Wo 2013104039 A 1
Diunggah oleh
Mladen Muskinja0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
55 tayangan8 halamana
Judul Asli
Wo 2013104039 a 1
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inia
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
55 tayangan8 halamanWo 2013104039 A 1
Diunggah oleh
Mladen Muskinjaa
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 8
Equipment for condensing electric current and equipment for transmitting electri
c current through air
WO 2013104039 A1
Abstract
The present invention relates to electromagnetic equipment that comprises, conce
ntrically arranged, a metallic disk, preferably a metallic disk (6), and at leas
t one first magnetic or electromagnetic field generator (9.1) (magnet) attached
to the shaft (4), near the disk (6), a second magnetic or electromagnetic field
generator (9.2) (magnet) being located at the end of said shaft (4) and attached
to a base (10), but not to the shaft (4), near the magnetic or electromagnetic
field generator (9.1) (magnet) attached to the shaft (4), with the poles facing
the poles of the latter. At least two electromagnetic field generators (12) and
(14) are arranged next to the shaft (4) with part of the metallic disk (6) there
between, the power source and the external loads (17) being connected to said de
vices, of which at least one is an inducer, and both of which are arranged near
the magnetic or electromagnetic field generators (9.1) and (9.2) (magnets), alig
ned with the shaft (4) in such a way that the magnetic and electromagnetic field
s thereof interact with the rotating shaft (4). The invention has various uses,
including the generation of electric voltage and the condensation of consumed re
active power, in order to transform this reactive power into useful electric pow
er. Another function is the generation of electric voltage and the transmission
of electric current through air.
Description translated from Portuguese (Portugal)
Descriptive Report of Patent for "COMPACTION EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT AND E
QUIPMENT FOR SPREAD OF ELECTRICITY IN THE AIR".
The present invention relates to a device for generating electromagnetic energy.
More specifically equipment capable of producing electricity using the return c
urrent consumption, and propagate the electric current in the air.
Description of the Related Art
Numerous projects are the mechanisms for the generation of electricity based on
electromagnetism, but the projects have hitherto known technical limitations of
generating capacity and ecological implications, that prevent use in economic sc
ale.
Obietivos the Invention
The proposed compaction equipment of electric current, comprising a device that
includes a shaft concentrically incorporating a hard metal, preferably an alumin
um disk, and also fixed to the shaft near the disk at least one magnetic field g
enerating device (magnet) or electromagnetic, with the end of the shaft but not
attached to it at least one other magnetic field generating device (magnet) or e
lectromagnetic fixed to a base, getting close to the magnetic field generating d
evice (magnet) or Electromagnetic fixed to the shaft, arranged with their poles
in comparison with that, and disposed adjacent to the axle, being part of the al
uminum disc between them, at least two devices for producing electromagnetic fie
ld - which are connected to the power source and the loads External - and at lea
st one an inductor, both disposed near the magnetic field generating devices (ma
gnets) or electromagnetic axis aligned so that their magnetic and electromagneti
c fields interacting up with the movement of the shaft.
The device object of the present invention operates as follows for the compressi
on of electric current: devices that generate electromagnetic fields are powered
by an external power source such as a dealership. Thus, the shaft is rotated th
rough electromagnetic induction and electric current received by the load induct
or.
The inductor, upon receiving the return current, causes confrontation and intera
ction of electromagnetic fields generated by devices that generate electromagnet
ic fields with magnetic fields of the magnets, then rotation occurs when the met
al disc which rotates the shaft and the magnet fixed to it along with its magnet
ic field. Thus, no generation of tension and compression of return of the electr
ic current to feed back a new load.
It is further proposed an apparatus for spread of electric current in the air, c
omprising a device that includes a device driving force to rotate a shaft which
incorporates a disc concentrically metal, preferably an aluminum disk, and also
fixed to the shaft near the disk at least one magnetic field generating device (
magnet) or electromagnetic, with the end of the shaft but not attached to it at
least one other magnetic field generating device (magnet) or electromagnetic fix
ed to a base, being near the magnetic field generating device (magnet) or Electr
omagnetic fixed to the shaft, arranged with their poles in confrontation with th
at, and arranged adjacent to the shaft, leaving part of the aluminum disk betwee
n them, at least two devices that generate electromagnetic fields - which are co
nnected to the power supply and the external load - and at least one of an induc
tor, both disposed near the magnetic field generating devices (magnets) or elect
romagnetic axis aligned so that their magnetic and electromagnetic fields intera
cting up, with the shaft.
