Managing Project Risks in Metals & Mining Sector in India: MMMM Symposium - Delhi
Diunggah oleh
Shrikant Pathak0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan19 halamanMining activity
Judul Asli
02SanjayGarg_28Sept2012
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniMining activity
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan19 halamanManaging Project Risks in Metals & Mining Sector in India: MMMM Symposium - Delhi
Diunggah oleh
Shrikant PathakMining activity
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 19
Managing Project Risks
in Metals & Mining
Sector in India
MMMM Symposium - Delhi
Sanjay Garg
Advisory Services Advisory Services
September, 2012
Content
Industry Profile 11
22 Source of Risks for Mining Projects
2
6
1
33
4
10
12
Managing Project Risks
Source of Risks for Metal Projects
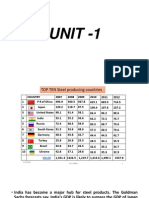
Metals and Mining Industry in India
20.8%
3.2%
2.0%
0.2%
The industry valued at $106.4 billion in 2010 and is
likely to growto $196.5 billion by 2014
Iron & steel is the largest segment followed by coal,
Aluminiumand Base Metals
Industry Segments (By Value)
2
73.8%
Iron & Steel Coal Aluminium
Base Metals Precious metals
& minerals
Source: IBEF, Data Monitor
Aluminiumand Base Metals
Globally India stands as the fourth largest producer of
iron ore and crude steel
Country is the net importer of steel
Metals and Mining : Current Scenario
Countrys crude steel production in 2010 was 68.3 MT, and currently fourth largest after China, Japan and USA
As per 12th five year plan, a 62 Million Tonnes of capacity addition is expected in Indian steel sector by 2017
Iron & Steel
Aluminum is the fastest growing non-ferrous metals with a current Production Capacity of 1.71 MT
As per 12th five year plan, domestic consumption of Aluminum will be 3.0 Million tonnes by 2017
Non Ferrous metals - Aluminum
Non Ferrous metals - Copper
3
Copper stands 3rd in tonnage consumption after steel and Aluminum in India with production of 0.16 MT in 2010
The per capita consumption of copper is 0.55 kg also fares poorly especially with China (5.5 kg)
Non Ferrous metals - Copper
India is 3rd in coal production country after China and USA with annual production of 532 million tons in 2010.
The total consumption of raw coal in the country was estimated to be 587 million tons in 2010
Coal
Source: Energy statistics 2011; Assocham , MoSPI Annual Reports, Ministry of mines
India is one of the major iron ore producers in the world and has enormous reserves of high grade iron ore
Iron Ore Production in 2010 was 219 Million Tons
Iron ore
Of the 1035 infrastructure
projects completed during
April 1992-March 2009, around
41 percent of the projects were
completed with cost over-runs
while 82 percent witnessed
time over-runs
Cost and Time overruns in Infrastructure projects (1/2)
Cost and Time Overruns in Infrastructure Projects (Apr'1992-Mar'2009)
43%
22%
33%
20%
47%
83%
54%
31%
19%
16%
42%
91%
61%
100%
80%
61%
98%
85%
95%
81%
91%
100%
C
i
v
i
l
A
v
i
a
t
i
o
n
C
o
a
l
P
e
t
r
o
c
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
s
P
e
t
r
o
l
e
u
m
P
o
w
e
r
R
a
i
l
w
a
y
s
R
o
a
d
s
a
n
d
H
i
g
h
w
a
y
s
S
h
i
p
p
i
n
g
a
n
d
P
o
r
t
s
S
t
e
e
l
T
e
l
e
c
o
m
m
u
n
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
U
r
b
a
n
D
e
v
e
l
o
p
m
e
n
t
4
Source: Project Implementation Status Report of Central Sector Projects - March 2010, MOSPI
A meager 97 projects (17 percent) of the scheduled
557 central infrastructure projects completed in fiscal
year 2009-10
A staggering 478 of the 1,005 projects monitored by
MOSPI i.e. around 50 percent of the infra projects
witnessed slippages by March 2010
Issue of infra project delays
persistent in the current times
C
i
v
i
l
A
v
i
a
t
i
o
n
P
e
t
r
o
c
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
