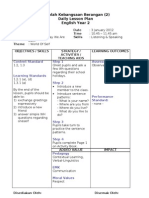
Lesson 2 - Verbs
Diunggah oleh
Akbarul AminHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lesson 2 - Verbs
Diunggah oleh
Akbarul AminHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lesson 2- Verbs
( 2) VERBS
Verbs are words that show action. Every sentence must have a verb. A verb is
not always one word. It may be made up of more than one word.
Auxiliary verbs
The words: am, is, are, was, and were are verbs. They are forms of the verb
to be. They are helping verbs called auxiliary verbs.
If the subject of a sentence is singular, the verb must be singular. If the
subject of a sentence is plural, the verb must be plural. The verb must agree
with the subject in number.
Examples of subjects and verbs being singular: The man is sleeping. She
goes to the market. The student does his homework every day. The train has
arrived.
Man, she, student and train are known as subjects.The subjects are all
singular.The verbs is, goes, does and has are all singular too.
Examples of subjects and verbs being plural: The men are sleeping. They
go to the market. The students do their homework every day. The trains have
arrived.
Men, they, students and trains are known as subjects. The subjects are
all plural. The verbs are, go, do and have are all plural too.
Singular subject/verb Plural subject/verb
1
st
I am do have eat We are do have eat
2
nd
You are do have eat You are do have eat
3
rd
He is does has eats They are do have eat
She is does has eats They are do have eat
It is does has eats They are do have eat
Other singular and plural subjects that take on singular and plural verbs:
Subjects with words like each, every, any, no, none and nobody
take on the singular verbs.
Examples: Each student is given a pen.
Every child is happy watching the show.
Nobody is allowed to walk on the grass.
Uncountable nouns always take singular verbs.
Examples: Rice is eaten in many countries.
There is oil on the floor.
Salt is added to make the food taste better.
Subjects with words like both, all, many, some, several and a
number of take on a plural verb.
Examples: Both of you have to come home early.
All of us want to be happy.
Some of my friends are female.
Two or more subjects joined by and always take a plural verb.
Examples: My brother and his friends like to play football.
His father and mother are watching television.
Transitive and intransitive verbs
The verb which needs an object to make its meaning clear or complete is called
a transitive verb.
Example: He feeds a cat. The word cat is called the object of the verb feeds.
The object can be a noun or a pronoun.
The intransitive verb does not need an object but the meaning is clear or
complete.
Example: He ran. The verb ran does not need an object. She reads every day.
(No object) He eats quickly. (No object)
The Finite verb
The finite verb changes with the subject. The subject is the person, thing, animal
or place we refer to. When the subject is in the first or second person or is
plural, the verb does not change. When the subject is in the third person or is
singular, the verb changes from, say, eat to eats. The verb eat is a finite
verb. Every sentence must have a finite verb.
Subject Singular subject Plural subject
First Person I eat We eat
Second Person You eat You eat
Third Person He eats They eat
Third Person She eats They eat
Third Person It eats They eat
The pen/s The pen is The pens are
The elephant/s The elephant does The elephants do not
The house/s The house has The houses have
The Infinitive
The infinitive is a verb that is followed by to and does not change with the
subject.
Subject Singular Subject Plural Subject
First Person I want to play. We want to play.
Second Person You want to play. You want to play.
Third Person He wants to play. They want to play.
She wants to play. They want to play.
It wants to play. They want to play.
The infinitive can take on an object. For example: He likes to read book. (To
read = infinitive; book = object).
Other usage of verbs to remember
1. When and is used to join two nouns or pronouns together, the verb is
usually in the plural.
Examples: Beef and mutton are meat.
He and I were classmates.
2. When we use two nouns for the same person or thing, the verb should be in
the singular.
Examples: My friend and classmate is very helpful.
Bread and butter is his only food.
3. When we use two nouns for the same person, we use the article the only
once and the verb should be in the singular.
Example: The shopkeeper and owner of the shop is my uncle.
4. When we refer to two different persons, we use the article twice and the
verb must be in the plural.
Example: The shopkeeper and the owner of the shop are my good
friends.
5. When we join two nouns and treat them as a whole, the verb is in the
singular.
Example: Bread and butter is his usual breakfast.
6. When a noun is a quantity or an amount, it is treated as a whole and the
verb is in the singular.
Examples: Ten kilometers is not a long way to travel.
Nowadays, fifty dollars is not a lot of money.