The device object of the present invention operates as follows for the propagati
on of electric current in the air: a driving force rotates the shaft, rotating m
etal disc and along with it the magnet that is attached to the shaft, comparing
with the magnetic field of the magnet that is fixed to the base. Thus, the magne
tic fields of the magnets interact with the electromagnetic field of the externa
l load. With this interaction of fields in rotation, the inductor starts to gene
rate voltage that will provide the potential difference (ddp) when closing the c
ircuit with the neutral or ground, can be used the neutral or ground feeding the
external load. Thus, the electric current through the interaction of magnetic f
ields and electromagnetic spreads in the air.
The present invention provides an apparatus for generating electrical voltage wh
ich generates energy by reusing the current drawn from sources consumers. Thus,
the device does not harm the environment when used as force generating their own
electricity, having a negligible consumption in relation to the current generat
ed.
The voltage generating equipment is compact and inexpensive, and can be used in
various types of machinery, equipment or application areas that require electric
ity to operate.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The present invention will be hereinafter described with the aid of drawings, bu
t which are not absolutely limiting where it can be observed other details and a
dvantages of the present invention.
The figures show:
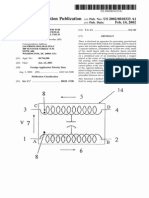
Figure 1 - illustrates the voltage generation device of the present invention;
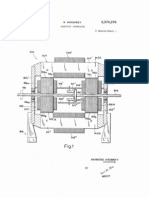
Figure 2 - shows the set of induced voltage generation device of the present inv
ention, and
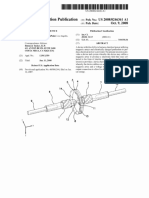
Figure 3 - shows the effect of the circulating current in the air and the circui
t device of the present invention.
Figure 4 - Diagram of the electrical circuit of the equipment for power generati
on and compression of electrical current.
Figure 5 - Diagram of the electrical circuit of the equipment for power generati
on and propagation of electrical current air.
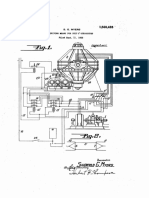
Detailed Description of the Invention Figure 1 shows a device for generating ele
ctricity can compress electrical current and propagate electrical current in the
air. The equipment comprises a driving force, in this example, a first electric
motor fixed to a central shaft 4 by a coupling pin 3 and 2.1. The pin 2.1 centr
alizes the axis of the motor 1 with a drive shaft 6 which is used to rotate the
shaft 4 through an electromagnetic field.
2.2 a pin centers at least two magnetic field generating devices, in this case,
magnets 9.1, 9.2 Central 4 to the shaft and a coupling metal couples the motor s
haft to the shaft of the first disk 4.
The central axis 4 is connected to a metal fixing sleeve which fixes the disk 5
and a holder 6 and at a higher bottom bracket clamping 8 which are used to faste
n the magnets 9.1, 9.2.
2.2 The pin is fixed to a base 10 and centralize the magnets 9.1 and 9.2, formin
g a magnetic field that repels, since the magnets 9.1, 9.2 are positioned with e
qual signs north pole, north pole or south south.
The device further comprises electromagnetic field generating device, in this ca
se an inductor 12 coupled to a support holder 10 and the other electromagnetic f
ield generator device, in this case a coil 14. The support bracket 10 is connect
ed to the coil 14 through a medium iron "U" type 13 that centralizes disk space
6 between the inductor 12 and the coil 14.
Although coils are shown, magnets and inductors in the present exemplary embodim
ent may be used other types of devices that generate electromagnetic fields, suc
h as at least one electromagnetic coil or magnet or electromagnetic induction, o
f any type and shape, including any combination and in amounts for each applicat
ion equipment.
The inductor 12 receives current from a power source 17, which can be any electr
ical circuit or electrical machine that generates or consumes electricity in per
forming work.
The coil 14 and the inductor 12 comprising at least one core of any geometric sh
ape. The core may be, for example, silicon iron. The core is formed by more than
a number of members, which together form one or more core windows.
The coil 14 may have a rounded shape, square columns with or without column. The
coil 14 rounded shape should be fully insulated with insulating material as its
phase: single phase, two phase or three phase.
So exemplary coil 14 square with central columns, the columns should be insulate
d with insulating material as its phases: single phase, two phase or three phase
. Already in the first coil without square column, the coil must be fully insula
ted with insulating material as its phases: single phase, two phase or three pha
se.
