Activity 4 Specimen Collection & Processing
Diunggah oleh
Porcha Pacsay0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan1 halamanThis document discusses specimen collection and processing for plasma and serum. Plasma is the liquid part of blood with anticoagulants while serum is the liquid part after clotting. Serum is clearer with no fibrinogen and takes longer to prepare. The document also discusses advantages of serum over plasma, heat inactivation of serum, washing red blood cells in preparation, common causes and ways to avoid hemolysis, and types of serology tests requiring serum or red blood cells.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Activity 4 Is
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses specimen collection and processing for plasma and serum. Plasma is the liquid part of blood with anticoagulants while serum is the liquid part after clotting. Serum is clearer with no fibrinogen and takes longer to prepare. The document also discusses advantages of serum over plasma, heat inactivation of serum, washing red blood cells in preparation, common causes and ways to avoid hemolysis, and types of serology tests requiring serum or red blood cells.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan1 halamanActivity 4 Specimen Collection & Processing
Diunggah oleh
Porcha PacsayThis document discusses specimen collection and processing for plasma and serum. Plasma is the liquid part of blood with anticoagulants while serum is the liquid part after clotting. Serum is clearer with no fibrinogen and takes longer to prepare. The document also discusses advantages of serum over plasma, heat inactivation of serum, washing red blood cells in preparation, common causes and ways to avoid hemolysis, and types of serology tests requiring serum or red blood cells.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
ACTIVITY 4
SPECIMEN COLLECTION & PROCESSING
PLASMA SERUM
Lighter than serum Light yellow
Anti-coagulated blood Coagulated blood
Less clearer Clearer
Present Fibrinogen,
Clotting factor,
No fibrinogen
Shorter to prepare Longer to prepare
ADVANTAGE OF SERUM OVER PLASMA
Avoid contamination with cations such as ammonia,
lithium, sodium, potassium which are present in plasma
Antigens are more present in serum
Serum is less likely to show hemolysis.
Serum does not contain anticoagulant which may draw
water out of cells and thereby dilute the sample.
Because of this, plasma values tend to be a little lower
than serum values
Some anticoagulants in plasma interfere with the
chemical reactions used to measure levels of the blood
constituents.
HEAT INACTIVATION
Process in which finished serum is placed in a heated
water bath and maintained at a temperature of 56C
for 30 minutes
Used in the past to inactivate the complement system
for immunoassays
To inactivate other undetermined inhibitors of cell
growth in culture such as complement, a group of
proteins present in sera that are part of the immune
response
But may also destroy heat labile growth factors,
vitamins, amino acids, and hormones present in
serum
WHY IS SUFFICIENT WASHING OF RBC
NECESSARY IN RCS PREPARATION?
The purpose of washing the RBC is to remove plasma,
which contains substance that may interfere with Ag-
Ab reaction
will remove residual plasma and cellular debris
Plasma may also interfere in the testing
COMMON CAUSES OF HEMOLYSIS
Use of non-sterile containers for collection or storage.
Contamination
Contamination of the sample by water.
A slow flow from the needle, due to obstruction of the
needle, or failure to insert into mid-vein.
Forcibly expelling blood through a needle.
Heating of samples, usually in car boots or through
back windows of car, or after prolonged exposure to
direct sunlight during collection.
Freezing.
HOW TO AVOID HEMOLYSIS
Do not centrifuge blood if it still has not clotted
properly.
Do not rim or ring the blood several times. This is one
major source of hemolysis.
Do not freeze whole blood right after collection.
Do not vigorously shake whole blood, to avoid
hemolysis in blood samples.
Do not expose the whole blood specimen to excessively
low and hot temperatures.
Do not prolong tourniquet application more than
necessary.
