Fina Examination 2012...
Diunggah oleh
Banu Priya0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
28 tayangan7 halamanThis document contains the answers to questions from multiple sections of an exam:
1. Section A contains answers to questions about plant cell structures and photosynthesis, including identifying organelles in a diagram and explaining their functions.
2. Section B contains answers to questions about enzyme kinetics and the effects of varying enzyme and substrate concentrations. Graphs are analyzed to determine reaction rates.
3. Section C involves constructing a food web based on organisms found in a paddy field and explaining population fluctuations over time.
4. Section D outlines an experimental plan to determine the concentration of a sugar solution that is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya tissue. The aim, hypothesis, variables, materials, procedure, and
Deskripsi Asli:
biology
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document contains the answers to questions from multiple sections of an exam:
1. Section A contains answers to questions about plant cell structures and photosynthesis, including identifying organelles in a diagram and explaining their functions.
2. Section B contains answers to questions about enzyme kinetics and the effects of varying enzyme and substrate concentrations. Graphs are analyzed to determine reaction rates.
3. Section C involves constructing a food web based on organisms found in a paddy field and explaining population fluctuations over time.
4. Section D outlines an experimental plan to determine the concentration of a sugar solution that is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya tissue. The aim, hypothesis, variables, materials, procedure, and
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
28 tayangan7 halamanFina Examination 2012...
Diunggah oleh
Banu PriyaThis document contains the answers to questions from multiple sections of an exam:
1. Section A contains answers to questions about plant cell structures and photosynthesis, including identifying organelles in a diagram and explaining their functions.
2. Section B contains answers to questions about enzyme kinetics and the effects of varying enzyme and substrate concentrations. Graphs are analyzed to determine reaction rates.
3. Section C involves constructing a food web based on organisms found in a paddy field and explaining population fluctuations over time.
4. Section D outlines an experimental plan to determine the concentration of a sugar solution that is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya tissue. The aim, hypothesis, variables, materials, procedure, and
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Please write down the Section As answer in the space below:Answer
Section B: Subjective question (33%)
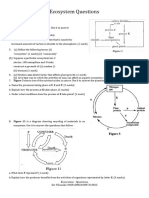
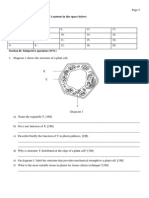
1. Diagram 1 shows the structure of a plant cell.
Diagram 1
a) Name the organelle T. [1M]
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.(1m)
b) Give one function of X. [1M]
modifies proteins/pack proteins into secretory vesicles.
c) Describe briefly the function of Y in photosynthesis. [2M]
Captures light energy [1m] and converts it to chemical energy [1m]
d) Why is structure Y distributed at the edge of a plant cell? [1M]
To absorb maximum amount of sunlight (1m)
e) On diagram 1, label the structure that provides mechanical strength to a plant cell. [1M]
f) Name one biotechnological technique which uses to produce plentiful of plant cells. [1M]
Plant tissue culture(1m)
2. Diagram 2.1 and 2.2 show the effects of both enzyme concentration and substrate concentration on the
rate of amylase reaction on starch.
1. 5. 9. 13. 17.
2. 6. 10. 14. 18.
3. 7. 11. 15. 19.
4. 8. 12. 16. 20.
X
Y
Diagram 2.1
Diagram 2.2
a) Based on both diagram, state a way to determine the rate of amylase reaction. [1M]
Measured the amount of starch used-up per unit time / measured the amount of glucose formed per
unit time.(1m)
b) Based on both diagrams, explain what is happened to enzyme molecules at point X and Y. [2M]
The enzyme molecule are said to be saturated [1m].
All the active sites are filled and engaged in catalysis. [1m]
c) Calculate the time taken for the hydrolysis of starch at point X. [1M]
Time taken at X: 0.8%/t=0.12%/min, t= 6.7 min
d) Explain the rate of reactions which occur at regions P and Q. [2M]
P region: The rate of enzymatic reaction increases with the increase of enzyme concentration [1m]
X
P
R
Y
Q
S
Q region: The rate of enzymatic reaction increases with the increase of substrate concentration [1m]
e) Explain the rate of reactions which occur at regions R and S. [2M]
R region: The increase of enzyme concentration will not cause the increase of the rate of enzymatic
reaction because the substrate concentration becomes limiting factor [1m]
S region: The increase of substrate concentration will not cause the increase of the rate of enzymatic
reaction because the enzyme concentration becomes the limiting factor [1m]
3. Diagram 3 shows the chemical process of light reaction during photosynthesis
Diagram 3
a) What is meant by photosynthesis? [1M]
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants synthesise organic compounds from carbon
dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight.(1m)
b) Based on diagram 3, name S, T and U. [3M]
S: oxygen (1m)
T: hydrogen ions(1m)
U: hydrogen atoms(1m)
c) Explain how the increase of light intensity affecting the production of S. [2M]
Increase in light intensity will increase the production of S (oxygen). [1m]
At high intensity of light more water molecule split to form hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. [1M]
d) Describe two physical structures of leaves to carry out photosynthesis efficiently. [2M]
The leaf has broad and flattened shape of lamina which increases the surface area for maximum
absorption of light. [1M]
The lamina is very thin so that light can penetrate easily. [1m]
OR Alternative answer: The lamina is very thin that allows diffusion of gases involved in
photosynthesis to take place efficiently. [1m].