One form of primary coil winding 14 is made with members of enamelled copper con
ductors and cross-section is defined as the iron used and the desired voltage co
il 14.
The power generator may be from 1 to 1000 KVA MVA may be lower or higher than th
is, being of the type single phase, biphasic, or triphasic.
In a preferred embodiment, the coil comprises a core 14 formed of laminated shee
ts oriented silicon iron. The core is formed by a number of members which togeth
er form one or more core windows.
The inductor 12 also provides any shape such as round, square, with or without c
olumns.
In a preferred embodiment, as can be seen in figure 2, the inductor 12 comprises
two columns with iron tablets, one above the other forming a shape like "U". Co
lumns are fully insulated conductor and a member 30 is wrapped in columns concen
trically, involving the columns of the inductor 12.
The driving member 30 is closed shorted ends, forming an artificial load. The nu
mber of turns and the cross section are calculated and sized according to the po
wer of the inductor (12).
Upon closing of the artificial load, the member (30) should be insulated to not
have contact points 21 and 22. A second conductive member is wound concentricall
y in the columns of the inductor 12 and the sizing and number of turns are calcu
lated according to the electric current reception desk where the term correspond
ing to paragraphs 21 and 22 of the ends of the conductive member 30 receiving cu
rrent loads external.
The captors of electrons from the earth and the captors of electrons from space
perform the function of capturing power generation. The captors of electrons fro
m space are described in the patent application n BR1020120008378 Brazilian, fro
m 13.01.2012. The sensor refers to an electromagnetic device for generating elec
tric current through the capture of free electrons. The electron earth sensors a
re described in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012,
which relates to a device for generating electromagnetic energy.
Compression of current consumed:
The term "electrical current consumed" refers to the return current from the pow
er factor of any energy source that produced 17 working consumption.
For the compression of electric current, the inductor 12 and the coil 14 is powe
red by an external power source such as the concessionaire. Thus, do not use the
electric bike 1 to rotate the shaft 4, the shaft 4 is rotated by electromagneti
c induction and the electric current of the loads received by the inductor 12.
When generating tension and compress electric current, voltage feeding the coils
14 and 12 inducers of equipment, there is only the generation of tension and co
mpression of the electrical current return for moving the shaft that can be of a
ny equipment that generates or consumes electrical current, which process the re
turn current in power to be reused.
It should be connected to the point (A) of the coil 14 to point 21 of inductor 1
2 which is connected to the stage, and the point (B) of the coil 14 is connected
to the neutral and may also be powered by the power supply neutral to be compac
ted 17.
The inductor 12 to receive electrical current from the power source to be compac
ted at point 21 (which is the phase inductor 12 which is connected to the point
(1a) of the coil 14 generates the return current will come out in packed form of
the power point 22 of the inductor 12 can connect any external load 17 of the p
oint 22 which is the output stage of the inductor 12 to the point (B) of the neu
tral coil consumption according to their potency compressed by physical effect a
nd the current flow 7. With this form of connection to the electric current is c
ompressed.
As can be seen in Figure 3, the generation of the electromagnetic field has the
opposite effect 7. The saw is compact as the rotation axis 4, which rotates thro
ugh electromagnetic induction generated by the current. The chain is compressed
in the form of power to be used again, regardless of the voltage and the frequen
cy of rotation of the shaft 4 will be transferred because the voltage and freque
ncy of the power coil 14 and the inductor 12 to the current that has been compre
ssed for reuse in power again working.
By feeding coil circuit 14 and the inductor 12, an electromagnetic field is gene
rated, where the phase must be connected in point 21 of inductor 12 which is con
nected to the point A of the coil 14, the load neutral is connected to point B t
he coil 14, the load 17 to be compressed must be connected at point 22 and the i
nductor coil to point B 14.
Thus, the load 17 is connected and comes to return current load 17 and the actua
l current will return to point 22 which point is the initial power output.
The inductor 12, to receive the return current in paragraph 22, the physical eff
ect happens 7 that will confront the electromagnetic field generated by the indu
ctor 14 and the coil 12, and the magnetic field of the magnets 9.1 and 9.2. Thro
ugh the interaction of electromagnetic fields and magnetic rotation occurs 6 dis
c, which rotates the shaft 4 and the magnet 9.1 along with its magnetic field. T
hus, the feed stream is compressed again for a new charge 17.