TEST DONE IN SEROLOGY REQUIRING:
SERUM
o Direct agglutination
o Indirect agglutination
o Coagulation
o Rapid plasma reagin
o Latex agglutination
o Widal test
o Hemagglutination inhibition test
RCS
o ABO and RH typing
o Identification panel test cell
o Indirect antiglobulin test
o Direct antiglobulin test
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Quality Assurance of Chemical ChemistryDokumen31 halamanQuality Assurance of Chemical ChemistryAsel AselBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Hemolysis of Sample?Dokumen3 halamanWhat Is Hemolysis of Sample?Chino Paolo Samson100% (1)
- Precollection Variables: A. Phyiologic FactorsDokumen2 halamanPrecollection Variables: A. Phyiologic FactorsAedren TrillanaBelum ada peringkat
- Sampling: Assistant Instructor. Jinan Hameed Source By:-Practical Clinical BiochemistryDokumen24 halamanSampling: Assistant Instructor. Jinan Hameed Source By:-Practical Clinical BiochemistryaddwrBelum ada peringkat
- Haemolysis Technical Bulletin AnzDokumen2 halamanHaemolysis Technical Bulletin Anznd1706Belum ada peringkat
- BloodDokumen3 halamanBloodnamithaBelum ada peringkat
- (HEMA) Practice QuestionsDokumen4 halaman(HEMA) Practice QuestionsElyssa VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- BloodcollectionDokumen49 halamanBloodcollectionMalathi VarnaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Year: Clinical BiochemistryDokumen12 halaman4 Year: Clinical BiochemistryAbdul hadiBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology 1 New EdDokumen50 halamanHematology 1 New EdRUBEN DAMAYOBelum ada peringkat
- CC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredDokumen6 halamanCC1-PRELIM-ACTIVITY AnsweredSky Angel RasonableBelum ada peringkat
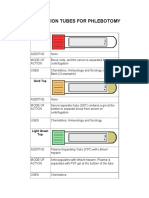
- Collection Tubes For Phlebotomy: Red TopDokumen12 halamanCollection Tubes For Phlebotomy: Red TopDrusilla LossBelum ada peringkat
- Coagulase PlasmaDokumen2 halamanCoagulase PlasmaHà Anh Minh LêBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Specimen Collection, Handling, and ProcessingDokumen36 halamanChapter 6 Specimen Collection, Handling, and Processingtagele hunegnawBelum ada peringkat
- Blood CollectionDokumen49 halamanBlood Collectionc toonzBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 05Dokumen34 halamanActivity 05Rezzy Mae Panadero OraBelum ada peringkat
- Common Tests Affected by Additive ContaminationDokumen4 halamanCommon Tests Affected by Additive ContaminationNazaqat FarooqBelum ada peringkat
- Haemolysis As Influence & Interference FactorDokumen4 halamanHaemolysis As Influence & Interference FactormohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Spotters-Mlt: Dr.S.Rashmi Dept. of BiochemistryDokumen19 halamanSpotters-Mlt: Dr.S.Rashmi Dept. of BiochemistrySamuvelrajBelum ada peringkat
- Specimen Collection GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanSpecimen Collection GuidelinesFathi MesoBelum ada peringkat
- AnticoagulantsDokumen47 halamanAnticoagulantsMARK VINCENT BAUTISTABelum ada peringkat
- DR Lim Report 2Dokumen9 halamanDR Lim Report 2KhAi EnBelum ada peringkat
- Hema 1 August 2021Dokumen84 halamanHema 1 August 2021Renz Gerard Amor100% (1)
- All Staph TestsDokumen33 halamanAll Staph Testsalhaitham alqmeBelum ada peringkat
- ANTICOAGULANT USED IN HAEMATOLOGY Introd PDFDokumen6 halamanANTICOAGULANT USED IN HAEMATOLOGY Introd PDFDarren WilliamBelum ada peringkat
- ANTICOAGULANT USED IN HAEMATOLOGY Introd PDFDokumen6 halamanANTICOAGULANT USED IN HAEMATOLOGY Introd PDFPrince HimansuBelum ada peringkat
- ANTICOAGULANTSDokumen5 halamanANTICOAGULANTSSenyonga EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Specimen Collection & Pre Analytical ErrorDokumen4 halamanSpecimen Collection & Pre Analytical Errors8903082Belum ada peringkat
- Eprubete. Culori. UtilizareDokumen3 halamanEprubete. Culori. UtilizareCuCUBelum ada peringkat
- Phlebotomy - 2021Dokumen36 halamanPhlebotomy - 2021Sumathi AkshayaBelum ada peringkat
- Purpose of AnticoagulantsDokumen12 halamanPurpose of AnticoagulantsDattatreyaBelum ada peringkat
- Collection TubeDokumen6 halamanCollection TubeChristiane ReaBelum ada peringkat
- Urine AnalysisDokumen63 halamanUrine AnalysisAdarshBijapurBelum ada peringkat
- Haemolysed or Clotted Samples 1Dokumen3 halamanHaemolysed or Clotted Samples 1Fathi MesoBelum ada peringkat
- AnticoagulantDokumen28 halamanAnticoagulantAvi DhakalBelum ada peringkat
- 9.0 Blood AnalysisDokumen11 halaman9.0 Blood Analysiskibitokstephen1Belum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0009898117305223 MainDokumen7 halaman1 s2.0 S0009898117305223 MainsdadsaBelum ada peringkat
