Medfriendly: "Where M Edical Information Is Easy To Understand"™
Diunggah oleh
ghifarihaikalJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Medfriendly: "Where M Edical Information Is Easy To Understand"™
Diunggah oleh
ghifarihaikalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
To understand what anion gap is, it is first necessary to understand a few other terms.
If you already
know the following terms, feel free to skip to the next section.
ION: An ion is an atom or a group of atoms that have an electric charge by gaining or losing one or
more electrons. An atom is the smallest part of a substance that can exist alone or in combination
with something else. An electron is a negatively charged particle that is smaller than an atom. Since
an electron has a negative charge, if an atom gains too many electrons it is considered negative
(because there will be more negative charges than positive charges). If an atom has too few electrons
it is considered positive (because there will be more positive charges than negative charges).
CATION: Cations are ions with a positive electric charge.
ANION: Anions are ions with a negative electric charge.
MedFriendly
"Where M
edical Information is Easy to Understand"
WHAT IS ANION GAP?
Anion gap (pronounced an-eye-on gap) is a measurement of the anions in the arterial blood (besides
chloride and bicarbonate anions). Arterial blood is blood in the arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that
carry blood away from the heart. Chloride is a combination of the element, chlorine, with another
element. Bicarbonate is a substance in the blood that prevents it from becoming too acidic or too
alkaline (non-acidic).
The anion gap measurement is taken from the blood serum or blood plasma. Blood serum is the
clear, thin, and sticky fluid part of the blood that remains after the blood has changed from a liquid into
a solid form. Serum does not contain blood cells, platelets (cells that help change the blood from a
liquid to solid form), or fibrinogen (a protein in the blood). The part of blood that contains these and
many other types of cells is known as plasma.
HOW IS ANION GAP MEASURED?
Anion gap is measured after taking a blood sample. One way to calculate the anion gap is to add the
number of chloride and bicarbonate anions together and subtract them from the number of sodium
and potassium cations. Sodium and potassium are two of the most important elements in the body.
By subtracting the chloride and bicarbonate anions from the sodium and potassium cations, the
resulting measurement provides an estimate of the total amount of anions in the blood (besides
chloride and bicarbonate anions). See the previous section for a discussion of chloride and
bicarbonate.
The main anions in the blood (besides chloride and bicarbonate) are phosphate (a type of salt),
organic acids (types of acids), sulfate (usually a combination of a metal with a type of acid called
sulfuric acid), and proteins in the blood plasma. See above for a description of blood plasma.
A less accurate way to measure anion gap is to take the number of chloride and bicarbonate anions
and subtract them from the number of sodium cations. This method is less accurate than the
previously mentioned method because it does not take the potassium cations into account. The
reason for this is because the level of potassium in the blood is usually very small. Even though it is
less accurate, most hospitals use this equation.
WHAT IS THE NORMAL LEVEL OF ANION GAP?
The normal level of anion gap is generally considered to be between 8 and 16 mEq (milliequivalents)
per liter of blood. A milliequivalent is a very small unit of weight that is about one thousandth of
a gram. To understand how small a gram is, you need about 453 grams just to get one pound. So just
imagine how small a millimole is. A liter is a measurement of the amount of space that a liquid takes
up in a container. As an example of how much a liter is, four liters of milk equals a little bit more than
one gallon of milk.
Sometimes the words "mmol (millimoles) per liter" are used instead of "milliequivalents per liter." In
most cases, a millimole is the same thing a milliequivalent. Usually, the number of anions in the blood
plasma (besides chloride and bicarbonate) equal 12 milliequivalents per liter.
It is worth noting that different hospitals use different ranges for determining normal blood count
levels. The difference in ranges is often due to the different levels of technology used to measure the
ions. So whereas one hospital may use the range of 8 to 14 milliequivalents per liter as the normal
range for anion gap, a hospital using a different machine may use a range of 8 to 16 milliequivalents.
The normal lab values from the instrument being used to measure the ions should always be used
when interpreting the anion gap level.
WHAT IS AN EXAMPLE OF AN ANION GAP CALCULATION?
Here is an example of an anion gap calculation, based on the most common method (subtracting the
chloride and bicarbonate anions from the sodium cations). For this example, the total number of
sodium cations is 140 milliequivalents (mEq) and the total number of chloride and bicarbonate ions
(added together) is 128 mEq. Thus, 140 mEq minus 128 mEq = 12mEq. Thus, the anion gap level is
12 mEq. This means that we are estimating that there are 12 mEq of anions per liter, other than the
chloride and bicarbonate anions. See the previous section for a description of milliequivalents.