The power source 17 may be any machine that generates or consumes electric curre
nt, ie, is a device that consumes power for its operation, resulting in return o
f the electric current to be compacted, or any machine that generates electrical
current through the capture and movement of electrons, providing electrical cur
rent to be compacted.
Thus, the device recycles the current consumption of any equipment or machine, m
aking the current consumption power be reused without having to return to the po
int of consumption external supply, ie the initial source.
The higher the speed, the greater the compression chain and the greater the comp
action of the current, the greater the power.
It is noteworthy that the devices generate electromagnetic fields 0:14 are power
ed by a power source, as the circuit shown in Figure 4, to generate tension and
compression electrical current.
Spread of current in the air:
The equipment can also be used to spread current in the air. For the spread of t
he air current, the inductor 12 and the coil 14 are not fed with energy from an
external source, only the electric motor 1 is powered to move the shaft 4, which
by the rotation generates tension in paragraphs 21 and 22 of inductor 12, and a
t the same time, the electric current propagates in air.
The equipment operates at a constant speed synchronized with low or high speed,
generating alternating electrical voltage and frequency applied to the terminals
of an inductor 12 due to the same rotation between the revolving field magnet f
ield of 9.1 with electrical current backfire 7 shown in Figure 3 and the magneti
c field produced by the magnets which is fixed to 9.2 0 basis.
The propagation of the air current is directly proportional to the rotation axis
, the greater the rotation, the higher the voltage generation inductor 12 and th
e current propagation in air.
The manner of connection for the generation and propagation of stress in the air
stream through the shaft 4 by rotating the disk 6 by any mechanism at a constan
t speed synchronized with either low or high rotation frequency, and generates a
n alternating voltage applied to the terminals points 21 and 22 of inductor 12 w
herein the entry point 21 and 22 of the external current becomes thus output ter
minals for powering loads.
Point 21 and point 22 will come out of the inductor 12 and the voltage frequency
generated according to rotation, or due to the similar movement of rotation bet
ween the rotating field and the magnetic field produced by the magnets 9.1 and 9
.2, and the coil 14 and the inductor 12 are not fed and are close to the magnets
9.1 and 9.2. Thus, the voltage is generated in the inductor 12 in paragraphs 21
and 22 of which will leave the stage. The neutral is connected to ground, and w
hen the neutral phase generation will leave the closing of the three coils 14 st
ar.
The electromagnetic field of magnets 9.1 and 9.2, as the rotation shaft 4 with t
he electromagnetic field produced between the magnets 9. and 9.2 and the inducto
r 12, expands the electric current through the electromagnetic field of magnets
9.1 and 9.2, where 9.1 is the magnet rotating with the shaft 4 and 6 with the di
sc, through the rotation of the electromagnetic field. As the phase lag is 360 d
egrees p to each other, with the rotating electromagnetic field on 360 , the phas
es cancel each other, and the chain expands in the free space in the air.
The engine or any other mechanism which can rotate the shaft 4 at a constant rot
ation, rotates the magnet 9.1 which is connected to the shaft 4 with the magneti
c field of the magnet 9 1 who is confronted with the magnetic field of the magne
t 9.2, which is fixed to the base 10.
Thus, the magnetic fields of the magnets 9.1 and 9.2 interact with the electroma
gnetic load 17, which may be the trap electrons. With this interaction of the ro
tating field, the inductor 12 starts to generate voltage in paragraphs 21 and 22
that will provide the potential difference (ddp) when closing the circuit with
the neutral or ground, you can use the neutral or earth that feeds external load
.
Thus, the electric current through the interaction of magnetic fields and electr
omagnetic spreads in the air.
The equipment can be used with any type of electric motor: single phase, two pha
se or three phase AC or DC at any voltage or combustion engine, or any other typ
e of mechanism that can rotate the shaft of the generator operating in a constan
t speed synchronized with rotation generating low or high frequency alternating
electric voltage and applied to the terminals of the inductor 12 due to the simi
lar movement of rotation between the rotating field and the magnetic field produ
ced by the magnets 9.1, 9.2.
Note that the electromagnetic field generating devices are 24:14 to feeding of l
oads, the electrical circuit as illustrated in Figure 5 for voltage generation a
nd propagation of electric current in the air.
Although the present invention has been described with reference to preferred em
bodiment and practical application thereof, it is apparent to those skilled in t
he art that a variety of types, formats, templates, gender, modifications and ch
anges that may be made or used without departing from the scope of the invention
which is intended to be defined by the appended claims.