- 601d86d7bd1bf57ebd1cba3d - 6004 200 Nccls Sickle CellDokumen5 halaman601d86d7bd1bf57ebd1cba3d - 6004 200 Nccls Sickle CellBruna Taillah Voroniuk RossetoBelum ada peringkat
- Diamedix CH50Dokumen4 halamanDiamedix CH50Nikon SinghBelum ada peringkat
- AnticagulantsDokumen4 halamanAnticagulantsm.alicmlt72Belum ada peringkat
- Group 3 Expt # 3: Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProceduresDokumen4 halamanGroup 3 Expt # 3: Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProceduresKriziaBelum ada peringkat
- TUBESDokumen1 halamanTUBESXamantha ZamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Blood AnalysisDokumen10 halamanBlood AnalysisHry WkBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 Specimen Processing Module PDFDokumen11 halamanLesson 3 Specimen Processing Module PDFTinBelum ada peringkat
- W9 Bacte LAB Identification of StaphylococcusDokumen27 halamanW9 Bacte LAB Identification of StaphylococcusAnne CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Plasma Proteins 1Dokumen72 halamanPlasma Proteins 1reuben kwotaBelum ada peringkat
- FolateDokumen15 halamanFolatecarineBelum ada peringkat
- BCB 411 - Lec 6Dokumen20 halamanBCB 411 - Lec 6NaushinKhanBelum ada peringkat
- Serologic Techniques: Chapter TwoDokumen44 halamanSerologic Techniques: Chapter TwoKevin TranBelum ada peringkat
- PhlebotomyDokumen37 halamanPhlebotomykreatura5100% (2)
- ReviewDokumen4 halamanReviewbaihern24Belum ada peringkat
- Phlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Dokumen5 halamanPhlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Gerald John PazBelum ada peringkat
- دورة هامة في التحاليل الطبية PDFDokumen308 halamanدورة هامة في التحاليل الطبية PDFkigm mkjBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Control2Dokumen32 halamanQuality Control2Mustafa KhandgawiBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Experiment Group 6Dokumen57 halamanBlood Experiment Group 6Melissa SalayogBelum ada peringkat
- Common Blood Collection Tubes, Their Additives andDokumen16 halamanCommon Blood Collection Tubes, Their Additives andGrymjoe Angin EmasBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Laboratory MedicineDokumen308 halamanIntroduction To Laboratory MedicineJane JeriesBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Collection (OCR)Dokumen32 halamanSample Collection (OCR)Brahmesh GuntamukkalaBelum ada peringkat
- Bachelor - S Virgin GirlDokumen442 halamanBachelor - S Virgin GirlJesahMacadizBelum ada peringkat
- Xiomai - The Sexy BadassDokumen116 halamanXiomai - The Sexy BadassMaria Shiela Mae Baratas75% (4)
- My Boyfriend Is A GangsterDokumen438 halamanMy Boyfriend Is A GangsterGenevieve100% (2)
- A Gangster Kiss (Book 2) - Forever YoursDokumen178 halamanA Gangster Kiss (Book 2) - Forever Yourstayah_16090100% (1)
- Bonitababyy - The Virgin's First Night - The Innocent SeductressDokumen62 halamanBonitababyy - The Virgin's First Night - The Innocent SeductressJasmine Primero100% (5)
- Xiomai - Saved by The Sex GodDokumen359 halamanXiomai - Saved by The Sex GodMaria Shiela Mae Baratas83% (6)
- My Gangster Ex (Completed)Dokumen965 halamanMy Gangster Ex (Completed)yeorimkawaii90% (21)
- A Night With MR ArrogantDokumen711 halamanA Night With MR ArrogantPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Playful DesiresDokumen238 halamanPlayful DesiresYssa Wattpad89% (9)
- A Detour To LoveDokumen165 halamanA Detour To LovePorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 5 TitrationDokumen1 halamanActivity 5 TitrationPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- My Cassanova GangsterDokumen454 halamanMy Cassanova GangsterMaria Shiela Mae BaratasBelum ada peringkat
- His Hired Baby MakerDokumen106 halamanHis Hired Baby MakerYeng SepleBelum ada peringkat
- Voiceless Haveyouseenthisgirl PDFDokumen471 halamanVoiceless Haveyouseenthisgirl PDFPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Wanted BabymakerDokumen162 halamanWanted BabymakerPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- ... The Perfect Stepbrother 2Dokumen147 halaman... The Perfect Stepbrother 2Aishiteru Qin HaiBelum ada peringkat
- Marriage ContractDokumen130 halamanMarriage ContractPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Montello High School of GangstersDokumen936 halamanMontello High School of GangstersLyzziefdo82% (44)
