Discussion
Diunggah oleh
Muhd Akmal0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
26 tayangan2 halamanwater sample
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniwater sample
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
26 tayangan2 halamanDiscussion
Diunggah oleh
Muhd Akmalwater sample
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
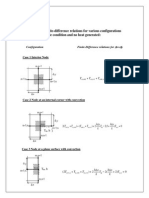
DISCUSSION
-first method (titration)
Based on the graph, notice that one equivalent point is achieve which means that at this point the
number of moles of [OH] ions is equal to number of moles of [H].The equivalence point is
divide by 2 to get the equation pH=pKa. This is shown by using Henderson-Hasselbalch
equation or at the expression for Ka
pH = pKa + log [base]/[acid]
where "base" and "acid" are the weak acid and its conjugate base.
At half equivalence point, the concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base are equal.
So that ratio is 1. The log of 1 is zero, so, the pH = pKa.
After analyzing the value of Ka, it concluded to be acetic acid. The unknown Ka value is is
1.061x10^-5 whereas actual value of Ka of acetic acid is merely different which is 1.76x10^-
5.As for the pKa value of the unknown acid is 4.98 whereas the pKa for acetic acid is 4.75.
-second method (half volume)
By using the second method ,the end point (point at which the uknown acid plus phenopthalein
indicator change colour from colorless to slightly pink. One commonly
used indicator is phenolphthalein, which is colorless in acidic and neutral solutions
but reddish pink in basic solutions. At the equivalence point, all the unknown acid present has
been neutralized by the added NaOH and the solution is still colorless. However, if we add just
one more drop of NaOH solution from the buret, the solution will immediately turn pink
because the solution is now basic.
The pKa of the uknown acid at the end point is 4.95(Ka= 1.122x10^-5) whereas the actual value
of the acetic acid is 4.75(Ka=1.76x10^-5) so the unknown acid may be the acetic acid and it only
differ in value that may come from the error from or lacks during conducting the experiments.
The main objective of the experiment is to determine the value of Ka and also to determine the
types of the unknown acid. However an error calculated based on the Ka is about 39.72% and
4.61% for pKa after comparing with theoretical value from the first method (titration) and about
4.04% for the pKa and 36.23% for the Ka of second method (half volume) .Therefore, a few
mistakes or lacks of awareness of the precautions that must be considered when conducting the
experiments may be the reasons.
First error may be come from the pH meter because it never gives the definite readings, as the
values are always changing rapidly.Thus one can never tell the accurate readings of pH
values.Therefore this will always affect the titration curve as well as pKa values which
correspond to the pKa values at half equivalence point.
Secondly, the error may be come from the parallax error,that happened during seeing the
reading of burette. The eyes should be perpendicular to the reading scale of the burette so the
reading of the burette made from this experiment met with parallax error that effects the results.
In addition,the pH electrode might have come into contact with the magnetic stirrer.Therefore
a problem might be encountered during the readings of pH value from the pH meter.
CONCLUSION
The experimental value for pKa and Ka of the unknown acid is 4.98 and 1.061x10^-5 for the first
method(titration) and for the second method (half volume) the value for pKa and Ka is 4.95 and
1.122x10^-5.theoretically the value for pKa and Ka for the unknown acid which is believed to be
acetic acid are 4.75 and 1.76x10^-5. An error calculated based on the Ka is about 39.72% and
4.61% for pKa after comparing with theoretical value from the first method (titration) and about
4.04% for the pKa and 36.23% for the Ka of second method (half volume) .Therefore, there is
only slighty different from the theoretical value compared from the experimental values for both
method.hence the unknown acid is identified as acetic acid and the value determined by the half
volume method is more accurate method.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CrystallizationDokumen37 halamanCrystallizationMuhd Akmal50% (2)
- Production of WhiskeyDokumen4 halamanProduction of WhiskeyMuhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- Liquid Liquid ExtractionDokumen55 halamanLiquid Liquid ExtractionMuhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 2Muhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2D Heat ConductionDokumen2 halamanTutorial 2D Heat ConductionMuhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- InductiveDokumen9 halamanInductiveMuhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- Chemsketch TutorialDokumen4 halamanChemsketch TutorialMuhd AkmalBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions PS2Dokumen9 halamanSolutions PS2Raeza Praditya HeryantoroBelum ada peringkat
