Assignment On Pollution
Diunggah oleh
Babita ChopraJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Assignment On Pollution
Diunggah oleh
Babita ChopraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Assignment on Pollution
Introduction
Environmental pollution is a multi-disciplinary science involving chemistry, physics, life
science, agriculture, medical science, public health, sanitary engineering etc. In broader
sense, it is the study of the sources, reactions, transport, effect and fate of chemical species
in the air, water and soil and the effect of human activity upon these.
Pollutant: A substance present in nature, in greater than natural abundance due to human
activity, which ultimately has a detrimental effect on the environment and therefrom on living
organisms and mankind. Examples are- lead, mercury, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide,
etc.
Contaminant: A material which does not occur in nature, but is introduced by human activity
into the environment, affecting its composition. A contaminant is classified as a pollutant when
it exerts a detrimental effect. Example- chlorine gas
Types of Pollution
Air
Causes of air pollution:
motor vehicle exhaust
power stations
car manufacturing
fertilizer factories
demolishing buildings
solvent evaporation
volcanic eruption
building roads
forest fires
Effect of air pollution:
Global warming, acid rain, smog, ozone depletion are some effects of air pollution
Water
Causes of water pollution:
man-made chemicals used in farming
heavy metals
waste from factories
sediment from the river bed
air pollution
thermal (heat) pollution
soil pollution from rubbish dumps
Effects of water pollution:
The water in the earths biosphere is used and reused again and again by all living things
Soil
Causes of soil pollution:
farming
mining and quarrying
household waste
demolition and putting up buildings
factory waste
Effects of soil pollution:
Experts say that lots of land each year becomes unusable for humans or animals.
Noise
Causes of noise pollution:
noisy roads and traffic
air traffic
rail traffic
household noise
industrial noise
Effects of noise pollution:
We hear and make sounds nearly all the time but too much noise can make us feel angry or
depressed. The time of day that noises are heard is very important.
Radiation
Pollution from radiation can be caused by:
nuclear power plants
making nuclear weapons
disposal of nuclear waste
mining for uranium
What can happen?
Radiation occurs naturally at low levels and is a useful source of power when concentrated.
It can also be very harmful to all living things if they are exposed to too much of it.
Light
Light pollution happens when outside lights, such as a streetlight or a security light, points
light upwards into the night sky.
This light gets scattered in the sky and makes an orange foggy glow to appear above a town.
What can happen?
It is likely that we wont be able to see the stars in the night sky if the amount of light pollution
isnt closely controlled.
CONSERVATION AND ENVIRONMENT MANAGEMENT
It is imperative that we carefully utilise our renewable resources of soil, water, plant and
animal life to sustain our economic development. Over exploitation of these is reflected in soil
erosion, siltation, floods, and rapid destruction of our forest, floral and wildlife resources. The
depletion of these resources often tends to be irreversible and since the bulk of our population
depends on these natural resources to meet the basic needs, it has meant a deterioration in
their quality of life.
Global petroleum deposits are likely to be exhausted within this century. Research is going on
for alternatives to fossil fuel (petroleum) based on biomass (green energy). Controlled nuclear
fusion holds the prospect of abundant energyif the relatively difficult deuterium-deuterium
fusion reaction can be utilised for energy production. This energy source will become
unlimited.
Solar energy is both renewable and non-polluting and provides ideal energy source. On a
global scale, tapping of only a small fraction of solar energy the earth can supply the entire
energy requirement.
In any new development project, due consideration must be given to the environmental, social
and cultural impacts. For this purpose, environmental experts must be involved in project
planning.
DISASTERS
NATURAL AND MANMADE DISASTERS
Sometimes there are drastic changes in environment due to natural disasters, e.g. cyclone,
typhoon, hurricane, tornado, earthquake, volcanic eruption etc. within a short time.
Bush fires, are another type of natural disasters, are of common occurrence in some regions
of the world due to hot summer and lightning. During the hot summer months bush fires are
common in Australia and in the Pacific coast arid areas in USA.
Man developed science and technology but over the years since the Industrial Revolution
(1780- todate) he continued to plunder natural resources thereby polluting the environment.
He degraded lands, destroyed forests, threw toxic wastes into rivers and seas and also
harmful gases into the atmosphere. This continuous load of manmade pollutants into
environment brought about adverse changes, which ultimately back-fired into series of
disasters from time to time.
