Marco Final Exam Study Prep2
Diunggah oleh
api-2306788760 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
33 tayangan26 halamanJudul Asli
marco final exam study prep2
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
33 tayangan26 halamanMarco Final Exam Study Prep2
Diunggah oleh
api-230678876Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 26
20.
Theories of change intervention
& planned change theory dilemmas &
critical issues lasting change
Change Management Study Guide
25. Planned organizational change key
determinants of successful/
unsuccessful approaches
31. Strategic change perspective
types of interventions application
A Study Guide Prepared for Alchemy by Marco Cassone
Theories of Change
!
3 (+) major theories of
organizational change:
!
Lewins Change Model
!
Action Research Model
!
Positive Model
!
Also Kotters Model of Change
TBDiscussed: How are change models similar or different?
Driving & Restraining Forces
Change as modification of those forces keeping a system stable.
Always more effective to decrease rather than increase forces.
Lewins
Change Model
Cyclical process:
Research provides
guide to action;
Results of action
assessed => info
for further action,
etc.
Action
Research
The Positive Model:
Not deficit-based.
!
Does not focus on Organizations problems
and how they can be solved
!
Focuses on what organization is doing
right and builds off those capabilities to
achieve better results
!
Theory: People tend to act in ways that
make their expectations occur
!
Uses Appreciative Inquiry (AI), a form of
social constructionism
Model of Change
Kotter
Similarities to
Lewins model:
Three distinct
phases:
Unfreeze,
Change,
Refreeze
TBD: How are change models similar/different?
!
All major models describe phases
by which planned change occurs
!
Overlap in emphasis on action is
preceded by preliminary stage
followed by closing stage
!
Emphasize involvement of
organizational members
!
OD recognizes: interaction btwn
consultant and organization will
affect the organization
Steps in Strategic Change
(S.W.O.T.)
Starting point for a change
program is defining the
total change strategy.
Business strategy and
organization design must
be aligned and changed
together to respond to
external/internal forces
and disruptions.
Strategic Analysis
Strategy Making
Strategy Change Plan
Implementation
External Forces Internal Forces
Competitor strategy Strategy modifications
New technologies New equipment
Business cycles New processes
Labor market shifts Workforce composition
Social change Job restructuring
Competition laws and
regulations
Compensation and benefits
Changes in natural
environment
Labor surpluses and
shortages
Generational trends Employee attitude
Three Basic Approaches to
Organization Change
Behavioral science techniques designed to
plan and implement change at work
1. Structural
2. Technical
3. Behavioral
Developing strategy: planning activities to
resolve difficulties, build on strengths
(Process)
TBD: Compare/contrast strategic change vs. planned change.
Structural Approach to Change
!
Changes that affect how elements of
organization relate to one another
!
Removing or adding layers to hierarchy
!
Downsizing associated with restructuring
!
Decentralization and centralization
!
Structural approaches:
!
Goal setting,
!
Quality circles,
!
Strategic planning
!
Changes in machinery, methods, automation, and processes
!
Changes help companies become more efficient and productive
!
Build a better mousetrap
!
Technical approaches:
!
Job design, redesign
!
Process consultation,
!
Quality-of-work-life (QWL)
!
TQM and Six Sigma
Technical Approach to Change
Behavioral Approach to Change
!
Emphasizes better utilization of
human resources by improving:
!
Morale
!
Motivation
!
Commitment of members
!
Behavioral approaches:
!
Survey feedback,
!
Team building,
!
Traditional OD
Integrated
Approach
OD
Comfort
Zone
16
Challenges of Complexity In Change
!
Change in situations characterised by
hard complexity is easier to achieve.
! Where most people understand and agree
on presenting problems in the situation
! With widely-shared assumptions about
relationships (compatible values, beliefs)
! Where quantitative criteria can be used to
test options for change
!
Change in situations of soft complexity,
where issues are contentious and there is
a high level of emotional involvement
among stakeholders is harder to achieve.
Change is Never Easy
Two important considerations are the magnitude of change
and the degree to which the client system is organized.
TBD: What are the key determinants of successful approaches?
OD Approach:
Organization
Iceberg
OD change
strategies must
consider all
overt/formal &
covert/informal
elements
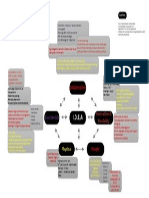
Proscis ADKAR Change Model
The Paradoxical Theory of Change
Based on the belief that change rests on the full acceptance of status quo;
assumes resistance is expected, healthy, and must be part of the process.
