ly a#ter 1' s .
1). A driver wished to !now how many vol"mes o# petrol had been "sed in each
!m . Ce placed a meas"ring instr"ment to the petrol tan! to meas"re the vol"me o# the petrol "sed in 3' !m , 1'' !m , 13' !m , 2'' !m , 23' !m , and
)'' !m . Ce tab"lated the reading in able ) .
Ta!le %
/a0 @lot graph V against s in a sheet o# graph paper .
/b0 he driver didnEt record the vol"me o# the petrol at the beginning o# the motion . Find o"t the val"e o# V when s = ' !m #rom the graph .
/c0 Calc"late the gradient o# the graph .
/d0 $tate the vol"me o# petrol that had been "sed in each !m .
1,.
Dord ,
W & <
ime ta!en #or 1'
oscillations , t & s
@eriod o#
oscillation , T & s
T
2
& s
2
W
T
2
& < s
>2
1.'
2.'
).'
,.'
4.A
1'.'
12.,
1,.,
'.5
1.'
1.2
1.,
Ta!le &
able , shows the experiment data obtained investigating the system o# oscillations by a weighted spring . he load "sed is ass"med to be acc"rate .
he time ta!en #or one oscillation is timed "sing a stop cloc! with scale divisions o# '.1 second and the :ero error is F'.3 seconds .
Physics Panel SMSSI
;istance , s & !m 3' 1'' 13' 2'' 23' )''
Gol"me o# the petrol , V & liter ,' ), 2( 22 14 1'
21
Introduction To Physics
/a0 *hat is "nderstood by zero error+
/b0 Complete the table , above.
/b0 Bxplain the s"itability o# the data recorded in able , . hen tab"late again the data that is corrected and give reasons #or the corrections
o# the data .
/c0 ;raw a graph to show the change o# the period o# oscillation with load . hen state a relationship between the load and the period o# swing o#
the weighted spring .
/d0 Bxplain why acc"rate and precise meas"rement are necessary in the st"dy o# @hysics .
Physics Panel SMSSI
22
Introduction To Physics
Physics Panel SMSSI
2)
Introduction To Physics
Physics Panel SMSSI
2,
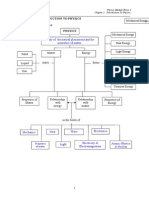
C h a p t e r 1
N a t u r a l
P h e n o m e n o n
E v e r y d a y
O b j e c t s
F i e l d s o f S t u d y
I n P h y s i c s
P h y s i c s C o n c e p t s
B a s e
u a n t i t i e s
! e r i v e d
u a n t i t i e s
P r e f i " e s
S c i e n t i f i c
N o t a t i o n
S y m b o l s #
$ n i t s
% a & n i t u d e
O n l y
S c a l a r
u a n t i t i e s
% a & n i t u d e #
! i r e c t i o n
' e c t o r
u a n t i t i e s
P h y s i c s u a n t i t i e s
( c c u r a c y
S e n s i t i v i t y
C o n s i s t e n c y
) a n d o m
E r r o r
S y s t e m a t i c
E r r o r
* e c h n i + u e s
t o ) e d u c e
E r r o r s
E r r o r
% e a s u r i n &
I n s t r u m e n t s
$ s i n & ( p p r o p r i a t e
I n s t r u m e n t s t o % e a s u r e
P h y s i c a l I n s t r u m e n t s
% e a s u r e m e n t s
, r i t e ) e p o r t
! r a -
C o n c l u s i o n s
I n t e r p r e t ! a t a
P r e s e n t ! a t a
* a b u l a t e ! a t a
, o r .
P r o c e d u r e s
S e l e c t
( p p a r a t u s
E " p e r i m e n t s
F o r m
/ y p o t h e s i s
I d e n t i f y
' a r i a b l e s
I d e n t i f y
u e s t i o n s
S c i e n t i f i c I n v e s t i & a t i o n s
I n t r o d u c t i o n * o P h y s i c s
%8<; %A@ F 8<R7;CH87< 7 @CI$8C$
Introduction To Physics
ETeMs Co"rse
Physics
$%J "n Aminah
*2&;4&$2&61
'roup " ( Cloc) *
1. %r. D"i Fwee $ing
2. %r. %ohd. Ka!i bin %d. $"hadi
). %r. 6oh Boon Cheng
;esigning an experiment
E+,ERIME-T
Dearning area : 1. 8ntrod"ction to @hysics
Dearning : 1.30 Analysing scienti#ic investigations
ob.ective
7b.ective : o st"dy the relationship between the length o# the pend"l"m
and the period o# oscillation.
Apparat"s : @end"l"m bob, string, retort stand, metre r"ler, stopwatch,
wooden pieces, clamp, protractor.
23
)etort Stand
Strin&
Pendulum Bob
0
,ei&ht
Strin&
Pendulum Bob
Protractor
,ooden Pieces
Introduction To Physics
%ethod :
1. ie one end o# the string to the pend"l"m bob.
2. Clamp another end o# the string between 2 wooden pieces which are placed on
a retort stand as shown in the diagram.
). %eas"re the length o# the pend"l"m bob, D =2'.' cm, by "sing a metre r"ler.
,. ;isplace the pend"l"m bob at an angle approximately 1'
o
.
3. Record the time #or 2' complete oscillations o# the pend"l"m, t
1.
4. Repeat the proced"res ,>3 to record another 2' complete oscillation time o#
the pend"l"m, t
2
.
5. Calc"late the mean o# both oscillation times and determine the period,
= t
mean
& 2'.
(. Repeat the proced"res ) to 5 with 3 di##erent lengths o# the pend"l"m, D=)'.'
cm, ,'.'cm, 3'.'cm, 4'.' cm and 5'.'cm.
A. ab"late the data.
1'. @lot a graph o# period, , against the length o# the pend"l"m, D and a graph
o#
2L
against D.
;ata able
D&cm
ime #or 2' oscillations & s
&s
2
& s
2
t
1
t
2
T
mean
2'.'
)'.'
,'.'