- 100 Days For Her HappinessDokumen149 halaman100 Days For Her HappinessPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- C Reactive ProteinDokumen2 halamanC Reactive ProteinPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Antigen That Is Present at Many Different Sites and CanDokumen8 halamanAntigen That Is Present at Many Different Sites and CanPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Techonolgy Curriculum 2003-2004Dokumen7 halamanTechonolgy Curriculum 2003-2004Porcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- My Drummer BoyDokumen328 halamanMy Drummer BoyPorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Playful DesiresDokumen238 halamanPlayful DesiresYssa Wattpad89% (9)
- Activity 3 - Antigens...Dokumen4 halamanActivity 3 - Antigens...Porcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- Catch Him He S in LoveDokumen214 halamanCatch Him He S in LovePorcha PacsayBelum ada peringkat
- #Break The Ice and Let The Love BeginDokumen172 halaman#Break The Ice and Let The Love BeginPorcha Pacsay100% (1)
- Iso 15189 Manual DocumentsDokumen10 halamanIso 15189 Manual DocumentsLisyaBelum ada peringkat
- Musawi - 36 MCQDokumen10 halamanMusawi - 36 MCQFull MarksBelum ada peringkat
- Group 2 - Clinical Chemistry 1Dokumen9 halamanGroup 2 - Clinical Chemistry 1julo_05100% (2)
- Ichroma™ COVID-19 Ab (With Ichroma™ II Reader) Test SystemDokumen6 halamanIchroma™ COVID-19 Ab (With Ichroma™ II Reader) Test SystemGopinath AgnihotramBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Guide To Laboratory Test Interpretation and Differential Diagnosis. Haematology and BiochemistryDokumen212 halamanPractical Guide To Laboratory Test Interpretation and Differential Diagnosis. Haematology and BiochemistryAgrovet Don Bosco100% (1)
- Student Industrial Work Experience SchemeDokumen27 halamanStudent Industrial Work Experience SchemeYARO TERKIMBIBelum ada peringkat
- 2.6.14. Bacterial EndotoxinsDokumen8 halaman2.6.14. Bacterial EndotoxinsCeangoBelum ada peringkat
- Blood & Biologicals Section 2Dokumen33 halamanBlood & Biologicals Section 2Louise Emy ViolettaBelum ada peringkat
- BloodDokumen8 halamanBloodnn nnBelum ada peringkat
- Tests/hour: Multiple Test Parameters High ThroughputDokumen4 halamanTests/hour: Multiple Test Parameters High ThroughputВадим Сагитов0% (1)
- Complete Textbook of Phlebotomy 5th Edition Hoeltke Solutions Manual 1Dokumen36 halamanComplete Textbook of Phlebotomy 5th Edition Hoeltke Solutions Manual 1waynehuberxkrqngifbt100% (24)
- Instructions For Use Ca: VITROS Chemistry Products Ca SlidesDokumen12 halamanInstructions For Use Ca: VITROS Chemistry Products Ca Slidesرحمة جمالBelum ada peringkat
- List of Medicines PDFDokumen88 halamanList of Medicines PDFsam0% (1)
- Rate List Medcis LabDokumen4 halamanRate List Medcis LabArpit GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Fuji Dri-Chem Slide: Tcho-PiiiDokumen1 halamanFuji Dri-Chem Slide: Tcho-Piiisusey tepaBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Transfusion ENGLISHDokumen40 halamanBlood Transfusion ENGLISHHajrahPalembangan100% (2)
- NRL Laboratory Collection ManualDokumen27 halamanNRL Laboratory Collection ManualZeeshan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Total Proteins & Albumin AnalysisDokumen16 halamanTotal Proteins & Albumin AnalysisMustafa KhandgawiBelum ada peringkat
- 7 5 16 Physiology of Red Blood CellsDokumen72 halaman7 5 16 Physiology of Red Blood CellsJoshua NyazonBelum ada peringkat
- Who TRS 924 A4Dokumen75 halamanWho TRS 924 A4Andres AbrilBelum ada peringkat
- Egyptian National Blood Transfusion Standards 2007 PDFDokumen41 halamanEgyptian National Blood Transfusion Standards 2007 PDFAshley Smith100% (2)
- Preanalytical Variables Influence On Laboratory Results and Patient CareDokumen4 halamanPreanalytical Variables Influence On Laboratory Results and Patient Caredarko_600054071Belum ada peringkat
- Internal Quality Control in Serological Tests For SyphilisDokumen7 halamanInternal Quality Control in Serological Tests For SyphilisAnonymous brvvLxoIluBelum ada peringkat
- Chart of Commonly Transfused Blood ProductsDokumen2 halamanChart of Commonly Transfused Blood Productsmara5140100% (8)
- Blood Components Process FlowchartDokumen1 halamanBlood Components Process FlowchartCatherine Constantino BaintoBelum ada peringkat
- Redcross PresentationDokumen3 halamanRedcross Presentationapi-291557491Belum ada peringkat
- Practical HaematologyDokumen70 halamanPractical HaematologyMustafa Khandgawi100% (1)
- BloodDokumen19 halamanBloodToday NewsBelum ada peringkat
- MKSAP Normal Lab ValuesDokumen2 halamanMKSAP Normal Lab Valuesdzhao09Belum ada peringkat
- Koate DVIDokumen7 halamanKoate DVIagnesroBelum ada peringkat