ANAT1014 Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Cycle 26-09-11 Lecture Slides-1
Diunggah oleh
ConstAntinos0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan23 halamanp
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inip
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
24 tayangan23 halamanANAT1014 Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Cycle 26-09-11 Lecture Slides-1
Diunggah oleh
ConstAntinosp
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 23
ANAT1014
Cardiovascular system and cardiac cycle
Dr Abigail Rickard
26
th
September 2011
Reset your response device..
1. Press and release Go or Ch
button
2. While light flashes red and green
3. Press 4 then 1 to set channel
to 41
4. Then press Go or Ch
5. Press and release 1/A light will
flash yellow to confirm
6. If this doesnt happen try again.
Overview
What is the cardiovascular system?
What are the features of the heart?
What does the heart do?
How does the heart function?
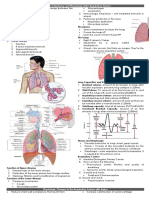
Components of the cardiovascular system
Heart
Aorta
Vena Cavae
Capillaries
Venules
Systemic circulation
Cardiac cycle - Blood flow through the heart
Superior & inferior vena cave
Pulmonary artery/vein
Aorta
Bicuspid and tricuspid valves
Right/Left atrium/ventricle
Diastole/Systole
Valves
Valves in action
The bicuspid valve is between...
1 2 3
57%
0%
43%
1. The left atrium &
left ventricle
2. The right atrium &
right ventricle
3. The left ventricle &
systemic arch
Coronary circulation
Coronary ostia
Left coronary artery
Right coronary artery
Coronary sinus
Myocardial energy metabolism
High dependence on
aerobic metabolism
(70-80% available O
2
at rest)
Primary metabolic
substrates are fatty acids
Glycogen and lactate
Heart muscle types
Purkinje Fibres Atrial Cells Ventricular cells
Shape Long and broad Elliptical Long and narrow
Length (m) 150-200 ~ 20 50-100
Diameter (m) 35-40 ~ 5 10-25
Intercalated disc/
gap-junctions
Very prominent;
abundant gap
junctions; fast end-
to-end transmission
Side-to-side as well
as end-to-end
transmission
Prominent end-to-
end transmission
Ventricular myocyte features
Cross-striations (myofibrils)
Thick myosin filaments
Thin actin filaments
Cross bridge formation
(cycling)
Mitochondria
What features allow for the rapid
electrical conductance in purkinje
fibres?
1 2 3 4
0% 0%
50% 50%
1. Mitochondria
2. Myosin and actin
filaments
3. Intercalated discs
and gap junctions
4. I dont know, I
wasnt listening
Cardiac cycle - Electrical activity across the heart
Sinoatrial node (SAN)
Atrioventricular node (AVN)
Purkinje fibres
Wave of depolarisation
Repolarisation/
Hyperpolarisation
Resting membrane
potential
ECG- P, QRS, T waves
Cardiac electrical activity
Pacemaker Cell (SA node)
Intrinsic depolarisation
known as automaticity
N.B. Membrane potential is
never flat
Ca
2+
- induced Ca
2+
release
from intracellular Ca
2+
storage organelle called
endoplasmic reticulum
- 65 mV
- 40 mV
Cardiac electrical activity
Ventricular Cell
Phase 0 - RAPID inward Na
+
current
(Upstroke, depolarisation)
Phase 1 Transient outward K
+
current
(Notch)
Phase 2 Outward Ca
2+
current
(Plateau)
Phase 3 Fast and Slow outward
rectifier K
+
currents (repolarisation)
Phase 4 Resting membrane potential
N.B. Notice upstroke of action potential is
FLAT
- 80 mV
The movement of which ions are
responsible for the upstroke of the
ventricular action potential (Phase 1)?
1 2 3 4
25%
0%
13%
63%
1. Na
+
2. Ca
2+
3. K
+
4. Mg
2+
Cardiac electrical activity
Whole heart
P wave - Atrial depolarisation
PR interval - AV nodal conduction
QRS complex - Ventricular
Depolarisation
T Wave - Ventricular
repolarisation
QT interval - Ventricular
depolarisation and repolarisation
P
R
Q S
T
PR
interval
QT
interval
Which of the following represents the
time for conduction across the AV
node?
1. P-R interval
2. Q-T interval
3. R-R interval
4. T wave
Summary
Features of the cardiovascular
system
Location and morphology of the
heart
Cardiac cycle
Electrical activity of the heart
Next time.....