It will be understood that each of the elements described above, or two or more
together may also find a useful application in other types of equipment and effe
cts that differ from the type described above.
Claims translated from Portuguese (Portugal)
CLAIMS
1 "compaction equipment ELECTRIC CURRENT" comprising a device characterized
by including a shaft (4) concentrically incorporating a hard metal (6), and also
fixed to the shaft (4), near the disc (6), and least a first magnetic field gen
erating device (magnet) or electromagnetic (9 1), with the end of the shaft (4),
but not attached to it, at least one second magnetic field generating device (m
agnet) or electromagnetic (9.2) , attached to a base (10), getting close to the
magnetic field generating device (magnet) or electromagnetic (9.2) fixed to the
shaft (4), arranged with their poles in confrontation with that, and arranged ad
jacent to the axis (4 ), being part of the metal disk (6) including at least two
electromagnetic field generating devices (12) and (14), which are connected to
the power supply and the external load (7), at least one a inductor, both dispos
ed near the magnetic field generating devices (magnets) or electromagnetic (9.1)
and (9.2) aligned with the axis (4) so ??that their magnetic and electromagneti
c fields interacting with the shaft (4) in rotation.
2. Compaction equipment according to claim 1, characterized in that the meta
l disk (6) is preferably of aluminum.
3. Compaction equipment according to claim 1, characterized in that it is co
nfigured for use in networks ettricas of low, medium and high voltages.
4. Compaction equipment, according to claims 1 and 3, characterized by the f
act that it is configured for use on electrical monophasic, biphasic or triphasi
c, any powers.
5. Compaction equipment according to claims 1, 3 and 4, characterized by the
fact that the electromagnetic field generating devices (12) and (14) are powere
d by a power source for generating voltage and compact electrical current. 6 "SP
READ APPARATUS FOR ELECTRIC CURRENT ON AIR" characterized by including a device
for driving power (1) for rotating a shaft (4) concentrically incorporating a ha
rd metal, preferably a hard metal (6), and also fixed to shaft (4) close to the
disc (6), at least a first magnetic field generating device (magnet) or electrom
agnetic (9.1) and the end of the shaft (4), but not attached to it at least a se
cond device magnetic field generator (magnet) or electromagnetic (9.2), attached
to a base (10), getting close to the magnetic field generating device (magnet)
or electromagnetic (9.2) fixed to the shaft (4), arranged with their poles in co
nfrontation with that, and disposed adjacent to the axis (4), being part of the
metal disk (6) including at least two electromagnetic field generating devices (
12) and (14), which are connected to the power source and external loads (17), a
t least one of an inductor, both disposed near the magnetic field generating dev
ices (magnets) or electromagnetic (9.1) and (9.2) aligned with the axis (4) so ?
?that their magnetic and electromagnetic fields interact with the shaft (4) in r
otation.
7. Equipment spread according to claim 6, characterized in that the metal di
sk (6) is preferably of aluminum.
8. Equipment spread, according to claim 6, characterized in that it is confi
gured for use in electrical networks of low, medium and high voltages.
9. Equipment propagation according to claims 6 and
8, characterized in that it is configured for use on electrical monophasic,
biphasic or triphasic, any powers.