e) Name a cell that is found in leaves which actively carry out photosynthesis. [1M]
Palisade mesophyll cell. (1m)
4. Diagram 4 shows the transport of respiratory gases in human body.
Light energy
e
e
Diagram 4
a) Name the structures labelled P and Q. [2M]
P: red blood cell/ erythrocyte (1m)
Q: alveolus (1m)
b) Explain how the process of gaseous exchange occurs between Q and blood capillaries. [3M]
The partial pressure of oxygen in Q (alveolus) is higher than the partial pressure of oxygen in blood
capillaries while the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in Q is lower than the partial pressure of
carbon dioxide in the blood capillaries. [1m]
A concentration gradient is formed between Q and blood capillaries. [1m]
Oxygen from Q diffuses into blood capillaries and carbon dioxide diffuses out from blood capillaries
into Q. [1m]
c) Name a complex chemical compound found in P. [1M]
Haemoglobin(1m)
d) Based on statement above, describe two similarities between X and Q. [2M]
The surfaces for both respiratory structures are constantly moist for the respiratory gases to dissolve
in them. [1m]
Both are found in numerous numbers. This provides a larger surface area for the diffusion of
gases.[1m]
Cell lining both of the respiratory structures are thin. This allows gaseous exchange to occur at a
faster rate. [1m]
e) Name the mechanism that enhancesthe gaseous exchange between X with water. [1M]
Countercurrent exchange mechanism.(1m)
Section C: Essay questions (10%)
1. The following organisms are found in a paddy field community.
X is the respiratory structure of fish which is specialised for gaseous exchange in
water.
Body cell
Blood capillary
Owl, Paddy plant, Rat, Grasshopper, Snake, Caterpillar, Frog
a).What is meant by food web? [2M]
Food web is the interconnected food chain. [1m]
it describes the actual feeding relationship within the community. [1m]
a) Based on above organism, construct a food web showing the interaction of all organisms. [2M].
Diagram 5
b) Diagram 5 shows the dynamic relationship between the population of a rat and owl in that paddy
field over the years. Explain the mechanism that occurs in this dynamic relationship. [6M]
Answer:
The population size of owl is smaller than the rat and lacks behind the rats population [1m].
When there are sufficient resources, an increase in the rat population is followed by an increase in
the owl population [1m].
Dramatic predation or other factors like spread of diseases, causes a drop in the population of the rat
[1m].
Rat
Owl
Hence the food for the owl becomes limited [1m]. Often, this plus other adverse circumstances like
spread of diseases lead to decline in the population of owl [1m].
The rat and owl regulate the population of each other constantly in a dynamic equilibrium [1m].
Section D: Paper 3 questions (17%)
1. A farmer has a papaya orchard. Since the product of his orchard is abundant, he decided to produce
papaya pickles. He sliced the papaya and immersed the slices in water and then soaked in the sugar
solution. When the papaya slices were immersed with water, the slices became turgid and increased in
their sizes. However, when the papaya slices were soaked in sugar solution, the slices became soft and
shrunken.
Based on the observation, plan an experiment to identify the concentration of sugar solution which
is isotonic to the cell sap of the papaya
Answer:
Problem statement:
What is the concentration of sugar solution which is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya cells?( m)
Aim of the experiment:
To identify the concentration of sugar solution that is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya cells.( m)
Hypothesis:
The concentration of sugar solution which is isotonic to the cell sap of papaya cells does not affect the mass
of papaya cells. ( m)
Variables:
Manipulated variable: Concentration of sugar solution.(1m)
Responding variable: mass of papaya slice.(1m)
Controlled variable: Surrounding temperature and time/ size of papaya slices.(1m)
Apparatus:
A razor blade, petri dishes, forceps, a ruler, 50ml beakers, an electronic balance and tissue paper
Materials
Freshly cut papaya slices, distilled water, sugar solution (0.1 M, 0.2 M, 0.3 M, 0.4 M, 0.5 M and 0.6 M). (
m)
Technique
Measure the mass of papaya slices with the electronic balance and determine the percentage differences in
mass. ( m)
Procedure:
