Intro GIS CST Session1
Diunggah oleh
Eng Bagaragaza Romuald0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan10 halamanvh,khjl.o/;
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inivh,khjl.o/;
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan10 halamanIntro GIS CST Session1
Diunggah oleh
Eng Bagaragaza Romualdvh,khjl.o/;
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 10
1
Introduction to GIS Introduction to GIS
Training Main Objective Training Main Objective
The objective of this training is to The objective of this training is to
provide participants with: provide participants with:
Basic theoretical and practical Basic theoretical and practical
knowledge/skills to GIS field, knowledge/skills to GIS field,
Understanding of concepts, tools and Understanding of concepts, tools and
methods to methods to
capture, store, query, analyze, display and capture, store, query, analyze, display and
visualize the spatial data visualize the spatial data
GIS Definitions (1)
Some main definitions from the literature are Some main definitions from the literature are
reviewed in this course: reviewed in this course:
Definition 1: GIS as a toolbox Definition 1: GIS as a toolbox
GIS is GIS is a powerful set of tools for collecting, a powerful set of tools for collecting,
storing, retrieving at will, transforming and storing, retrieving at will, transforming and
displaying spatial data from the real world for a displaying spatial data from the real world for a
particular set of purposes particular set of purposes ( (Burrough and
McDonnell 1998 p. 11). ).
GIS=Geographic(Geospatial)Information
System
Geographic; WHERE WHERE something is located on something is located on
earth earth
Information; WHAT WHAT it is (its size, name, value it is (its size, name, value
etc) etc)
System; to help to help MANAGE MANAGE and use the data. and use the data.
2
GIStakesmapsintothecomputer...
Separate layers
for different types
of features
...andlinkstoinformation
Location offeaturesfromtherealworldislinked
to information about those features stored in a
relationaldatabase.
AllGIShave:
HARDWARE:
Computer,printer,datastorage,scanner,digitizer.
SOFTWARE:
Input,output,analysis,databasemanagement.
LIVEWARE:
Skilledpeopleandorganisationalsupport.
SPATIALDATA:
Informationreferencedtoitslocationontheearth
surface.
8
GIS and Spatial data
- Spatial data is the data that relates to the
geographic location of features and their
boundaries on earth, such as natural or
man-made features.
- It describes both the location of a
geographic feature and its attributes.
3
SpatialData
WHATISIT?
Informationaboutanything
thatisreferencedtotheEarth.
WHEREDOESIT
COMEFROM?
Satellites
Aerialphotographs
Maps
Fieldobservations
GIS Definitions (2)
GIS is a system of hardware, software, GIS is a system of hardware, software,
data, people, organization, and data, people, organization, and
institutional arrangement for institutional arrangement for collecting collecting, ,
storing storing, , analysing analysing, and , and disseminating disseminating
information above areas of the earth. information above areas of the earth.
( ( Durker Durker and and Kjerne Kjerne 1989, cited in Chrisman 2002 p.12 1989, cited in Chrisman 2002 p.12). ).
Basic components of GIS
There are four main There are four main
components of GIS that components of GIS that
are software, hardware, are software, hardware,
data and people, data and people,
Whereas Whereas ESRI (2001) ESRI (2001)
includes includes method method as a as a
fifth component. fifth component.
All the components need All the components need
to be in balance, if the to be in balance, if the
system is to function system is to function
satisfactorily. satisfactorily.
Basic components of GIS
Software Software
Software refers to computer programs that Software refers to computer programs that
provide the functions and tools to store, analyze, provide the functions and tools to store, analyze,
and display geographic information. and display geographic information.
GIS vendors advertise their products with special GIS vendors advertise their products with special
features and different GIS software packages features and different GIS software packages
can vary widely in cost, functionality and user can vary widely in cost, functionality and user
friendliness friendliness
4
Basic components of GIS
Hardware Hardware
Hardware refers to the computer components on which a Hardware refers to the computer components on which a
GIS operates. GIS operates.
The central processing unit is the core part of computer The central processing unit is the core part of computer
hardware that performs all the data processing and analysis hardware that performs all the data processing and analysis
tasks. tasks.
Today, GIS software runs on a wide range of hardware Today, GIS software runs on a wide range of hardware
types, from centralized computer servers to desktop types, from centralized computer servers to desktop
computers. computers.
Hardware capabilities affect processing speed, ease of use Hardware capabilities affect processing speed, ease of use
and the types of output available. and the types of output available.