s
P
e
t
r
o
l
e
u
m
P
o
w
e
r
R
a
i
l
w
a
y
s
R
o
a
d
s
a
n
d
H
i
g
h
w
a
y
s
S
h
i
p
p
i
n
g
a
n
d
P
o
r
t
s
S
t
e
e
l
T
e
l
e
c
o
m
m
u
n
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
U
r
b
a
n
D
e
v
e
l
o
p
m
e
n
t
% of projects with Cost overrun % of projects with Time overrun
Cost and Time overruns in Infrastructure projects (2/2)
5
Source : MOSPI Annual Report 2011-12
Content
Industry Profile 11
22 Source of Risks for Mining Projects
2
6
6
33
4
10
12
Managing Project Risks
Source of Risks for Metal Projects
Source of Mining Project Risks
Accuracy of
Business
Plans
Exploration inaccuracy
Assumptions on Demand & Price
Cost of capital over long gestation Period
Mine Closure Costs
Execution
Geological Risks -Faults,
Dykes, washout
Quality & Quantity of
Manpower
Breakdowns of M/c
Environmental Impact like
Legislative &
Political
Fraud
Nationalization
Change in Policies e.g. share
of Profit
MMDR Act
Regulatory
Limit of Harmful Content
Ban on certain technology
Approval Procedures
Mining
7
Infrastructure
Dependence on Government for Development
Remote Locations making it difficult to develop & maintain local Infrastructure
High Capital requirement
Loss in
Mining
Reduced % of extraction-
Technology vs Cost
Quality
Variations in quality of Ore
across
Land
Acquisition
Changing Laws
Local resistance
Political interference
Environmental
Environmental Impact like
Disturbance of water Table,
Grnd wtr Contamination
Accident & Health Hazards
Economic-social-
Psychological-political
Mining
Project
Risks
The procedure in grant of mineral concessions for a mining lease
Mining Lease (ML) Application
Revenue department No
Objection Certificate (NOC)
Forest Dept. NOC
Collector/DGM
Mining Officers
Recommendations
Collectors Recommendation
DGM
State Secretary & Commissioner (Mines)
8
Source: A Guide to Investment in Indias Mineral Sector, FIMI, January 2010
State Secretary & Commissioner (Mines)
Approval of State Mines Minister
Concurrence of Ministry of Mines,
GOI for schedule minerals
State Secretary and Commissioner
(Mines)
Collector
Issues of ML by Mining Dept.
There are about 57
Windows for approval
of a Mining Lease in
the case of Coal
Mining
Regulatory Overview
Mining
Legislations
Mines
Mines and
Minerals
(Development
Offshore
Areas Mineral
(Development
Mining in India is regulated by the Mines and Minerals
Development and Regulation (MMDR) Act , 1957; the
Mines Act, 1952; and Offshore areas mineral act 2002
The MMDR Act is comprised of :
o The Mineral Concession Rules, 1960 : It outline the
procedures and conditions for obtaining a
Reconnaissance Permit or a Prospecting License or
Policy Framework
9
Source: FIMI, IBEF
Mines
Act,1952
(Development
and
Regulation)
Act, 1957
(Development
and
Regulation)
Act 2002
Mineral
Concession
Rules, 1960
Mineral
Conservation
and
Development
Rules, 1988
State Minor
Mineral
Concession
Rules
Reconnaissance Permit or a Prospecting License or
a Mining Lease, for all minerals other than
petroleumand natural gas
o The Mineral Conservation and Development Rules,
1988 lay down guidelines for ensuring mining on a
scientific basis
o The State Mineral Concession Rules empowers state
governments to formulate the Minor Mineral
Concession Rules and grant mineral concessions
The Draft MMDR Bill 2011 is pending approval of the Parliament and Presidents assent . The new act proposes changes in
procedure for granting Mining Lease, set up of a District Mineral Foundation to be funded through a profit sharing framework
amongst others
Delay in Mining
The recent Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) report pointed out that the production in most
of the mines has been held up for want of forest clearance and land acquisition adding to the delay
26 blocks were awaiting the approval
of environment management plan