1. Seven petri dishes are prepared and labelled 1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7.
2. Each petri dish is filled with the following solutions respectively:
Petri dish 1: Distilled water
Petri dish 2: 0.1 M sugar solution
Petri dish 3: 0.2 M sugar solution
Petri dish 4: 0.3 M sugar solution
Petri dish 5: 0.4 M sugar solution
Petri dish 6: 0.5 M sugar solution
Petri dish 7: 0.6 M sugar solution
3. A papaya fruit is cut into seven cylindrical strips of 50 mm long and 1mm thick
4. Each strip is patted dry with a piece of tissue paper
5. The mass of each strip is weighed and recorded
6. Each strip is then placed in a petri dish which is completely covered with sugar solution
7. After soaking for an hour each strip is removed from its respective petri dish and patted dry
8. The mass of each strip is weighed again and recorded
9. The results are tabulated. A graph of the percentage of differences in mass against the concentration
of the sugar solution is plotted.
Presentation of data:
Conclusion:
The hypothesis is accepted. When the papaya cells are immersed in an isotonic solution, there is no net gain
in mass and size. Based on the graph, the concentration of the cell sap of papaya tissue is______M
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Biology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNDokumen15 halamanBiology Form 4 Sem 1 p2 2016 JWPNMiz KarstzBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 9701 On23 P41Dokumen19 halamanBiology 9701 On23 P412190ibrahimazeemBelum ada peringkat
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Itaconate in A Water-Cyclohexane-TritonDokumen7 halamanCatalytic Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Itaconate in A Water-Cyclohexane-Tritonxinyi zhangBelum ada peringkat
- Set8ans 10Dokumen5 halamanSet8ans 10Agustina Evania DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Short Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Dokumen42 halamanShort Answers Chapter 1 Page 3Leen AlodatBelum ada peringkat
- Thermo Final ReportDokumen30 halamanThermo Final ReportharshBelum ada peringkat
- tmpBB6B TMPDokumen9 halamantmpBB6B TMPFrontiersBelum ada peringkat
- Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyDokumen102 halamanModule SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyKen Yew PiongBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Bio SBP 2011 AnsDokumen23 halamanModul Bio SBP 2011 AnsAlan WangBelum ada peringkat
- Membrane Prob.Dokumen12 halamanMembrane Prob.Riki BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles by Modified Sol-Gel ProcessDokumen9 halamanSynthesis of Silica Nanoparticles by Modified Sol-Gel ProcessMeruyert KarimBelum ada peringkat
- All F1 Exams Set ThreeDokumen114 halamanAll F1 Exams Set Threeotaku senpaiBelum ada peringkat
- November Midterm 2021Dokumen9 halamanNovember Midterm 2021PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal 2 Membran Fuell From Chitosan & ABSDokumen8 halamanJurnal 2 Membran Fuell From Chitosan & ABSMochammad Rendra PascariansyahBelum ada peringkat
- (230 Marks) : (1 Mark)Dokumen44 halaman(230 Marks) : (1 Mark)Areg ManukyanBelum ada peringkat
- EcosystemDokumen2 halamanEcosystemJAPHET NKUNIKABelum ada peringkat
- GenPhysics DREMT1-1 Orias 1Dokumen5 halamanGenPhysics DREMT1-1 Orias 1Andrew OriasBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 3 2Dokumen53 halamanPaper 3 2Mohammad HamdanBelum ada peringkat
- S5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEDokumen16 halamanS5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEmunyanezaolivier422Belum ada peringkat
- Biology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolDokumen17 halamanBiology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolAlexCuiBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)Dokumen9 halamanTopic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)한서현Belum ada peringkat
- Optimal Production of Biohydrogen Gas Via Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MEC) in A Controlled Batch Reactor SystemDokumen6 halamanOptimal Production of Biohydrogen Gas Via Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MEC) in A Controlled Batch Reactor SystemairsrchBelum ada peringkat
- Jawapan Kertas 2 Bio JulaiDokumen8 halamanJawapan Kertas 2 Bio Julaizulhariszan abd mananBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Dokumen0 halamanAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanBelum ada peringkat
- Emulsion Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate, Ethylene, and N-Methylol AcrylamideDokumen6 halamanEmulsion Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate, Ethylene, and N-Methylol Acrylamideramitkatyal21881Belum ada peringkat
