Practice Exam 1110 2012
Diunggah oleh
Latasha Steele0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
159 tayangan6 halamanThis document contains a practice exam for a surveying and GIS course. It includes 5 survey-related questions and provides context, instructions, and space for students to show their work. The questions cover topics like GPS systems, setting out building foundations, volume calculations, traverse adjustments, leveling, and more. Students are instructed to show units, use diagrams where helpful, and sign the document with their student number and name.
Deskripsi Asli:
Practice Exam
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document contains a practice exam for a surveying and GIS course. It includes 5 survey-related questions and provides context, instructions, and space for students to show their work. The questions cover topics like GPS systems, setting out building foundations, volume calculations, traverse adjustments, leveling, and more. Students are instructed to show units, use diagrams where helpful, and sign the document with their student number and name.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
159 tayangan6 halamanPractice Exam 1110 2012
Diunggah oleh
Latasha SteeleThis document contains a practice exam for a surveying and GIS course. It includes 5 survey-related questions and provides context, instructions, and space for students to show their work. The questions cover topics like GPS systems, setting out building foundations, volume calculations, traverse adjustments, leveling, and more. Students are instructed to show units, use diagrams where helpful, and sign the document with their student number and name.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
STUDENT NAME: ......................................................
STUDENT NUMBER: .....................................................
STUDENT SIGNATURE:.......................................................
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES
SCHOOL OF SURVEYING AND GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING
GMAT1110 SURVEYING & GIS
PRACTICE EXAM
Time allowed: 2 hours
Total number of questions: x
(note usually 4 but I have 5 example questions here)
Questions are not of equal value.
(The maximum mark (and part mark) of each question is listed at the end of the question.)
Answer all questions. Total marks 80
State the units of all numbers unless numbers are unitless.
Candidates may bring UNSW approved calculators, drawing instruments or
rules.
The following aids will be provided:
Examination book
Print your student number and name, and sign on the top right hand corner.
Answers must be written in ink. Except where they are expressly required,
pencils may only be used for drawing, sketching or graphical work.
SEE OVER
QUESTION 1
(a) The three (3) segments of the Global Positioning System are:
(i) space;
(ii) control; and
(iii) user.
Briefly describe each of the three (3) segments and how they interact together to provide position
for users.
(b) What is the difference between absolute and relative positioning? What do surveyors use for
highest precision surveying?
(c) How many satellites are required for a 3D position determination? Why?
(12 + 4 + 4 = 20 Marks)
QUESTION 2
You are required to set out the position of the foundations of a building to be located parallel to and
offset 2.00m from the west side boundary of your subject parcel of land. Council requires that the
front, north west corner of the structure should be at least 5.00 m from the front boundary which has a
bearing of 88. The internal angle of the NW corner of the block is 92 and the block is 30 metres deep
and 13m wide with right angles at the SW and SE corners. The building is rectangular in shape being
15m along the west side and 10 m along the north. You have an optical theodolite, tripod, and steel
tape in the field.
a) How do you ensure where the location of the cadastral boundary is?
b) Given that the cadastral boundary has been clearly identified, describe how you would setout
the building corners to ensure centimetre accuracy. Include diagrams to aid your answer.
c) What checks could you make to ensure that the building was correctly setout?
d) Describe the steps that you would then take to safeguard your setout work.
(4 + 8 + 4 + 4 = 20 Marks)
A cadastral discussion will be conducted during the revision session to illustrate more about cadastral
surveying.
QUESTION 3
(a) The RL of a proposed dam wall is 190.000. From a contour plan of the area the following
information is obtained:
RL
Area (m
2
)
150 1050
160 3185
170 11835
180 45715
190 158200
If the contour interval is 10 metres, what volume of water (in cubic metres) will the dam hold
when full?
(ANS: 1 403 600 m
3
, 1 261 733 m
3
(prismoidal))
(b) Compute the adjusted bearings of all lines in the closed link traverse below.