10. Equipment propagation according to claims 6, 8 and 9, characterized by t
he fact that the electromagnetic field generating devices (12) and (14) are feed
ing points of loads, to generate and propagate the electric current voltage in a
ir.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Wo 2013104042 A 1Dokumen7 halamanWo 2013104042 A 1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Bruce DePalma - Free Energy - Homopolar GeneratorDokumen17 halamanBruce DePalma - Free Energy - Homopolar GeneratorZsolt Szakács100% (1)
- Ele GenDokumen10 halamanEle Gensanju08388458Belum ada peringkat
- Pezde Se SSDokumen24 halamanPezde Se SSRo Ha-haBelum ada peringkat
- Wo 2013104041 A 1Dokumen9 halamanWo 2013104041 A 1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- US6404089B1 - Electrodynamic Field Generator - Google PatentsDokumen114 halamanUS6404089B1 - Electrodynamic Field Generator - Google PatentsТи КоBelum ada peringkat
- Us 7531930 PatentDokumen11 halamanUs 7531930 Patentsebastian.gonczarekBelum ada peringkat
- Minted States Patent 1191 1111 3,760,286: Kelly (45) Sept. 18, 1973Dokumen6 halamanMinted States Patent 1191 1111 3,760,286: Kelly (45) Sept. 18, 1973Victor Von DoomBelum ada peringkat
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDokumen9 halamanMotionless Electromagnetic GeneratorViswa TejaBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Guide To Free Energy' Devices: United States Patent 6,362,718 Dated: 26th March 2002 InventorsDokumen18 halamanA Practical Guide To Free Energy' Devices: United States Patent 6,362,718 Dated: 26th March 2002 InventorsitaloBelum ada peringkat
- SChapter 34Dokumen9 halamanSChapter 34stban murilloBelum ada peringkat
- Bruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachineDokumen7 halamanBruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachinebanzailoicBelum ada peringkat
- Bruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachineDokumen7 halamanBruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachineHaris DizdarevicBelum ada peringkat
- TermoionicGenerator Rexresearch - Com Jamesthermelgenr JamesthermogenerDokumen5 halamanTermoionicGenerator Rexresearch - Com Jamesthermelgenr Jamesthermogenermarco santancheBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of A Corona-Discharge Based Electrostatic MotorDokumen10 halamanAnalysis of A Corona-Discharge Based Electrostatic MotorhmxzBelum ada peringkat
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDokumen8 halamanMotionless Electromagnetic Generatorraja100% (1)
- Magnacoaster Patent WillisDokumen22 halamanMagnacoaster Patent WillisMikolas*Belum ada peringkat
- Electrostatic AccelaratorDokumen18 halamanElectrostatic AccelaratorPradeepBelum ada peringkat
- Kromrey Converter US3374376Dokumen8 halamanKromrey Converter US3374376kishbud100% (1)
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 315, January 14, 1882Dari EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 315, January 14, 1882Belum ada peringkat
- Wo 2013104043 A 1Dokumen9 halamanWo 2013104043 A 1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Essay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextDokumen24 halamanEssay (Article) About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextDavid Plata0% (1)
- Us 20020018333Dokumen15 halamanUs 20020018333Victor Von DoomBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical SystemDokumen42 halamanElectrical SystemSamiha Maysoon NooriaBelum ada peringkat
- March 19, 1968 - R, Kromrey I 3,374,376: Electric GeneratorDokumen8 halamanMarch 19, 1968 - R, Kromrey I 3,374,376: Electric GeneratorVlad AdrianBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis On Electromagnetic Car PDFDokumen3 halamanSynopsis On Electromagnetic Car PDFyrikkiBelum ada peringkat
- Ya, Zad: Nov. 5, 1968 J. O. Bur KE 3,409,820Dokumen3 halamanYa, Zad: Nov. 5, 1968 J. O. Bur KE 3,409,820Anton DremlyugaBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Electrical SystemDokumen18 halamanAircraft Electrical SystemAma Serwaa YeboahBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen10 halamanElectrical Generator: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSalooBelum ada peringkat
- Nicola Tesla Electroradiant EffectDokumen16 halamanNicola Tesla Electroradiant Effectrodolfo barbosaBelum ada peringkat
- A Project On Pizeoelectric Crystal Based InverterDokumen66 halamanA Project On Pizeoelectric Crystal Based InverterThakur Vivek SinghBelum ada peringkat
- SeminarDokumen24 halamanSeminarpraveenpv7100% (2)
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDokumen12 halamanMotionless Electromagnetic GeneratorRajesh Chary100% (2)
- US3409820 Electric Power Apparatus - James.O.burke.1964Dokumen3 halamanUS3409820 Electric Power Apparatus - James.O.burke.1964joeymusaki676Belum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIDokumen38 halamanElectromagnetism 2: Factors Affecting Induced EMIChello Marielle San GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Us 13,610,971Dokumen8 halamanUs 13,610,971Сергей КолесниковBelum ada peringkat