3'.'
4'.'
5'.'
24
Introduction To Physics
*2;1'$)61
6R7H@ 1 : 1. %r. D"i Fwee $ing
2. %r. %ohd. Ka!i Bin $"hadi
). %r. 6oh Boon Cheng
Learning Area ". Introduction To ,hysics
&s
D&cm
6raph against D
2
&s
2
D&cm
6raph
2
against D
25
Introduction To Physics
Subject 1 Physics
Year 1 Form Four
Topic 1 Introduction *o Physics
Learning Outcomes 1 Student should be able to1
12E"plain -hat base +uantities and derived +uantities are2
320ist base +uantities and their units2
420ist some derived +uantities and their units2
Duration 1 3 Periods 5 67 %inutes 8
Subject Content 1 $nderstandin& Base uantities and !erived uantities
Activities 1 12 Students -ill be &iven several situations re&ardin&
base +uantities -hich are related to their daily activities2
32 uestions -ill be put for-ard for student to ans-er2
42 Students -ill then -atch several animations re&ardin&
base +uantities and derived +uantities2
92 *eacher -ill &ive e"planation on base +uantities and
2(
Introduction To Physics
derived +uantities usin& animation2
:2 Students -ill -rite notes themselves2
Moral Values 1 )isin& (-areness
Creative & Critical Thinking Skills 1 (nalysin&; inter<relatin& and problem solvin&2
Teaching Ais 1 0aptop; 0C! Projector; *e"t Boo.
Steps Content !roceure " Activities #otes
Introduction
517 minutes8
Pupils shall
be able to
relate base
+uantities
-ith daily
activities2
Pupils to discuss the use of a ruler or measurin&
tape; balance; -atch and compose -hat are the
units used by these instrument that help us in our
daily activities2
uestions for students2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
!evelopment
One
537 minutes8
)efer to
(ppendi" (
*he teacher -ill access the Po-erPoint slide to
demonstrate five important base +uantities2
(ctivity
Sheet
5)efer to
(ppendi" (8
!evelopment
*-o
51: minutes8
)efer to
(ppendi" B
,ith the help of the computer; the teacher -ill be
able to display prefi"es uses in physics +uantities
that follo- the SI unit2
*eacher &ives e"amples to help the pupils to
have a better idea of SI unit2
*he teacher -ill encoura&e the pupils to find out
more on base +uantities2 (nd to have a short
discussion as to -hy SI units are preferred over
other units2
Computer
(nimation
Computer;
0C!
Projector
!evelopment
*hree
51: minutes8
!erived
+uantities
can be
derived from
base
+uantities2
,ith the help of the computer; the teacher states
a fe- e"amples to help the pupils to a have a
better understandin& of the units of derived
+uantities2 *eacher &ives e"amples to help the
pupils to have a better idea of derived +uantities2
Second
Metre
Time
Length
Time
nt Displaceme
Velocity = = =
Po-erPoint
(nimation
)efer *o
(ppendi" B
2A
Introduction To Physics
Steps Content !roceure " Activities #otes
!evelopment
Four
517 minutes8
'olume = 0en&th " ,idth " /ei&ht
Volume
Mass
Density =
Time
Velocity of Change
on ccelerati
M M
=
Force = %ass " (cceleration
,or. = Force " !isplacement
Po-erPoint
(nimation
Closure
517 minutes8
*eacher consolidates the concept learnt2
*he teacher -ill as. the pupils to do e"tra
e"ercise as an enrichin& activity2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
Appendi/ A
$ase %uantities 0ym!ol S& 'nit 0ym!ol
0en&th l %etre m
%ass m >ilo&ram kg
*ime t Second s
8 (mphere A
*emperature T >elvin K
Based +uantities are physics +uantities; -hich cannot be; defined in any other physics +uantities
anymore2
Appendi/ B
Physic +uantities -ith lar&e value or e"treme small value can be -ritten follo-in& SI unit -ith a
prefi" added in front of the based +uantities2
!re(i)es 1alue S*mbol
)'
Introduction To Physics
*era 17
13
*
?i&a 17
@
G
%e&a 17
A
M
>ilo 10
3
K
!esi 17
<1
d
Centi 17
<3
c
%ili 17
<4
m
%icro 17
<A
Nano 17
<@
n
Pi.o 17
<13
p
Subject 1 Physics
Year 1 Form Four
Topic 1 Introduction *o Physics
Learning Outcomes 1 Student should be able to1
%easure physical +uantities usin& appropriate instruments2
Duration 1 1 Period 5 97 %inutes 8
Subject Content 1 $nderstandin& %easurements
Activities 1 12 Students -ill be &iven several situations re&ardin&
measurements related to their daily activities2
32 uestions -ill be put for-ard for student to ans-er2
42 Students -ill then -atch several animations re&ardin&
measurin& +uantities2
92 *eacher -ill &ive e"planation on measurin& physical
+uantities2
Moral Values 1 Bein& than.ful and risin& a-areness
Creative & Critical Thinking Skills 1 (nalysin&; inter<relatin& and problem solvin&2
Teaching Ais 1 0aptop and 0C! Projector
Steps Content !roceure " Activities #otes
Introduction
5: minutes8
Choosin& the
appropriate
12 *eacher -ill discuss conte"tual e"ample
related to the daily activities of a student2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
)1
Introduction To Physics
Steps Content !roceure " Activities #otes
instruments2 32 *eacher -ill display 4 pac.et of su&ar -ith
different mass2
Student -ill be as.ed to estimate the mass
based on the dia&ram2 uestions for students2
!evelopment
One
517 minutes8
!ifferent types
of objects and
conditions use
different tools
to measure its
+uantities2
(ctivity sheets -ill be distributed to all
students2 Students are &iven 17 minutes to
complete the activity2
Student -ill learn ho- to use appropriate
measurin& tools to do different types of
measurements2
(ctivity Sheet
5)efer to
(ppendi" (8
!evelopment
*-o
517 minutes8
0en&th
%etre rule
%ass
Balance
*ime
Stop ,atch
Electricity
'oltmeter
(mmeter
*hen teacher -ill &ives e"planations to the
students after listenin& to their ans-ers and
then introduces them to the concept of
measurin& physical +uantities and ho- to
measure them2
Computer
(nimation
Computer;
0C!