Basic components of GIS
Hardware components for GIS can be categorized into Hardware components for GIS can be categorized into
four major types: four major types:
Input devices Input devices, which includes digitizer, scanner, , which includes digitizer, scanner,
keyboard keyboard
Storage devices Storage devices includes, hard disc, CD ROM, etc includes, hard disc, CD ROM, etc
Processing devices: Processing devices: CPU ( Central Processing Unit) CPU ( Central Processing Unit)
and and
Output device Output device includes printers, plotter, and monitor. includes printers, plotter, and monitor.
Basic components of GIS
Data Data
Locations and other characteristics of natural Locations and other characteristics of natural
features and human activities on, above and features and human activities on, above and
under the earth under the earth s surface s surface
There is wide variety of data sources: primary There is wide variety of data sources: primary
and secondary data and secondary data
Primary and secondary data have Primary and secondary data have three three
dimensions dimensions: : spatial, temporal, or thematic. spatial, temporal, or thematic.
Spatial: Spatial: spatial dimension of data includes spatial dimension of data includes
various symbols that communicate to the user various symbols that communicate to the user
information about the location of the feature being information about the location of the feature being
observed observed
Basic components of GIS Basic components of GIS
Temporal Temporal: The temporal dimension provides a record of : The temporal dimension provides a record of
when the data were collected (or the record to which data when the data were collected (or the record to which data
applies). applies).
Thematic/attribute Thematic/attribute: :
The thematic dimension shows the characteristic of a The thematic dimension shows the characteristic of a
real world feature to which the data refer. real world feature to which the data refer.
In GIS, thematic data are often referred as non In GIS, thematic data are often referred as non- -spatial, spatial,
or attribute, data. or attribute, data.
5
Basic components of GIS Basic components of GIS
People People
GIS technology is of very limited value without GIS technology is of very limited value without
skilled people to manage the system and develop skilled people to manage the system and develop
plans for applying it to real plans for applying it to real- -world problems. world problems.
GIS users range from technical specialists who GIS users range from technical specialists who
design and maintain the system, to those who use design and maintain the system, to those who use
it to help them perform their everyday work. it to help them perform their everyday work.
WhyuseGIS?
You can QUICKLY make maps of your data
ANY TIME you need to and PREVIEW them
onscreen.
You can easily examine SPATIAL
RELATIONSHIPS and PATTERNS in your
datausingspatialanalysis.
FindWHATTYPE ofobjectsare
locatedinaPARTICULARPLACE.
FindWHERE objectsofa
PARTICULARTYPE orcombination
oftypesarelocated.
GIS...whatcanyoudowithit?
DatabaseQuery
Layer1:Wells
Layer2:Rivers
Layer3:Buildings
Layer4:Soils
1
2
3
4
eg.Alandfilllocatedneartothearea
coveredbythesedatalayershasreleased
atoxicsubstanceintheenvironment.
Q.Whatistheenvironmentalofthat
landfillimpacts?
6
1-21
GIS Functions GIS Functions
Query
Query
Analyze
Analyze
Store
Store
Display
Display
Capture
Capture
GIS should be capable of the following fundamental GIS should be capable of the following fundamental
operations in order to find solutions to real operations in order to find solutions to real- -world problems. world problems.
Data input
Data input
Output
Output
1-22
GIS functions: Data capturing GIS functions: Data capturing
Hardcopy maps
Hardcopy maps
GPS
GPS
GIS
Data
Coordinates
Coordinates
Digital data
Digital data
A GIS must provide methods for inputting geographic (coordinate) A GIS must provide methods for inputting geographic (coordinate)
and tabular (attribute) data. and tabular (attribute) data.
The more input methods available, the more flexible the GIS. The more input methods available, the more flexible the GIS.
Data input Data input
Data input refers to the procedure of encoding data into a Data input refers to the procedure of encoding data into a
computer computer- -readable form and writing the data to the GIS readable form and writing the data to the GIS
database. database.
This process involves acquiring, reformatting, geo This process involves acquiring, reformatting, geo- -
referencing, compiling, and documentation of the data. referencing, compiling, and documentation of the data.
The creation of an accurate and well documented The creation of an accurate and well documented
database is the most important task of GIS. database is the most important task of GIS.
As geographic database is expensive, data entry is an As geographic database is expensive, data entry is an
important consideration. important consideration.
Storage and management of data Storage and management of data
GIS store data in digital format, which can GIS store data in digital format, which can
be much more efficient than using paper be much more efficient than using paper
maps and survey sheets. maps and survey sheets.
Two basic data models for geographic data Two basic data models for geographic data
storage: storage: vector and raster model. vector and raster model.
