Anadrill - 2 Days Stuck Pipe 2nd
Diunggah oleh
bhuvanchaudhariDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anadrill - 2 Days Stuck Pipe 2nd
Diunggah oleh
bhuvanchaudhariHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Stuck Pipe Prevention
Prentice & Hill, LLC
Second Day
Differential Sticking
Causes
High Differential Pressures
Excessive Mud Weight
Drawn Down Formations
Poor Well Planning
Well Bore Contact
Poor Filter Cake
Little or No Pipe Motion
Solids Induced Pack-off
Formation Loose w/ Little or No Bonding
Insufficient Hydrostatic to Hold Back
Formation
UNCONSOLIDATED FORMATIONS
Causes
Pack-off Due to
Unconsolidated Formations
Prevention
Gel up Mud / Run Hi Vis Sweeps
Control Drill
Spot Gel Pill Prior to TOH
Plan / Anticipate:
Solids Induced Pack-off
Increase Mud Weight, if possible
Use Under-saturated Water Base Mud
Pump Fresh Water Sweeps
Design Casing to Handle Collapse Loads
Causes
MOBILE / PLASTIC FORMATIONS
Formation Extrudes Into Well Bore Due to
Overburden Forces.
Prevention
Proper Well Planning:
Solids Induced Pack-off
Causes
Control Drill & Ream Connections
Anticipate Reaming on Trips
FRACTURED / FAULTED FORMATIONS
Prevention
Loose Chunks of Rock Fall into Well Bore
Plan / Anticipate
Solids Induced Pack-off
Causes
Raise Mud Weight, if possible
Set Casing Appropriately
OVER-PRESSURED SHALE COLLAPSE
Prevention
Shale Pops Off Wall Due to Pressure
Plan / Anticipate
Solids Induced Pack-off
Causes
Use Inhibited Mud System
Minimize Exposure Time
Be Prepared for Gumbo Attack
REACTIVE FORMATIONS
Prevention
Mud Filtrate Reacts Chemically with Formation
Plan / Anticipate
Solids Induced Pack-off
Causes
Increase Annular Velocities
Better Mud Properties
Subject of another section
POOR HOLE CLEANING
Prevention
Not Removing Cuttings From Well Bore
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
KEYSEATING
Minimize Dog Leg Severity
Case Off Curves Soon After Building
Use Keyseat Wiper
Make Frequent Wiper Trips
Back Ream Out of Hole
Abrupt Change in Well Bore Path (Dog Leg)
Long Hole Section Below Dog Leg
Prevention
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
UNDERGAUGE HOLE
Always Gauge Bit & Stabilizers IN and OUT
Run Gauge Protected Bits & Stabilizers
Ream Suspected Undergauge Sections
Undergauge Bit and/or Stabilizers
Coring (Core heads slightly U.G.)
Prevention
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
LEDGES & DOGLEGS
Run Packed Hole Assemblies
Ream on Trips Through Problem Zones
Limber BHAs
Hard - Soft Interbedded Formation
Prevention
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
SHOE JOINT BACKS OFF
Do Not Overdisplace Cement
Thread Lock Bottom 3 Joints of Casing
Drill Out Carefully
Prevention
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
JUNK
Good Housekeeping on Rig Floor
Keep Hole Covered
Inspect Equipment Frequently
Prevention
Something Manmade is Loose in the Hole
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
CEMENT BLOCKS
Set All Casing As Close To TD As Possible
Ream Casing Shoe & Open Hole Plugs
Before Drilling Ahead
Hard Cement Falls In From Casing Shoe or From
Open Hole Cement Plug
Prevention
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
GREEN CEMENT
Wash Down Carefully to Top of Cement
Pre-Treat Mud Before Drilling Green
Cement
Prevention
Run BHA Into Un-set Cement
Mechanical / Wellbore Geometry Sticking
Causes
LINER & SQUEEZE CEMENTING
Hazards in Liner Cementing
Too Much Excess
Overdisplacement
Squeeze Cementing
Hold Pressure on Back Side, If Possible
Use Cement Retainers
DO NOT Cement Up a Squeeze Packer (RTTS)
Cementing Yourself in the Hole
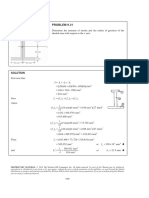
Trend Analysis
Plot Property -vs- Depth or Time and Analyze
Drag on each Connection
Torque -vs- Depth
PWD -vs- Time
Soap Box
Pressure While Drilling
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
1 2 3 4 5
Time
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
Pressure While Drilling
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
1 2 3 4 5
Time
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
Pressure While Drilling
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
1 2 3 4 5
Time
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
Drag on Trip
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
11000
4
0
0
0
0
6
0
0
0
0
8
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
2
0
0
0
0
1
4
0
0
0
0
1
6
0
0
0
0
1
8
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
Weight
D
e
p
t
h
Recovery
Our Best Preventive Efforts Have FAILED
WERE STUCK !!