Projector
!evelopment
*hree
517 minutes8
Concept %ap
of Chapter 11
Introduction *o
Physics
*eacher -ill discuss -ith the students and
dra- a concept map re&ardin& +uantities and
measurin& tools2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
)efer *o
(ppendi" B
)2
Introduction To Physics
Steps Content !roceure " Activities #otes
Closure
5: minutes8
%easurin&
Instruments1
%etre rule;
Balance; Stop
,atch;
'oltmeter;
(mmeter
*eacher consolidates the concept learnt2 Po-erPoint
(nimation
Subject 1 Physics
Year 1 Form Four
Topic 1 Introduction *o Physics
Learning Outcomes 1 Student should be able to1
%easure physical +uantities usin& appropriate instruments2
Duration 1 1 Period 5 97 %inutes 8
Subject Content 1 $nderstandin& %easurements
Activities 1 12 Students -ill be &iven several situations re&ardin&
measurements related to their daily activities2
32 uestions -ill be put for-ard for student to ans-er2
42 Students -ill then -atch several animations re&ardin&
measurin& +uantities2
92 *eacher -ill &ive e"planation on measurin& physical
+uantities2
Moral Values 1 Bein& than.ful and risin& a-areness
Creative & Critical Thinking Skills 1 (nalysin&; inter<relatin& and problem solvin&2
Teaching Ais 1 0aptop and 0C! Projector
Steps Content !roceure " Activities
Teacher+s Classroom
Language
#otes
Introduction
5: minutes8
Choosin& the
appropriate
instruments2
12 *eacher -ill discuss
conte"tual e"ample
related to the daily
activities of a student2
32 *eacher -ill display 4
pac.et of su&ar -ith
?ood mornin&2
(re you all ready for today
lessonB
0et revie- -hat -e have
learn in the previous class2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
))
Introduction To Physics
Steps Content !roceure " Activities
Teacher+s Classroom
Language
#otes
different mass2
Student -ill be as.ed to
estimate the mass based
on the dia&ram2
uestions for students2
No- let have a loo. at the
slide sho-n on the screen2
12 ,hich pac.et of su&ar is
heavierB
32 In your opinion; -hat is
the appropriate measurin&
instrument to measure the
pac.et su&arB
!evelopment
One
517 minutes8
!ifferent types
of object and
condition use
different tools
to measure its
+uantities2
(ctivity sheet -ill be
distributed to all students2
Students are &iven 17
minutes to complete the
activity2
Student -ill learn ho- to
use appropriate
measurin& tools to do
different types of
measurement2
I -ill distribute an activity to
be completed2 Cou have
ten minutes to complete the
activities2 Cou may discuss
the activity -ith your friend2
(ctivity Sheet
5)efer to
(ppendi" (8
!evelopment
*-o
517 minutes8
0en&th
%etre rule
%ass
Balance
*ime
Stop ,atch
Electricity
'oltmeter
(mmeter
*hen teacher -ill &ives
e"planations to the
students after listenin& to
their ans-ers and then
introduces them to the
concept of measurin&
physical +uantities and
ho- to measure them2
0ets discuss the result of
your activity2
No-; lets -atch some
animations related to
measurements2
Computer
(nimation
Computer;
0C!
Projector
!evelopment
*hree
517 minutes8
Concept %ap
of Chapter 11
Introduction *o
Physics
*eacher -ill discuss
toðer -ith the students
and dra- concept map
re&ardin& +uantities and
measurin& tools2
No- -e -ill see ho- much
-e have learn in this topic
and -hat are -e &oin& to
learn in the comin& lesson2
Po-erPoint
(nimation
)efer *o
(ppendi" B
Closure %easurin& *eacher consolidate the Can any of you tell me -hat
),
Introduction To Physics
Steps Content !roceure " Activities
Teacher+s Classroom
Language
#otes
5: minutes8 Instruments1
%etre rule;
Balance; Stop
,atch;
'oltmeter;
(mmeter
concept learn2 have -e learn in todayDs
lessonB
,e have learnt about
measure physical +uantities
usin& appropriate
instruments2 *hey are1
0en&th
%etre rule
%ass
Balance
*ime
Stop ,atch
Electricity
'oltmeter
(mmeter
)3
Introduction To Physics
Appeni) A
(C*I'I*C S/EE*
RECO'-I2I-' A,,RO,RIATE I-0TRUME-T0 FOR MEA0URI-'
Choose the appropriate tools to match -ith the picture &iven2
Stop ,atch %icrometer Scre- ?au&e %etre )ule Balance
(mmeter 'ernier Callipers ,aist ,atch %easurin& *ape
Object %easurin& *ools
Buildin& ,idth
)unnin& *ime
Boo. *hic.ness
Bulb %ass
%u& !iameter
0en&th of >ey
)4
Introduction To Physics
Appeni) A
12 ,hat are the five base +uantities of physicsB
a2 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
b2 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
c2 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
d2 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
e2 2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
32 ,hich of the belo- are not physics +uantitiesB
a2 /eat
b2 *emperature
c2 !e&ree of /eat
d2 Ener&y
42 ,hat is measurementB
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
92 *he mass of a piece of hair are best -ritten in1
a2 &ram
b2 mili&ram
c2 micro&ram
d2 nano&ram
:2 ,hich is not true about measurin& instrumentsB
a2 %easurin& Instruments can &ive measurements close to the actual value2
b2 %easurin& Instruments uses less of physics +uantities2
c2 %easurin& Instruments can &ive 177E measurin& accuracy2
4. A micrometer screw ga"ge is "sed to meas"re the thic!ness o# a piece o# metal. *hich
o# the #ollowing meas"rements represent the acc"racy obtained thro"gh the
meas"rement+
a2 4 mm
b2 32A mm
c2 32A4 mm
d2 32A43 mm
5. A wood bloc! meas"ring 2.' cm x 1.3 cm x 1., cm. he vol"me o# the wood bloc! is:
a2 923
b2 923 " 17
<3
)5
Introduction To Physics
c2 923 " 17
<4
d2 923 " 17
<A
e2 923 " 17
<:
&ntrouction To !h*sics
DB$$7< @DA< 7HD8<B
$"b.ect : @hysics
Iear : Form Fo"r
)(
N"antity O %eas"ring 8nstr"ments
%eas"ring
N"antity
%easurin&
E+uipment
Compare ;i##erentiate
@ersistence Acc"racy $ensitivity
1$ystem Brror2
%eas"ring
echni9"e
@roblem $olving
Introduction To Physics
opic : 8ntrod"ction to physics
Dearning 7"tcomes : $t"dents sho"ld be able to :
1. Bxplain what is physics
2. Recogni:e the physics in everyday ob.ects
and nat"ral phenomena
;"ration : 2 periods / (' min"tes 0
$"b.ect Content : Hnderstanding @hysics
Activities : 1. $t"dents will carry o"t 2 short experiments
2. $t"dents will watch an animation o# the inertia
). N"estions will be p"t #orward #or st"dents to
answer
,. $t"dents will disc"ss some application o#
the inertia in a real live.