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesDari EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Science Reviewer For Grade 11 STEMDokumen19 halamanScience Reviewer For Grade 11 STEMRoxanne GloriaBelum ada peringkat
- Jawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)Dokumen45 halamanJawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)azamsensei94% (32)
- Gaseous ExchangeDokumen4 halamanGaseous ExchangeArvin DiNozzoBelum ada peringkat
- Compartment ModelsDokumen47 halamanCompartment ModelsVincent100% (1)
- 1.1 - 1.6 Practice Data-Based QuestionsDokumen11 halaman1.1 - 1.6 Practice Data-Based QuestionsNatalia Sojo ConchasBelum ada peringkat
- Revision For SA1 (Students' Copy)Dokumen7 halamanRevision For SA1 (Students' Copy)SUNDARI SIVASANKARBelum ada peringkat
- QB Update 1A ch04 eDokumen8 halamanQB Update 1A ch04 e008 proartBelum ada peringkat
- Scheme For Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2Dokumen7 halamanScheme For Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2RuoQi LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Questions For Form Five Students That Can Lead For Their Excel in SPMDokumen14 halamanBiology Questions For Form Five Students That Can Lead For Their Excel in SPMZati Mohd RazibBelum ada peringkat
- April Exam SL - MSDokumen13 halamanApril Exam SL - MSannaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ReportDokumen7 halamanLab Reportapi-387734904Belum ada peringkat
- Cell and Membrane Physiology and Biophysics: Group 5 Section 1-CDokumen6 halamanCell and Membrane Physiology and Biophysics: Group 5 Section 1-CKevin CalaraBelum ada peringkat
- Biology f1 MsDokumen8 halamanBiology f1 MswilliammakuuBelum ada peringkat
- A Novel Method For Synthesis of Silica NanoparticlesDokumen7 halamanA Novel Method For Synthesis of Silica NanoparticlesAsheesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- STPM Biology (Ecosystem - Structure Que)Dokumen3 halamanSTPM Biology (Ecosystem - Structure Que)charlie avalBelum ada peringkat
- Iodination Lab Report1Dokumen5 halamanIodination Lab Report1Sherlock Wesley ConanBelum ada peringkat
- Dy (III) Ionic LiquidsDokumen7 halamanDy (III) Ionic LiquidsKhalil OukebdaneBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokumen27 halamanNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAlok PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Aqa 74011 SQPDokumen24 halamanAqa 74011 SQPRobert EdwardsBelum ada peringkat
- Science CambridgeDokumen16 halamanScience CambridgeSubashini Muniandy100% (1)
- Healthcare Insulin ProblemDokumen16 halamanHealthcare Insulin ProblemTaufiq JaiBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2 SolutionDokumen4 halamanProblem Set 2 SolutionKaram Jaradat100% (2)
- Adsorption StudyDokumen8 halamanAdsorption StudyZeleke ZewdeBelum ada peringkat
- 6021 Fall 2004Dokumen547 halaman6021 Fall 2004combatps10% (1)
- Transport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsDokumen10 halamanTransport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsOTIENO ELIJAHBelum ada peringkat
- MM Draft 1 Antonio Moncayo Nov21 Recuperado - RCDokumen6 halamanMM Draft 1 Antonio Moncayo Nov21 Recuperado - RCAntonio MoncayoBelum ada peringkat
- Tran IOP2021 NKLPhuongDokumen8 halamanTran IOP2021 NKLPhuongPhuong CRBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionDari EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Riverine Ecosystem Synthesis: Toward Conceptual Cohesiveness in River ScienceDari EverandThe Riverine Ecosystem Synthesis: Toward Conceptual Cohesiveness in River ScienceBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesDari EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsDari EverandPhysical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsMitsuru NagasawaBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsDari EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Sukma 27032018Dokumen1 halaman1 Sukma 27032018Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Sukma (Latty)Dokumen1 halaman1 Sukma (Latty)Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review 2.1 Past Studies On Youtube Videos As A Learning ToolDokumen3 halamanLiterature Review 2.1 Past Studies On Youtube Videos As A Learning ToolBanu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Answer Causal ComparativeDokumen6 halamanAnswer Causal ComparativeBanu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Correlation and Causal Comparative ResearchDokumen34 halamanCorrelation and Causal Comparative ResearchBanu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- I.) UNIT 9 Cloud SocietyDokumen32 halamanI.) UNIT 9 Cloud SocietyBanu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 (Be Wise, Think Twice) ToDokumen11 halamanChapter 4 (Be Wise, Think Twice) ToBanu Priya100% (1)