A verb is used in different forms as follow:
Simple Present Tense eat
Simple Past Tense ate
Present Particle is eating
Past Particle has eaten
Future Tense will eat
THE PRESENT TENSE
1. The Present Simple
Used for a habitual or repeated action, that is, for something that we do
always, every day, often, usually, etc.
Example: He plays football on Sundays.
Used for a general truth or a fact, that is, for something that is true.
Example: Night follows day.
Used for something or an action happening now.
Example: See how she walks.
Used instead of the future tense.
Example: He arrives tomorrow.
Used instead of the past tense, to make something look more real.
Example: The tiger comes; it catches the boy.
Used instead of the present perfect tense.
Example: We hear that the king is dead.
Used to introduce a quotation, that is, to repeat words spoken or written by
someone else.
Example: Shakespeare says: Neither a borrower nor a lender be.
2. The Present Continuous Tense
Used to show that something is still happening, that is, an action is still
going on at the time of speaking. It shows that the action is not yet complete.
Example: He is writing a letter.
Used instead of the future tense. We usually say the time when this future
action will take place
Example: He is going to Japan next week.
Used to use the phrase is going which means about to.
Example: It is going to rain.
Used to show an action which happens many times. We often use always
with this expression.
Example: He is always getting into trouble.
3. The Present Perfect Tense
Used to show an action which has just been completed or a past action when
the time is not mentioned. The action may be a recent one or it may be one
which happened a long time ago.
Example: I have finished reading the book.
There have been many changes in this country.
Used for an action that has been going on from the past until now, that is,
something that happened in the past but is going on still.
Example: I have lived here for ten years.
Used often with just, already, recently, never, yet and (in questions)
with ever.
Example: I have already told them about the plan
She has never replied to my letter.
Have you ever been to London?
Used often to answer questions which contain a verb in the Present Perfect
tense.
Example: Where have you been? I have been to London to see the
Queen.
What have you lost? I have lost all my money.
4. The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Used for an action just completed or continued up to now.
Example: He has been talking for an hour.
THE PAST TENSE
1. The Past Simple Tense
Used to describe a completed past action when the time of the action is
mentioned.
Example: I went to the cinema yesterday.
Used to show for a past action that was completely done in the past.
Example: My mother made a cake and we all ate it.
Used to express a habitual past action.
Example: He always came home late.
2. The Past Continuous Tense
Used for an action that was going on in the past when something else
happened.
Example: While they were watching television, the light went out.
Used to show an action that was going on at a certain time in the past.
Example: I was eating my dinner at 7 oclock last night.
Used for two actions that were going on at the same time in the past.
Example: While his father was reading the newspaper, his mother
was cooking.
3. The Past Perfect Tense
Used for an action that was completed before another action took place.
Example: I had left the house before he arrived.
Used in the Indirect or Reported Speech.
Example: I have read the book. He said that he had read the book.
4. The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Used for an action that had been going on in the past before another action
occurred in the past.
Example: She had been cooking when we visited her.
THE FUTURE TENSE
The Future Tense is used to show some action or happening in the future.
Future Simple + Going To
1. Simple Future Tense is used to show future action or that something will
happen in the future.
Example: We will complete the work tomorrow.
2. Going to is used to express a future action that has been planned in
advance.
Example: We are going to Japan next week.
3. Future Continuous Tense is used to show continuous action at some future
time.
Example: I shall be seeing both of you tomorrow.
4. Future Perfect Tense is used for an action which will have finished by some
future time or date which is mentioned or before another action has begun.
Example: I shall have finished this job by seven oclock.
I shall have finished this job by the time you arrive.
5. Future Perfect Continuous Tense. This continuous tense is formed with
shall/will have been + a present particle.