%oral Gal"es : Being than!#"l
Creative and Critical hin!ing $!ills : 8nter>relating and problem solving
eaching Aids : Daptop and DC; pro.ector
)A
Introduction To Physics
$CR8@8<6
$B@$ C7<B< AC8G88B$ <7B$
$et ind"ction
/ 1' min"tes0
he ideas o# physics eacher shows some ob.ect into the class and the st"dents
give their opinion in a gro"p disc"ssion.
/a0 Cow to meas"re the length o# table+
/b0 *hat is the diameter o# a pencil+
;evelopement
$tep 1
/13 min"tes0
he physicsian scientist eacher shows some o# the #amo"s physicsian scientist and
the st"dents #ind the biodata #rom text boo! or re#erence
boo!s.
/a0 Find their #amo"s discovery
/b0 Find their #amo"s e9"ation
@hoto #rom text boo!
$tep 2
/13 min"tes0
he nat"re phenomena /i0 eacher shows a video o# nat"ral phenomena .
$t"dents will give their opinion in a grop"
disc"ssion activity.
/ii0 he teacher explain to the st"dents a#ter listening
to their answers and introd"ces them to the
terminology in physics.
$tep )
/2' min"tes0
Bxamples o# physics
#ield
eacher tell the st"dents a certain physics #ield in their li#e.
Also teacher shows an example o# apparat"s and related
them in a concept o# physics
$tep ,
/1' min"tes0
<ame some o#
physiciant and their
discovery
eacher shows the physics scientist and their discovery
which is gave a lot o# advantage #or o"r li#e. ;ownloaded #rom
internet
Clos"re
/1' min"tes0
Be than!#"l eacher explain to the st"dents why they sho"ld pro"d and
than!#"l to the physics scientist.
,'
Introduction To Physics
,1
Introduction To Physics
DB$$7< @DA< 2
$HB?BC : @hysics
IBAR : Form Fo"r
7@8C : N"antities o# @hysics
DBAR<8<6 7HC7%B$ : $t"dents sho"ld be able to
1. Bxplain what base 9"antities and derived 9"antities are.
2. Dist base 9"antities and their "nits.
). Dist some derived 9"antities and their "nits.
,. Bxpress 9"antities "sing pre#ixes.
;HRA87< : wo periods /(' min"tes0
$HB?BC C7<B< : Base and derived 9"antities.
AC8G88B$ : 1. $t"dents will be given some o# the physical 9"antities.
2. eacher will given an explanation what base 9"antities and derived
9"antities are.
). $t"dents will then to identi#y physical 9"antities and classi#y them
into base 9"antities and derived 9"antities.
,. $t"dents will solve the problems involling base and derived
9"antities.
%7RAD GADHB$ : 1. Being systematic
2. Caving an interest and c"riosity towards and invironment.
CRBA8GB A<; CR88CAD C8<J8<6 $J8DD$ :
1. 6ro"ping and classi#ying
BACCBR A8; : Daptop and DC; pro.ector
$B@$ C7<B< @R7CB;HRB$ & AC8G88B$ RB$7HRCB$
& <7B$
$et ind"ction
/1' min"tes0
N"antities
o# physics
1. $t"dents are introd"ced to the topic.
hey are as!ed what the 9"antities o#
o# physics are.
2. eacher as!s some o# the st"dents,
what the apparat"s co"ld be "sed to
meas"re the distance, time, c"rrent,
mass and temperat"re.
). eacher as!s some o# the st"dents,
what apparat"s co"ld be "sed to
meas"re #orce , acceleration and
,2
Introduction To Physics
velocity.
;evelopment
/2' min"tes0
$B@ 1:
$B@ 2:
$B@ ):
Base
9"antities
and derived
9"antities
@hysical
9"antities
other than
the base
9"antities
are !nown
as derived
9"antities.
A derived
9"antities is
combination
o# di##erent
base
9"antities.
eacher gives explanations to the
st"dents a#ter listening to their answers
and than introd"ces them the di##erents o#
the base 9"antities and the derived
9"antities o# physics.
he st"dents list down all the base
9"antities o# physics.
he st"dents list down all the derived
9"antities o# physics.
eacher gives the examples how to
represent the derived 9"antities by
combination o# base 9"antities.
co"rseware
Clos"re
/1' min"tes0
@hysical
9"antities
are base
9"antities
and derived
9"antities.
1.eacher notes down all the #ive
physical 9"antities are chosen a base
9"antities.
2. eacher notes down the example o# the
derived 9"antities.
). eacher gives the example how to
represent a derived 9"antities by
combination o# di##erent base
9"antities.