Some examples of manmade disasters are: London smog, Minamata disease, nuclear
explosions, Bhopal disaster, Chernobyl disaster and Gulf War Hazards.
Nuclear Explosions. Two bombs were dropped by USA during World War II (Aug 6 and 9,
1945) on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan. These instantly killed about 6 lakhs people,
wiped out the two cities and unleashed radioactive fallout which has caused generations to
suffer from various diseases including genetic disorder. Radiation continues to damage
plants, soil and biosphere* in the region.
*the environment consists of four segments- atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and
bioshphere.
Global Warming or Green House Effect
Among the constituents of the atmosphere, only carbon dioxide and water vapour strongly
absorb infrared radiation (14000 to 25000 nm) and effectively block a large fraction of the
earths emitted radiation. The radiation thus absorbed by carbon dioxide and water vapour is
partly re-emitted to the earths surface. The net result is that the earths surface gets heated
up by a phenomenon called the greenhouse effect.
The current global trend in deforestation along with increased combustion of fossil fuels have
a cumulative effect on the net increase in carbon dioxide content (present 356 ppm, 50%).
Carbon dioxide has the potential to rival nuclear wars in terms of massive irreversible damage
to the environment. It is the major greenhouse gas but there are other greenhouse gases-
methane (CH
4
, 19%), chlorofluorocarbons (CFC, 17%), nitrous oxide (N
2
O, 4%) and water
vapour (2%).
Ozone Hole
In september, 1980 scientists reported a large hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica. CFC
was the prime suspect for causing ozone depletion. It was established that one molecule of
CFC is capable of destroying one lakh O
3
molecule in the stratosphere. The extreme
chemical stability and nontoxicity of CFCs enable them to persist for years in the atmosphere
and to enter the stratosphere. Depletion of ozone layer above the earth surface helps to
penetrate harmful rays from the sun to the earth.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nebosh Exams Questions and Answers - Nebosh Question Paper 2021Dokumen4 halamanNebosh Exams Questions and Answers - Nebosh Question Paper 2021faceji67% (3)
- The Art and Practice of Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine. NIGEL CHINGDokumen794 halamanThe Art and Practice of Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine. NIGEL CHINGИгорь Клепнев100% (13)
- When Workers Rate The BossDokumen3 halamanWhen Workers Rate The BossSHIVANGI MAHAJAN PGP 2021-23 BatchBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology - Field Work - Lockdown 2020 AssignmentDokumen14 halamanEcology - Field Work - Lockdown 2020 Assignmentapi-240330821100% (1)
- Biomes Kinds of EcosystemDokumen4 halamanBiomes Kinds of EcosystemDesiree G. SacasanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem & Diversity PDFDokumen23 halamanEcosystem & Diversity PDFSSr ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Renewable and Nonrenewable ResourcesDokumen34 halamanRenewable and Nonrenewable Resourcesapi-266789822100% (1)
- Types of EcosystemDokumen2 halamanTypes of EcosystemnaweedBelum ada peringkat
- Coasts Key Word Glossary (1) MDokumen5 halamanCoasts Key Word Glossary (1) MRia PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrology AssignmentDokumen21 halamanHydrology AssignmentchrisleepeiingBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionDokumen71 halamanLecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionСаманати СоринBelum ada peringkat
- Fluvial Landfrom (Final)Dokumen29 halamanFluvial Landfrom (Final)Prakash Singh100% (1)
- Coastal EcosystemsDokumen27 halamanCoastal EcosystemsDasariBelum ada peringkat
- Acid RainDokumen19 halamanAcid RainRObin KhanBelum ada peringkat
- The Planet EarthDokumen62 halamanThe Planet EarthJohn OsborneBelum ada peringkat
