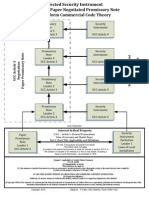
Common Law Contract Template
Diunggah oleh
Amy PachecoJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Common Law Contract Template
Diunggah oleh
Amy PachecoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Common Law Contract Template
1. Definition of Contract
2. Applicable Law - Common Law.
A. Common law v UCC.
1) More Specific UCC requirements of a
merchant - to - merchant situation.
3. Contract Formation.
A. Offer.
1) Intent to Contract-Mutual Assent
a) Solicitations
b) Advertisements
2) Definite Terms Mutual Assent Defenses.
a) Cure for Indefinite Terms
i. Part Performance
ii. Agree to agree later.
B. Acceptance.
1) Rejection/Termination of Offer
2) Common Law Acceptance
a) Mirror Image Rule
b) Acceptance through Silence
3) Revocation of Offer
a) Irrevocable Offers
i. Part performance
ii. Standard Option Contract
4) Mail Box Rule
C. Consideration.
a) Bargained for Exchange.
i. Sham/Nominal Consideration.
b) Legal Detriment.
i. Illusory Promise.
Unfettered Right of Termination
c) Promissory Estoppel / Detrimental
Reliance
D. Modification
1) Common Law Modification
a) New consideration required
b) Accord & Satisfaction
c) Substituted Agreement
4. Statute of Frauds
A. *Land Contracts
1) Part Performance Exception
B. *One Year Rule
1) Full Performance by one Party
C. Suretyship
1) Main Purpose Rule Exception
D. Marriage
E. Satisfaction by SOF by Memorandum
5. Parol Evidence Rule
A. Traditional or Four Corners Rule
B. Modern or Corbin View
1) Total Integration v. *Partial Integration.
a) Merger Clause.
2) *Missing Terms.
6. Contract Defenses.
A. Mistake.
1) Misunderstanding
2) Unilateral mistake.
3) Mutual mistake.
B. Pressure
1) Duress
2) Fraud
3) Misrepresentation
C. Illegality
1) Unconscionability
2) Illegal
3) Capacity
7. Performance /Conditions
A. Unilateral v Bilateral Contract
B. Expressed Conditions
C. Constructive Conditions
D. Implied Conditions
E. Excuse of Conditions
1) Hindrance
2) Waiver
F. Discharge of Performance.
1) Impossibility of Performance.
2) Financial Impracticability.
3) Frustration of Purpose.
8. Breach of Contract Claim
A. Prospective Inability to Perform/Voluntary
Disablement
1) Right to Adequate Assurance of
Performance .
B. Anticipatory Repudiation.
1) Retraction or Repudiation
2) Mitigation of Damages
C. Substantial Performance
1) Material v. Minor Breach of Contract
2) Termination of Performance for Material
Breach.
9. Remedies
A. Common Law Remedies
1) Mitigation.
2) Expectation Damages.
3) Liquidated Damages.
a) Reasonableness of amount
4) Consequential Damages.
a) Arise naturally
b) .Remote or unusual consequences.
5) Incidental Damages
6) Other Remedies
a) Reliance Interests
b) Recission/discharge of Contract
c) Specific Performance
d) Reformation
10. Third Party Issues
A. Third Party Beneficiary
1) Intended/Incidental Beneficiary
2) Vesting of Rights
3) Rights to Sue
B. Assignment.
1) Elements of Assignment
2) Effect of Assignment
3) Limitations on Assignments
4) Revocability of Assignments
5) Right to Sue
C. Delegation
1) Elements of Delegation
2) Limitations on Delegations
3) Right to Sue
4) Novation.