,. he st"dents do the exercises shown on
the screen.
co"rseware
*7RJ $CBB
%HD8@DB CC78CB NHB$87<$
1. *hich is not a base 9"antities o# physics+
A. ;istance C. Jelvin
B. %ass ;. ime
2. *hich o# the #ollowing shows the #orm"la o# #orce "sing the base 9"antities+
,)
Introduction To Physics
A. mass C. mass P length
length P mass mass
B. mass P length ;. mass P time
time P time length P length
). 2, ? is e9"al to
A. 2, < C. 2, !gms
>1
B. 2,<m ;. 2, !gms
>2
,. *hich o# the #ollowing can state in the "nit @ascal.
A. @ress"re C. Hpthr"st
B. $"r#ace tension
3. %oment"m is represented by base 9"antities as #ollows :
A. mass and length C. length and time
B. mass and time ;. mass, length and time
$RHCHRB; NHB$87<
*rite down #ive o# the base 9"antities and its symbol in the table below:
Base 9"antities $ymbol
1.
2.
).
,.
3.
/3 mar!s0
,,
Introduction To Physics
B$$AI NHB$87<$
1. ;erived the given 9"antities as base 9"antities:
a. %oment"m
b. Acceleration
c. ;ensity /) mar!s0
2. ;erived the "nit o# the #ollowing 9"antities "sing the base 9"antities "nit.
a. Gelocity
b. Force
c. Gol"me
d. *or! /, mar!s0
A00I'-ME-T $
Desson @lan 7"tline
$"b.ect : @hysics
Iear : Form Fo"r
opic : 8<R7;HC87< 7 @CI$8C$
Dearning 7"tcomes : $t"dents sho"ld be able to :
1. explain what base 9"antities and derived 9"antities are.
2. list base 9"antities and their "nits.
). list some derived 9"antities and their "nits.
,. express 9"antities "sing pre#ixes
3. express 9"antities "sing scienti#ic notation.
4. express derived 9"antities as well as their "nits in terms o# base 9"antities and
base "nits.
5. solve problems involving conversion o# "nits.
;"ration : wo periods / (' min"tes 0
$"b.ect Content : 1.2 Hnderstanding base 9"antities and derived 9"antities
Activities : 1. eacher will gave an explanation on how important
scienti#ic meas"rements and examples are in daily li#e.
2. eacher will give an explanation on the di##erence between base and derived
9"antities with their "nits.
). eacher describes how to "se pre#ix.
,. N"estions will be p"t #orward #or st"dents to answer.
3. $t"dents will then solve the problems involving base and derived 9"antities, pre#ix
and conversion "nits.
,3
Introduction To Physics
%oral Gal"es Q Being than!#"l and raising awareness.
Creative and critical hin!ing s!ills : "nderstanding, analy:ing, inter>relating and problem solving.
eaching Aids : Daptop and DC; @ro.ector, so#tware.
A00I'-ME-T $ ".$ Understanding !ase 3uantities and deri4ed 3uantities
$cripting 7"tline :
0teps Content ,rocedure -otes
8ntrod"ction
/ 3 min"tes 0
8ntrod"cing physics
9"antity
eacher introd"ces the topic by
as!ing the st"dents to give
examples on ob.ects to be
meas"red .
eacher gives an explanation on
how important the scienti#ic
meas"rements are.
.
C; & comp"ter
animations
;evelopment 7ne
/ 1' min"tes 0
;e#ining base 9"antities eacher di##erenciates the
examples given by st"dents on
base 9"antities and their "nits in
diagram.
eacher gives the explanation on
base 9"antities, their "nits and
symbols.
eacher introd"ces derived
9"antities by de#ining and giving
the examples, symbols and "nits.
;iagrams
;evelopment
wo /23 mins 0
;e#ining derived
9"antities
> Bxpress 9"antities
"sing pre#ixes.
eacher gives explanations on the
di##erences between base and
derived 9"antities.
$t"dents disc"ss the list o# val"es
o# pre#ixes and their observations
#rom nano to giga.
Activities
;evelopment
hree /13 min"tes0
;isc"ss the "se o#
scienti#ic notation to
express large and small
n"mbers.
$t"dents are given wor! sheets
and they try to answer the
9"estions on base and derived
9"antities, "sing pre#ixes and
scienti#is notations.
6ro"p activities
and disc"ssion
;evelopment
Fo"r /2' min"tes 0
@roblem solving $t"dents are allowed to come in
#ront o# the class to participate in
problem solving activity.
@roblem solving
,4
Introduction To Physics
eacher disc"sses the answers
with the st"dents.
Clos"re
/ 3 min"tes 0
$"mmari:e he teacher concl"des by
s"mmari:ing the lesson
Lesson plan outline
$"b.ect : @hysics
Iear : Form ,
opic : 8ntrod"ction to @hysics.
Dearning o"tcomes : $t"dent sho"ld be able toQ
/10 %eas"re physical 9"antities "sing appropriate instr"ments.
/20 Bxplain acc"racy and consistency.
/)0 Bxplain sensitivity.
;"ration : 2 periods
$"b.ect content : Hnderstanding meas"rements
Activities : /10 $t"dents will be given several sit"ations on meas"rement.
/20 N"estion will be p"t #orward #or st"dents to answer.
/)0 $t"dent choose the appropriate instr"ment #or a given
meas"rement.
/,0 ;isc"ss consistency and acc"rancy "sing the the distrib"tion
o# g"nshots on target.
/30 ;isc"ss the sensitivity o# vario"s instr"ments.
%oral val"es : being systematic and cooperative.
Creative and critical thin!ing s!ill : analy:ing, inter>relating and problem solving.
eaching Aids : Daptop and DC; pro.ector.
LE00O- ,LA- %
$HB?BC: @CI$8C$
IBAR: F7R% ,
7@8C: 8<R7;HC87< 7F @CI$8C$
DBAR<8<6 7HC7%B$:
$t"dent sho"ld be able to:
a0 identi#y variables in a given sit"ation
b0 #orm a hypothesis
,5
Introduction To Physics
c0 design and carry o"t a simple experiment to test the hypothesis
;HRA87<: (' %in"tes
$HB?BC C7<B<: 1.3 Analysing scienti#ic investigations
AC8G88B$:
10 $t"dents will be shown a stim"li o# pend"l"m hanging by a thread o# di##erent lengths.