WHY IS IT HELPFUL TO MEASURE ANION GAP?
Measuring anion gap helps to diagnose and treat a condition known as acidosis. Acidosis is when
there is too much acid in the blood. There are many different types of acidosis, and each type is
named for its cause. Some examples are listed below.
WHAT DOES IT MEAN IF THE ANION GAP LEVEL IS TOO HIGH?
It is generally accepted that if the anion gap level is 20 or above, this signals a problem. Too high of
an anion gap level can mean that there is acidosis (too much acid in the blood) due to diabetes
mellitus. The high anion gap level can also be due to lactic acidosis, in which the high level of acid is
due a buildup of a substance called lactic acid. Lactic acid buildup is what causes the burning feeling
in your muscles when lifting weights for many repetitions. A high anion gap can also be due to drug
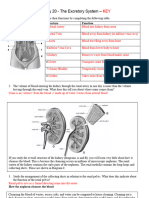
poisoning or kidney failure. The kidneys are two organs located on each side of the spine, behind the
stomach. The kidneys filter (remove) wastes from the blood. When the anion gap is high, further tests
are usually needed to diagnose the cause of the problem.
WHAT DOES IT MEAN IF THE ANION GAP LEVEL IS TOO LOW?
If the anion gap level is too low, this can mean that the person has hyponatremia (a decreased level
of sodium in the blood). It can also mean that the person has multiple myeloma, which is cancer of
the bone marrow. Bone marrow is a tissue that fills the center of long bones. Additional testing needs
to be done to find out the reason for the anion gap level being too low.
IF THE ANION GAP IS NORMAL, CAN ACIDOSIS BE PRESENT?
Yes, but it is unlikely. Thus, an increase or decrease in anion gap can mean that acidosis is present,
but the absence of an increase or decrease does not always mean that acidosis is not present.
WHAT ELSE IS ANION GAP KNOWN AS?
Anion gap is also known as the cation-anion difference.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM "ANION GAP?"
Anion gap comes from the Greek word "anion" meaning "backward going," and the Old English word
"gapa" meaning "hole." Put the words together and you have "backward going hole.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Wikipedia - Anion Gap (CHECKED)Dokumen6 halamanWikipedia - Anion Gap (CHECKED)vitruvianxyzBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandMetabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Alkaline Ionized WaterDokumen3 halamanAlkaline Ionized Waterladia100% (1)
- Electrolyte Imbalance, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandElectrolyte Imbalance, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Jurnal DM 2Dokumen7 halamanJurnal DM 2Elang SudewaBelum ada peringkat
- Zaragoza Fibrosis QuisticaDokumen6 halamanZaragoza Fibrosis QuisticaJanael Marcelo ArceBelum ada peringkat
- Anionic GapDokumen6 halamanAnionic GapZulkarnainBustamamBelum ada peringkat
- Defination and Types of Anionic GapDokumen6 halamanDefination and Types of Anionic GapZulkarnainBustamamBelum ada peringkat
- ABG, CBC, BONE Marrow BiopsyDokumen34 halamanABG, CBC, BONE Marrow Biopsymarthonsilva123Belum ada peringkat
- The Anion Gap and The Bicarbonate GapDokumen8 halamanThe Anion Gap and The Bicarbonate GapChamika HuruggamuwaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes ImbalanceDokumen36 halamanElectrolytes ImbalanceSai100% (1)
- Anion GapDokumen6 halamanAnion Gapmuhamad givariBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Exrection Worksheet KeyDokumen5 halaman3 - Exrection Worksheet KeyJenny YoonBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Components: HormonesDokumen4 halamanNormal Components: Hormonesmark paylessBelum ada peringkat
- Blood ChemDokumen24 halamanBlood Chemqwerty masterBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment: Submitted by Ali Ahmed Roll No #12164Dokumen12 halamanAssignment: Submitted by Ali Ahmed Roll No #12164Zafar Iqbal ManjBelum ada peringkat
- ABGsDokumen8 halamanABGsafzal sulemaniBelum ada peringkat
- 66 Part 1Dokumen10 halaman66 Part 1Dinu Tiberiu GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Abg - AssDokumen5 halamanAbg - AssLeigh AgonoyBelum ada peringkat
- Such Thing As An Anion Gap Metabolic Alkalosis. There Is Also No Such ThingDokumen3 halamanSuch Thing As An Anion Gap Metabolic Alkalosis. There Is Also No Such ThingMwanja MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Ranal SystemDokumen35 halamanRanal SystemAdil IrshadBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolytes - P3 Oct3Dokumen12 halamanElectrolytes - P3 Oct3Edward Vladimir MoncayBelum ada peringkat
