Prelim Part Table
Diunggah oleh
Shawn LeeHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Prelim Part Table
Diunggah oleh
Shawn LeeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
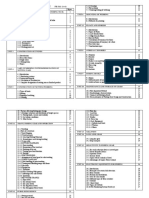
Specific
Objective
s
Contents
Teaching
/Learning
Activities
Values
Infused
Time
Allotment
Referenc
e
Evaluatio
n
CHAPTE
R 1
Introducti
on
1.1
History of
Organic
Chemistr
y
a. Michel
Chevreul
b.
Friedrch
Wohler
1.2
Sources
of
Organic
Compou
nd
a.
Isolation
from
Nature
b.
Synthesi
s in the
Laborato
ry
c. Other
Important
Sources
1.3
Function
al
Groups
a.
Alcohols
b.
Aldehyde
s
c.
Amines
d.
Carboxyli
Logical
Presenta
tion
Listening
Skills
1.5 hours Carrey F.
().Organi
c
Chemistr
y 6th
Edition
Smith J.
G.
().Organi
c
Chemistr
y
Internatio
nal
Edition
McMurry.
J.
().Funda
mentals
of
Organic
Chemistr
y 5th
Edition
Gilbert,
J. &
Martin,
S.
().Experi
mental
Organic
Chemistr
y 2nd
Edition
Solomon
s, T.W.
().Funda
mentals
of
Organic
Chemistr
y 4th
c Acid
e. Esters
f. Ethers
g. Alkyl
Halides
h.
Ketones
i. Nitriles
j.
Sulfonic
Acids
k. Thiols
1.4
Structure
s of
Organic
Compou
nds and
Lewis
Electron
Dot
Formula
1.5
Hybridiza
tion
a. Types
of Hybrid
Orbital
A. sp3
hybrid
orbital
B. sp2
hybrid
orbital
C. sp
hybrid
orbital
b. Types
of
Bonding
A.
Sigma
bond
B. Pi
Bond
Edition
Pasto et
al.,
().Experi
ments
and
Techniqu
es in
Organic
Techniqu
es
CHAPTE
R 2
Hydrocar
bons
(Alkanes
1.5 hours Written
Quiz on
Chapter
1
and
Cycloalk
anes)
2.1
Introducti
on and
Structure
of
Hydrocar
bons
a.
Categori
es of
Organic
Compou
nds
A.Aliphati
c
Compou
nds
B.
Aromatic
Compou
nds
C
Cyclic
Compou
nds
D.
Heterocy
clic
Compou
nds
b. Types
of
Hydrocar
bons
A.
Saturate
d
B.
Unsatura
ted
c.
Families
of
Hydrocar
bons
A.
Alkanes
B.
Alkenes
C.
Alkynes
D.
Aromatic
Hydrocar
bons
d. Types
of
Carbon
Atoms
A.
Quaterna
ry
Carbons
B.
Tertiary
Carbons
C.
Seconda
ry
Carbons
D.
Primary
Carbons
e.
Structura
l
Formulas
A.
Straight
chain
alkanes
B.
Branche
d chain
alkanes
2.2
Definition
of
Isomeris
m
a. Types
of
Isomers
A.
Constituti
onal
Isomers
B.
Geometri
c
Isomers
2.3
Characte
ristics of
alkanes
and
cycloalka
nes
2.4
Nomencl
ature of
alkanes
and
cycloalka
nes
2.5 Cis-
Trans
Isomeris
m in
Cycloalk
anes
2.6
Alkanes
A.
Physical
Propertie
s of
Alkanes
B.
Boiling
Point and
Melting
Point
2.7
Reaction
s
A.
Combusti
on
B.
Halogen
ation
2.8
Hydrocar
bon
Resourc
es
A.
Natural
Gas and
Petroleu
m
B. Coal
CHAPTE
R 3
Hydocar
bons
(Alkenes
and
Alkynes)
3.1
Characte
ristics of
Alkenes
and
Alkynes
3.2
Structure
and
Nomencl
ature of
Alkenes
and
Alkynes
3.3
Stereoiso
merism
of
Alkenes
A. Cis
isomer
B.
Trans
isomer
3.4
Propertie
s of
Alkenes
and
Alkynes
3.5
Types of
Reaction
s
1.5 hours Written
Quiz on
Chapter
2
common
to
Alkenes
A.
Addition
Reaction
B.
Eliminati
on
C.
Substituti
on
D.
Rearrang
ement
3.6
Definition
of
Halogen
ation,
Hydratio
n,
Hydroge
nation,
Oxidation
3.7
Meaning
of
Polymeri
zation
3.8
Types of
Synthetic
Polymers
A.
Addition
Polymers
B.
Condens
ation
Polymers
3.9
Classific
ation of
Polymers
A.
Elastome
rs
B.
Fibers
C.