20 $t"dents will then identi#y all the possible variables
)0 $t"dents will then #orm a hypothesis.
,0 $t"dents will then write the #rame wor! o# the experiment and investigate the hypothesis.
30 $t"dents will then write a report
%7RAD GADHB$: apply scienti#ic s!ill
CRBA8GB O CR88CAD C8<J8<6: analysing, applying
BACC8<6 A8;$: Daptop, DC; and 7C@
5 Appendi/ 6
Format o7 Reporting
<ame:
Form: ;ate:
1. itle:
2. 8n#erence:
). Cypothesis:
,. Aim:
3. Gariables:
Manipulative
Dependent
4. Constant variable
5. Apparat"s
(. @roced"re
A. Cow to #ix manip"lative variable
1'. Cow to meas"re dependent
variable
11. Repeating proced"re
12. ab"late data
1). 6ra# and Concl"sion
1,. @reca"tion
,(
Introduction To Physics
LE00O- ,LA- OUTLI-E
".8 Analysing 0cienti7ic In4estigation
0TE,0 CO-TE-T ,ROCE9URE0 #
ACTI1ITIE0
RE0OURCE0 #
-OTE0
$et 8nd"ction
/1' min"tes 0
Hnderstanding
the problem
1. eacher shows 2 sets o#
pend"l"m hanging #rom
di##erent lengths and as! the
st"dent to compare each periodic
time.
Hsed two sets o#
pend"l"m hanging
with di##erent
length.
;evelopment
$tep 1
/2' min"tes0
$tep 2
/)' min"tes0
$tep )
/13 min"tes0
8denti#y the
variablesQ
%anip"lative,
;ependent and
Constant
variable.
;esign a simple
experiment to
test the
hypothesis.
Complete the
experiment
report.
1. eacher 9"estions the
st"dents that g"ide them to
identi#y the variables.
2. eacher raises 9"estions so
that the st"dents #orm the
hypothesis and the
relationship o# two variables.
). eacher explains how to
cond"ct the experiment and
how to meas"re the variables.
,. eacher than distrib"tes a
#ormat o# reporting the
experiment to the st"dents
and explains how to complete
the #ormat.
3. eacher divides the st"dents
into gro"ps and distrib"tes the
apparat"s.
4. eacher as!s the st"dents to
#inish the experiment within
2' min"tes and display the
data #or corrections /i# any0.
5. he teacher then as!s the
st"dents to complete the reports
Apparat"s and
diagram shown in
text boo!.
$ee appendix
Clos"re
/3 min"tes0
Hnderstanding
how to analyse
scienti#ic
investigation
he teacher emphasi:es the #low
in doing scienti#ic investigation
and the scienti#ic method o#
reporting.
,A
Introduction To Physics
3'
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Indian Institute of Remote Sensing Edusat Based Course On RS, Gis and Gps Examination - Module 1Dokumen10 halamanIndian Institute of Remote Sensing Edusat Based Course On RS, Gis and Gps Examination - Module 1Nitin MadeshiaBelum ada peringkat
- Busbar SyatemDokumen8 halamanBusbar SyatemSanjeewa HemaratneBelum ada peringkat
- Physics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDokumen10 halamanPhysics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Word14Dokumen5 halamanPhysics Word14FaadumomizankaahiyeBelum ada peringkat
- MCR3U Exam Review 2013Dokumen9 halamanMCR3U Exam Review 2013Hari MenonBelum ada peringkat
- Tranophysintlab 2 ReportfinalDokumen9 halamanTranophysintlab 2 Reportfinalapi-249588785Belum ada peringkat
- MrJacksonMaths Foundation Calculator Paper IDokumen20 halamanMrJacksonMaths Foundation Calculator Paper IRussell JacksonBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Frequencies of A Tapered Cantilever Beam of Constant Thickness and Linearly Tapered WidthDokumen9 halamanNatural Frequencies of A Tapered Cantilever Beam of Constant Thickness and Linearly Tapered WidthAleksandar Nikolic100% (1)
- C-Report1 (Gravity System)Dokumen7 halamanC-Report1 (Gravity System)Ah Leng LauBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 1Dokumen7 halamanExercise Form 1 Chapter 1gayathiremathibalanBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel As Physics Syllabus 2001 General Items Module - Phy 1Dokumen6 halamanEdexcel As Physics Syllabus 2001 General Items Module - Phy 1Sam LankaBelum ada peringkat
- Swinburne University of Technology: School of Engineering (Sarawak Campus)Dokumen19 halamanSwinburne University of Technology: School of Engineering (Sarawak Campus)Sekut TawarBelum ada peringkat
- Short CircuitDokumen40 halamanShort Circuitrajpre1213Belum ada peringkat
- Handout3 26Dokumen7 halamanHandout3 26Festus SimbolonBelum ada peringkat
- Crochet DressDokumen7 halamanCrochet DressWilma Jayakumar0% (1)
- Report Ohms LawDokumen2 halamanReport Ohms LawMohamad Rizal Mukhtar100% (1)
- Module 1 (Introduction To Science)Dokumen6 halamanModule 1 (Introduction To Science)Ashley OliverBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Sains Sec A Sec B Tahun 4Dokumen20 halamanSoalan Sains Sec A Sec B Tahun 4selvadz00Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideDokumen19 halamanChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideSyazwana ElleasBelum ada peringkat
- As11 Physics Solved 02 New Sol JVCDokumen18 halamanAs11 Physics Solved 02 New Sol JVCkishor0786Belum ada peringkat
- Ii Item de Selección Única Y Múltiple. Encierra La Letra de LaDokumen4 halamanIi Item de Selección Única Y Múltiple. Encierra La Letra de LaConstanza Rojos AlmunaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Fifth Sem NewDokumen13 halamanAssignment Fifth Sem NewAlop AgaBelum ada peringkat
- Ithaca College Math Day Competition MARCH 31, 2008Dokumen6 halamanIthaca College Math Day Competition MARCH 31, 2008Prashant JainBelum ada peringkat