Forest clearance was awaited in
53 blocks
Survey
10
Source: The CAG report
land acquisition had not taken place
in 62
Mine plans had not been approved
in four
Mining leases were not granted for 58
blocks
Survey
observation of 68
non-producing
blocks
Content
Industry Profile 11
22 Source of Risks for Mining Projects
2
6
11
33
4
10
12
Managing Project Risks
Source of Risks for Metal Projects
Continuous up gradation
Accuracy of
Business
Plans
Assumptions on input costs Ore , Power
Assumptions on Demand & Price
Cost of capital over long gestation Period
Changing Competition Scenario
Selection of Technology & Source
Execution
Quality of skilled manpower
Availability of Manpower due
to seasonal variations
Availability of Tools &
machinery
Legislative &
Political
Tax & levies
Allocation of resources
Labor Laws
Industrial Policy
Regulatory
Multiple Approval Procedures
Emission Norms
Source of Metal Project Risks
12
Infrastructure
Dependence on Government for Development
Remote Locations making it difficult to develop & maintain local Infrastructure
High Capital requirement
Technology
&
Performance
Continuous up gradation
requirement to maintain
profitability
Capability to Integrate
components to assure
performance of plant
Supplies of
Plant
Equipment
Dependence on multiple sources
of suppliers both domestic and
Imported
Fluctuation in delivery times and
costs due to cyclic demands
Land
Acquisition
Changing Laws
Local resistance
Political interference
Environmental
Environmental Impact like
Ground water
Contamination
Accident & Health Hazards
Economic-social-
Psychological-political
Metal
Project
Risks
Industry Profile 11
22
2
6
Source of Risks for Mining Projects
Content
13
33
Source of Risks for Metal Project
4
10
12
Managing Project Risks
Managing Project Risks is a process to be managed across the
lifecycle of a project
Impact or Severity of Risks, not taken up for mitigation, may
increase exponentially
Risks are dynamic and undergo change over period of time
Managing Project Risks
14
Risks are dynamic and undergo change over period of time
Create the Framework for the Project
Scope
Stakeholders
External & Internal Dependencies
Understand the possible sources for the Risks
Subject Matter Experts
Industry experience
Close Expired Risks
Risk Management Team
Project Risk Management Process
15
Identify & Quantify Risk Events
Workshops
Institutionalize appropriate process
Analyze , Evaluate & Categorize
Risk Management Team
Subject matter Experts
Process Consultants
Prepare & Approve Mitigation Plans
Risk Management Team
Subject matter Experts
Process Consultants
Implement & Monitor Mitigation Plans
Responsible Agency/Person
Risk Management Team
Combat currency & Commodity price volatility, using
metals price and currency hedging strategies along with
hedging inputs to production
Hedging
Identify underperforming assets, and accordingly shut
down or divest them
Investments & Divestment
Optimize logistic configuration between mines, plants,
railways and ports
Partner with government on sharing models to achieve
economies of scale
Infrastructure Constraints
1. Active Compliance monitoring
Compliance monitoring & Whistle blowing
Mitigation Strategies . (1/2)
16
For Exploration for more accurate estimations
For Execution to improve timelines and margins
For Operations for higher efficiencies and greater
returns
For Integration of Technologies for Guaranteed
Performance
Use technologies
down or divest them
Industry consolidation, automation, investment in
energy assets could be other options
2. Increasing due diligence & Fraud Control initiatives
around third parties and
3. Actively encouraging internal whistle-blowing
Creation of exploration bonds in lines of infrastructure
bonds to create a central cash reserve, to be used for
mining exploration.
