Final Practice Answers
Diunggah oleh
Amthe ManDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Final Practice Answers
Diunggah oleh
Amthe ManHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 1
Physics 201 Final ExamPractice
Equations:
x = x
0
+ v
0
t + at
2
v = v
0
+ at
v
2
= v
0
2
+ 2a(x-x
0
)
v = (v v
0
)/2
v = x/t
a = v/t
v
x
= vcos()
v
y
= vsin()
v
2
= v
x
2
+ v
y
2
F = ma
F
12
= - F
21
F
G
= mg
F
fr
=
k
F
N
F
fr
s
F
N
F(G) = Gm
1
m
2
/r
2-
a
r
= v
2
/r
p = mv
F = p/t
Impulse = Ft = p
mv
1
+ mv
2
= mv
1
+ mv
2
= I
= rFsin()
tan() = v
y
/v
x
W = Fdcos()
KE
t
= mv
2
GPE = mgy
KE
0
+ PE
0
+ W = KE
f
+ PE
f
SPE = kx
2
E = (F/A)/(l/l
0
)
Material Elastic modulus Ultimate strength (tension)
Steel 200x10
9
N/m
2
500x10
6
N/m
2
brass 100x10
9
N/m
2
250x10
6
N/m
2
Aluminum 70x10
9
N/m
2
200x10
6
N/m
2
Concrete 20x10
9
N/m
2
2x10
6
N/m
2
Nylon 5x10
9
N/m
2
500x10
6
N/m
2
1. Define the following terms:
Velocity:
Static Friction:
Impulse:
Elastic modulus:
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 2
Spring constant:
Torque:
2. A light body and a heavy body have the same kinetic energy. Which has the greater
momentum?
The heavy one. The lighter body will have a velocity greater by the root of the ratio of
velocities, v
2
= (m
1
/m
2
)
1/2
v
1
, so when multiplied by the mass to get momentum, the larger
one will have more momentum
3. When climbing a steep hill on a bicycle, one often will put the bike in lowest
gear. Does this correspond to the largest diameter or smallest gear on the
back wheel? Explain why, explicitly mentioning the most relevant of the
physics ideas we have studied and how it relates.
This is the largest gear on the back wheel. Using the largest gear maximizes the
torque that a foot (via the chain) can put on the back wheel. Since the radius of
the wheel is fixed, this will increase the force exerted on the ground by the tire.
4. Here is an acceleration graph of a car. Draw the velocity graph on the right
Acceleration graph
-2.5
-2
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
0 2 4 6 8 10
time (s)
a
c
c
e
l
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
(
m
/
s
2
)
Velocity graph
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 2 4 6 8 10
time (s)
v
e
l
o
c
i
t
y
(
m
/
s
)
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 3
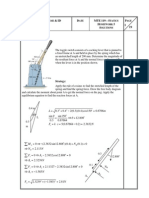
5. Draw a torque diagram for the pole being lifted by the cable in this picture.
6. A low friction cart rolls on a ramp. The graph on the left shows its kinetic energy as a
function of time. Sketch its potential energy in the graph on the right.-
Kinetic Energy
0
10
20
30
40
50
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time (s)
E
n
e
r
g
y
(
J
)
Potential Energy
0
10
20
30
40
50
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time (s)
E
n
e
r
g
y
(
J
)
Describe the general motion of the cart between t=0 and t=6.
The cart starts near the top of the ramp, not moving at the beginning, and it rolls down
the ramp, speeding up.
7. Draw a momentum diagram for a rifle and the bullet it fires at 150 m/s.
F
T rope->pole
F
G Earth->pole
F
f ground->pole
F
N ground->pole
Before
After
p
rifle
p
bullet
p
rifle
p
bullet
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 4
8. The tension on a 90 cm nylon guitar string is 54 N. If the diameter is 2.0 mm,
how much is it stretched? What would the upper limit of force that can be
applied if one uses a safety factor of 10?
E = (F/A)/(L/L
0
) => L = (F*L
0
)/(E*A)
A = r
2
= 3.1416*(0.001 m)
2
= 3.14x10
-6
m
2
L = (54 N * 0.90 m)/(5x10
9
N/m
2
* 3.14x10
-6
m
2
)
= 0.003 m = 3 mm
stress = max stress/safety factor = 500x10
6
N/m
2
/10 = 5x10
7
N/m
2
= F/A
F = 5x10
7
N/m
2
* 3.14x10
-6
m
2
= 157 N
9. Tarzan (mass of 75 kg) rescues Jane by swing in at 4.5 m/s and grabbing her
so that they then swing off at 2.7 m/s. What must be Janes mass?