Bearing XP = 321 33 18
Bearing YQ = 88 16 17
P
A
Y
X
Q
B
Point Observed Angle
X
121 48' 17"
A
144 32' 53"
B
138 29' 44"
Y
169 02' 25"
(5 + 10 = 15 Marks)
(ANS: XA- 83 21 39, AB - 118 48 50, BY- 77 18 38, YQ - 88 16 17)
QUESTION 4
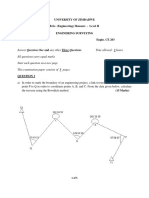
Upon arriving at the property development site you are working on, you find the surveyor has been
struck by lightning and lies dead on the ground! Luckily the field notes are undamaged. You pry the
field book out of the surveyors rigid hand and note that enough survey work has been completed for
you to takeover the calculations. (Good thing you did Craigs GMAT1110 course you think to
yourself). The field notes are given below:
Diagram not to scale. Diagram is a 2D plan representation. Not 3D!!
Using the field notes, compute the bearing and distance of all the property lines (dashed). Note that the
bearing of line AB is given.
Hints:
Compute the bearings of BC and CD.
Assuming any arbitrary coordinates for A such as (E100.000, N200.000), compute the
coordinates of B, C & D.
Compute coordinates of P, R & S from B, C & D respectively and then compute the bearings and
distances of the property lines.
Compute the area of the property APRS in m
2
using the zig zag method?
(20 + 5 = 25 marks)
`(ANS: AP - 356 26 20, 29.688, PR - 260 01 32, 22.585, RS -184 52 27, 22.891,
SA - 96 22 49, 26.195, Area = 632 m
2
)
QUESTION 5
(a) Describe the test for collimation error in an automatic level. How can you minimise this error in
the field?
(b) What is the Australian levelling datum based upon? What is it called?
(c) Why is a backsight or foresight more reliable than an intermediate sight? How could you make
an intermediate sight more reliable?
(d) i) Reduce the following level run using the rise and fall method.
ii) What is the misclose of this level run?
iii) Calculate RLs of each point.
BS IS FS Chainage (m) Remarks
1.981
BM A (RL 127.865)
1.324
p
*3.090 124.5 Overhead pipe
3.593 r
3.803 4.038 s
2.510 t
*2.943 162.7 Overhead pipe
4.096 v
3.291 BM B (RL 126.317)
*denotes inverted staff readings
(e) Level pegs for the following points on a building project are to be set out:
Car park 99.500
Factory floor 100.755
Paving - office entrance 99.300
Office floor 99.855
A BS of 1.752 is taken to a TBM (RL = 100.000). What staff readings are required to set the
pegs at the given levels?
(f) From the calculations from part (d) above calculate the gradient of the overhead pipe. Express
your answer as a ratio.
(3 + 2 + 2 + 7 + 4 + 2 = 20 Marks)
(ANS: d) Misclose 0.003m, RL OH Pipe ch 124.5 132.936, RL OH Pipe ch 162.7 132.554,
e) car park 2.252, Factory floor 0.997, Paving office entrance 2.452, Office floor 1.897,
f) Grade = 1:100)
FORMULAE
D
H
Gradient
A
=
| |
|
.
|
\
| +
=
+ + + =
=
A + A =
|
.
|
\
|
A
A
=
= A
= A
2
) ( 4 ) ( 3 ) ( 2 ) (
4
sin
tan
cos
sin
2 1
2 2
1
A A
d V
times four heights thrice heights twice heights once heights
grid of area unit
V
ZA D dist Hz
N E D
N
E
D N
D E
u
u
u
( )
+ + + = areas odd areas even A A
D
V
N
_ 2 _ 4
3
1
( ) ( ) areas ermediate int area Bottom area Top
CI
V _ 2 _ _
2
+ + =
misclose
l
ecision Pr Traverse
= _ where l = traverse distances
( ) ( ) ( )
c
C Sin
b
B Sin
a
A Sin
= =
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Advance SurveyingDokumen4 halamanAdvance Surveyingrohith51Belum ada peringkat
- 2 PSC Guide For Civil Engineers, DeojiDokumen708 halaman2 PSC Guide For Civil Engineers, DeojiLbs Dolidar100% (1)
- Plane Table SurveyingDokumen22 halamanPlane Table SurveyingParth AnajwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Survey - I - CT-114Dokumen2 halamanSurvey - I - CT-114Alimayar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying Model QuestionDokumen2 halamanSurveying Model QuestionMahesh Kumar K BBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Civil Engineering Questions and AnswersDokumen18 halamanBasic Civil Engineering Questions and AnswersrangaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-II CurvesDokumen42 halamanUnit-II CurvesPRAVIN KHANDVEBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Auto CadDokumen31 halamanIntroduction To Auto CadazhiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ZWCAD: Drawing Plane FiguresDokumen26 halamanIntroduction To ZWCAD: Drawing Plane FiguresKapil MannBelum ada peringkat
- SurveyorDokumen47 halamanSurveyorakash nair100% (3)