- Orbiting Multi-Rotor Homopolar System: Institute For High Temperatures, Russian Academy of Science, Izhorskaya 13Dokumen7 halamanOrbiting Multi-Rotor Homopolar System: Institute For High Temperatures, Russian Academy of Science, Izhorskaya 13Dan BeesonBelum ada peringkat
- Report in Eng Conv DocuDokumen5 halamanReport in Eng Conv DocuRex Albert TejadillaBelum ada peringkat
- Meyer Patent 1Dokumen25 halamanMeyer Patent 1jonasrodon1624Belum ada peringkat
- (Free Energy) Kunel PatentDokumen9 halaman(Free Energy) Kunel PatentIra Weinstein100% (1)
- The 1-Kilowatt "Battery"Dokumen6 halamanThe 1-Kilowatt "Battery"Jaffar HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Testatika Princip PDFDokumen0 halamanTestatika Princip PDFmanos306Belum ada peringkat
- Study of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelDokumen6 halamanStudy of Electricity Generated by Ceiling Fan & Car WheelSaru TVBelum ada peringkat
- Brevet Generator US20080246361A1Dokumen14 halamanBrevet Generator US20080246361A1eubogdan2013Belum ada peringkat
- 45 24985 EE328 2016 1 2 1 Lecture2allDokumen51 halaman45 24985 EE328 2016 1 2 1 Lecture2allHoppohigdi786 Hoppohigdi786Belum ada peringkat
- DC Machines: Engr. Rovenson V. SevillaDokumen20 halamanDC Machines: Engr. Rovenson V. SevillaEna Leanica DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Russian SEGDokumen9 halamanRussian SEGrichcollins6217Belum ada peringkat
- TT Brown's Electrokinetic Generator PatentDokumen7 halamanTT Brown's Electrokinetic Generator PatentJason Warden0% (1)
- Referat BuzoDokumen11 halamanReferat BuzoAnaBelum ada peringkat
- 1) Hydroelectric DamsDokumen9 halaman1) Hydroelectric DamsKaren BritanicoBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machine BMT 3013: Chapter 1: Single and Three Phase TransformerDokumen81 halamanElectrical Machine BMT 3013: Chapter 1: Single and Three Phase TransformerSyahidah MohdBelum ada peringkat
- E2063 Teknologi Elektrik 2 UNIT6Dokumen16 halamanE2063 Teknologi Elektrik 2 UNIT6dbu2952Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2Dokumen25 halamanUnit 2Dr.Sakthivel SBelum ada peringkat
- SeminarDokumen10 halamanSeminarswathisreejith6Belum ada peringkat
- Tesla Coil ReportDokumen15 halamanTesla Coil ReportSAVITRI GURJARBelum ada peringkat
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 421, January 26, 1884Dari EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 421, January 26, 1884Belum ada peringkat
- Mushroom Production GuideDokumen123 halamanMushroom Production GuideMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Espacenet DocumentDokumen1 halamanEspacenet DocumentMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Espacenet DocumentDokumen1 halamanEspacenet DocumentMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- More Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceDokumen5 halamanMore Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Sand2012 0304Dokumen64 halamanSand2012 0304Emma GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Us7224077 PDFDokumen6 halamanUs7224077 PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Energy Systems (Johnson)Dokumen449 halamanWind Energy Systems (Johnson)Mario Shawn Hayden Jr100% (1)
- Book Cultivation Merged MushroomDokumen278 halamanBook Cultivation Merged MushroomHussain1006100% (2)
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDokumen3 halamanWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Dokumen7 halamanUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- 1974008662Dokumen4 halaman1974008662Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0148513 A1Dokumen18 halamanUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0148513 A1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Us7224077 PDFDokumen6 halamanUs7224077 PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Course Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus) : Daily Program On Delphy Mushroom FarmDokumen2 halamanAdvanced Course Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus) : Daily Program On Delphy Mushroom FarmMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- JPS54159538A Original Document 20200712174721Dokumen4 halamanJPS54159538A Original Document 20200712174721Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- PR-14D Operating Instructions: 144 X 144 X 50 MMDokumen2 halamanPR-14D Operating Instructions: 144 X 144 X 50 MMMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Online Course Mushrooms: HAS Training and ConsultancyDokumen2 halamanOnline Course Mushrooms: HAS Training and ConsultancyMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDokumen3 halamanWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Application PDFDokumen6 halamanApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Application PDFDokumen2 halamanApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDokumen3 halamanWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- PatentsDokumen7 halamanPatentsMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Application PDFDokumen3 halamanApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Double-Channel: Submersible PumpsDokumen4 halamanDouble-Channel: Submersible PumpsMladen Muskinja0% (1)