Improved Transparency of Business Plans to attract
investors
Tie up with Reputed Industry Players to enhance
Reputation and reduce perceived risks
Capital Generation
Attract foreign players in the formof Joint ventures
Training and development for Industry specific skill sets
Improve Living conditions to attract personnel
Employ Technical Consultants to bridge gap
Human Capital ( Competency & Quantity) Constraint
Train & Develop internal resources in good
management techniques
Employ Professionals/Consultants to set up and run
Project Management Offices
Run Systematic Risk Management Programs
Project Management Skills
Engage Local Stakeholders Engage with the Government
Mitigation Strategies . (2/2)
17
Communication and information Dissemination
Establish Effective Social Responsibility Programs
Engage with local NGOs
Provide Employment Opportunities to local population
Through Industry Forums to Create Awareness &
Influence policies
To undertake joint initiatives to address gaps
To facilitate approvals and improve communication
Build pressure groups
Create and maintain a separate fund for restoration
Enforce Discipline at sites and Monitor Compliance
Provide adequate resources ( equipment & personnel)
Use Technology
Health, Safety & Environment Protection
Thank You
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- PEST AnalysisDokumen15 halamanPEST AnalysisAbinash BiswalBelum ada peringkat
- India's Growing Coal Demand and Import NeedsDokumen13 halamanIndia's Growing Coal Demand and Import NeedsNaman RawatBelum ada peringkat
- Iluka YoyoDokumen38 halamanIluka YoyoYOYOBelum ada peringkat
- Feasibility Report On The Production of Direct Reduced IronDokumen5 halamanFeasibility Report On The Production of Direct Reduced IronEngr Faiq ChauhdaryBelum ada peringkat
- MPT RoadmapDokumen20 halamanMPT RoadmapAlek Al HadiBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Industry in IndiaDokumen20 halamanSteel Industry in Indiaranjit pisharodyBelum ada peringkat
- Mike Jolley - President Director PT Rio Tinto IndonesiaDokumen24 halamanMike Jolley - President Director PT Rio Tinto IndonesiaAhmad AshariBelum ada peringkat
- Draft National Non-Ferrous Metals Scrap Recycling Policy HighlightsDokumen60 halamanDraft National Non-Ferrous Metals Scrap Recycling Policy Highlightsbondkh1118Belum ada peringkat
- Lead PDFDokumen4 halamanLead PDFlaxmiccBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On Mining in IndiaDokumen8 halamanResearch Paper On Mining in Indiafzgzygnp100% (1)
- Dgms Strategic Plan 2011Dokumen68 halamanDgms Strategic Plan 2011gulab111Belum ada peringkat
- Steel Making NotesDokumen22 halamanSteel Making NotesVipin NandaBelum ada peringkat
- SNL Permitting Delay Report-OnlineDokumen32 halamanSNL Permitting Delay Report-OnlineheatherBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding the Economic and Environmental Drivers of the Global Copper IndustryDokumen34 halamanUnderstanding the Economic and Environmental Drivers of the Global Copper IndustryKavya MadanuBelum ada peringkat
- American Journal Research on Nigerian Bitumen Coating SteelDokumen11 halamanAmerican Journal Research on Nigerian Bitumen Coating SteelVõ Quang KiệtBelum ada peringkat
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., IndiaDokumen7 halamanDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University Visakhapatnam, A.P., IndiaDileep ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- Investment Opprtunity in MiningDokumen10 halamanInvestment Opprtunity in MiningssprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Decarbonizing Steel PresentationDokumen27 halamanDecarbonizing Steel PresentationMitone DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Scanning of Steel Industry PPT by Arshpreet and PoojaDokumen23 halamanEnvironmental Scanning of Steel Industry PPT by Arshpreet and PoojaBrahamdeep KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Transforming India's Minerals Sector PotentialDokumen32 halamanTransforming India's Minerals Sector Potentialsreejit.mohanty4016Belum ada peringkat