- Survey NotesDokumen25 halamanSurvey NotesSai VikasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 PDFDokumen22 halamanChapter 1 PDFJoylyn Agapay LorenBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering-Graphics PPSXDokumen284 halamanEngineering-Graphics PPSXGaurav GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Compass Traversing: Sharfan UpaulDokumen40 halamanCompass Traversing: Sharfan UpaulSumaira Majeed 09Belum ada peringkat
- Civil - I NotesDokumen22 halamanCivil - I NotesJanarthanan JaganBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Surveying SolutionsDokumen17 halamanAdvanced Surveying SolutionsKen Lim100% (1)
- Height of Instrument MethodDokumen17 halamanHeight of Instrument MethodkoppolusrinivasuluBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 05 TraverseDokumen16 halamanChapter 05 TraverseJac YuenBelum ada peringkat
- 436 33 Powerpoint Slides CHAPTER 1Dokumen69 halaman436 33 Powerpoint Slides CHAPTER 1Anonymous PeFQLw19Belum ada peringkat
- Levelling and SurveyingDokumen7 halamanLevelling and Surveyinghazmee100% (5)
- Laboratory Manual (CIV 210) Engineering Surveying (2018-19) (For Private Circulation Only)Dokumen76 halamanLaboratory Manual (CIV 210) Engineering Surveying (2018-19) (For Private Circulation Only)gyanendraBelum ada peringkat
- Survey Fly Levelling Field BookDokumen1 halamanSurvey Fly Levelling Field BookBipul MainaliBelum ada peringkat
- Mocktest Survey2Dokumen13 halamanMocktest Survey2Hemam Prasanta0% (1)
- Lecture 1 Survey 1Dokumen35 halamanLecture 1 Survey 1m saadullah khanBelum ada peringkat
- Job # 4. Base Line Measurement Using Jaderin's MethodDokumen6 halamanJob # 4. Base Line Measurement Using Jaderin's MethodUsama Bin YousufBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Engineering Survey: by Engr. Waqas HaroonDokumen67 halamanAdvanced Engineering Survey: by Engr. Waqas HaroonWaqas HaroonBelum ada peringkat
- CurveDokumen40 halamanCurveLakshmipathi GBelum ada peringkat
- Road Alignment and Setting OutDokumen32 halamanRoad Alignment and Setting OutJEAN DE DIEU MUVARA100% (1)
- Engineering Surveying ExamDokumen3 halamanEngineering Surveying Examaogu100% (2)
- Traversing Notes - Surveying II - Sudip Khadka - CivilengineeringDokumen37 halamanTraversing Notes - Surveying II - Sudip Khadka - CivilengineeringSudip KhadkaBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying & GeomaticsDokumen14 halamanSurveying & GeomaticsRenjith S Anand0% (1)
- LevelingDokumen50 halamanLevelingvinoBelum ada peringkat
- Theodolite TraversingDokumen6 halamanTheodolite TraversingEngr Ishfaque TunioBelum ada peringkat
- Survey 1 Lab Manual 2017-18Dokumen48 halamanSurvey 1 Lab Manual 2017-18M NANDITHA CIVIL STAFFBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To TheodoliteDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To TheodoliteJitendra Kumar SahBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying II Manual 10 11Dokumen34 halamanSurveying II Manual 10 11dskumar49Belum ada peringkat
- Surveying MCQDokumen18 halamanSurveying MCQSantosh Rai100% (1)
- Unit 2 Part 2Dokumen33 halamanUnit 2 Part 2Akram AliBelum ada peringkat
- Advance Surveying (CE4G) Computation of AreaDokumen40 halamanAdvance Surveying (CE4G) Computation of AreaChristine Joy AbricaBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying I Lab ManualDokumen33 halamanSurveying I Lab ManualRishabh RajBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Engg Mcqs 4Dokumen14 halamanHighway Engg Mcqs 4Zeeshan Ahmad0% (1)
- Concrete Form WorkDokumen3 halamanConcrete Form Workjack.simpson.changBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 CurvesDokumen47 halamanChapter 1 Curvesaduyekirkosu1scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Levelling PDFDokumen21 halamanLevelling PDFRahul Sinha100% (3)
- Chapter 5 - CurvesDokumen24 halamanChapter 5 - CurvesHassan YousifBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 - Supplement To FW1 - Compass Traverse and AdjustmentsDokumen6 halamanLecture 5 - Supplement To FW1 - Compass Traverse and AdjustmentsAndreaMiccaBautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundermental Surveying - Theory and Practice PDFDokumen28 halamanFundermental Surveying - Theory and Practice PDFSupriya Roy100% (1)
- Survey 1 Practical Report On Linear MeasDokumen8 halamanSurvey 1 Practical Report On Linear MeasanzaniBelum ada peringkat