7
Querying data Querying data
One common type of GIS query is to One common type of GIS query is to
determine what exists at a particular determine what exists at a particular
location. location.
User understands where features of User understands where features of
interest are, but wants to know what interest are, but wants to know what
characteristics are associated with them. characteristics are associated with them.
1-26
Querying data Querying data
Identifying specific features Identifying specific features
Identifying features based Identifying features based
on conditions on conditions
You can select the powerlines
that are of 30KV.
You can select the powerlines
that are of 30KV.
Manipulating Manipulating and analysing data and analysing data
You can perform analysis to obtain the answers to a You can perform analysis to obtain the answers to a
particular question or find solutions to a particular particular question or find solutions to a particular
problem. problem.
Three common types of geographic analysis are: Three common types of geographic analysis are:
Proximity analysis: Proximity analysis:
GIS can be used to investigate the relationship of GIS can be used to investigate the relationship of
features in terms of features in terms of nearness, connecti vity nearness, connecti vity or or
other properties of distance. other properties of distance. It is also known as
neighbourhood analysis
Manipulation Manipulation and analysing data and analysing data
Overlay analysis Overlay analysis: :
The integration of different data layers involves a The integration of different data layers involves a
process called overlay. process called overlay.
This overlay, or spatial join, can integrate data on This overlay, or spatial join, can integrate data on
soils, slope, and land use for sustainable land soils, slope, and land use for sustainable land
resources management. resources management.
Network analysis Network analysis: This type of analysis : This type of analysis
examines how linear features are examines how linear features are connected connected and and
how easily resources can how easily resources can flow through flow through them them
8
Display Display
For many types of geographic operations, the For many types of geographic operations, the
end result is usually best visualized as a map end result is usually best visualized as a map
or graph. or graph.
Maps are efficient for storing and Maps are efficient for storing and
communicating geographic information. communicating geographic information.
Maps can be integrated with reports, Maps can be integrated with reports,
photographic images, and other digital media. photographic images, and other digital media.
1-30
Display Display
Maps
Maps
Reports
Reports
Altitude and Malaria Cases per 100000 inhabitants
Generated by ArcGIS 22/10/2008
altitude x total07_pop
3.000 2.500 2.000 1.500
50.000
45.000
40.000
35.000
30.000
25.000
20.000
15.000
10.000
5.000
0
altitude
total07_pop
total07
total07
Count
total07_pop
Graphs
Graphs
1-31
Output Output
rwanda.mxd
Document
Document
Internet
Internet
Paper map
Paper map
GIS
Data
rwanda.jpg
Image
Image
Representing features in vector data Representing features in vector data
Abstracting real Abstracting real- -world entities: world entities:
Three basic geometric shapes are used for Three basic geometric shapes are used for
geographic features: points, lines, and geographic features: points, lines, and
areas. areas.
These shapes are also called geometric These shapes are also called geometric
objects, geometric features, or feature objects, geometric features, or feature
types. types.
9
1-33
Representing features in vector data Representing features in vector data
Real Real- -world entities are abstracted into three world entities are abstracted into three
basic shapes basic shapes
Points
Points
Health Centers
Health Centers
Lines
Lines
Streets
Streets
Areas/Polygons
Areas/Polygons
Land cover
Land cover
1-34
Components of geographic Components of geographic
data data
Three general components to geographic Three general components to geographic
information information
Attributes
Attributes
Geometry
Geometry
Streets
Behavior
Behavior
Streets and
lakes may not
intersect
Rules:
Components of geographic data Components of geographic data
Geometry Geometry
Geometry represents the geographic features associated with Geometry represents the geographic features associated with
real real- -world locations. Geographic features are abstracted into world locations. Geographic features are abstracted into
points, lines, or areas. points, lines, or areas.
Attributes Attributes
Attributes provide descriptive characteristics of the geographic Attributes provide descriptive characteristics of the geographic
features. features.
Behavior Behavior
Behavior means geographic features can be made to follow Behavior means geographic features can be made to follow
certain types of editing, display, or analysis rules, depending certain types of editing, display, or analysis rules, depending on on
circumstances defined by the user. circumstances defined by the user.
