Heliobacter Pylori
Diunggah oleh
shailesh2840 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
49 tayangan1 halamanMEDICAL BOOKS
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniMEDICAL BOOKS
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
49 tayangan1 halamanHeliobacter Pylori
Diunggah oleh
shailesh284MEDICAL BOOKS
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
Patient Information Cut Out And Keep Section
AUTHOR: PROFESSOR JOHN MURTAGH
!
Copyright of Professor John Murtagh and Australian Doctor. This patient handout may be photocopied or printed out by a doctor free of charge for patient information purposes.
Helicobacter pylori
IT is now recognised that several
disorders of the upper GI tract
are caused by infection with
Helicobacter pylori. Some years
ago Dr Barry Marshall, an Aus-
tralian gastroenterologist, postu-
lated that peptic ulcers and gas-
tritis might be caused by
bacteria. He was eventually
proved to be correct.
What is H pylori?
H pylori is a bacterium that
resides on the inside lining of the
stomach. It has special features
that allow it to survive in the
highly acidic environment of the
stomach. In some people it may
lie dormant and cause no prob-
lem.
However, in certain circum-
stances it has the ability to pene-
trate the protective lining of the
stomach, infect it and damage it
by the production of special irri-
tating chemicals. This then
allows the acid in the stomach
to further upset the damaged
area.
What disorders does H pylori
cause?
H pylori affects both the
stomach and duodenum, the
short part of the small bowel
which receives food from the
stomach.
These disorders include:
n
Stomach ulcers (also called gas-
tric ulcers).
n
Gastritis, which is inflamma-
tion of the stomach lining.
n
Duodenal ulcers.
n
Some stomach cancers.
The common factor in these
conditions is inflammation of the
lining of the stomach. It does not
appear to cause gastro-
oesophageal reflux disease, heart-
burn or dyspepsia in the absence
of an ulcer.
How common is H pylori and
who gets it?
The presence of H pylori in
the stomach is common. It is
estimated that about 40-50% of
people older than 40 are
infected with H pylori but many
have no symptoms or problems.
Older people are more likely to
develop problems as their
immune system becomes less
effective with age.
How is H pylori acquired?
It appears that it is usually
acquired in childhood before
the age of 10. Infection follows
direct contact with other chil-
dren whose attenti on to
hygiene has probably been
poor.
The transmission includes
sharing food or eating utensils
and kissing. There seems to be
little risk of transmission between
adults or from adults to children
as long as good hygiene is prac-
tised.
There is no evidence that ani-
mals including household pets or
infected food or water are reser-
voirs of infection.
How is H pylori infection
diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made by one
of several special tests that are
available.
Urea breath test
In this relatively simple test a
small dose of specially prepared
urea is swallowed and the
breath is analysed a short time
later for carbon dioxide gas.
The bacteria have the unique
ability to make this chemical
alteration.
Gastroscopy
During a gastroscopy, samples
from the lining of the stomach
can be collected and tested for
H pylori. A pathologist can
identify the presence of the
bug in the biopsy specimen.
Blood test
A specific blood test can diag-
nose the presence or past his-
tory of infection but at this stage
it is not as useful as the other
tests.
How is H pylori treated?
Treatment is unusual and
complex because a combination
of drugs is needed to eradicate
the bugs which are good at
hiding under the mucous lining
of the stomach. At this stage
there is no single drug that has
been found effective.
There are several different
effective drug combinations,
which usually include two antibi-
otics (eg, tetracycline, metron-
idazole, amoxycillin, clar-
ithromycin) and an ulcer-healing
drug.
This modern treatment is gen-
erally effective. An eradication of
H pylori in about 80-90% of
cases can be expected. The
chances of becoming reinfected
after successful treatment are low.
What are the usual treatment
rules?
n
All the drugs should be taken
as directed.
n
It is necessary to take the drugs
for 7-14 days.
n
You should not drink alcohol
during treatment.
n
Side effects are common.
n
Follow-up testing is essential.