- Deforestation: Causes, Consequences and SolutionsDokumen8 halamanDeforestation: Causes, Consequences and SolutionsÄlejÄndro Quevedo RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - The Hydrosphere - BBDokumen35 halamanChapter 6 - The Hydrosphere - BBtausmanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: Department of Environmental Science, Pub Kamrup CollegeDokumen8 halamanEcosystem: Department of Environmental Science, Pub Kamrup CollegeDebajit SarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Instruments Required For Prismatic Compass SurveyDokumen5 halamanInstruments Required For Prismatic Compass SurveyTEN TV100% (1)
- 3.1 WeatheringDokumen25 halaman3.1 WeatheringSipu GiriBelum ada peringkat
- Food ResourcesDokumen28 halamanFood ResourcesGanesh ChandrasekaranBelum ada peringkat
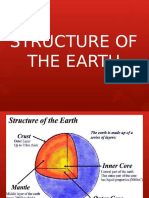
- Earth Structure..Dokumen10 halamanEarth Structure..Maitum Gemark BalazonBelum ada peringkat
- PollutionDokumen13 halamanPollutionRahul VatsBelum ada peringkat
- Desert Eco SystemDokumen6 halamanDesert Eco SystemSiva PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Cycles and FlowsDokumen28 halamanCycles and FlowsRogers Talemwa WakefieldBelum ada peringkat
- Soil Forming FactorsDokumen3 halamanSoil Forming FactorsDylanOSullivanBelum ada peringkat
- HPPT 1Dokumen127 halamanHPPT 1manaseessau5Belum ada peringkat
- Ozone Layer DepletionDokumen12 halamanOzone Layer Depletionnandkishore_singhBelum ada peringkat
- Four SpheresDokumen9 halamanFour SpheresKESAVADASANTHOREBelum ada peringkat
- Pedology PDFDokumen23 halamanPedology PDFManvi SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- SOILS LectureDokumen38 halamanSOILS LectureGagandeep Singh WaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Modern Agriculture PDFDokumen3 halamanEffects of Modern Agriculture PDFkaleemullah100% (1)
- Alternating CurrentDokumen39 halamanAlternating CurrentRichard GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological SuccessionDokumen6 halamanEcological Successionsimran bhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- ch03 Sec2Dokumen26 halamanch03 Sec2api-272720493Belum ada peringkat
- McConnell 3e PPT Ch14Dokumen66 halamanMcConnell 3e PPT Ch14Ken AguilaBelum ada peringkat
- Formation of Sedimentary RocksDokumen12 halamanFormation of Sedimentary RocksBalqis yasin100% (1)
- presentasi-GEOTHERMAL ENERGYDokumen19 halamanpresentasi-GEOTHERMAL ENERGYFika Rachmadian PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Global WarmingDokumen28 halamanGlobal Warmingapi-264756260Belum ada peringkat
- Earth Science Week 3Dokumen10 halamanEarth Science Week 3LmaoBelum ada peringkat
- Food ChainsDokumen7 halamanFood ChainsCenando BodanioBelum ada peringkat
- FA-2 Activity-2 Topic-: Water ResourcesDokumen18 halamanFA-2 Activity-2 Topic-: Water ResourcesBobby SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Coral Bleaching PowerpointDokumen9 halamanCoral Bleaching Powerpointapi-251801064Belum ada peringkat
- Biomes and EcosystemsDokumen31 halamanBiomes and EcosystemsFrance KennethBelum ada peringkat
- Eco-Column LabDokumen4 halamanEco-Column Labapi-450985871Belum ada peringkat
- Grassland EcosystemDokumen9 halamanGrassland EcosystemjasmineBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 19 1202494607519429 3Dokumen70 halamanChapter 19 1202494607519429 3Delfin ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Dictionary PDFDokumen95 halamanDictionary PDFFaiza Faizan100% (1)
- Weathering and ErosionDokumen17 halamanWeathering and ErosionArnav HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter5 Momentum and Impulse StudentDokumen25 halamanChapter5 Momentum and Impulse StudentHema JothyBelum ada peringkat
- BKP L 1 Introductiontosoilscience 141214011854 Conversion Gate01Dokumen23 halamanBKP L 1 Introductiontosoilscience 141214011854 Conversion Gate01qadriranaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 9 Desert Features and Landforms PDFDokumen4 halamanLecture 9 Desert Features and Landforms PDFaliBelum ada peringkat
- 03 BiosphereDokumen37 halaman03 BiosphereRonel A GaviolaBelum ada peringkat
- Meteorology and Natural Purification ProcessesDokumen50 halamanMeteorology and Natural Purification ProcessesJessa Mae ManzanoBelum ada peringkat
- 8 WeatheringDokumen21 halaman8 Weatheringnayvalente11Belum ada peringkat