What Do We Do Now?
Identifying the Problem:
Why are we stuck?
Stuck Pipe Handbook Flowcharts
Problem Diagnosis
Computer Intelligent System on Network at
Cambridge Facility
Charts in Front of Sedco Forex Handbook
Solving the Problem:
What do we do now?
First Actions
Solids Induced Stuck Pipe
Stop pumps & bleed pressure to 500 psi
Hold pressure & cycle drill string up to MUT
with no up/down movement
Try pumping if pressure bleeds off
Begin working pipe up/down - max 50K
overpull
Formation Movement / Poor Hole Cleaning
First Actions
Solids Induced Stuck Pipe
Do not commence jarring
Increase standpipe pressure to 1500 psi
Work pipe
Commence secondary procedures
Continued
First Actions
Differential Sticking
Circulate at maximum allowable rate
Set compression w/ 50% MUT
Pull tension w/ 50% MUT
Secondary Procedures
Overbalanced, Filter Cake, Contact Area
First Actions
Mechanical Sticking
Maintain circulation
Jar in opposite direction of last movement
Light loads (50K) w/ systematic increases
Secondary procedures
Dogleg, Keyseat, Junk, Undergauge
First Actions
Locating the Problem:
Where are we stuck?
Pipe Stretch Measurements
Pipe Stretch Equation
F
L W
L
000 , 735
L = Length of Free Pipe (ft)
L = Length of Stretch (in)
F = Incremental Force (lbs)
W = Weight of Drill Pipe (lb/ft)
Locating the Problem:
Where are we stuck?
Pipe Stretch Measurements
Free Point Tool
Review Stuck Pipe Handbook Procedures
Stuck Here
Pull On DP
Measure Stretch
Here
Measure Stretch
Here
Free
Point
Tool
Solids Induced Stuck Pipe
Jarring
Back off and wash over
Secondary Procedures
Differential Sticking
Attack Filter Cake -- Spotting Fluid
Spot within 4 hrs of sticking
Omit after 16 hrs
Rule of Thumb - Soak minimum 20 hrs and a
maximum 40 hrs
Secondary Procedures
Pipe Releasing Agents
Spotting Fluids
Pump shear thinning spacer
Viscosity: 100 rpm value > drilling mud
50 to 100 bbl spacer
Calculate volume of PRA - Example
Spot at highest allowable pump rate
Work pipe (up/down, torque) while soaking
Differential Sticking
Reduce Hydrostatic
Cut Mud Weight
U Tube - Kick it free
Caution - Well May Come In
Back Off and Wash Over
Secondary Procedures
Mechanical Sticking
Jar in opposite direction of last pipe
movement
Back Off and Wash Over
Secondary Procedures
Acid Pills
Calcium Formations, Strip Filter Cake
Typically 7.5% to 15% HCl
Cover stuck zone
Pump acid quickly to bit
Large water spacers
Work pipe while soaking
Circulate out after 5 minutes
Secondary Procedures
Fresh Water Pills
Mobile Salt
Cover stuck zone plus 20 bbl inside drill
string
OBM - Viscous weighted spacer
Maintain overpull while soaking
Repeat after 2 hrs
Secondary Procedures
Drilling Jars - Benefits
Jar stuck pipe immediately
Minimize fishing / sidetrack potential
Minimize surface loads (safety)
Something to do while waiting on tools
Mechanical Jars
Most basic type of jar
Sliding sleeve inside shoulder sleeve
Holding mechanism locks hammer
Overpull stretches drill string
Sudden release when holding mechanism is
overcome
Mechanical Jars - Advantages
Remain locked until loaded
More freedom of placement in string
No special tripping procedures
Do not jar unexpectedly
Short jar cycle
Cost