Use momentum.
m
Tarzan
v
tarzan before
= (m
Tarzan
+m
Jane
)v
after
75 kg * 4.5 m/s = (75 kg + m
Jane
)2.7 m/s
75 kg (4.5 m/s 2.7 m/s) = m
Jane
2.7m/s
m
Jane
= 50 kg
10. Sally and Johnny take their sled up to the top of a 25 m high hill. If friction
and air resistance could be ignored, how fast will they be traveling when they
get to the bottom?
p
Tarzan
p
Jane
p
Tarzan
+ p
Jane
PE KE
At top
PE KE
At bottom
y = 25 m
g = 9.8 m/s
2
PE = KE
mgy = mv
2
gy = v
2
v = sqrt(2gy)
v = sqrt(2 x 9.8m/s
2
x 25 m)
v = 22. 1 m/s
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 5
11. A 1200 kg car rounds a level curve of radius 75 m at 20 m/s. What is the
frictional force on the car? What is the minimum coefficient of friction that
must exist between the tires and the road?
F
x
) F
f
= ma = mv
2
/r = 1200 kg*(20 m/s)
2
/75 m = 6400 N
F
r
= F
N
= mg = *1200 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
= 6400 N
= 0.54
12. How much work must be done to push a 0.5 kg stroller with a 25 kg child up a
ramp that is 15 meters long and 1.2 meters high if friction can be ignored? If
there is a force from the ramp and the wheels of 10 N retarding the stroller,
what will be the total work done?
F
along ramp
) F
N hand
- F
G
sin F
f
= ma = 0
F
perp. ramp
) F
N ramp
F
G
cos = ma = 0
sin = 1.2 m / 15 m
without friction:
F
N hand
= F
G
sin = 25.5 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
* 1.2m/15m
= 19.99 N
W = F*d = 19.99 N * 15 m = 300 J
with friction
F = 19.99 N + 10 N = 29.99 N
W = F*d = 29.99 N = 450 J
r
v
a
F
G Earth->car
F
f road->car
F
N road->car
F
N ramp->stroller
F
G Earth->stroller
F
N hand->stroller
F
f ramp->stroller
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 6
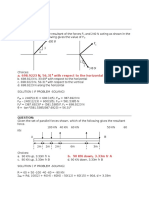
13. A 100 kg sign is to be hung from an overhang
as shown. The cable on the right is attached at
the end and the other 2/3 of the way to the
other end. How much force must be on each
cable?
Statics problem: sum forces = 0, sum torques =0
F
y
) F
T1
+ F
T2
F
G
= 0
use pivot at left end,
) 0.5*L*F
G
+ 0.667*L*F
T2
= 0
F
T2
= (0.5/0.6667)*(100 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
) = 735 N
F
T1
= 100 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
735 N = 245 N
Eat at Joes
F
T1
F
T2
F
G
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 7
14. Real world problem. Fill in ONLY the indicated steps of the FOCUS and
DESCRIBE steps. DO NOT SOLVE THE PROBLEM
A 15 meter long ship crane is unloading a 400 kg crate. It consists of a 60 kg
boom (pole) atached to the deck with a hinge, and a horizontal cable to hold it up
attached at the middle of the boom. What must be the tension on the horizontal
cable when the boom is tilted from the vertical by 40 degrees? What will be the
horizontal and vertical forces of the boom on the deck of the ship?
EVERYDAY LANGUAGE What are you trying to find?
Sketch with Given Information
Forces on boom (cable, pivot)
What are the physics principle(s)?
Forces, torque
Physics Description Define Variables
Diagram
Quantitative Relationships (Write down ONLY the equations needed to solve this
problem.)
F
x
) F
Nx
F
T cable
= 0
F
y
) F
Ny
F
G
F
T load
= 0
) -LF
G
sin(180
o
-50
o
)+ LF
T cable
sin(180
o
-40
o
) LF
T load
sin(180
o
-50
o
) = 0
F
T cable->boom
F
G Earth->boom
F
N pivot->boom
F
T load->boom
F
T cable
= ?
F
T load
= 400 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
F
G
= 60 kg * 9.8 m/s
2
F
Nx
= ?
F
Ny
= ?
= 40
o
L = ?
Name _______________________
Physics 201 final 2002 version A Page 8
Real world problem. Fill in ONLY the indicated steps of the FOCUS and
DESCRIBE steps. DO NOT SOLVE THE PROBLEM
A military airlift is going to drop supplies to soldiers looking for Al Queda fighters
on a small level area the mountains of Afghanistan. If the plane is moving
towards the target at 200 km/h and 250 m above the target area, at what
distance before the target should it drop the packet? (Ignore air resistance.)
EVERYDAY LANGUAGE What are you trying to find?