- Field Report On Ecology, Biodiversity and Health Hazards of Shyamnagar Upazila, SatkhiraDokumen28 halamanField Report On Ecology, Biodiversity and Health Hazards of Shyamnagar Upazila, SatkhiraBodrud-Doza Zion0% (1)
- Acid and BaseDokumen20 halamanAcid and BaseChris MaBelum ada peringkat
- Sci Cheat SHeet For MOAT (Text)Dokumen1 halamanSci Cheat SHeet For MOAT (Text)whatthefailBelum ada peringkat
- Geography FinishedDokumen42 halamanGeography FinishedStork0% (1)
- Natural ResourcesDokumen25 halamanNatural ResourcesGOWRI M100% (1)
- Marine EnvironmentDokumen51 halamanMarine EnvironmentKhate Anne CanlasBelum ada peringkat
- P-N Junction DiodeDokumen32 halamanP-N Junction Diodesashi_s2Belum ada peringkat
- Metal Resources and Energy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsDari EverandMetal Resources and Energy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Ranking Universities in West Africa 2022Dokumen1 halamanTop 10 Ranking Universities in West Africa 2022Bright OtchereBelum ada peringkat
- Public Opinion On Idea of Digitalising Rural CommunityDokumen11 halamanPublic Opinion On Idea of Digitalising Rural CommunityINSTITUTE OF LEGAL EDUCATIONBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding My Benefits: Pre - Auth@Dokumen2 halamanUnderstanding My Benefits: Pre - Auth@Jonelle Morris-DawkinsBelum ada peringkat
- PulseoximetryDokumen2 halamanPulseoximetryRakshith NagarajaiahBelum ada peringkat
- 11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadDokumen3 halaman11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadS. TAMIZHANBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Drug Information 2000Dokumen66 halamanWHO Drug Information 2000Rajib ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- 2014-1 Mag LoresDokumen52 halaman2014-1 Mag LoresLi SacBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokumen26 halamanSafety Roles and ResponsibilitiesAlvin Garcia Palanca100% (1)
- NT90004212Dokumen58 halamanNT90004212Jelena ĆukBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 - Health-Optimizing Physical EducationDokumen13 halamanModule 3 - Health-Optimizing Physical EducationLazyy TanakaBelum ada peringkat
- Pork TocinoDokumen1 halamanPork TocinoMaria Ivz ElborBelum ada peringkat
- Task 1 FinalDokumen4 halamanTask 1 FinalAlᎥyⱥภBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster Readiness Risk Reduction: Quarter 2-Module 13: DRR-related Laws and PoliciesDokumen16 halamanDisaster Readiness Risk Reduction: Quarter 2-Module 13: DRR-related Laws and PoliciesUel Cabz LaquihonBelum ada peringkat
- Hira of RCC WorkDokumen2 halamanHira of RCC WorkGyanendra SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 India Accessibility Standards and Guidelines For Civil Aviation - EnglishDokumen110 halaman2022 India Accessibility Standards and Guidelines For Civil Aviation - EnglishDisability Rights AllianceBelum ada peringkat
- Project ProposalDokumen3 halamanProject ProposalSkrrtt SkrrttBelum ada peringkat
- Rockwool Slab Data Sheet - (ProRox Formerly RW Slab)Dokumen7 halamanRockwool Slab Data Sheet - (ProRox Formerly RW Slab)stuart3962Belum ada peringkat
- The Barrier To Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice Among Novice TherapistsDokumen11 halamanThe Barrier To Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice Among Novice TherapistsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- DSM 5Dokumen33 halamanDSM 5Grace Marie100% (2)
- Professional Self ConceptDokumen11 halamanProfessional Self Conceptgladz25Belum ada peringkat
- DR John Chew (SPMPS President) PresentationDokumen50 halamanDR John Chew (SPMPS President) PresentationdrtshBelum ada peringkat
- TorigwiltresumeDokumen2 halamanTorigwiltresumeapi-231010151Belum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen2 halamanDaftar PustakaameliaaarrBelum ada peringkat
- SRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterDokumen37 halamanSRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterBrandon Dempe100% (1)
- HRMDokumen20 halamanHRMSyeda AleenaBelum ada peringkat
- Field Visit PresentationDokumen33 halamanField Visit PresentationNib IndranilBelum ada peringkat
- RLE Module 3F Course Module and Procedure Guide 2Dokumen7 halamanRLE Module 3F Course Module and Procedure Guide 2KaiBelum ada peringkat