Example: I shall have been married for exactly ten years next
Saturday.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideDari EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Verb 2Dokumen3 halamanVerb 2Rajeev RanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Learn English 1 with Audio and Video: Learn English, #1Dari EverandLearn English 1 with Audio and Video: Learn English, #1Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (8)
- IIBPS PO Exam Free Study Material General English GrammarDokumen16 halamanIIBPS PO Exam Free Study Material General English GrammarAmitPandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering English Articles A, AN, and THE: Learn to Use English Articles Correctly in Every English Sentence!Dari EverandMastering English Articles A, AN, and THE: Learn to Use English Articles Correctly in Every English Sentence!Belum ada peringkat
- New PP StructureDokumen31 halamanNew PP Structuregalih febriandryBelum ada peringkat
- Learn English Is FunDokumen71 halamanLearn English Is Funika_nikanBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Summary 1-11Dokumen17 halamanTugas Summary 1-11sherinaBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastDokumen7 halamanSimple Past: USE 1 Completed Action in The PastYsa YesoBelum ada peringkat
- Verb Tenses EnglishDokumen41 halamanVerb Tenses EnglishSAIF KHANBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar TensesDokumen27 halamanGrammar Tenseswendy nguBelum ada peringkat
- Farah Salma Nisrina - TensesDokumen15 halamanFarah Salma Nisrina - TensesfarahBelum ada peringkat
- Dosier AlvaroDokumen22 halamanDosier AlvaroFernando Muñoz MontesinosBelum ada peringkat
- English Tenses 2023Dokumen5 halamanEnglish Tenses 2023erick robayoBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Dokumen27 halamanSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Andreea GîleaBelum ada peringkat
- Mid TermDokumen13 halamanMid Termelsa lestariBelum ada peringkat
- Group Work Past Continuous and Active Vs Passive VoiceDokumen16 halamanGroup Work Past Continuous and Active Vs Passive VoiceJervàcio ChambalBelum ada peringkat
- Past Tense WorksheetDokumen6 halamanPast Tense WorksheetEmanAbdel-HaqBelum ada peringkat
- Tenses Oft He Verb QWDokumen9 halamanTenses Oft He Verb QWvincentc84Belum ada peringkat
- English Tenses PDFDokumen6 halamanEnglish Tenses PDFRizwan GhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDokumen11 halamanSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsNicolás De los riosBelum ada peringkat
- The Simple Present TenseDokumen23 halamanThe Simple Present TenseohsiambnoBelum ada peringkat
- InglesDokumen10 halamanInglesMalquito Rafael ChaprecaBelum ada peringkat
- Modulo 7 Grammar ReferencesDokumen19 halamanModulo 7 Grammar ReferencesLEMMY RICHBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDokumen16 halamanSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohBelum ada peringkat
- Verb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsDokumen43 halamanVerb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsRoxana TudoseBelum ada peringkat
- Present Tense PaperDokumen18 halamanPresent Tense PaperMega PuspiytaBelum ada peringkat
- PortafolioDokumen6 halamanPortafolioSunny 95Belum ada peringkat
- English ProjectDokumen18 halamanEnglish ProjectAbdul Musawer ShinwariBelum ada peringkat
- English TaskDokumen14 halamanEnglish TaskSitiaisyah Batusangkar100% (2)
- Past TenseDokumen14 halamanPast Tensepandu MBelum ada peringkat
- Tense TheoryDokumen33 halamanTense TheoryAnamaria Blajan-LazaBelum ada peringkat
- PRESENT PERFECT Vs PAST TENSE-Shania SalsabilaDokumen10 halamanPRESENT PERFECT Vs PAST TENSE-Shania Salsabila28– Shania SalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- английский грамDokumen4 halamanанглийский грамСофия СтерховаBelum ada peringkat
- WALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesDokumen56 halamanWALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesLaurentiu IonescuBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar ReviewDokumen35 halamanGrammar ReviewLuManBelum ada peringkat
- Past TenseDokumen4 halamanPast TenseSiddhant RajakBelum ada peringkat
- Present SimpleDokumen116 halamanPresent SimplekpmadhunBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5 Grammar ReviewDokumen58 halamanLesson 5 Grammar ReviewKai Jo-hann BrightBelum ada peringkat
- Active / Passive Verb FormsDokumen37 halamanActive / Passive Verb FormshusnaBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen6 halamanTensesMeklitBelum ada peringkat
- TENSEDokumen12 halamanTENSEButt ButtBelum ada peringkat
- Tiempos InglésDokumen43 halamanTiempos InglésFrancisca Ponce HilleBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianDokumen37 halamanSimple Past Past Continuous Past Perfect: Group 2: Abirami Tee Sha Ney Loh Jia Wei Tan Wei JianAbirami SanmugumBelum ada peringkat
- Materi TensesDokumen37 halamanMateri TensesNoviartiBelum ada peringkat
- PAST Tenses - PPTDokumen24 halamanPAST Tenses - PPTbaba ioanaBelum ada peringkat