- Opti Lion Ops Guide EnglishDokumen163 halamanOpti Lion Ops Guide EnglishAsif KhanBelum ada peringkat
- High Anion Gap Metabolic AcidosisDokumen6 halamanHigh Anion Gap Metabolic AcidosisharvardboyBelum ada peringkat
- ABG & VBG - Arterial and Venous Blood Gas - Interpreting ResultsDokumen6 halamanABG & VBG - Arterial and Venous Blood Gas - Interpreting ResultsmmmmzBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 20 Notes 2018Dokumen6 halamanLecture 20 Notes 2018Omed ZarifiBelum ada peringkat
- Pulse OximetryDokumen91 halamanPulse Oximetryapi-205902640Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheungDokumen12 halamanPharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheungdoctorirfanBelum ada peringkat
- TonicityDokumen6 halamanTonicitypavelbdsBelum ada peringkat
- Anion GapDokumen1 halamanAnion GapTochukwu IgboanugoBelum ada peringkat
- ABG and ABG AnalysisDokumen21 halamanABG and ABG AnalysislouellaBelum ada peringkat
- Ion Exchange - Simple To UnderstandDokumen140 halamanIon Exchange - Simple To UnderstandAlaitzB100% (3)
- Acute and Chronic Metabolic Acidosis (Base Bicarbonate Deficit)Dokumen8 halamanAcute and Chronic Metabolic Acidosis (Base Bicarbonate Deficit)Kim XiaoBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheungDokumen12 halamanPharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheunglovehopeBelum ada peringkat
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Dokumen14 halamanHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817Belum ada peringkat
- Anion GapDokumen13 halamanAnion GapLuis Gerardo Alcalá GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Easy Way To Interpret ABG ValuesDokumen7 halamanEasy Way To Interpret ABG ValuesDoyTanBelum ada peringkat
- Iii. Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations Hematology October 24, 2014 Examination Result Normal Values InterpretationDokumen22 halamanIii. Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations Hematology October 24, 2014 Examination Result Normal Values InterpretationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaBelum ada peringkat
- About Pulse OximetryDokumen16 halamanAbout Pulse OximetrySrdjan DimitrijevicBelum ada peringkat
- Bahasa InggrisDokumen12 halamanBahasa InggrisNadea AmandaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid & ElectrolytesDokumen85 halamanFluid & ElectrolytesAdarshBijapurBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Blood: Dr. Pramesh DograDokumen46 halamanIntroduction To Blood: Dr. Pramesh DograPramesh DograBelum ada peringkat
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDokumen28 halamanArterial Blood Gas Analysishendra_darmawan_4Belum ada peringkat
- Water LoseDokumen29 halamanWater LoseJAKLIN EMPOLBelum ada peringkat
- ABG MMHG InterpretationDokumen92 halamanABG MMHG InterpretationManmeet SBelum ada peringkat
- Ray KurzweilDokumen5 halamanRay KurzweilTri Nguyen0% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokumen8 halamanFluid and Electrolyte BalanceSujatha AluguriBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Hadi Kuncoro, S.Farm., Apt., M.Farm - Elektrolit, Non Elektrolit Dan Zwitter IonDokumen16 halamanDr. Hadi Kuncoro, S.Farm., Apt., M.Farm - Elektrolit, Non Elektrolit Dan Zwitter IonCiBelum ada peringkat
- Water BalanceDokumen9 halamanWater BalanceKim Mae ComendadorBelum ada peringkat
- Intake OutputDokumen52 halamanIntake Outputkirti thakurBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of PH QFRDokumen2 halamanDetermination of PH QFRsyareeisyeeBelum ada peringkat
- VII. Laboratory Exams Name of Examination: Complete Blood Count DefinitionDokumen4 halamanVII. Laboratory Exams Name of Examination: Complete Blood Count DefinitionMark Ianne AngBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodialysis: Diffusion and Ultrafiltration: Ramin SamDokumen17 halamanHemodialysis: Diffusion and Ultrafiltration: Ramin SamEvelina Navi BraginskiyBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology: Subjective DataDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology: Subjective DataLoela Emia ZamorasBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Gravity and Chloride Concentration Volume, Acidity, Specific Gravity and Chloride ConcentrationDokumen11 halamanSpecific Gravity and Chloride Concentration Volume, Acidity, Specific Gravity and Chloride ConcentrationOlyver SangBelum ada peringkat