- Mining and The Sustainable Development GoalsDokumen7 halamanMining and The Sustainable Development GoalshbBelum ada peringkat
- Eia Report of A CEMENT INDUSTRYDokumen19 halamanEia Report of A CEMENT INDUSTRYabdullah al mahinBelum ada peringkat
- Captive Coal Block Development Issues in IndiaDokumen8 halamanCaptive Coal Block Development Issues in IndiaVeneet VishalBelum ada peringkat
- CKBC ReportDokumen19 halamanCKBC Reportomkar kothuleBelum ada peringkat
- BBDIT-Conference 22mar2014 PDFDokumen34 halamanBBDIT-Conference 22mar2014 PDFK S MEERABelum ada peringkat
- Carbon Credits and Kyoto ProtocolDokumen33 halamanCarbon Credits and Kyoto ProtocolKKKANAHIYABelum ada peringkat
- Jayaram Ponnada Lopamudra Panda Monisha Ranjit Pisharody: Mining and MetallurgyDokumen20 halamanJayaram Ponnada Lopamudra Panda Monisha Ranjit Pisharody: Mining and MetallurgyMadhur ShahBelum ada peringkat
- E-Book on Mining Sector: Structure, Role, and PoliciesDokumen70 halamanE-Book on Mining Sector: Structure, Role, and PoliciesKPrasanna Kumar VarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Rare Earth MineralsDokumen32 halamanRare Earth Mineralsamanamu436Belum ada peringkat
- AnantaQUEST Tech Case Study FileDokumen2 halamanAnantaQUEST Tech Case Study FileDhanunjai IitbBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 5 Science and Society QuizDokumen1 halamanCh. 5 Science and Society QuizJulia Taylor HaddenBelum ada peringkat
- K 8 - Tushar Jhaveri - NACE InternationalDokumen12 halamanK 8 - Tushar Jhaveri - NACE InternationalDineshBelum ada peringkat
- Mip 538 Seminar Report LethiumDokumen17 halamanMip 538 Seminar Report LethiumLASER LIONBelum ada peringkat
- Regional Perspectives on India's Growing Steel IndustryDokumen40 halamanRegional Perspectives on India's Growing Steel IndustryHarshita VoraBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Level of Criticality of Lithium For Electrification of The Global Automobile FleetDokumen20 halamanWhat Is The Level of Criticality of Lithium For Electrification of The Global Automobile Fleetcelestinjonathan1996Belum ada peringkat
- Daewoo International: December 2010Dokumen38 halamanDaewoo International: December 2010Angelica MeloBelum ada peringkat
- Cement Industry Growth & Environmental ImpactDokumen4 halamanCement Industry Growth & Environmental ImpactPankaj SawankarBelum ada peringkat
- Facts About Graphite As A Strategic MineralDokumen3 halamanFacts About Graphite As A Strategic MineralRichard J MowatBelum ada peringkat
- Nigeria's Federal Republic National Minerals and Metals PolicyDokumen73 halamanNigeria's Federal Republic National Minerals and Metals PolicySafia DalhatuBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Transformation of Mineral Sector Through TechnologyDokumen21 halamanDigital Transformation of Mineral Sector Through Technologynaziha MJBelum ada peringkat
- 015-038 GaylardDokumen24 halaman015-038 GaylardJob MateusBelum ada peringkat
- Metis Coal Report Brochure Full May 1Dokumen8 halamanMetis Coal Report Brochure Full May 1arorakgarima100% (1)
- Sinter Write UpDokumen262 halamanSinter Write Uprmsh301Belum ada peringkat
- Eco Project ReportDokumen21 halamanEco Project Reportswapnil_thakre_1Belum ada peringkat