- Earthwork Mass Diagrams Moved2Dokumen10 halamanEarthwork Mass Diagrams Moved2Shafiullah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Engineeringinterviewquestions Com RCC Structures Design Multiple Choice QuestionDokumen87 halamanEngineeringinterviewquestions Com RCC Structures Design Multiple Choice QuestionRajeev BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Engineering Drawing: CE-122 (For EEE Dept.) No. of Credit-0.75 1.5 Hours/weekDokumen48 halamanCivil Engineering Drawing: CE-122 (For EEE Dept.) No. of Credit-0.75 1.5 Hours/weekOpu Debnath100% (1)
- Surveying Lab ManualDokumen26 halamanSurveying Lab Manualandy_tatte32Belum ada peringkat
- Chain Corrections - NotesDokumen7 halamanChain Corrections - Notesprakash0% (2)
- L-1/T-2/CE Date: 30/01/2012Dokumen15 halamanL-1/T-2/CE Date: 30/01/2012SK Adnan IslamBelum ada peringkat
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level II Enginering Surveying MAY 2012 Engin. CE 203Dokumen5 halamanUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level II Enginering Surveying MAY 2012 Engin. CE 203Mercy SimangoBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical Methods SL P1 ADokumen16 halamanMathematical Methods SL P1 AAbbey HeBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics CXC 2011Dokumen12 halamanMathematics CXC 2011dggoode100% (1)
- 10th సోషల్ బిట్స్.జి సైదేశ్వర రావు.Dokumen2 halaman10th సోషల్ బిట్స్.జి సైదేశ్వర రావు.Navadeep NavadeepBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1Dokumen8 halamanAdditional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1lornarifaBelum ada peringkat
- PSSC Maths QP PDFDokumen27 halamanPSSC Maths QP PDFlalrajnesh1102100% (1)
- CVEN2303 - Workshop 6 Corrected SolutionDokumen5 halamanCVEN2303 - Workshop 6 Corrected SolutionLatasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - The Principle of WorkDokumen28 halamanLecture 4 - The Principle of WorkLatasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- CVEN3304 Lecture 1a SlideDokumen79 halamanCVEN3304 Lecture 1a SlideLatasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- Cven2302 Final Exam 2011Dokumen4 halamanCven2302 Final Exam 2011Latasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- Cven3501 Week 2 NotesDokumen13 halamanCven3501 Week 2 NotesLatasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- 1131calcprobonly MoodleDokumen53 halaman1131calcprobonly MoodleLatasha SteeleBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Instruções John Deere D170 (56 Páginas)Dokumen2 halamanManual de Instruções John Deere D170 (56 Páginas)Antonio CostaBelum ada peringkat
- MyNotes ConcreteDokumen18 halamanMyNotes ConcreteKarl Si AkoBelum ada peringkat
- Maison À BordeauxDokumen5 halamanMaison À BordeauxSpam TestBelum ada peringkat
- Jadual 6 MpobDokumen11 halamanJadual 6 MpobTipah HafizahBelum ada peringkat
- POH NAVAJO Pa-31Dokumen438 halamanPOH NAVAJO Pa-31Mantenimiento CMA68475% (4)
- Project Review 1 ScheduleDokumen1 halamanProject Review 1 ScheduleH R VALABelum ada peringkat
- ASTM C158-02 (2012) Strength of Glass by Flexure (Determination of Modulus of Rupture)Dokumen9 halamanASTM C158-02 (2012) Strength of Glass by Flexure (Determination of Modulus of Rupture)Cristian Perez100% (1)
- Role of QAQC Eng.Dokumen38 halamanRole of QAQC Eng.arunkumar100% (2)
- CP R70 Smart View Monitor Admin GuideDokumen106 halamanCP R70 Smart View Monitor Admin Guideoorhan41Belum ada peringkat
- Sagar Ovhalkar (Site)Dokumen2 halamanSagar Ovhalkar (Site)Dayanand WasateBelum ada peringkat
- Amplitude Shift KeyingDokumen3 halamanAmplitude Shift KeyingPurnendh ParuchuriBelum ada peringkat
- XRD ProcedureDokumen2 halamanXRD Procedurepullo123Belum ada peringkat
- Data SheetDokumen2 halamanData SheetAsalamEilujBelum ada peringkat
- Product Catalogue: Your Specialist in Flow DrillingDokumen64 halamanProduct Catalogue: Your Specialist in Flow DrillingВасяBelum ada peringkat
- Bends - Route SelectionDokumen6 halamanBends - Route SelectionanishsrBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Pressure Gauge XP2i PSI Data Sheet USDokumen5 halamanDigital Pressure Gauge XP2i PSI Data Sheet USAbdurrachman JalaludinBelum ada peringkat
- Dataproducts - LZR 1260 Laser Printer (1989)Dokumen6 halamanDataproducts - LZR 1260 Laser Printer (1989)Bobby ChippingBelum ada peringkat
- ASHRAE Fundamentals 2005 - SI Units - Extract of Tables PDFDokumen40 halamanASHRAE Fundamentals 2005 - SI Units - Extract of Tables PDFSufian SarwarBelum ada peringkat
- Passive Cooling of The Green Roofs Combined With Night-Time Ventilation and Walls Insulation in Hot and Humid RegionsDokumen25 halamanPassive Cooling of The Green Roofs Combined With Night-Time Ventilation and Walls Insulation in Hot and Humid Regionsshailesh gautamBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Surveys Cattell PDFDokumen16 halaman04 Surveys Cattell PDFBrenda MaggBelum ada peringkat