Sketch with Given Information
horizontal distance
What are the physics principle(s)?
motion in 2-D
Physics Description Define Variables
Diagram
Quantitative Relationships (Write down ONLY the equations needed to solve this
problem.)
x
f
= x
0
+v
ox
t
y
f
= y
0
+ at
2
200 km/h
250 m
x
v
x
y
v
y
a
y
x
o
= ?
x
f
= 0 m
v
0x
= 200 km/h
= 55.5 m/s
t
0
= 0 s
y
o
= 250 m
y
f
= 0 m
v
0x
= 0 m/h
a
y
= -9.8 m/s
2
t
f
= ?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Tutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Dokumen10 halamanTutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Jan ScarBelum ada peringkat
- CH18Dokumen91 halamanCH18Ow Yong Chaan LoungBelum ada peringkat
- Beam Deflection TheoryDokumen12 halamanBeam Deflection TheoryquadmagnetoBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Dynamics of A Particle HWT - 1Dokumen13 halamanSolutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Dynamics of A Particle HWT - 1varunkohliinBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 303K Test 2 SolutionsDokumen11 halamanPHY 303K Test 2 SolutionsbrunosipodBelum ada peringkat
- Compression Member PDFDokumen45 halamanCompression Member PDFSanjeevJadhav100% (1)
- Examples - PhysicsDokumen8 halamanExamples - Physicslaila1001Belum ada peringkat
- Plate Girder DesignDokumen8 halamanPlate Girder Designkalpanaadhi100% (1)
- Mecanica de Los solidosII,,Cantidad de MovimientoDokumen79 halamanMecanica de Los solidosII,,Cantidad de MovimientoXavi GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Work Ower EnergyDokumen31 halamanWork Ower EnergyOmprakash Dhaka100% (2)
- Mobile Problem Statics: PhysicsDokumen16 halamanMobile Problem Statics: PhysicsMalvin Roix OrenseBelum ada peringkat
- Compression MemberDokumen45 halamanCompression MemberSatyasapath RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Sol Cap 13 L7Dokumen129 halamanSol Cap 13 L7Jesus Feijoo100% (2)
- Fe DynamicsDokumen29 halamanFe DynamicsSabih Hashim AlzuhairyBelum ada peringkat
- HW 06 SolnDokumen19 halamanHW 06 SolnKristin Dikiciyan100% (1)
- Central Force MotionDokumen38 halamanCentral Force MotionCukeepz GhoffarBelum ada peringkat
- Print EEDokumen14 halamanPrint EEMarie Joy EngayBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 SolutionsDokumen78 halamanChapter 14 SolutionsBlake Cheney100% (1)
- CH 14 Kinetics of Particles Work and EnergyDokumen19 halamanCH 14 Kinetics of Particles Work and EnergyKhaled Obeidat100% (2)
- Of Momentm, Work Is Equated To A Change in Kinetic EnergyDokumen4 halamanOf Momentm, Work Is Equated To A Change in Kinetic EnergyAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Ispravci - Cvrstoca 2Dokumen10 halamanIspravci - Cvrstoca 2Mile Konfuzije JunglistBelum ada peringkat
- 4d Work Energy FR Practice Problems ANSWERSDokumen22 halaman4d Work Energy FR Practice Problems ANSWERSJanel Edwards100% (1)
- A5 SolutionDokumen7 halamanA5 Solutionskata999Belum ada peringkat
- DynamicsDokumen80 halamanDynamicsalexBelum ada peringkat
- Formula SheetDokumen1 halamanFormula SheetLouisGómezBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm II 12 AnsDokumen3 halamanMidterm II 12 AnsAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 18 PDFDokumen91 halamanChapter 18 PDF이희인Belum ada peringkat
- Cam Dynamics PDFDokumen10 halamanCam Dynamics PDFLakshman Prakash100% (1)
- Es 62Dokumen6 halamanEs 62Enrico Luis Caube BalisalisaBelum ada peringkat
- Vibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.UDokumen82 halamanVibration and Control: Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Y.T.Udora901Belum ada peringkat
- Allen Neetug2013 Phy-With SolutionDokumen8 halamanAllen Neetug2013 Phy-With SolutionrnsseturajBelum ada peringkat
- Phy 106 DiscussionDokumen10 halamanPhy 106 DiscussionKenny GildmanBelum ada peringkat
- Clutches and BrakesDokumen77 halamanClutches and BrakesVenu Gopal100% (1)
- Nonlinear GuideDokumen17 halamanNonlinear Guidepiv0ter_betterBelum ada peringkat
- MTE119 - Solutions Hw5Dokumen19 halamanMTE119 - Solutions Hw5Amy TrevinoBelum ada peringkat
- GEAS Solving - CompiledDokumen22 halamanGEAS Solving - Compiledcajaro100% (1)
- Siao, Benjie Jr. F. - StaticsDokumen9 halamanSiao, Benjie Jr. F. - Staticsbenjie siaoBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Force Analysis Planar Solutions Chapter 12Dokumen36 halamanDynamic Force Analysis Planar Solutions Chapter 12Velmurugan ThiagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Resoluções de Exercícios - Cap. 24 - Princípios de Física Vol. 3Dokumen17 halamanResoluções de Exercícios - Cap. 24 - Princípios de Física Vol. 3HDExtremeBelum ada peringkat