11. Quasi-Contract
A. Traditional (Majority) Rule.
1) No Recovery for Breaching Party
B. Minority Rule and Modern Trend.
1) For the Plaintiff
a) Restitution Benefit Conferred. Damage
Caused
2) For the Defendant
a) Quantum Meruit
i. Restitution Recovery in Quasi-
Contract.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Anti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActDari EverandAnti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure Outline 2 (Fall 09) AlgeroDokumen16 halamanCivil Procedure Outline 2 (Fall 09) AlgeroEboni FrempongBelum ada peringkat
- Equitable Remedies and InjunctionsDokumen17 halamanEquitable Remedies and InjunctionsMark Michael StrageBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty of Business Law Module AssessmentsDokumen15 halamanFaculty of Business Law Module Assessmentsraynold raphaelBelum ada peringkat
- BBOXX Solar Franchise AgreementDokumen12 halamanBBOXX Solar Franchise Agreementbugti1986Belum ada peringkat
- Commonwealth Caribbean Contract - Kodilinye, Gilbert, Kodilinye, M2Dokumen417 halamanCommonwealth Caribbean Contract - Kodilinye, Gilbert, Kodilinye, M2Crystal100% (2)
- Legal-EquityDokumen3 halamanLegal-Equitylakmali546Belum ada peringkat
- Doctrine of MistakeDokumen10 halamanDoctrine of MistakeAnushi AminBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure OutlineDokumen59 halamanCivil Procedure OutlineThomas JeffersonBelum ada peringkat
- Condensed Bar Notes for MS/NY Bar ExamsDokumen79 halamanCondensed Bar Notes for MS/NY Bar ExamsAlex McPettersonBelum ada peringkat
- Foster Civ Pro OutlineDokumen36 halamanFoster Civ Pro OutlineKarla Garcia100% (1)
- Constitutional Law - Hassel - Fall 2011Dokumen31 halamanConstitutional Law - Hassel - Fall 2011James E. WoulfeBelum ada peringkat
- Grounds of AppealDokumen12 halamanGrounds of AppealIRTribunalBelum ada peringkat
- FRCP Outline From OnlineDokumen16 halamanFRCP Outline From Onlinemeteor1216Belum ada peringkat
- Criminal Law Outline in ColorDokumen20 halamanCriminal Law Outline in Colorsarahlaraa100% (1)
- Civ Pro 1Dokumen42 halamanCiv Pro 1Rein DrewBelum ada peringkat
- The Interstate Commerce Lie Exposed: How the Federal Government Expanded its Powers Beyond Constitutional LimitsDokumen5 halamanThe Interstate Commerce Lie Exposed: How the Federal Government Expanded its Powers Beyond Constitutional Limitslemieuxm327Belum ada peringkat
- Dead Man S Statute Can Be WaivedDokumen10 halamanDead Man S Statute Can Be WaivedowenBelum ada peringkat
- Tort Outline .. Internet SourceDokumen43 halamanTort Outline .. Internet SourceColeman HengesbachBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative LawDokumen3 halamanAdministrative LawRafeliza CabigtingBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 18Dokumen13 halamanAssignment 18Derrick Sparks0% (1)
- Civil ProcedureDokumen4 halamanCivil ProcedurejaimeboyceBelum ada peringkat
- Criminal Law - Fairfax - Common Law Attack Sheet - 3Dokumen10 halamanCriminal Law - Fairfax - Common Law Attack Sheet - 3champion_egy325Belum ada peringkat
- Glazer - Bail FINALDokumen13 halamanGlazer - Bail FINALJames TurnerBelum ada peringkat
- Remedies On Rejection of GoodsDokumen14 halamanRemedies On Rejection of GoodsArasan ArasanBelum ada peringkat
- International Law OutlineDokumen14 halamanInternational Law OutlineTheresa CalimagBelum ada peringkat
- An Overview of Article 78 Practice and Procedure 05-21-09Dokumen81 halamanAn Overview of Article 78 Practice and Procedure 05-21-09test123456789123456789Belum ada peringkat
- ConLaw II Class Notes on Post-Civil War AmendmentsDokumen20 halamanConLaw II Class Notes on Post-Civil War AmendmentsAngelaBelum ada peringkat
- Drivers LIcenseDokumen1 halamanDrivers LIcenseNat WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure OutlineDokumen10 halamanCivil Procedure OutlineMichael CantorBelum ada peringkat