This formula shows the conditions necessary for a collective paradigm shift:
! D = allowing participants to voice dissatisfactions with the current state
! A = engaging with an aspired future state
! FA = first steps and longer-term actions focused on getting commitment
and momentum to make the difference
! B = the belief in collectively shifting to be dramatically different
! O = engaging and enrolling others
Dissatisfactions (D) x Aspirations (A) x
First Actions (FA) x Belief (B) x Others (O)
Transformational
Breakthrough (TB)
=
(Dannemiller, 2000)
Key Considerations
For Lasting Change
!
Effective change depends on
diagnosis of underlying causes
to organization problems
!
Consider multiple change
processes and diversity of
stakeholders
!
Create a culture supportive of
social change and innovation
!
Increased member involvement
in change process:
!
Participatory action research,
action learning, self design
!
Help members gain
competence to design
organization continuously
TBD: How do you distinguish change?
Proactive
Change:
Change
embedded in
strategy & DNA
Reactive
Change:
Change
management as
OD intervention
When is planned change necessary?
When is strategic change critical and important?
When is a change-friendly strategy, culture, and identity smart?
AGILITY
Business!
Capacity!
ADAPT
to
LEARN!
Ability
to
CHOICES!
Creating
Strategy means:!
THINKING!
Scenario
Creating choices means:!
Key to Worleys
Sustainable
Effectiveness
Where change
inspires growth
& innovation
Convergence:
Implementing
Perceiving
Strategizing
Testing
Strategizing: How MGT teams
pair an aspirational purpose
with a widely-shared strategy
and manage the climate and
commitment to execution
Perceiving: Broadly, deeply, and
continuously monitoring the
environment to sense changes
and communicating these
perceptions to leaders
Testing: How an
organization sets up,
runs, and learns
from experiments
Implementing: How
changes are planned
and performance
impacts measured
Worleys Agility Pyramid (view from top)
Share successful &
unsuccessful approaches to
planned organization change
Share real-life applications
of different strategic
change interventions
Final Discussion: Stories from the Field
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Lister Hr3 ManualDokumen119 halamanLister Hr3 ManualRichard Gomez Cueva100% (2)
- Bianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)Dokumen385 halamanBianca Premo - The Enlightenment On Trial - Ordinary Litigants and Colonialism in The Spanish Empire-Oxford University Press (2017)David Quintero100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Report - Roche Pharmaceuticals LTD (Human Resource Planning & Development) 222Dokumen23 halamanReport - Roche Pharmaceuticals LTD (Human Resource Planning & Development) 222jawwadraja100% (1)
- Cassone Transformative Listening Thesis 7-24-14Dokumen101 halamanCassone Transformative Listening Thesis 7-24-14api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Post-American World For AlchemyDokumen9 halamanPost-American World For Alchemyapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Fab 4 I D e A ObservationsDokumen1 halamanFab 4 I D e A Observationsapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Msod620 Blue Team Paper FinalDokumen17 halamanMsod620 Blue Team Paper Finalapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone Learning Journal Summary March 2014Dokumen3 halamanCassone Learning Journal Summary March 2014api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Xcassone Reflection Paper Msod 620Dokumen5 halamanXcassone Reflection Paper Msod 620api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Six Degree AlchemyDokumen14 halamanSix Degree Alchemyapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Book Summary Notes Post American World FinalDokumen4 halamanBook Summary Notes Post American World Finalapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Marco Cassone 60b29a1c 5f80 4f24 Ad08 6344215913a7Dokumen1 halamanMarco Cassone 60b29a1c 5f80 4f24 Ad08 6344215913a7api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Sdi Interpretive GuideDokumen7 halamanSdi Interpretive Guideapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Marcos PDC Oct 2013Dokumen1 halamanMarcos PDC Oct 2013api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone 616 Individual Learning JournalDokumen5 halamanCassone 616 Individual Learning Journalapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Palleschi RecommendationDokumen1 halamanPalleschi Recommendationapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Ocai Omicron Prime Culture Report Ver 6Dokumen9 halamanOcai Omicron Prime Culture Report Ver 6api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone Learning Journal SummaryDokumen2 halamanCassone Learning Journal Summaryapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Complexity Alchemy PresentationDokumen42 halamanComplexity Alchemy Presentationapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Ai Alchemy SlidedeckDokumen25 halamanAi Alchemy Slidedeckapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone M Admissions EssayDokumen1 halamanCassone M Admissions Essayapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Marcos Shortened Profile For AlchemyDokumen11 