- RR1002A01 Term Paper ECO515 Term PaperDokumen18 halamanRR1002A01 Term Paper ECO515 Term Paper980bhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Draft SpeechDokumen3 halamanDraft SpeechSrikanth SrikantiBelum ada peringkat
- Map FinalDokumen21 halamanMap FinalLud PasBelum ada peringkat
- SpecializedDokumen378 halamanSpecializedMA. CHRISTINA BUSAINGBelum ada peringkat
- Megharaja CBS01Dokumen89 halamanMegharaja CBS01Naveen S GBelum ada peringkat
- Cliffs Chromite Booklet - Feb4 E - WebDokumen25 halamanCliffs Chromite Booklet - Feb4 E - WebNetNewsLedger.comBelum ada peringkat
- Strengthen Pakistan's Coal Power SectorDokumen6 halamanStrengthen Pakistan's Coal Power SectorMalik Wasiq MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- 649 D 4212 Cceb 01688027666Dokumen52 halaman649 D 4212 Cceb 01688027666Varshith SureshBelum ada peringkat
- Carbon credits in India's thermal power sectorDokumen24 halamanCarbon credits in India's thermal power sectorAnshulBhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Outlook For Selected Critical Minerals in Australia 2021 Report-1Dokumen39 halamanOutlook For Selected Critical Minerals in Australia 2021 Report-110evenwoodcloseBelum ada peringkat
- International Mining - 2014Dokumen76 halamanInternational Mining - 2014scrane@Belum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0892687523000900 MainDokumen15 halaman1 s2.0 S0892687523000900 MainMartín José Valenzuela DíazBelum ada peringkat
- Draft Policy On Promotion of Greenfield Investments in The Steel SectorDokumen10 halamanDraft Policy On Promotion of Greenfield Investments in The Steel SectorAbhijeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- GO TRAIN SYSTEM MAPDokumen1 halamanGO TRAIN SYSTEM MAPShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Notification NICL Administrative OfficersDokumen7 halamanNotification NICL Administrative OfficersRushi BageBelum ada peringkat
- DSfixDokumen5 halamanDSfixCesare PaolinoBelum ada peringkat
- Various Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsDokumen15 halamanVarious Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Project Management: A Survey of Current Practices and ImplicationsDokumen15 halamanProject Management: A Survey of Current Practices and ImplicationsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- CSP 2013 Analysis: Topic Number of Questions Difficulty LevelDokumen2 halamanCSP 2013 Analysis: Topic Number of Questions Difficulty LevelvramavathBelum ada peringkat
- Game ProgramingDokumen4 halamanGame ProgramingShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Finding Potential Corporate Sponsors 1.2 Preparing Information Brochure1.3 Deci Ding The Entry Fees For Teams 1.4 Pricing of TicketsDokumen1 halaman1.1 Finding Potential Corporate Sponsors 1.2 Preparing Information Brochure1.3 Deci Ding The Entry Fees For Teams 1.4 Pricing of TicketsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Month Projected SellsDokumen3 halamanMonth Projected SellsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Various Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsDokumen15 halamanVarious Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- New Text DocumentDokumen1 halamanNew Text DocumentShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Various Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsDokumen15 halamanVarious Songs, Their Meanings, How To Interpret SongsShrikant PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Retention and Risk Reduction DecisionsDokumen4 halamanRisk Retention and Risk Reduction DecisionsNicole BrownBelum ada peringkat
- MBA FUTURES AT MURDOCH UNIVERSITYDokumen8 halamanMBA FUTURES AT MURDOCH UNIVERSITYDulana JayaratneBelum ada peringkat