- TenseDokumen14 halamanTenseapi-214243994Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Sentence StructuresDokumen20 halamanBasic Sentence StructuresCarla GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar HandoutDokumen10 halamanGrammar Handoutstonegrave68Belum ada peringkat
- English GrammarDokumen76 halamanEnglish GrammarMihaela Neculai100% (1)
- Verb Perfect and ProgressiveDokumen12 halamanVerb Perfect and ProgressiveJoanne JoanneBelum ada peringkat
- TensesDokumen28 halamanTensesKalai ShanBelum ada peringkat
- Eng Gram Mod 5 TensesDokumen5 halamanEng Gram Mod 5 Tensesvikas1onlyBelum ada peringkat
- GrammarDokumen8 halamanGrammarOrlando BloominBelum ada peringkat
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dokumen25 halamanUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodBelum ada peringkat
- English Tenses: Nurse Educator TeamDokumen31 halamanEnglish Tenses: Nurse Educator Teamroslina niodeBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDokumen28 halamanSimple Past: USE 2 A Series of Completed ActionsDiamun FikriBelum ada peringkat
- When or WhileDokumen9 halamanWhen or Whilemohammad515Belum ada peringkat
- Grammar TensesDokumen28 halamanGrammar TensesKoko AlayzaBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Pronouns Year 3Dokumen10 halamanSlide Pronouns Year 3Akbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Jobs Actions Puzzle ShapedDokumen1 halamanJobs Actions Puzzle ShapedclintoniteBelum ada peringkat
- Pronouns 1Dokumen19 halamanPronouns 1Atupan M. MaritesBelum ada peringkat
- PPT 82 PronounsDokumen18 halamanPPT 82 PronounsAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Jobs Search What Will You BeDokumen2 halamanJobs Search What Will You BejesusjaviermartinBelum ada peringkat
- Job Suffix MatchingDokumen1 halamanJob Suffix MatchingjesusjaviermartinBelum ada peringkat
- Job Suffix MatchingDokumen1 halamanJob Suffix MatchingjesusjaviermartinBelum ada peringkat
- Jobs Word Fragment: Find The Correct Pieces and Put Them Together To Form Job Related WordsDokumen1 halamanJobs Word Fragment: Find The Correct Pieces and Put Them Together To Form Job Related WordsBianca VeriatoBelum ada peringkat
- Job Definition MatchDokumen1 halamanJob Definition Matchjesusjaviermartin33% (3)
- Jobs Suffix CrosswordsDokumen2 halamanJobs Suffix CrosswordsVivita GuzmánBelum ada peringkat
- Jobs Board Games BeginnersDokumen1 halamanJobs Board Games Beginnersronnin246Belum ada peringkat
- Jobs Matching2Dokumen1 halamanJobs Matching2Akbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Theme: Topic: Content StandardDokumen3 halamanTheme: Topic: Content StandardMuhammad NazwanBelum ada peringkat
- Jobs Actions Puzzle ShapedDokumen1 halamanJobs Actions Puzzle ShapedclintoniteBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Literacy: Skills For LifeDokumen11 halamanAdult Literacy: Skills For LifeAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- RPH Bi Y2Dokumen22 halamanRPH Bi Y2Noorhasliza Halim88% (8)
- Royal Castle Floor PlanDokumen3 halamanRoyal Castle Floor Planecontent2013100% (1)
- WH WordsDokumen2 halamanWH WordsAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Job Definition MatchDokumen1 halamanJob Definition Matchjesusjaviermartin33% (3)
- Y1 Unit 01 Flashcards PDFDokumen9 halamanY1 Unit 01 Flashcards PDFmeksu83Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 9 - ConjunctionsDokumen2 halamanLesson 9 - ConjunctionsAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Tips To ScoreDokumen20 halamanTips To ScoreEzy ZainalBelum ada peringkat
- UPSR Worksheet HolidayDokumen2 halamanUPSR Worksheet HolidayAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 7 - PronounsDokumen2 halamanLesson 7 - PronounsAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5 - Indirect SpeechDokumen2 halamanLesson 5 - Indirect SpeechAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 8-Prepositions: Examples of Prepositions Showing TimeDokumen2 halamanLesson 8-Prepositions: Examples of Prepositions Showing TimeAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 - ArticlesDokumen2 halamanLesson 6 - ArticlesAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 4 - AdverbsDokumen2 halamanLesson 4 - AdverbsAkbarul AminBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - AdjectivesDokumen3 halamanLesson 3 - AdjectivesAkbarul Amin100% (2)
- "Like and Dislike" Noun.: The Verbs Can Be Followed by A For Example: I Like I Like StrawberriesDokumen2 halaman"Like and Dislike" Noun.: The Verbs Can Be Followed by A For Example: I Like I Like StrawberriesGabriel Bickel Figueroa100% (1)
- Our Findings Show Lessons 1-2-3-4Dokumen10 halamanOur Findings Show Lessons 1-2-3-4Ihsane Dz100% (2)
- StrayDokumen31 halamanStrayapi-237778434Belum ada peringkat
- Continguts Anglès 4tDokumen1 halamanContinguts Anglès 4tceipGMBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanLesson PlanEhab GaballahBelum ada peringkat
- Isn't or Doesn't Worksheet: Esl / Efl ResourcesDokumen2 halamanIsn't or Doesn't Worksheet: Esl / Efl ResourcesKenny Junior Mercedes Rojas100% (1)