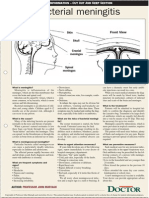
Helicobacter pylori
microscope
appearance
Stomach
Gastritis
Stomach ulcer
Duodenal
ulcer
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Helicobacter Pylori, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokumen7 halamanHelicobacter Pylori, Diagnosis and TreatmentTrifan_DumitruBelum ada peringkat
- Peptic Ulcers: H. Pylori andDokumen8 halamanPeptic Ulcers: H. Pylori andbivhutibhusanaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori) Is A BacteriumDokumen2 halamanHelicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori) Is A BacteriumnasirkgnBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?Dokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?Ifah Inayah D'zatrichaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori:: SymptomsDokumen6 halamanHelicobacter Pylori:: SymptomsZaid AbdulqadirBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Refrat H.pyloriDokumen35 halamanBahan Refrat H.pyloriTitis Kusuma AnindyaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori: What Is Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Who Is Affected by It?Dokumen3 halamanHelicobacter Pylori: What Is Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Who Is Affected by It?BBD BBDBelum ada peringkat
- Completed Eng ResearchDokumen9 halamanCompleted Eng ResearchRachna KhatriBelum ada peringkat
- Gastric UlcerDokumen2 halamanGastric Ulcersaby abbyBelum ada peringkat
- Elicobacter-Pylori: Jump To Nav IgDokumen6 halamanElicobacter-Pylori: Jump To Nav IgmenkadudumenkaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori) Infection FactsDokumen38 halamanHelicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori) Infection FactsPieter SteenkampBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori (H - Pylori)Dokumen10 halamanHelicobacter Pylori (H - Pylori)Zaid AbdulqadirBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori Infection and TreatmentDokumen3 halamanHelicobacter Pylori Infection and Treatmentto van quyenBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter PyloriDokumen33 halamanHelicobacter Pyloritummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (6)
- H.pylori ReportDokumen11 halamanH.pylori ReportbatoulezoonaseraldeenBelum ada peringkat
- Infection Of Helicobacter Pylori, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandInfection Of Helicobacter Pylori, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- H. Pylori Gastritis Diagnosis and TreatmentDokumen27 halamanH. Pylori Gastritis Diagnosis and TreatmentHeersh Raof100% (1)
- Prof. Abbas HayatDokumen37 halamanProf. Abbas HayatAmirabbas SaffariBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?Dokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?toantran87Belum ada peringkat
- Hematemesis Melena Due To Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Duodenal Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDokumen6 halamanHematemesis Melena Due To Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Duodenal Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature ReviewWahyu Agung PribadiBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?Dokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylori: How Common Is H. Pylori Infection?Tariq Hussain RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter PyloriDokumen21 halamanHelicobacter PyloriFarhang PrintingBelum ada peringkat
- HP DietDokumen8 halamanHP DietSivamani SelvarajuBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori InfectionDokumen8 halamanHelicobacter Pylori InfectionNovitaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter PyloriDokumen4 halamanHelicobacter Pylorimoonfire2009Belum ada peringkat
- Microbiology: Dr. Murad Ibrahim Miss Jumana WadiDokumen43 halamanMicrobiology: Dr. Murad Ibrahim Miss Jumana WadiNoor AliBelum ada peringkat
- H PyloriDokumen23 halamanH PyloriYashoda Amarasekera100% (1)
- Helicobacter Pylori Eradication RacgpDokumen6 halamanHelicobacter Pylori Eradication Racgpnoogu100% (1)
- Giardiasis and FecalysisDokumen2 halamanGiardiasis and Fecalysiskmpg11Belum ada peringkat
- H.Pylory (Helicobacter) : Ali Muhammad Chrpa HazharDokumen22 halamanH.Pylory (Helicobacter) : Ali Muhammad Chrpa Hazharyıldız kubeBelum ada peringkat
- Causes: GastroenteritisDokumen5 halamanCauses: Gastroenteritispragna novaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory and Digestive Diseases: Tuberculosis, Influenza, Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokumen6 halamanRespiratory and Digestive Diseases: Tuberculosis, Influenza, Peptic Ulcer DiseaseAngela OngBelum ada peringkat
- GastritisDokumen79 halamanGastritisSheiljessBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori: Eradication - An Update On The Latest TherapiesDokumen5 halamanHelicobacter Pylori: Eradication - An Update On The Latest TherapiesBaim FarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Thursday, May 14, 2009: Management in Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokumen25 halamanThursday, May 14, 2009: Management in Peptic Ulcer DiseaserajenderBelum ada peringkat