The relative position of features determines relationships
Topology mathematically models connectivity, adjacency, and
coincidence
Using spatial relationships Using spatial relationships
Kibuye is contained by
Karongi District
Kibuye is contained by
Karongi District
Karongi has an area
Karongi has an area
Kibuye is
adjacent to Lake
Kivu
Kibuye is
adjacent to Lake
Kivu
The road connects
Kibuye with Gitarama
The road connects
Kibuye with Gitarama
10
GIS Applications GIS Applications
Mapping Mapping
Land use planning and management Land use planning and management
Environmental studies Environmental studies
Natural resource mapping and management Natural resource mapping and management
Land survey, mapping and demarcation Land survey, mapping and demarcation
Mineral exploration Mineral exploration
Natural hazard prediction and management Natural hazard prediction and management
Geological studies Geological studies
GIS Applications GIS Applications
Engineering design and planning Engineering design and planning
Marketing and Retailing Marketing and Retailing
Urban Management and Planning Urban Management and Planning
Agriculture Agriculture
Coastal management Coastal management
Water Resource Management Water Resource Management
Soil Resource Management Soil Resource Management etc. etc.
Urban planning Urban planning
Remera
Land use, urban planning, land scape
analysis
J une
1984
J uly
1999
End for Session 1 End for Session 1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Condition Monitoring System For Hydro TurbinesDokumen4 halamanCondition Monitoring System For Hydro TurbinesEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Identification of Principal Factors Causing UnbalancedDokumen6 halamanIdentification of Principal Factors Causing UnbalancedEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- A I RS: David G. Dorrell, William ThomsonDokumen11 halamanA I RS: David G. Dorrell, William ThomsonEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Interturn Short-Circuit Detector For Turbine-Generator Rotor WindingsDokumen6 halamanInterturn Short-Circuit Detector For Turbine-Generator Rotor WindingsEng Bagaragaza Romuald100% (1)
- A Smart Experimental Setup For Vibration Measurement andDokumen11 halamanA Smart Experimental Setup For Vibration Measurement andEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing Destructive Effects of Water Hammer in Hydropower Plant PenstocksDokumen25 halamanPreventing Destructive Effects of Water Hammer in Hydropower Plant PenstocksEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Kapl Turb Inc93 PDFDokumen16 halamanKapl Turb Inc93 PDFEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Erosion Wear On Francis Turbine Components DueDokumen26 halamanErosion Wear On Francis Turbine Components DueEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Water Hammer Analysis of A Run-of-River Hydroelectric Power Plant in Lower Himalaya: A Case StudyDokumen9 halamanWater Hammer Analysis of A Run-of-River Hydroelectric Power Plant in Lower Himalaya: A Case StudyEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Fatigue Life Study of Francis Pump Under Reverse GDokumen15 halamanFatigue Life Study of Francis Pump Under Reverse GEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Nr. Crt. Frequency Possible Cause Vibration Amplitude Direction ObservationsDokumen3 halamanNr. Crt. Frequency Possible Cause Vibration Amplitude Direction ObservationsEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Wave Calculation of An Air CushionDokumen27 halamanStudy On Wave Calculation of An Air CushionEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing DestructiveDokumen25 halamanPreventing DestructiveEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Analysis of Vibration Sources of Hydro Aggregates in Operating RegimeDokumen8 halamanCritical Analysis of Vibration Sources of Hydro Aggregates in Operating RegimeEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Modelling and Transient Simulation of Water Flow in Pipelines Using Wanda Transient SoftwareDokumen10 halamanModelling and Transient Simulation of Water Flow in Pipelines Using Wanda Transient SoftwareEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Sediment Erosion in Hydro Turbines 1Dokumen414 halamanSediment Erosion in Hydro Turbines 1Eng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Selection of Guide Vane Pro Le For Erosion Handling in Francis TurbinesDokumen9 halamanSelection of Guide Vane Pro Le For Erosion Handling in Francis TurbinesEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Bur EralDokumen108 halamanBur EralEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Open-Channel 1Dokumen63 halamanMicrosoft PowerPoint - Open-Channel 1Eng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- RPHC4 - District Profile-Gasabo - 0Dokumen149 halamanRPHC4 - District Profile-Gasabo - 0Eng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture7 Open ChannelDokumen26 halamanLecture7 Open ChannelEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- WS - Chap 1& 2&3Dokumen28 halamanWS - Chap 1& 2&3Eng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