- Us 1560428Dokumen5 halamanUs 1560428Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- US8047090B2 Original Document 20200618185937Dokumen9 halamanUS8047090B2 Original Document 20200618185937Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Application PDFDokumen2 halamanApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- US9140341B2 Original Document 20200618185302Dokumen32 halamanUS9140341B2 Original Document 20200618185302Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- FR2876163A1Dokumen8 halamanFR2876163A1Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- United States Patent: Annis (10) Patent No .: US 9, 742, 252 B2Dokumen14 halamanUnited States Patent: Annis (10) Patent No .: US 9, 742, 252 B2Mladen MuskinjaBelum ada peringkat
- Emi HLDokumen8 halamanEmi HLUtkarsh SatishBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 5 KSSMDokumen267 halamanPhysics Form 5 KSSMWei Ling Chong100% (1)
- International Journal of Heat and Mass TransferDokumen13 halamanInternational Journal of Heat and Mass TransferfatinBelum ada peringkat
- Charging System TheoryDokumen20 halamanCharging System TheoryTesfahun TegegneBelum ada peringkat
- RPC Assignment 2Dokumen4 halamanRPC Assignment 2Jericho MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 (Part 1)Dokumen29 halamanTopic 4 (Part 1)Azib HamizanBelum ada peringkat
- Program Intervensi Fizik SPM Bil 4 T5Dokumen6 halamanProgram Intervensi Fizik SPM Bil 4 T5sitisalmaherangBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4 AC MachinesDokumen19 halamanModule 4 AC MachinesAffan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT VI Solid State Devices: Two Common Schematic SymbolsDokumen69 halamanUNIT VI Solid State Devices: Two Common Schematic SymbolsMonte CarloBelum ada peringkat
- Karnataka 2nd Puc MQP 2023 Physics PDFDokumen4 halamanKarnataka 2nd Puc MQP 2023 Physics PDFAkash AkashBelum ada peringkat
- EM IV - LecDokumen14 halamanEM IV - LecBala RajuBelum ada peringkat
- EC-Lab - Application Note #05 2005 Precautions For Good Impedance Measurements I - IntroductionDokumen5 halamanEC-Lab - Application Note #05 2005 Precautions For Good Impedance Measurements I - IntroductionR.SubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010Dokumen38 halamanCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010honey1002Belum ada peringkat
- Lakshya JEE Fastrack 2024 - Test PlannerDokumen2 halamanLakshya JEE Fastrack 2024 - Test Plannerkumariavivek1966Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Alternating CurrentsDokumen23 halaman2 Alternating CurrentsKunalWadhawanBelum ada peringkat
- 1965 Simulation of Symmetrical Induction Machinery KrauseDokumen16 halaman1965 Simulation of Symmetrical Induction Machinery KrauseFabiana SinghBelum ada peringkat
- EMI NotesDokumen13 halamanEMI Notesdfgh athtBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Class12 Project-2Dokumen13 halamanPhysics Class12 Project-2jujuBelum ada peringkat
- A Review Paper On Contactless Braking SystemDokumen5 halamanA Review Paper On Contactless Braking SystemNneji JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Questions On Principles of Electro Mechanical Energy ConversionsDokumen10 halamanQuestions On Principles of Electro Mechanical Energy Conversionskibrom atsbhaBelum ada peringkat
- Eddycurrentsensor PCB SENSOR 2010Dokumen8 halamanEddycurrentsensor PCB SENSOR 2010Siphesihle NkosiBelum ada peringkat
- ABB Fxe400 - Copa-Xe, Mag-XeDokumen56 halamanABB Fxe400 - Copa-Xe, Mag-Xebiotech666Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Impact of Harmonics On Induction MotorDokumen5 halamanElectrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Impact of Harmonics On Induction Motorsupriya rakshitBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling and Simulation of Hydropower Station Using Matlab SimulinkDokumen55 halamanModeling and Simulation of Hydropower Station Using Matlab SimulinkEhab AL-HialyBelum ada peringkat
- EEP305 Electric Drives Laboratory PDFDokumen14 halamanEEP305 Electric Drives Laboratory PDFAmit Singh100% (1)
- Underground Wireless Communication Using Magnetic Induction 1Dokumen14 halamanUnderground Wireless Communication Using Magnetic Induction 1shaluchackoBelum ada peringkat
- DC Motors PDFDokumen30 halamanDC Motors PDFMADHUSUDHAN BOYABelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETDokumen31 halamanElectrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETOneil Prettyboyswagg LeitchBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Grade-12 Physics CH 06 Electromagnetic-Induction1Dokumen15 halamanNCERT Grade-12 Physics CH 06 Electromagnetic-Induction1Raunak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- AC Generator (Alternator) - Construction and WorkingDokumen4 halamanAC Generator (Alternator) - Construction and WorkingSACHIN SINGHBelum ada peringkat