- Citrix Xenserver ® 6.0.2 Emergency Network Reset: Published Wednesday, 29 February 2012 1.0 EditionDokumen6 halamanCitrix Xenserver ® 6.0.2 Emergency Network Reset: Published Wednesday, 29 February 2012 1.0 EditionJuan CarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Heavy Duty 2.5 Ton Long Frame Floor Jack Product ManualDokumen3 halamanHeavy Duty 2.5 Ton Long Frame Floor Jack Product ManualChris Epler100% (2)
- Bloor Research On Data MigrationDokumen13 halamanBloor Research On Data MigrationivahdamBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Class 7 Geography WaterDokumen9 halamanNCERT Class 7 Geography Waterbalamurali_aBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation Rail Beam (Hoist Capacity 3 Ton)Dokumen4 halamanCalculation Rail Beam (Hoist Capacity 3 Ton)Edo Faizal2Belum ada peringkat
- Debug 1214Dokumen3 halamanDebug 1214Pandji AsmaraBelum ada peringkat
- Oilon 4A Monox en StandardDokumen16 halamanOilon 4A Monox en StandardWilbert Consuelo CotrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Using A GMR Effect Sensor To Measure The Current in A Wire by Means of Its Magnetic FieldDokumen6 halamanUsing A GMR Effect Sensor To Measure The Current in A Wire by Means of Its Magnetic FieldManeesha WijesingheBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inDokumen784 halamanPile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inTatiana RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- 545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresDokumen24 halaman545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresrichkidBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDari EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (21)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDari EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDari EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDari EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignDari EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Distillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationDari EverandDistillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsDari EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDari EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersBelum ada peringkat
- Lees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlDari EverandLees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Dari EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDari EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Troubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersDari EverandTroubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsDari EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsBelum ada peringkat
- The Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationDari EverandThe Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersDari EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersBelum ada peringkat
- A New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesDari EverandA New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesBelum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Halogens, Noble Gases and Lanthanides and Actinides | Children's Chemistry BookDari EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Halogens, Noble Gases and Lanthanides and Actinides | Children's Chemistry BookBelum ada peringkat
- Coulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesDari EverandCoulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesAjay Kumar RayBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesDari EverandPulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Fun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksDari EverandFun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsDari EverandHandbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsH. W. HibbottPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Cathodic Protection: Industrial Solutions for Protecting Against CorrosionDari EverandCathodic Protection: Industrial Solutions for Protecting Against CorrosionBelum ada peringkat
- Bioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringDari EverandBioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringGuang YangBelum ada peringkat
- High Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesDari EverandHigh Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesBelum ada peringkat