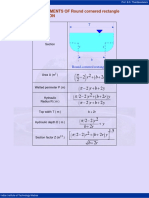
- GEOMETRIC ELEMENTS OF Round Cornered Rectangle Channel SectionDokumen1 halamanGEOMETRIC ELEMENTS OF Round Cornered Rectangle Channel SectionEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
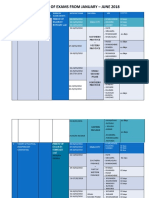
- DL Timetable 2018Dokumen10 halamanDL Timetable 2018Eng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Module1: Open Channel FlowDokumen7 halamanModule1: Open Channel FlowEng Bagaragaza RomualdBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- OcrDokumen16 halamanOcrBeena JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Day 3 Polygons Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanDay 3 Polygons Lesson PlanBA RTBelum ada peringkat
- Valence Bond Theory VBTDokumen32 halamanValence Bond Theory VBTAsif AhnafBelum ada peringkat
- Hot and Cold ApplicDokumen33 halamanHot and Cold Appliccamille_12_15100% (1)
- RCC-DI-AC PipeDokumen10 halamanRCC-DI-AC PipeNaveen NagisettiBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Calculus MIdTermsDokumen5 halamanPre Calculus MIdTermsLamette Austria Ayong0% (1)
- Triosonate in F (TWV 42-F7)Dokumen17 halamanTriosonate in F (TWV 42-F7)EDMILSON BRUNO DO NASCIMENTOBelum ada peringkat
- 16 - Bit RISC Processor Design For Convolution Application Using Verilog HDLDokumen64 halaman16 - Bit RISC Processor Design For Convolution Application Using Verilog HDLchandra sekhar100% (1)
- Soiling Rates of PV Modules vs. Thermopile PyranometersDokumen3 halamanSoiling Rates of PV Modules vs. Thermopile PyranometersAbdul Mohid SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Javascript Html5 CanavasDokumen13 halamanJavascript Html5 CanavasmihailuBelum ada peringkat
- BSS - Report - Effect of Heat in A Building DemonstratorDokumen15 halamanBSS - Report - Effect of Heat in A Building DemonstratorAh Mok100% (1)
- Development and Experimental Evaluation of Machine Learning Techniques For An Intelligent Hairy Scalp Detection SystemDokumen29 halamanDevelopment and Experimental Evaluation of Machine Learning Techniques For An Intelligent Hairy Scalp Detection SystemBilly GeneBelum ada peringkat
- 23AE23 DS enDokumen4 halaman23AE23 DS enBhageerathi SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Ruby On Rails 3 Cheat SheetDokumen7 halamanRuby On Rails 3 Cheat SheetJarosław MedwidBelum ada peringkat
- Reverse Engineering Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanReverse Engineering Cheat Sheetalfredhitchcock_007100% (2)
- Physical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeDokumen28 halamanPhysical Quantities and Unit: 9th GradeAlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Development of An Additive Manufactured Component by Topology OptimisationDokumen6 halamanDesign and Development of An Additive Manufactured Component by Topology OptimisationJon SnowBelum ada peringkat
- Comptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseDokumen5 halamanComptector & Chiller (Cdu) Controller (Fx32C Series) : Precaution For UseFcma0903100% (1)
- Os ND06Dokumen3 halamanOs ND06kevinbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Analiza Procesa Ocenjivanja Na Časovima Matematike - BaucalDokumen22 halamanAnaliza Procesa Ocenjivanja Na Časovima Matematike - BaucalНевенка ЈовановићBelum ada peringkat
- HV Filter Carts 1Dokumen2 halamanHV Filter Carts 1paulpopBelum ada peringkat
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis of A Process of Reflow Lead-Free SolderingDokumen5 halamanFailure Mode and Effects Analysis of A Process of Reflow Lead-Free SolderingSRIDHAREEE61Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mech. 2Dokumen32 halamanFluid Mech. 2Leslie Owusu MensahBelum ada peringkat
- Histograms - 2Dokumen6 halamanHistograms - 2Sonia HalepotaBelum ada peringkat
- Creative Computing v06 n12 1980 DecemberDokumen232 halamanCreative Computing v06 n12 1980 Decemberdarkstar314Belum ada peringkat
- Programming For Problem SolvingDokumen5 halamanProgramming For Problem SolvingAPOLLO Sem 4 I.T.Belum ada peringkat
- Mit BBM (Ib), Ipm-Session 2.4Dokumen32 halamanMit BBM (Ib), Ipm-Session 2.4Yogesh AdhateBelum ada peringkat
- Low Temperature Plastics - EnsingerDokumen4 halamanLow Temperature Plastics - EnsingerAnonymous r3MoX2ZMTBelum ada peringkat
- W.R. Klemm (Auth.) - Atoms of Mind - The - Ghost in The Machine - Materializes-Springer Netherlands (2011)Dokumen371 halamanW.R. Klemm (Auth.) - Atoms of Mind - The - Ghost in The Machine - Materializes-Springer Netherlands (2011)El equipo de Genesis ProjectBelum ada peringkat
- PET524 Saturation 1Dokumen12 halamanPET524 Saturation 1Ronald NgueleBelum ada peringkat