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Test 2Dokumen5 halamanUniversiti Teknologi Mara Test 2Najwa NaqibahBelum ada peringkat
- Column A A. Branches of ScienceDokumen7 halamanColumn A A. Branches of ScienceRonz de BorjaBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Ujian Fizik Tingkatan 4 Dwibahasa Physics Form 4 Monthly Test Question PaperDokumen10 halamanSoalan Ujian Fizik Tingkatan 4 Dwibahasa Physics Form 4 Monthly Test Question PaperNadiah Raffique100% (1)
- Physics Lab Report.Dokumen23 halamanPhysics Lab Report.Muhammad Sohag HussainBelum ada peringkat
- PCK 1-3 and Practical 1-6Dokumen20 halamanPCK 1-3 and Practical 1-6Ronny WeiBelum ada peringkat
- 4NADokumen10 halaman4NAjiashengroxBelum ada peringkat
- Level 1: Sixty People Were Asked To Name Their Favourite Season. The Results Are Given Below: Season Number of PeopleDokumen24 halamanLevel 1: Sixty People Were Asked To Name Their Favourite Season. The Results Are Given Below: Season Number of PeopleManish GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 16: Mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct AnswerDokumen5 halamanPractice Test 16: Mark The Letter A, B, C, or D On Your Answer Sheet To Indicate The Correct AnswerHuyen NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Home Project Workshop Nodal Centers News & Events Survey Forum Contact Us LoginDokumen15 halamanHome Project Workshop Nodal Centers News & Events Survey Forum Contact Us LoginRajesh BaabuBelum ada peringkat
- DTC Controller Design For IM With Wavelet Noise Reduction European Journal of Scientific Research - 2013Dokumen12 halamanDTC Controller Design For IM With Wavelet Noise Reduction European Journal of Scientific Research - 2013khalafgaeidBelum ada peringkat
- !angent (Ines - ClassworkDokumen53 halaman!angent (Ines - ClassworkjazzmathewBelum ada peringkat
- MrJacksonMaths Higher Non Calc Paper 1Dokumen21 halamanMrJacksonMaths Higher Non Calc Paper 1Russell Jackson100% (2)
- Section A: Answer All Questions Given in This SectionsDokumen10 halamanSection A: Answer All Questions Given in This SectionsNur HaziraBelum ada peringkat
- List of FormulaeDokumen17 halamanList of FormulaemarlontaylorBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation Calculator JDokumen21 halamanFoundation Calculator Jstephanie_jackson1982Belum ada peringkat
- Cem 3005W Tutorial On Stereochemistry and Nmr/Conformation: Solutions April 2013Dokumen6 halamanCem 3005W Tutorial On Stereochemistry and Nmr/Conformation: Solutions April 2013Zama MakhathiniBelum ada peringkat
- Mailam Engineering College: Unit-III (2 & 16 Marks)Dokumen10 halamanMailam Engineering College: Unit-III (2 & 16 Marks)Subathra Devi MourouganeBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware Components For Automation and Industrial Control: Review QuestionsDokumen6 halamanHardware Components For Automation and Industrial Control: Review QuestionsJAIN2013Belum ada peringkat
- Ma 4704 Tutorials PageDokumen21 halamanMa 4704 Tutorials PageMohamed Essam AbdelmeguidBelum ada peringkat
- Civil 151 Fluid Mechanic Laboratory Experiment Manual 2 Fluid Flow MeasurementDokumen5 halamanCivil 151 Fluid Mechanic Laboratory Experiment Manual 2 Fluid Flow Measurementsunleon31Belum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Analysis of Chiral HoneycombDokumen6 halamanFinite Element Analysis of Chiral HoneycombMahesh07aero21Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Lab Notes: Physics 6 Los Angeles Harbor College J. C. Fu R. F. WhitingDokumen56 halamanPhysics Lab Notes: Physics 6 Los Angeles Harbor College J. C. Fu R. F. WhitingmskrierBelum ada peringkat
- PSCAD Course Notes 01Dokumen73 halamanPSCAD Course Notes 01JenniferKujanpaa100% (1)
- Hooke's Law LabDokumen4 halamanHooke's Law Labhafiz_yusoff1620Belum ada peringkat
- Expt5 Electronics Eee202uapDokumen3 halamanExpt5 Electronics Eee202uapsabitavabiBelum ada peringkat
- D 1 Mud Exercise LabDokumen3 halamanD 1 Mud Exercise LabAnonymous T32l1RBelum ada peringkat
- Bangladesh Informatics Olympiad 2010 (National)Dokumen9 halamanBangladesh Informatics Olympiad 2010 (National)Science Olympiad BlogBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of Kinematic Viscosity 1. Purpose: Laboratory Experiment #1Dokumen5 halamanMeasurement of Kinematic Viscosity 1. Purpose: Laboratory Experiment #1kothapalli21Belum ada peringkat
- Trail FZK 2013Dokumen4 halamanTrail FZK 2013FarishaAmoiBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Electronic Laboratory Equipment 1967-68: Pergamon Electronics Data SeriesDari EverandMedical Electronic Laboratory Equipment 1967-68: Pergamon Electronics Data SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringDari EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Singular Points of Complex Hypersurfaces (AM-61), Volume 61Dari EverandSingular Points of Complex Hypersurfaces (AM-61), Volume 61Belum ada peringkat
- Test Gear and Measurements: A Collection of Useful and Tested Circuit Design Ideas'Dari EverandTest Gear and Measurements: A Collection of Useful and Tested Circuit Design Ideas'Belum ada peringkat
- Methods of Radar Cross-section AnalysisDari EverandMethods of Radar Cross-section AnalysisJ.W. Jr. CrispinBelum ada peringkat