- Peptic Ulcer Disease and H. PyloriDokumen8 halamanPeptic Ulcer Disease and H. PyloriAminahNatashaBelum ada peringkat
- MD Guide to the Stomach and DuodenumDokumen27 halamanMD Guide to the Stomach and Duodenumraed faisalBelum ada peringkat
- An Alternate Natural Remedy For Symptomatic Relief of Helicobacter Pylori Dyspepsia 2327 5146 1000200Dokumen5 halamanAn Alternate Natural Remedy For Symptomatic Relief of Helicobacter Pylori Dyspepsia 2327 5146 1000200gomitadelimonBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure 2Dokumen2 halamanBrochure 2vemcintosh219100% (1)
- Patient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDokumen93 halamanPatient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDay MedsBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence-Based Treatment of Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokumen9 halamanEvidence-Based Treatment of Peptic Ulcer DiseaseRandi AnugerahBelum ada peringkat
- Gastritis: Inflammation of The Gastric Mucosa or The StomachDokumen32 halamanGastritis: Inflammation of The Gastric Mucosa or The StomachItzel MahiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Stool Culture: BackgroundDokumen1 halamanStool Culture: BackgroundboroumandBelum ada peringkat
- Morbid AnatomyDokumen46 halamanMorbid AnatomyStephanie AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Biochemistry of The Gastrointestinal TractDokumen4 halamanClinical Biochemistry of The Gastrointestinal TractReuben JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation GastroenteritisDokumen58 halamanCase Presentation GastroenteritisShereen Manabilang100% (3)
- Diarrhea CaseDokumen8 halamanDiarrhea CaseStarr NewmanBelum ada peringkat
- Background: View Media GalleryDokumen6 halamanBackground: View Media Galleryprayitno tabraniBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Stomach FluDokumen49 halamanGastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Stomach Flukinasal21Belum ada peringkat
- Gastritis Diagnosis and Treatment GuideDokumen18 halamanGastritis Diagnosis and Treatment GuideBeatrice Sandra ChelaruBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoid Feve1Dokumen9 halamanTyphoid Feve1Jonas Galeos100% (1)
- Pesticide Poisoning from Contaminated WatermelonsDokumen5 halamanPesticide Poisoning from Contaminated Watermelonsnathan brionesBelum ada peringkat
- H PyloriDokumen7 halamanH PyloriBBD BBDBelum ada peringkat
- H Pylori and CandidaDokumen2 halamanH Pylori and Candidaps piasBelum ada peringkat
- Amebia PDFDokumen6 halamanAmebia PDF04lubna_869632400Belum ada peringkat
- MODULE 12 - Foodborne DiseasesDokumen16 halamanMODULE 12 - Foodborne DiseasesFil HynneyBelum ada peringkat
- MICROPARADokumen61 halamanMICROPARAKyla RamonesBelum ada peringkat
- AGE ReadingsDokumen6 halamanAGE ReadingseljhayrosBelum ada peringkat
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- SCE en 011-101 Hardware Configuration S7-1200 R1709Dokumen56 halamanSCE en 011-101 Hardware Configuration S7-1200 R1709shailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- SCE - EN - 011-100 Unspecific Hardware Configuration S7-1200 - R1709Dokumen46 halamanSCE - EN - 011-100 Unspecific Hardware Configuration S7-1200 - R1709shailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- SCE en 011-001 Firmware Update S7-1200 R1709Dokumen31 halamanSCE en 011-001 Firmware Update S7-1200 R1709shailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Hangover: Organs of The Body Susceptible To Damage by Excessive/prolonged Use of AlcoholDokumen1 halamanHangover: Organs of The Body Susceptible To Damage by Excessive/prolonged Use of Alcoholshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Thumb sucking guide under 40 charsDokumen1 halamanThumb sucking guide under 40 charsshailesh284100% (1)
- Siemens S71200-1500Dokumen126 halamanSiemens S71200-1500justinBelum ada peringkat
- SCE - EN - 000-000 Concept - and Module Description - R1503Dokumen14 halamanSCE - EN - 000-000 Concept - and Module Description - R1503shailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- ISA ComplianceDokumen1 halamanISA Complianceshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- 4 6 8 Channel Temperature ScannerDokumen1 halaman4 6 8 Channel Temperature Scannershailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- CU240B-2 DP Data SheetDokumen1 halamanCU240B-2 DP Data Sheetshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Chlamydia InfectionDokumen1 halamanChlamydia Infectionshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Teeth grinding (bruxism) causes, symptoms, treatmentDokumen1 halamanTeeth grinding (bruxism) causes, symptoms, treatmentshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Child Happy, RearingDokumen1 halamanChild Happy, Rearingshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Meningitis BacterialDokumen1 halamanMeningitis Bacterialshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Crying BabyDokumen1 halamanCrying Babyshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- FeverDokumen1 halamanFevershailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Eating