- Mandukya Upanishad: Word-For Word Translation With Grammatical NotesDokumen34 halamanMandukya Upanishad: Word-For Word Translation With Grammatical Notesmichael8douglas8neel100% (3)
- Anul Scolar 2010-2011 Profesor: Disciplina: Limba Engleza Cls. A VIII-a, 2h/sapt., L1 Manual: High Flyer (Upper Intermediate), Editura LongmanDokumen3 halamanAnul Scolar 2010-2011 Profesor: Disciplina: Limba Engleza Cls. A VIII-a, 2h/sapt., L1 Manual: High Flyer (Upper Intermediate), Editura LongmanDaniela MincaBelum ada peringkat
- 1bac 2 - Quiz 2 S 2Dokumen2 halaman1bac 2 - Quiz 2 S 2Moha Zahmonino100% (2)
- VoiceDokumen11 halamanVoiceShakilBelum ada peringkat
- Pronoun Lesson 1Dokumen5 halamanPronoun Lesson 1api-361542056Belum ada peringkat
- Rules On Word FormationDokumen24 halamanRules On Word FormationCriscel Joy Luis Sambrano0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan JaromayDokumen5 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan JaromaySam Henessey Maramag Navarro90% (10)
- Introducing YourselfDokumen10 halamanIntroducing YourselfJuly Mania SembiringBelum ada peringkat
- Module 8 English VerbDokumen4 halamanModule 8 English VerbJester OlidorBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 22 Comparative StructuresDokumen14 halamanUnit 22 Comparative StructuresDoãn DạBelum ada peringkat
- Table of English Tenses 1Dokumen1 halamanTable of English Tenses 1Maria Jose Carrasco100% (1)
- Polish Numbers - Cardinal and OrdinalDokumen3 halamanPolish Numbers - Cardinal and OrdinalJack DempseyBelum ada peringkat
- Thieves Cant From Dragon 66Dokumen10 halamanThieves Cant From Dragon 66Josh JasperBelum ada peringkat
- Present ContinuousDokumen1 halamanPresent ContinuoushhhBelum ada peringkat
- Hospitality English ClassDokumen21 halamanHospitality English ClassChitato MilkyBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 1 LPDokumen5 halamanGrade 1 LPAlbert Joe AbrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Derivational Suffix ListDokumen6 halamanDerivational Suffix ListBrent LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Link ErsDokumen3 halamanLink ErsNeagu CristianaBelum ada peringkat
- DLP 4asDokumen7 halamanDLP 4asAiza PentinioBelum ada peringkat
- Athenaze Teacher's Handook 2Dokumen144 halamanAthenaze Teacher's Handook 2Cristiano Valois85% (92)
- ScanlonsLatinGrammarComplete PDFDokumen617 halamanScanlonsLatinGrammarComplete PDFGiuseLong100% (5)
- 'Ask' Inquire': Indirect Form orDokumen2 halaman'Ask' Inquire': Indirect Form orRitika BadhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Navigate Upper-Intermediate Wordlist Unit 4Dokumen3 halamanNavigate Upper-Intermediate Wordlist Unit 4joel zapanaBelum ada peringkat
- TOEFL Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanTOEFL Lesson PlanFree HakkiBelum ada peringkat
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Dari EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (81)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageDari EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguagePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (429)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonDari EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundDari Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (13)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageDari EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguagePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (916)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (4)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideDari EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- The Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachDari EverandThe Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsDari EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsBelum ada peringkat
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllDari EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (83)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsDari EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (15)
- How to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OneDari EverandHow to Write a Sentence: And How to Read OnePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (115)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (81)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesDari EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (151)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingDari EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (26)
- Abominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionDari EverandAbominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- How To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessDari EverandHow To Get Your Point Across In 30 Seconds Or LessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (308)
- The Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsDari EverandThe Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (205)
- Learn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDari EverandLearn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (47)