Availability
Mechanical Jars - Disadvantages
Load may not be varied
Jarring immediate once load is reached
Large shock to hoisting equipment
Rig may not pull over holding force
Difficult to load in deviated wellbores
Hydraulic Jars
Oil reservoir w/ orifice & bypass valve
Oil bleeds slowly until piston reaches
bypass valve
Hydraulic delay
Hydraulic Jars - Advantages
Allows time to set drilling brake
No torque needed to operate
Torque does not affect load
Varied impact force
Use in deviated holes
Hydraulic Jars - Disadvantages
May jar unexpectedly
Tripping more time consuming
Longer jar cycle
More expensive
Availability
Reasons Jars Fail to Fire
Incorrect weight - calculation incorrect
Pump open force exceeds compression
force
Stuck above jar
Jar mechanism failed
Jar not cocked
Drag too high to load jar
Reasons Jars Fail to Fire (cont.)
Jar firing not felt at surface
Torque trapped in mechanical jar
No patience
Accelerators - Functions
Compensate for short string
Compensate for hole drag slowing
contraction
Act as a reflector to jar shock wave
Intensify jar blow
Jar / Accelerator Placement
Considerations
Sticking point
Jar direction required
Differential risk
Neutral point of tension / compression
Buckling point
Drag in the hole section
Depth of hole section
Placement - Vertical Holes
Above buckling point at maximum WOB
Two DCs above jars
No stabilizers above jars
Accelerators needed in shallow hole
sections
Placement - Deviated Holes
Do not run jars buckled
Avoid tension / compression neutral point
Calculate measured weight reading required
Account for hole drag
Jar Placement Programs
Do not typically account for buckling
Accurately calculate and account for pump
open forces
Maximize jar impact at stuck point
Example - Griffith Oil Tools
Fishing - Overshots
Catches OD of fish
Right hand torque operated
Always run a bumper sub
Circulating sub
Basket grapple
More sturdy, Easier to release
Spiral grapple
Stronger hold, Use in slim hole
Wall hooks
Fishing - Spears
Catches ID of pipe
Consider stop ring
Risk back off of wash pipe
Rope spears
Fishing - Taps
Use when overshot or spear cannot be used
Taper Tap - Screws inside fish
Box Tap - Screws over fish
Cannot be released & subject to breakage
String shot cannot be run through taper tap
Excessive torque will split box tap
Fishing - Junk
Magnets
Junk Baskets
Confusion Blocks
Mills
Pilot, Tapered, Concave, Flat-Bottom, Section,
Fluted, Watermelon
Fishing - Milling
Pilot
Tapered
Concave
Flat-Bottom
Section
Fluted
Watermelon
Washover Operations
Run minimum size required - clearance
inside, " clearance outside
Maximum length 600' drill pipe, 300' BHA
Conditioning trip
Easy to differentially stick
Run jars in deeper hole sections
Steady feed when cutting formation
Jerky feed when going over tool joints
Washover Shoes
Short tooth mills (mill tooth) for medium to
hard formations
Long tooth mills for soft formations
Cut faster
Hang easier
Harder to get over top of fish
Flat bottom for stabilizers, reamers, tool
joints, etc.
Solving the Problem:
What do we do now?
THE OTHER OPTION:
S I D E T R A C K
Free Point and Back Off as Deep as Possible
Go Around the Fish
What Do We Do Now?