DisordersDokumen1 halamanEating Disordersshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- BereavementDokumen1 halamanBereavementshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- CopdDokumen1 halamanCopdshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Ac Cute Wry NeckDokumen1 halamanAc Cute Wry Neckshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Child Happy, RearingDokumen1 halamanChild Happy, Rearingshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- OCP, CombinationDokumen1 halamanOCP, Combinationshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Crisis, Coping WithDokumen1 halamanCrisis, Coping Withshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- How to Monitor Blood Glucose Levels at HomeDokumen1 halamanHow to Monitor Blood Glucose Levels at Homeshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- ConcusionDokumen1 halamanConcusionshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Snuffling InfantDokumen1 halamanSnuffling Infantshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Plaster InstructionsDokumen1 halamanPlaster Instructionsshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Neck Pain, Post AccidentDokumen1 halamanNeck Pain, Post Accidentshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Anal FissureDokumen1 halamanAnal Fissureshailesh284Belum ada peringkat
- Protein TherapeuticsDokumen14 halamanProtein TherapeuticsSumanth Kumar ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Plantar Wart Treatment and CausesDokumen7 halamanPlantar Wart Treatment and CausesulfaraudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Med 1 - 1st Shift - Lec - HEENT Neck ExaminationDokumen3 halamanMed 1 - 1st Shift - Lec - HEENT Neck ExaminationRJLeddaBelum ada peringkat
- Bentonite Trugel 100 2007-09Dokumen1 halamanBentonite Trugel 100 2007-09Tanadol PongsripachaBelum ada peringkat
- Generalized Eruptive Syringoma Case ReportDokumen3 halamanGeneralized Eruptive Syringoma Case ReportYola TamngeBelum ada peringkat
- Lab FindingsDokumen3 halamanLab FindingsRonica GonzagaBelum ada peringkat
- Olivia Gant Case/ Turner Kelly Renee IndictmentDokumen17 halamanOlivia Gant Case/ Turner Kelly Renee IndictmentLeigh EganBelum ada peringkat
- Basal Cell CarcinomaDokumen134 halamanBasal Cell CarcinomaMore AmoBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminum Safety Data Sheet SummaryDokumen6 halamanAluminum Safety Data Sheet SummarySaul MontielBelum ada peringkat
- What Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesDokumen5 halamanWhat Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesKiara Denise TamayoBelum ada peringkat
- Suzanne Somers Knockout: Interviews With Doctors WhoDokumen24 halamanSuzanne Somers Knockout: Interviews With Doctors WhoThomas0% (1)
- Life Sciences p1 Gr10 QP Nov2019 - Eng DDokumen16 halamanLife Sciences p1 Gr10 QP Nov2019 - Eng DSkhethelo NdlangisaBelum ada peringkat
- CrashcardDokumen5 halamanCrashcardYuniBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology Janis Kuby .Page001Dokumen1 halamanImmunology Janis Kuby .Page001microkannanBelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge, Attitude & Practice On Human Papillomavirus Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Healthcare ProvidersDokumen9 halamanKnowledge, Attitude & Practice On Human Papillomavirus Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Healthcare ProvidersHari PrasathBelum ada peringkat
- Angio Dysla SiaDokumen14 halamanAngio Dysla SiaNicoleta Popa-FoteaBelum ada peringkat
- Abdullah Abdulaziz AbulabanDokumen2 halamanAbdullah Abdulaziz AbulabanArpita PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Prediction in PythonDokumen6 halamanBreast Cancer Prediction in PythonIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Monitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesDokumen11 halamanMonitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesMihaela BarbuBelum ada peringkat
- Leydig Cells TumoursDokumen3 halamanLeydig Cells TumoursVladislav GramaBelum ada peringkat
- Hormones Secreted by Endocrine GlandsDokumen5 halamanHormones Secreted by Endocrine Glandsaditya7324Belum ada peringkat
- OsteosarcomaDokumen25 halamanOsteosarcomaDimas PrasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Pra PTS Xi SMS 2Dokumen11 halamanPra PTS Xi SMS 2Ammar KhadafiBelum ada peringkat
- dōTERRA Clove OilDokumen5 halamandōTERRA Clove OilJacqui Decker100% (2)
- Cancer of LarynxDokumen46 halamanCancer of LarynxVIDYABelum ada peringkat
- Final Surgical Long Case Collection by Classof2016 PMCDokumen32 halamanFinal Surgical Long Case Collection by Classof2016 PMCStudentBelum ada peringkat
- CataractDokumen5 halamanCataractTriXie SorrillaBelum ada peringkat
- LHOC Transition 02.21.24 Patient Letter V5Dokumen1 halamanLHOC Transition 02.21.24 Patient Letter V5Pat ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Pulses Lesson Plan 2Dokumen9 halamanPulses Lesson Plan 2rebecca ganubBelum ada peringkat
- Orthopedics TraumatologyDokumen8 halamanOrthopedics TraumatologyCpopBelum ada peringkat