Regulation of cardiac cycle
Blood flow and pressure
Malfunctions and their consequences
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Subsea Master Thesis FINALDokumen80 halamanSubsea Master Thesis FINALConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Assignment & Practicals OverviewDokumen5 halamanAssignment & Practicals OverviewConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- 99020115Dokumen13 halaman99020115ConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Economics Hydraulic Fracturing Using Wall-Building AdditivesDokumen7 halamanEconomics Hydraulic Fracturing Using Wall-Building AdditivesConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Repository RafK PublicDokumen64 halamanRepository RafK PublicConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- 01 Borre PaaskeDokumen23 halaman01 Borre PaaskeConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- 2012.10.11 APSG28 Jonathan Martin Subsea Positioning Through The Ages FinalDokumen62 halaman2012.10.11 APSG28 Jonathan Martin Subsea Positioning Through The Ages FinalConstAntinos100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- ANAT1014 Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Cycle 26-09-11 Lecture Slides-1Dokumen23 halamanANAT1014 Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Cycle 26-09-11 Lecture Slides-1ConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Root Cause Failure Analysis Rev 2Dokumen69 halamanRoot Cause Failure Analysis Rev 2clcoolleo100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Redundancy in Steel Frames With Masonry Infill Walls: Hosein Ghaffarzadeh, Robab Naseri GhalghachiDokumen7 halamanRedundancy in Steel Frames With Masonry Infill Walls: Hosein Ghaffarzadeh, Robab Naseri GhalghachiConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- 16 V 01 P 0024Dokumen7 halaman16 V 01 P 0024ConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- ALWCDokumen3 halamanALWCConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Q 21-27Dokumen5 halamanQ 21-27ConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- WG Graduate BrochureDokumen6 halamanWG Graduate BrochureConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- NSTM Chapter 582 Mooring TowingDokumen150 halamanNSTM Chapter 582 Mooring Towingvzagkas50% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Slowly-Varying 2. Order Wave Forces On Large StructuresDokumen34 halamanSlowly-Varying 2. Order Wave Forces On Large StructuresConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Examples of General Exam QuestionsDokumen1 halamanExamples of General Exam QuestionsConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Solution 2009-10gDokumen9 halamanExam Solution 2009-10gConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Exam Solution 2009-10gDokumen9 halamanExam Solution 2009-10gConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Exam Questions Trainingr34Dokumen6 halamanExam Questions Trainingr34ConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- 2010 Soils Exam PaperDokumen5 halaman2010 Soils Exam PaperConstAntinosBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDokumen20 halamanCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBRITNEY ALEXANDRA VERMINSHUBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic and Pulmonary CirculationDokumen13 halamanSystemic and Pulmonary CirculationLuis eduardo bolaño vilaBelum ada peringkat
- HP 1 Practice ProblemsDokumen20 halamanHP 1 Practice ProblemshekoBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsDokumen5 halamanPhysiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsGustavo TejerinaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Module WK 1-2Dokumen8 halamanGrade 9 Module WK 1-2Llena Grace GloryBelum ada peringkat
- Echo A. A.made PermadiDokumen1 halamanEcho A. A.made PermadiIndrayaniBelum ada peringkat
- HLTAAP002 CardiovascularDokumen56 halamanHLTAAP002 CardiovascularJesse SimonBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- (Harsh Mohan) Textbook of Pathology (6th Ed.) - 433-476Dokumen44 halaman(Harsh Mohan) Textbook of Pathology (6th Ed.) - 433-476Ananta DasBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFDokumen4 halamanScience Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFFarah Sofea Razali91% (11)
- Lvot o IiDokumen179 halamanLvot o Iimona300Belum ada peringkat
- Kuliah 1 OVERVIEW Titipan Dari (DR Pipiet)Dokumen465 halamanKuliah 1 OVERVIEW Titipan Dari (DR Pipiet)Gangsar DamaiBelum ada peringkat
- Four Chambers of The HeartDokumen7 halamanFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Sounds: Pabish Joe P S KGMCDokumen29 halamanHeart Sounds: Pabish Joe P S KGMCsangeedhBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMDokumen3 halamanConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMSparsh MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular System PDFDokumen9 halamanStructure and Function of The Cardiovascular System PDFteuuuuBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Case Classification For The National Birth Defects Prevention StudyDokumen9 halamanGuidelines For Case Classification For The National Birth Defects Prevention Studyjorge davidBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of The Circulatory SystemDokumen47 halamanEvolution of The Circulatory SystemWwwanand111Belum ada peringkat
- Science Quarter 1-LIVING THINGS: Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDokumen32 halamanScience Quarter 1-LIVING THINGS: Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemRobert Cruz67% (6)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Blood Clotting MechanismDokumen20 halamanThe Blood Clotting Mechanismzynab123Belum ada peringkat
- 112 NotesDokumen9 halaman112 NotesDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDokumen16 halamanCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDokumen8 halamanCardiovascular Systemomar farooqBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart FailureDokumen45 halamanEvaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart FailureFreddy PanjaitanBelum ada peringkat
- Autopsy SlaughterbeckDokumen7 halamanAutopsy SlaughterbeckWilfried HandlBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 23Dokumen171 halamanChapter 23Arpit PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System ConditionsDokumen4 halamanCardiovascular System ConditionsNinjaBelum ada peringkat
- TEE Surgical Decision Making - June2020 PDFDokumen43 halamanTEE Surgical Decision Making - June2020 PDFalina100% (1)
- 224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFDokumen9 halaman224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFB. ChillBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 1 Life - ProcessesDokumen32 halamanChapter - 1 Life - ProcessesAadil MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy (Eng)Dokumen194 halamanAnatomy (Eng)Saeed SaeedBelum ada peringkat