- Robertson Motion For AcquittalDokumen8 halamanRobertson Motion For AcquittalPat ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law Oultine-PersonalDokumen5 halamanCon Law Oultine-PersonalAshley DanielleBelum ada peringkat
- Damages: BY Gayathri Praharshitha. K SAP ID - 00000441047 Submitted To - Prof. Silla RamsundarDokumen17 halamanDamages: BY Gayathri Praharshitha. K SAP ID - 00000441047 Submitted To - Prof. Silla RamsundarKandlagunta Gayathri PraharshithaBelum ada peringkat
- Property 1L GuideDokumen2 halamanProperty 1L Guidevnord_1Belum ada peringkat
- Wills and TrustsDokumen33 halamanWills and TrustsTalluri RambabuBelum ada peringkat
- 28 USC 1441 Removal GenerallyDokumen1 halaman28 USC 1441 Removal GenerallyHugo CatalanBelum ada peringkat
- Contract Remedies GuideDokumen11 halamanContract Remedies GuidetragicallyohioBelum ada peringkat
- Mcqs - Contracts: Academic Year 2018-2019 (Second Semester)Dokumen13 halamanMcqs - Contracts: Academic Year 2018-2019 (Second Semester)KatBelum ada peringkat
- CONTRACTS OUTLINE - JamesDokumen65 halamanCONTRACTS OUTLINE - JamesRebekahBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure Fall 2013 Course OverviewDokumen34 halamanCivil Procedure Fall 2013 Course OverviewAndrew PecoraroBelum ada peringkat
- Step 09 - Oath of Office Laws.Dokumen1 halamanStep 09 - Oath of Office Laws.Kevin TalbertBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure Guide: Personal Jurisdiction, Service of Process, Subject Matter Jurisdiction & VenueDokumen5 halamanCivil Procedure Guide: Personal Jurisdiction, Service of Process, Subject Matter Jurisdiction & Venuehmmwhoo123Belum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure II: Pleadings and ResponsesDokumen9 halamanCivil Procedure II: Pleadings and ResponsesCarter CarsonBelum ada peringkat
- Discovery FRCP SimplifiedDokumen72 halamanDiscovery FRCP SimplifiedRenee FisherBelum ada peringkat
- Substantive Protection of Economic InterestsDokumen16 halamanSubstantive Protection of Economic InterestsPaulPits100% (1)
- Florida ConstitutionDokumen81 halamanFlorida ConstitutionamrodrgzBelum ada peringkat
- I Concurrent Estates Attack SheetDokumen14 halamanI Concurrent Estates Attack SheetDrew RymerBelum ada peringkat
- Bananas, Bikinis, GirlsDokumen3 halamanBananas, Bikinis, GirlsA. CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Personal JurisdictionDokumen63 halamanChapter 2: Personal Jurisdictiondiannecl-1100% (1)
- Judicial ReviewDokumen10 halamanJudicial ReviewPearl BajpaiBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law NotesDokumen54 halamanAdministrative Law NotescrosbeBelum ada peringkat
- How To Save The RepublicDokumen16 halamanHow To Save The RepublicEric TittoBelum ada peringkat
- My Property OutlineDokumen101 halamanMy Property OutlineAl TeelBelum ada peringkat
- The 14 Amendment Never Passed: DisclaimerDokumen5 halamanThe 14 Amendment Never Passed: DisclaimerDavid-CrockettBelum ada peringkat
- 74 1 The Long Story of Notice and Personal JurisdictionDokumen82 halaman74 1 The Long Story of Notice and Personal JurisdictionKevin YohburtBelum ada peringkat
- Due Process PresentationDokumen18 halamanDue Process Presentationapi-324270925Belum ada peringkat
- Commercial Paper & Secured TransactionsDokumen12 halamanCommercial Paper & Secured Transactionscatherine6claire100% (1)
- For AllDokumen29 halamanFor AllA. CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- Contempt of CourtDokumen13 halamanContempt of CourtKhoo KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Breach of Contract - Cause of Action - MeaningDokumen4 halamanBreach of Contract - Cause of Action - MeaningteacheziBelum ada peringkat
- Downes vs. BidwellDokumen4 halamanDownes vs. BidwelljeiromeBelum ada peringkat
- The Appropriations Law Answer Book: A Q&A Guide to Fiscal LawDari EverandThe Appropriations Law Answer Book: A Q&A Guide to Fiscal LawBelum ada peringkat