halamanMarcos Shortened Profile For Alchemyapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone Complexity in Di InitiativesDokumen9 halamanCassone Complexity in Di Initiativesapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone Ppov Paper 621Dokumen4 halamanCassone Ppov Paper 621api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- MGT Reset 10 TakeawaysDokumen14 halamanMGT Reset 10 Takeawaysapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- SwanncassonepatagoniapairpaperDokumen11 halamanSwanncassonepatagoniapairpaperapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone 616 Post-Session Emlyon Evaluation PaperDokumen6 halamanCassone 616 Post-Session Emlyon Evaluation Paperapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Msod620 Cango Pres FinalDokumen85 halamanMsod620 Cango Pres Finalapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Closing Session PosterDokumen1 halamanClosing Session Posterapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Ai in Practice Imagining A Bright Future ChesleyDokumen47 halamanAi in Practice Imagining A Bright Future Chesleyapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Cassone Reflection Paper Msod 620Dokumen5 halamanCassone Reflection Paper Msod 620api-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- Diversity & Inclusion DiscussionDokumen9 halamanDiversity & Inclusion Discussionapi-230678876Belum ada peringkat
- AYLS Annual Report 2019 LampDokumen136 halamanAYLS Annual Report 2019 LampHigh FourBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Question Paper Computer GraphicsDokumen4 halamanSample Question Paper Computer Graphicsrohit sanjay shindeBelum ada peringkat
- STEEL STRUCTURES KHARGHAR SKYWALK AND NIFT INSTITUTE Ms PPT 2007Dokumen30 halamanSTEEL STRUCTURES KHARGHAR SKYWALK AND NIFT INSTITUTE Ms PPT 2007Harsh chhedaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 Evidencias Clase 7 L Reading - Young PilotsDokumen4 halamanTopic 2 Evidencias Clase 7 L Reading - Young PilotsJam C. PoloBelum ada peringkat
- Program Documentation Lesson 10Dokumen32 halamanProgram Documentation Lesson 10Armechelyn DerechoBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Typing History of TypingDokumen9 halamanComputer Typing History of TypingRamBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Gallery: AccountabilityDokumen15 halamanCrystal Gallery: AccountabilityJitesh ManwaniBelum ada peringkat
- ABB - Composite Station Post InsulatorsDokumen6 halamanABB - Composite Station Post InsulatorsDominic SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Option MCQ-Human Resource Management (205) : Clarifying Handling People Maintaing Relationship (C) Both (A) and (B)Dokumen4 halamanOption MCQ-Human Resource Management (205) : Clarifying Handling People Maintaing Relationship (C) Both (A) and (B)MukulBelum ada peringkat
- Probability spaces and σ-algebras: Scott SheffieldDokumen12 halamanProbability spaces and σ-algebras: Scott SheffieldRikta DasBelum ada peringkat
- DLPDokumen2 halamanDLPEunice Junio NamionBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson4 1515Dokumen14 halamanLesson4 1515gm hashBelum ada peringkat
- Pdpa CraDokumen3 halamanPdpa CraAdyrah RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionnaireDokumen5 halamanQuestionnairePrisca FolorunsoBelum ada peringkat
- Research TopicsDokumen15 halamanResearch TopicsmalinksBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions - BlockchainDokumen1 halamanImportant Questions - BlockchainHarsh Varshney100% (1)
- 14.ergonomic Workstation Design For Science Laboratory (Norhafizah Rosman) PP 93-102Dokumen10 halaman14.ergonomic Workstation Design For Science Laboratory (Norhafizah Rosman) PP 93-102upenapahangBelum ada peringkat
- Applied-Signed Product Cordial Labeling and - Santhi.mDokumen6 halamanApplied-Signed Product Cordial Labeling and - Santhi.mImpact JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Sebu6100-02 MDokumen74 halamanSebu6100-02 MSa CruCerBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring PovertyDokumen47 halamanMeasuring PovertyPranabes DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- As 4587-1999 Water Mist Fire Protection Systems - System Design Installation and CommissioningDokumen10 halamanAs 4587-1999 Water Mist Fire Protection Systems - System Design Installation and CommissioningSAI Global - APAC100% (1)
- Wind Load On StructuesDokumen14 halamanWind Load On StructuesNasri Ahmed mohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Pdlgfu15: PDLGFU15 User's GuideDokumen327 halamanPdlgfu15: PDLGFU15 User's Guidejose antonio carazoBelum ada peringkat
- Dramix: Dramix Economic Concrete Reinforcement For Safe Floors On PilesDokumen9 halamanDramix: Dramix Economic Concrete Reinforcement For Safe Floors On PilesMohammad IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Education During The Ancient Period Primitive EducationDokumen5 halamanEducation During The Ancient Period Primitive EducationEn CyBelum ada peringkat
- 67 - Es - Ut Republic Csalamade BooDokumen47 halaman67 - Es - Ut Republic Csalamade BooTyler LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Activity Completion ReportDokumen1 halamanDepartment of Education: Activity Completion ReportJanineJavier100% (1)