- International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)Dokumen8 halamanInternational Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)inventionjournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry ProjectDokumen16 halamanChemistry ProjectSagnik DeBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Gas TestDokumen6 halamanBlood Gas TestyudhafpBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 MCNDokumen14 halamanChapter 1 MCNLawrence NemirBelum ada peringkat
- Schilling Test BrochureDokumen2 halamanSchilling Test BrochureLyn OdchigueBelum ada peringkat
- SalpingitisDokumen25 halamanSalpingitisAnonymous NDAtNJyKBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmo Physio-Transport 2Dokumen35 halamanPulmo Physio-Transport 2Mich Therese AbejeroBelum ada peringkat
- Formation of Faeces and DefecationDokumen11 halamanFormation of Faeces and Defecationbiologi88Belum ada peringkat
- PoultryDokumen2 halamanPoultryDineshkumar NdkBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsDokumen11 halamanComparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsmichiparisBelum ada peringkat
- UH Kelas XIIDokumen7 halamanUH Kelas XIIElismawati AzmarBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesDokumen9 halamanBlood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesEduardo Rios DuboisBelum ada peringkat
- 0610 s17 QP 31Dokumen24 halaman0610 s17 QP 31BioScMentor-1Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDokumen11 halamanCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- Anders Sandberg - Asatru The Nordic Subtradition of The Verbena Cd9 Id1061308219 Size156Dokumen16 halamanAnders Sandberg - Asatru The Nordic Subtradition of The Verbena Cd9 Id1061308219 Size156Baud WolfBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis SlidesDokumen18 halamanTuberculosis SlidesmedeviBelum ada peringkat
- Post Thoracotomy Physiotherapy ManagementDokumen25 halamanPost Thoracotomy Physiotherapy ManagementSiva Shanmugam100% (5)
- Reaction Paper On UniverseDokumen1 halamanReaction Paper On Universefor_you882002100% (1)
- Make Money With VestigeDokumen46 halamanMake Money With Vestigejameser123100% (1)
- Savage Worlds Cheatsheets PowersDokumen15 halamanSavage Worlds Cheatsheets Powersschwartz5350Belum ada peringkat
- Cheat Sheet 2Dokumen2 halamanCheat Sheet 2oushaBelum ada peringkat
- The Muscular SystemDokumen32 halamanThe Muscular SystemNicholas ReubenBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of Mammalian IngestionDokumen6 halamanPhysiology of Mammalian IngestionEbooks For YouBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Class VIII Science Chapter 8 Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen11 halamanNCERT Class VIII Science Chapter 8 Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeAbhasBelum ada peringkat
- Skilled Birth Attendant PostersDokumen16 halamanSkilled Birth Attendant PostersPrabir Kumar Chatterjee100% (1)
- 30 Dec JoBs BY KHALIQ HASSAN - Watermarked PDFDokumen4 halaman30 Dec JoBs BY KHALIQ HASSAN - Watermarked PDFKamran Talpur100% (1)
- Agglutination ReactionsDokumen28 halamanAgglutination ReactionscyrhenmieBelum ada peringkat
- Cytoskeletal AbnormalitiesDokumen80 halamanCytoskeletal Abnormalitieschinnnababu89% (9)
- Sense OrgansDokumen6 halamanSense Organsannmarie100% (1)
- Bones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingDokumen21 halamanBones: Defination: Bone Is Highly Vascular, Living, Constantly ChangingMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuBelum ada peringkat
- Curbside Form DR Judy Morgan's Naturally Healthy PetsDokumen6 halamanCurbside Form DR Judy Morgan's Naturally Healthy Petsgale diazBelum ada peringkat
- Baylissascaris LarvisDokumen136 halamanBaylissascaris LarvisAlejoDubertiBelum ada peringkat
- Kozier's Peri Operative NSG ChecklistDokumen15 halamanKozier's Peri Operative NSG ChecklistMichaelBelum ada peringkat
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDari EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDari EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDari EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Oxygen: The molecule that made the worldDari EverandOxygen: The molecule that made the worldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (108)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDari EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDari EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesDari EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDari EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDari EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (20)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugDari EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesDari EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)