Sidetrack or Fish?
Its Purely a Matter of Economics
Sidetrack is a good choice when:
Fish Inexpensive or Recovery Unlikely
Hole is Cheap (read Fast) to Drill
Soft Formation - Easy to Kick Off
Spread Rate (Total Daily Cost) is HIGH
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 1 Bid Guidance: 1.1 Evaluate Request For QuoteDokumen2 halaman1 Bid Guidance: 1.1 Evaluate Request For QuotebhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- B1 - Appendix 1 PDFDokumen4 halamanB1 - Appendix 1 PDFbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- B1 - Appendix 1 PDFDokumen4 halamanB1 - Appendix 1 PDFbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Rig Move ManualDokumen45 halamanRig Move Manualjrladdu100% (24)
- Adani EOI For Various Services 17 July 19 - 1Dokumen1 halamanAdani EOI For Various Services 17 July 19 - 1bhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- B1 Supporting MaterialDokumen1 halamanB1 Supporting MaterialbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- B1 Supporting MaterialDokumen1 halamanB1 Supporting MaterialbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Annexure I Instructions To BiddersDokumen67 halaman1 Annexure I Instructions To BiddersbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Tender Document Cleaning of EnginesDokumen130 halamanTender Document Cleaning of EnginesbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Ongc RigDokumen34 halamanOngc RigbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Union Commercial Performance Utilisation Rigs 39 2015 Chap 4Dokumen17 halamanUnion Commercial Performance Utilisation Rigs 39 2015 Chap 4bhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Rig Move ManualDokumen45 halamanRig Move Manualjrladdu100% (24)
- Contractor Safety Manual SectionsDokumen2 halamanContractor Safety Manual SectionsbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Division of Youth Corrections: Internal Emergency Response and Two-Way Radio EtiquetteDokumen10 halamanDivision of Youth Corrections: Internal Emergency Response and Two-Way Radio EtiquettebhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Oil SpilDokumen1 halamanOil SpilbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Verification of fitness and certification requirements for offshore drilling rigsDokumen9 halamanVerification of fitness and certification requirements for offshore drilling rigsbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Contractor Safety ProceduresDokumen19 halamanContractor Safety ProceduresAshok PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Division of Youth Corrections: Internal Emergency Response and Two-Way Radio EtiquetteDokumen10 halamanDivision of Youth Corrections: Internal Emergency Response and Two-Way Radio EtiquettebhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- HSE Capability AssessmentDokumen5 halamanHSE Capability Assessmentsjmpak76% (17)
- Signature PageDokumen1 halamanSignature PagebhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Contractor Safety Manual SectionsDokumen2 halamanContractor Safety Manual SectionsbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Drilling EngineeringDokumen26 halamanBasic Drilling EngineeringbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Ahts - Anchor Handling Tug Supply VesselsDokumen10 halamanAhts - Anchor Handling Tug Supply VesselsbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Rig BookDokumen463 halamanRig Bookalibay4life97% (68)
- Anadrill - 2 Days Stuck Pipe 1stDokumen45 halamanAnadrill - 2 Days Stuck Pipe 1stbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance Note On Schedule IV-V (Mobile Drilling Rig) - Part1Dokumen2 halamanGuidance Note On Schedule IV-V (Mobile Drilling Rig) - Part1bhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Z-8000-BB-4076 - Water Injection SystemDokumen158 halamanZ-8000-BB-4076 - Water Injection Systembhuvanchaudhari100% (2)