- GUIDELINES ON INTERNAL CONTROL & COMPLIANCE IN BANKS-Bangladesh BankDokumen138 halamanGUIDELINES ON INTERNAL CONTROL & COMPLIANCE IN BANKS-Bangladesh BankArup SahaBelum ada peringkat
- FatigueRiskManagementinAviation v4Dokumen9 halamanFatigueRiskManagementinAviation v4Tun Thit SaBelum ada peringkat
- API Spec Q1 9th Edition Quality ManagementDokumen3 halamanAPI Spec Q1 9th Edition Quality Managementdav0% (1)
- Disaster Management - Handout PDFDokumen104 halamanDisaster Management - Handout PDFLukmaan Ias50% (2)
- PCM Part 2 Compilation PDFDokumen53 halamanPCM Part 2 Compilation PDFmatt jaudianBelum ada peringkat
- Application of The Fmea Technique in A Project Risk AnalysisDokumen7 halamanApplication of The Fmea Technique in A Project Risk AnalysisjmpbarrosBelum ada peringkat
- Managers and The Legal Environment 9th Edition Bagley Test BankDokumen25 halamanManagers and The Legal Environment 9th Edition Bagley Test BankDrRubenMartinezMDspcg100% (56)
- AOM 2023-001 Low Utilization of LDRRMF (Reviewed)Dokumen5 halamanAOM 2023-001 Low Utilization of LDRRMF (Reviewed)Kean Fernand BocaboBelum ada peringkat
- TSA - Guidence of PlansDokumen101 halamanTSA - Guidence of PlansvisvisvisvisBelum ada peringkat
- Bpo Module4Dokumen95 halamanBpo Module4rochelle regencia100% (3)
- Operations Management IT O13Dokumen248 halamanOperations Management IT O13Jorge Cronwell Montaño Vásquez100% (1)
- Professional Examination PDFDokumen35 halamanProfessional Examination PDFDeepak Gupta71% (7)
- Siemens Offshore DrillingDokumen16 halamanSiemens Offshore DrillingLuka Maka MalicBelum ada peringkat
- Translink 2014 Annual ReportDokumen104 halamanTranslink 2014 Annual ReportCKNW980Belum ada peringkat
- FAA SMS Briefing To ICAO HSCL 2010 v21Dokumen25 halamanFAA SMS Briefing To ICAO HSCL 2010 v21YasirRazaBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Domains Questions Project ManagerDokumen8 halamanRisk Domains Questions Project ManagermakeencvBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Data - Not For Operational Use: 3Rd Edition, October 2019Dokumen15 halamanSample Data - Not For Operational Use: 3Rd Edition, October 2019Emon Khan0% (1)
- PM Best PracticeDokumen42 halamanPM Best PracticeSeverin Ignatius CorryBelum ada peringkat
- Fraud - Internal Auditing PDFDokumen4 halamanFraud - Internal Auditing PDFJaJ08Belum ada peringkat
- Health Care Leadership PDFDokumen396 halamanHealth Care Leadership PDFiahmad9Belum ada peringkat
- Preventa Solutions For Efficient Machine Safety: Catalogue 2014Dokumen242 halamanPreventa Solutions For Efficient Machine Safety: Catalogue 2014Oriel BabiloniaBelum ada peringkat
- Disaster ManagementDokumen26 halamanDisaster Managementkalaiselvi_velusamy100% (3)
- Organizational structure of an oil and gas companyDokumen1 halamanOrganizational structure of an oil and gas companyFarrukh Zaman BhuttoBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 31073 Risk Management - Vocabulary - Moving From ISO Guide 73 Version 2009 To ISO 31070 Versio 2022Dokumen23 halamanISO 31073 Risk Management - Vocabulary - Moving From ISO Guide 73 Version 2009 To ISO 31070 Versio 2022Alex DaliBelum ada peringkat
- ALS Tank Integrity ServicesDokumen2 halamanALS Tank Integrity ServicesghanBelum ada peringkat
- Syngneta India Limited Annual Report 2018-19Dokumen152 halamanSyngneta India Limited Annual Report 2018-19Saikumar SawantBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 13485:2016 and How It Impacts Medical Device CompaniesDokumen16 halamanISO 13485:2016 and How It Impacts Medical Device Companiescrystaldelune100% (4)
- 1280 2556 1 SMDokumen7 halaman1280 2556 1 SMAbdurahman AbdBelum ada peringkat