- Automorphic Forms on Adele Groups. (AM-83), Volume 83Dari EverandAutomorphic Forms on Adele Groups. (AM-83), Volume 83Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 MaterialsDokumen30 halamanChapter 1 MaterialsMNYBelum ada peringkat
- Narrative EssayDokumen4 halamanNarrative EssayMNYBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Physics (Teacher)Dokumen22 halamanIntroduction To Physics (Teacher)MNYBelum ada peringkat
- Speech StudentDokumen3 halamanSpeech StudentMNYBelum ada peringkat
- Information Transfer - F4Dokumen26 halamanInformation Transfer - F4MNY100% (1)
- Fromula ExcelDokumen1 halamanFromula ExcelMNYBelum ada peringkat
- List Out The Qualities of A High Achiever by Using Bubble MapDokumen3 halamanList Out The Qualities of A High Achiever by Using Bubble MapMNYBelum ada peringkat
- newSLA VocabularyDokumen26 halamannewSLA VocabularyMNYBelum ada peringkat
- Uhf 6033: Dynamics of Leadership: Ismail KailaniDokumen22 halamanUhf 6033: Dynamics of Leadership: Ismail KailaniMNYBelum ada peringkat
- 07 JPNT FZK f4 Module1Dokumen10 halaman07 JPNT FZK f4 Module1MNYBelum ada peringkat
- Napping HouseDokumen6 halamanNapping Houseapi-495876823Belum ada peringkat
- Principles and Distinctive Characteristics of CBIDokumen1 halamanPrinciples and Distinctive Characteristics of CBIAnnisaBelum ada peringkat
- Educational TechnologyDokumen18 halamanEducational TechnologyKristina De Peralta Willy83% (12)
- Q2 Week C - IntersubjectivityDokumen18 halamanQ2 Week C - IntersubjectivityLiza Buemio86% (7)
- Gate Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanGate Lesson Planapi-337286598Belum ada peringkat
- Science of Happiness PSYC 201 Syllabus Fall 2014Dokumen7 halamanScience of Happiness PSYC 201 Syllabus Fall 2014gman61693Belum ada peringkat
- SIT101 Unit Outline (Trimester 1/2 2012-2019)Dokumen12 halamanSIT101 Unit Outline (Trimester 1/2 2012-2019)kenneth n bullockBelum ada peringkat
- Kenya National Education Sector Strategic Plan - NESP PDFDokumen129 halamanKenya National Education Sector Strategic Plan - NESP PDFChristine MwauraBelum ada peringkat
- Perception of Pupil Teachers' Regarding Micro Teaching SessionsDokumen3 halamanPerception of Pupil Teachers' Regarding Micro Teaching SessionsEditor IJTSRDBelum ada peringkat
- Online Vs Traditional EducationDokumen3 halamanOnline Vs Traditional EducationIzatul AzmaBelum ada peringkat
- Assistant Professor, Department of Management Studies, Bishop Heber College, Trichy - 17. E-Mail: Phone: WebDokumen3 halamanAssistant Professor, Department of Management Studies, Bishop Heber College, Trichy - 17. E-Mail: Phone: WebkingsleyBelum ada peringkat
- Rta Question Stems For ParentsDokumen2 halamanRta Question Stems For Parentsapi-258656532Belum ada peringkat
- Aldine ISD Settlement Agreement With DOJ Civil Rights DivisonDokumen10 halamanAldine ISD Settlement Agreement With DOJ Civil Rights DivisonlanashadwickBelum ada peringkat
- St. Mary of The Assumption School HandbookDokumen19 halamanSt. Mary of The Assumption School HandbookTed JutrasBelum ada peringkat
- Statistics Homework Help, Statistics Tutoring, Statistics Tutor - by Online Tutor SiteDokumen30 halamanStatistics Homework Help, Statistics Tutoring, Statistics Tutor - by Online Tutor SitemathhomeworkhelpBelum ada peringkat
- Final IPDokumen26 halamanFinal IPJamie KoronkiewiczBelum ada peringkat
- Dissertations Projects and Synoptic ModulesDokumen6 halamanDissertations Projects and Synoptic ModulesadriangauciBelum ada peringkat
- 2a - EET442 - Route To P Eng (Student) PDFDokumen114 halaman2a - EET442 - Route To P Eng (Student) PDFAzlan AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Brandon High School Graduates 2013Dokumen10 halamanBrandon High School Graduates 2013The Brandon SunBelum ada peringkat
- Brand Awareness Is Related To The Strength of The Brand Node in Memory, As Reflected byDokumen1 halamanBrand Awareness Is Related To The Strength of The Brand Node in Memory, As Reflected byAashish GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- CBCP Monitor Vol. 17 No. 24Dokumen20 halamanCBCP Monitor Vol. 17 No. 24Areopagus Communications, Inc.Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3 CELTADokumen3 halamanAssignment 3 CELTAHam Naz80% (5)
- Allen HolbergDokumen2 halamanAllen Holbergsahooavinash0% (1)
- Korean Popular Music, Its Past and The FutureDokumen4 halamanKorean Popular Music, Its Past and The Futureraizen1Belum ada peringkat
- Area 3-Curriculum & Instruction (TED) 2Dokumen41 halamanArea 3-Curriculum & Instruction (TED) 2Audrey Kristina MaypaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109Dokumen2 halamanAnatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109arudenstineBelum ada peringkat
- 11 02 16Dokumen26 halaman11 02 16WoodsBelum ada peringkat
- Multiplication Lesson Plan (Repeated AdditionDokumen5 halamanMultiplication Lesson Plan (Repeated AdditionHamadBelum ada peringkat
- Ciri-Ciri Dan Kepentingan Komponen Pedagogi KontemporariDokumen2 halamanCiri-Ciri Dan Kepentingan Komponen Pedagogi KontemporariAzfieza LailiBelum ada peringkat
- Princeton-Graduate School Costs and Funding - 2017-18Dokumen33 halamanPrinceton-Graduate School Costs and Funding - 2017-18Sathyanarayanan DBelum ada peringkat