Plastics
3.10
Important
Alkenes
and
Alkynes
Prelimina
ry Exams
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Parenteral PPT (Part-4)Dokumen64 halamanParenteral PPT (Part-4)monoj5859Belum ada peringkat
- Canons 14 17Dokumen80 halamanCanons 14 17Shawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Fishing Gear Technology Fe-311Dokumen29 halamanFishing Gear Technology Fe-311Piyush Ranjan Behera100% (1)
- Canon 10-13Dokumen58 halamanCanon 10-13Shawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Polyester Fibers: Fig.1: Production of Polyethylene TerephthalateDokumen12 halamanPolyester Fibers: Fig.1: Production of Polyethylene TerephthalateShailendra Mishra100% (1)
- Lecture 3-Leather Finishing MaterialsDokumen101 halamanLecture 3-Leather Finishing MaterialsJULKAR NAYEENBelum ada peringkat
- Canons 20 22Dokumen58 halamanCanons 20 22Shawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Canons 18 19Dokumen36 halamanCanons 18 19Shawn Lee100% (1)
- Writ of Kalikasan and Writ of Continuing Mandamus DigestsDokumen12 halamanWrit of Kalikasan and Writ of Continuing Mandamus DigestsShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Duties To SocietyDokumen10 halamanDuties To SocietyShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Not Treasonous:: Title One I. Crimes Against National SecurityDokumen6 halamanNot Treasonous:: Title One I. Crimes Against National SecurityShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Corpo DigestDokumen8 halamanCorpo DigestShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Plaintiff-Appellee vs. vs. Defendant-Appellant Sabiniano Balagtas Francisco R. Sotto Solicitor General Felix V. Makasiar Solicitor August M. AmoresDokumen7 halamanPlaintiff-Appellee vs. vs. Defendant-Appellant Sabiniano Balagtas Francisco R. Sotto Solicitor General Felix V. Makasiar Solicitor August M. AmoresShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- ExamDokumen3 halamanExamShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law I: San Beda College Mendiola, Manila College of LawDokumen10 halamanConstitutional Law I: San Beda College Mendiola, Manila College of LawShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 170740-2015-Republic v. Heirs of BorbonDokumen11 halaman170740-2015-Republic v. Heirs of BorbonShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Petitioners vs. vs. Respondents: en BancDokumen63 halamanPetitioners vs. vs. Respondents: en BancShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Republic Vs Castellvi, 58 SCRA 336Dokumen22 halamanRepublic Vs Castellvi, 58 SCRA 336Add AllBelum ada peringkat
- 171045-2015-Secretary of The Department of Public WorksDokumen67 halaman171045-2015-Secretary of The Department of Public WorksShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 124079-1998-Municipality of para Aque v. V.M. RealtyDokumen10 halaman124079-1998-Municipality of para Aque v. V.M. RealtyShawn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Unika Hole SawDokumen21 halamanUnika Hole SawQin DieselBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer Project For Class 12thDokumen11 halamanPolymer Project For Class 12thVinod KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- ITW Product Catalog33 PDFDokumen1 halamanITW Product Catalog33 PDFjohnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Pharmaceutics Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Dokumen28 halamanChapter 5 Pharmaceutics Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Ayodele olumideBelum ada peringkat
- Petroleum Industry Life CycleDokumen53 halamanPetroleum Industry Life CycleAinnur Syabiha100% (1)
- Glazing ReportDokumen7 halamanGlazing ReportMayanka PopliBelum ada peringkat
- Polyflon Ptfe D-210: Aqueous DispersionDokumen1 halamanPolyflon Ptfe D-210: Aqueous DispersionRajanSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Polyethylene TerephthalateDokumen4 halamanPolyethylene TerephthalateClarisse Joyce GenerBelum ada peringkat
- NovellDokumen6 halamanNovellEdwin JonatanBelum ada peringkat
- The Tara Handpump: Dhaka-BangladeshDokumen178 halamanThe Tara Handpump: Dhaka-BangladeshLovasoa Mbolamanana Joseph AndrianirianaBelum ada peringkat
- FHWA-low-temp Crack StudyDokumen4 halamanFHWA-low-temp Crack StudyRohan parmarBelum ada peringkat
- Protein SurfatanDokumen19 halamanProtein Surfatanmeilana23Belum ada peringkat
- CIDEX OPA Technical Info AP-2000304Dokumen8 halamanCIDEX OPA Technical Info AP-2000304Ahmed EljenanBelum ada peringkat
- Philips FR M 8928444 GC9220Dokumen126 halamanPhilips FR M 8928444 GC9220Bart KleijwegtBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Blanket MSDSDokumen7 halamanFire Blanket MSDSSanthoshBelum ada peringkat
- Características de Las Mangueras y Acoplamientos Dayco (Inglés)Dokumen59 halamanCaracterísticas de Las Mangueras y Acoplamientos Dayco (Inglés)Hono LocoBelum ada peringkat
- Botmed Herbs MelDokumen14 halamanBotmed Herbs Melapi-26938624100% (1)
- Ch3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Dokumen51 halamanCh3e4 Stereoselective Synthesis MW Handout Reorganised 021111Kethavath VenkateshBelum ada peringkat
- Pump 84962 B Section c8 Page 240b HydrauDokumen8 halamanPump 84962 B Section c8 Page 240b Hydrauleaw81Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - SemisolidDokumen20 halamanChapter 4 - SemisolidHely PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Organization Replication Repair: DR S K BansalDokumen71 halamanOrganization Replication Repair: DR S K BansalSanjiv BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Fixings & Supports: Section GuideDokumen9 halamanFixings & Supports: Section GuideMihaila BogdanBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of PreservationDokumen7 halamanMethods of PreservationmtcengineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Bison Power Adhesive BisoniteDokumen1 halamanBison Power Adhesive BisoniteRadu ConstantinBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 18 TestDokumen10 halamanTopic 18 TestumerBelum ada peringkat
- Hairy Root CultureDokumen16 halamanHairy Root Culture121321055008Belum ada peringkat