- Solar SecretsDokumen44 halamanSolar SecretsKen HeathBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Induction and Its PropagationDokumen25 halamanElectromagnetic Induction and Its PropagationAmy Pacheco100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction and Its PropagationDokumen25 halamanElectromagnetic Induction and Its PropagationAmy Pacheco100% (1)
- Selection of Legal MaximsDokumen298 halamanSelection of Legal MaximsAmy PachecoBelum ada peringkat
- Code 4Dokumen32 halamanCode 4Kristijan KopsejakBelum ada peringkat
- Contracts I OutlineDokumen20 halamanContracts I Outlinecrlstinaaa89% (18)
- Assignment Topic Name of StudentsDokumen4 halamanAssignment Topic Name of StudentsBhavani PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Torta Notes Complete Protected UnlockedDokumen76 halamanTorta Notes Complete Protected UnlockedDom GabquezBelum ada peringkat
- Torts DoctrinesDokumen56 halamanTorts DoctrinesElwell MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Defenses To Negligence: Chapter ObjectivesDokumen53 halamanDefenses To Negligence: Chapter Objectivesandy falconBelum ada peringkat
- Exclusion WarrantiesDokumen21 halamanExclusion WarrantiesKiki PapadBelum ada peringkat
- Torts and Damages: San Beda College of LawDokumen43 halamanTorts and Damages: San Beda College of LawVincent De VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Week6 Tute Answers Contract FormationDokumen6 halamanWeek6 Tute Answers Contract FormationGeoffrey ScarlettBelum ada peringkat
- Law of Contract: Undue Influence: Section 10Dokumen3 halamanLaw of Contract: Undue Influence: Section 10AnanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Obligations and Sources of ObligationsDokumen1 halamanObligations and Sources of ObligationsJustz LimBelum ada peringkat
- 0802MP 2 ContractDokumen102 halaman0802MP 2 ContractAlfred ChuBelum ada peringkat
- IBA Master Substantive Project 2014 - Insurance Committee PDFDokumen210 halamanIBA Master Substantive Project 2014 - Insurance Committee PDFBM Ariful IslamBelum ada peringkat
- JLUI Business Laws IntroductionDokumen55 halamanJLUI Business Laws IntroductionAjit JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Assignment On Aspects of ContractDokumen20 halamanSample Assignment On Aspects of ContractInstant Assignment HelpBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Breach of Contract and RemediesDokumen34 halaman04 Breach of Contract and RemediesMacjim Frank44% (9)
- Real Estate Fall 2014 - Rosenblatt (Long Summary)Dokumen95 halamanReal Estate Fall 2014 - Rosenblatt (Long Summary)Ciera BriancaBelum ada peringkat
- BU231 Complete Notes 48 PagesDokumen49 halamanBU231 Complete Notes 48 PagesCherie HeBelum ada peringkat
- INDIAN CONTRACT ACT ESSENTIALSDokumen80 halamanINDIAN CONTRACT ACT ESSENTIALSnishantBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Questions With The Past Year Reference:: The Contract and Agency Act: 1872Dokumen45 halamanSummary of Questions With The Past Year Reference:: The Contract and Agency Act: 1872ShoayebBelum ada peringkat
- Obli MCQDokumen7 halamanObli MCQasdasdasdasdasdas100% (1)
- Contracts and Specific ReliefDokumen45 halamanContracts and Specific ReliefSunil SahuBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Indian Contract Act-Part 1 PDFDokumen86 halaman2 Indian Contract Act-Part 1 PDFPranav DagarBelum ada peringkat
- Ultimate Law Exam WeaponDokumen62 halamanUltimate Law Exam WeaponPanda ArjBelum ada peringkat
- Contracts - Doctrine of FrustrationDokumen17 halamanContracts - Doctrine of Frustrationharsh100% (2)
- G.R. No. 203697 - DigestDokumen2 halamanG.R. No. 203697 - DigestNikka Marah NayveBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Contract Act EssentialsDokumen40 halamanIndian Contract Act EssentialsShivati Singh KahlonBelum ada peringkat
- EQUITYDokumen4 halamanEQUITYjunkacc1123Belum ada peringkat