- Basic Drilling EngineeringDokumen26 halamanBasic Drilling EngineeringBinh ChuBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Drilling: - The Following 3 Factors Are Important in Drilling A WellDokumen39 halamanBasics of Drilling: - The Following 3 Factors Are Important in Drilling A WellbhuvanchaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Universal Law of GravitationDokumen6 halamanUniversal Law of GravitationKrish AggrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Public Science Public GoodDokumen6 halamanPublic Science Public GoodAbilBelum ada peringkat
- How To Determine BasicityDokumen10 halamanHow To Determine Basicityccy9489Belum ada peringkat
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDokumen22 halamanCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneBelum ada peringkat
- Tellurantimony in Romania: First Occurrences in EuropeDokumen10 halamanTellurantimony in Romania: First Occurrences in EuropeTzontonelBelum ada peringkat
- Design of LintelsDokumen6 halamanDesign of LintelsAbheeshekGoelBelum ada peringkat
- Index: Lathe MachineDokumen33 halamanIndex: Lathe MachinedakshBelum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDY: Advanced Analysis of Reciprocating Engines, Compressors and Gas PipelinesDokumen4 halamanCASE STUDY: Advanced Analysis of Reciprocating Engines, Compressors and Gas PipelinesabdulbasitbBelum ada peringkat
- Propeller design and analysis program systemDokumen6 halamanPropeller design and analysis program systemChahbi RamziBelum ada peringkat
- Preliminary Lab Calculations To Determine Beam Modulus of ElasticityDokumen7 halamanPreliminary Lab Calculations To Determine Beam Modulus of ElasticityAlex WallaceBelum ada peringkat
- Zeta-Potential Measurements On Micro Bubbles GeneratedDokumen9 halamanZeta-Potential Measurements On Micro Bubbles Generatedggg123789Belum ada peringkat
- Thermofluids Exit ReviewDokumen73 halamanThermofluids Exit Reviewben richBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Properties of Halo Nuclei: H.-W. HammerDokumen25 halamanUniversal Properties of Halo Nuclei: H.-W. HammerHicham Al FalouBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2: Estimating Avogadro's NumberDokumen4 halamanLab 2: Estimating Avogadro's NumbersabrinaBelum ada peringkat
- SMR PYQs 7-9Dokumen6 halamanSMR PYQs 7-9TRY UP GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Biophotonics201210 DLDokumen44 halamanBiophotonics201210 DLAntoniopiBelum ada peringkat
- MAT105 Course Outline and Chapter 1 OverviewDokumen52 halamanMAT105 Course Outline and Chapter 1 OverviewJane CarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Manufacturing of Pneumatic Pipe Bending MachineDokumen5 halamanDesign and Manufacturing of Pneumatic Pipe Bending MachineSriram MuruganBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Foldable Bridge 2017 PrintDokumen48 halaman11 Foldable Bridge 2017 PrintChockalingam AthilingamBelum ada peringkat
- AAI Junior Executive ATC Exam SyllabusDokumen2 halamanAAI Junior Executive ATC Exam Syllabusgexewaw568Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Mechanical Engineering (Draw The PV Diagram in Each Problem)Dokumen2 halamanBasic Mechanical Engineering (Draw The PV Diagram in Each Problem)nidhul07Belum ada peringkat
- Stress FormulaDokumen7 halamanStress Formulaavinash singhBelum ada peringkat
- Solucionario de Problemas de Momento de InerciaDokumen23 halamanSolucionario de Problemas de Momento de InerciaEsteban Huacasi VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Norsok R 002Dokumen43 halamanNorsok R 002karthickmectrBelum ada peringkat
- HW 3Dokumen2 halamanHW 3DrMohamed MansourBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 0013794486900366 Main PDFDokumen9 halaman1 s2.0 0013794486900366 Main PDFEmanuel CarvalhoBelum ada peringkat
- S7 17 30 UGMs Vs MGMB Procenin Geomet 2017 ChileDokumen22 halamanS7 17 30 UGMs Vs MGMB Procenin Geomet 2017 Chileosden515100% (1)
- Thermosense: Occupancy Thermal Based Sensing For Hvac ControlDokumen8 halamanThermosense: Occupancy Thermal Based Sensing For Hvac ControledgardoboieroBelum ada peringkat
- Biomass Gasification AK RajvanshiDokumen21 halamanBiomass Gasification AK RajvanshiBharat AggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- PROJCTDokumen32 halamanPROJCTSwati Agarwal100% (1)