- Fina Examination Paper 20122Dokumen6 halamanFina Examination Paper 20122Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen4 halamanPresentation 1Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Past Year 1995Dokumen48 halamanPast Year 1995Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Dokumen9 halamanIT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Dokumen8 halamanIT Bio F4 Topical Test 3 (BL)Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Year Exam Bio 2014Dokumen6 halamanMid Year Exam Bio 2014Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin ChartDokumen4 halamanVitamin ChartBanu Priya100% (1)
- Endangered Ecosystem Kami 3Dokumen34 halamanEndangered Ecosystem Kami 3Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Dokumen24 halamanRespiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Banu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Shi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineDokumen11 halamanShi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineJavier BlancBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Second Quantization: 1.1 Single-Particle Hilbert SpaceDokumen6 halamanIntroduction To Second Quantization: 1.1 Single-Particle Hilbert Space김띵Belum ada peringkat
- Atlantis Is Discovered - Atlantis in Middle Danubian Depression (Pannonian Basin) A New Location of Atlantis IslandDokumen31 halamanAtlantis Is Discovered - Atlantis in Middle Danubian Depression (Pannonian Basin) A New Location of Atlantis Islandpaulct2004721260% (10)
- Meal Planning Guide e BookDokumen7 halamanMeal Planning Guide e BookA'isha TijjaniBelum ada peringkat
- PT3 Guided WritingDokumen8 halamanPT3 Guided WritingDayang Haffizah Abg AbdillahBelum ada peringkat
- Vanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019Dokumen6 halamanVanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019mituBelum ada peringkat
- Research Argumentative EssayDokumen6 halamanResearch Argumentative EssayHoney LabajoBelum ada peringkat
- A Slice of History - Pizza Turim 4-7-15Dokumen2 halamanA Slice of History - Pizza Turim 4-7-15Mae Princess BolivarBelum ada peringkat
- A-ZKD-13 (ZKD-59 (A) ) : Mechanical ParameterDokumen1 halamanA-ZKD-13 (ZKD-59 (A) ) : Mechanical Parameterwissam zaatuorBelum ada peringkat
- NHouse SelfBuilder Brochure v2 Jan19 LowresDokumen56 halamanNHouse SelfBuilder Brochure v2 Jan19 LowresAndrew Richard ThompsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 TurbineDokumen56 halamanChapter 4 TurbineHabtamu Tkubet EbuyBelum ada peringkat
- Barilla SpaDokumen11 halamanBarilla Spavariapratik100% (1)
- P eDokumen22 halamanP eKiks AshBelum ada peringkat
- Green Engine 2 PDFDokumen7 halamanGreen Engine 2 PDFharivardhanBelum ada peringkat
- (Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFDokumen302 halaman(Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFmarcosBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Quarter - Summative Test in TleDokumen2 halaman2nd Quarter - Summative Test in TleRachelle Ann Dizon100% (1)
- DattadasDokumen4 halamanDattadasJéssica NatáliaBelum ada peringkat
- Local AnesthesiaDokumen55 halamanLocal AnesthesiaAhmed MagdyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodDokumen6 halamanChapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodMbali MagagulaBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Money Box: Pig (Assembly Instructions) : The Movements Work Better With Heavier CoinsDokumen6 halamanMoving Money Box: Pig (Assembly Instructions) : The Movements Work Better With Heavier CoinsjuanBelum ada peringkat
- A Duality Principle For The Entanglement Entropy of Free Fermion SystemsDokumen12 halamanA Duality Principle For The Entanglement Entropy of Free Fermion SystemsCroco AliBelum ada peringkat
- IPC 4552 Cuprins - ENIG PDFDokumen3 halamanIPC 4552 Cuprins - ENIG PDFMarlon CornejoBelum ada peringkat
- AP Human Geography Review Unit 2Dokumen18 halamanAP Human Geography Review Unit 2BaselOsman50% (2)
- Fourth Quarter ExamDokumen4 halamanFourth Quarter Examjanice gumabao50% (4)
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeDokumen4 halamanThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1Belum ada peringkat
- 4th Six Weeks RecoveryDokumen8 halaman4th Six Weeks RecoveryAshley HighBelum ada peringkat
- KRC1 Start-Up PDFDokumen29 halamanKRC1 Start-Up PDFRafael50% (2)
- Rockwell Allen BradleyDokumen73 halamanRockwell Allen BradleymaygomezBelum ada peringkat
- Sunday Afternoon, October 27, 2013: TechnologyDokumen283 halamanSunday Afternoon, October 27, 2013: TechnologyNatasha MyersBelum ada peringkat
- JCB R135 & R155-HD Skid Steer-New BrochureDokumen8 halamanJCB R135 & R155-HD Skid Steer-New BrochureAshraf KadabaBelum ada peringkat