- ochmII Alcohol Groiup ReactionDokumen8 halamanochmII Alcohol Groiup Reactionptc2win4cahBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Pressure Manometer2 2013Dokumen3 halamanTutorial Pressure Manometer2 2013Muhd Akmal100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Porosity or PermeabilityDokumen30 halamanPorosity or PermeabilitytabibkarimBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 41 Lab Formal Report 01 - Preparation of Buffers & Amino Acids As AmpholytesDokumen13 halamanChem 41 Lab Formal Report 01 - Preparation of Buffers & Amino Acids As AmpholytesFaith VillahermosaBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Manual: 2700 Series Benchtop MetersDokumen60 halamanInstruction Manual: 2700 Series Benchtop Meterssebastian florez sernaBelum ada peringkat
- Denver Instruction & Operation ManualDokumen24 halamanDenver Instruction & Operation ManualestramilsolutionBelum ada peringkat
- Italian - L'Equilibrio Acido Base - Christopher VaseyDokumen139 halamanItalian - L'Equilibrio Acido Base - Christopher VaseyDino Contenti50% (2)
- Review of Related Literature Align WithDokumen4 halamanReview of Related Literature Align WithJoshua VidalBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction - Inorganic Chemistry: Biology 2121Dokumen20 halamanIntroduction - Inorganic Chemistry: Biology 2121shyamBelum ada peringkat
- Ash Well 1957Dokumen33 halamanAsh Well 1957Eko Isro RiyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Ionization of WaterDokumen18 halamanIonization of WaterrodneyperuBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Base Equilibrium Practice TestDokumen3 halamanAcid Base Equilibrium Practice Testapuszis100% (2)
- Advanced Placement Chemistry TestDokumen15 halamanAdvanced Placement Chemistry TestBobBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure Asphalt Slurry Seal Microsurfacing Global enDokumen24 halamanBrochure Asphalt Slurry Seal Microsurfacing Global enعبد الرحيم كريم حسينBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calibrate and Use A PH Meter - 14 Steps (With Pictures)Dokumen4 halamanHow To Calibrate and Use A PH Meter - 14 Steps (With Pictures)Shumraiz MBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry and Energy Storage Systems Module 1 Notes 2018Dokumen24 halamanElectrochemistry and Energy Storage Systems Module 1 Notes 2018Mohith BC100% (1)
- Water Pollution ProjectDokumen58 halamanWater Pollution ProjectLaxmitej ManchikantiBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chem Exam 1 (CH1-3) 2Dokumen4 halamanAnalytical Chem Exam 1 (CH1-3) 2Jules BrunoBelum ada peringkat
- Complexometry TitartaionDokumen50 halamanComplexometry TitartaionHaritBelum ada peringkat
- 4500-F Fluoride : 4-82 Inorganic Nonmetals (4000)Dokumen8 halaman4500-F Fluoride : 4-82 Inorganic Nonmetals (4000)ShadiaMilenaOquendoMuñozBelum ada peringkat
- Reference Guide To Manual Processing of INDUSTREX Films: Recommended Chemicals and Mixing InstructionsDokumen2 halamanReference Guide To Manual Processing of INDUSTREX Films: Recommended Chemicals and Mixing InstructionsHz albertoBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 1 L1 W1Dokumen51 halamanChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Standardization of A Primary Standard and Determination of Concentration by Acid-Base TitrationDokumen2 halamanStandardization of A Primary Standard and Determination of Concentration by Acid-Base TitrationTheophilus FrimpongBelum ada peringkat
- CSST-10X Hazcom GuideDokumen74 halamanCSST-10X Hazcom GuideLuis Rafanan AbiogBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of H PO or Citric Acid Using Volumetric and Ph-Metric TitrationsDokumen2 halamanDetermination of H PO or Citric Acid Using Volumetric and Ph-Metric TitrationsMayfurBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 4 PDFDokumen7 halamanExperiment 4 PDFsaiBelum ada peringkat
- NSC CHEMISTRY Grade 9 June 2017Dokumen42 halamanNSC CHEMISTRY Grade 9 June 2017Julesa JamesBelum ada peringkat
- Mowiol Brochure en KSEDokumen105 halamanMowiol Brochure en KSEmorrisnorrisBelum ada peringkat
- CoC Oral Exam Preparation 6-Boiler Operation and WTDokumen5 halamanCoC Oral Exam Preparation 6-Boiler Operation and WTThusitha DalpathaduBelum ada peringkat
- Is 3025 23 1986 PDFDokumen7 halamanIs 3025 23 1986 PDFSunny RohillaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 6 Semester 2Dokumen121 halamanChemistry Form 6 Semester 2Thivyaapriya SambamoorthyBelum ada peringkat