- (Answer - 540 N) : Supplied by Freestudy - Co.uk © D.J.DUNNDokumen11 halaman(Answer - 540 N) : Supplied by Freestudy - Co.uk © D.J.DUNNomar_sool2Belum ada peringkat
- Brilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013Dokumen21 halamanBrilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013cshubham23Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 22Dokumen62 halamanLecture 22adilafzalkhan4264Belum ada peringkat
- Solucionario Capitulo 23 Paul E TippensDokumen13 halamanSolucionario Capitulo 23 Paul E TippensEmanuel Trejos Giraldo100% (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringDari EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationDari EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationBelum ada peringkat
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianDari EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeDari EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeBelum ada peringkat
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Dari EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Belum ada peringkat
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDari EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- VLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesDari EverandVLF Radio Engineering: International Series of Monographs in Electromagnetic WavesBelum ada peringkat
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesDari Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesBelum ada peringkat
- Flexible Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Formworks For The Production of Curved Textile-Reinforced ConcreteDokumen9 halamanFlexible Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Formworks For The Production of Curved Textile-Reinforced ConcreteHau NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Final 2010Dokumen8 halamanFinal 2010Hakkı ÇelimliBelum ada peringkat
- Which Elements Are Essential For Human LifeDokumen9 halamanWhich Elements Are Essential For Human LifeJordon AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- What Is DispersionDokumen10 halamanWhat Is DispersionRalph Jester CapunoBelum ada peringkat
- Options For High Temperature Well StimulationDokumen11 halamanOptions For High Temperature Well StimulationFra FraBelum ada peringkat
- AAC. Submittal BOMBAS ARMSTRONGDokumen3 halamanAAC. Submittal BOMBAS ARMSTRONGLuis Carlos Perez OstosBelum ada peringkat
- Bsi BS en 12091 - 2013Dokumen14 halamanBsi BS en 12091 - 2013alferedBelum ada peringkat
- Calculations - Guidlines For Control Valve Sizing - SelectionDokumen40 halamanCalculations - Guidlines For Control Valve Sizing - SelectionShubham KeniBelum ada peringkat
- Factor Affecting Rate of Reaction ExerciseDokumen3 halamanFactor Affecting Rate of Reaction ExerciseRafiq IrdhinaBelum ada peringkat
- New Formulations and Test Comparison For The Classification of PVC Cables Under EU Regulation N° 305/2011 For Construction ProductsDokumen29 halamanNew Formulations and Test Comparison For The Classification of PVC Cables Under EU Regulation N° 305/2011 For Construction ProductsTien Dung PhanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDokumen51 halamanIntroduction To Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemNaveen Prakash Noronha50% (2)
- ACFrOgDsH3VyGwJDuLIBt9Sb 9enHJVEr0wP6B4wcrzTyWYmDY0qum5oJr 24rwY8FiIS46xaikTY 0o2CHJ8zrKcxUSEUp5hET5mc If6XGNyx28ua5LgMCy1VggwoEOSEFMwCl2mncwNfWGIq7Dokumen10 halamanACFrOgDsH3VyGwJDuLIBt9Sb 9enHJVEr0wP6B4wcrzTyWYmDY0qum5oJr 24rwY8FiIS46xaikTY 0o2CHJ8zrKcxUSEUp5hET5mc If6XGNyx28ua5LgMCy1VggwoEOSEFMwCl2mncwNfWGIq7Rudiery ReisBelum ada peringkat
- Structured Packing Manual PDFDokumen20 halamanStructured Packing Manual PDFnedian_2006Belum ada peringkat
- Crystallization PDFDokumen74 halamanCrystallization PDFMohammed Akif ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Flow Cytometry May 10 PDFDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To Flow Cytometry May 10 PDFSilviaGonzalezSierraBelum ada peringkat
- 10.03.12 Density Lab ReportDokumen3 halaman10.03.12 Density Lab ReportCyou97100% (1)
- Q6f559Brev1 DRGDokumen1 halamanQ6f559Brev1 DRGVivek SavaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- As Chemistry Unit 2 NotesDokumen26 halamanAs Chemistry Unit 2 NotesArchitBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 28Dokumen12 halamanExperiment 28William RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Grade FOSS: Report Period 2 - Weather and Water and Diversity of LifeDokumen21 halaman6 Grade FOSS: Report Period 2 - Weather and Water and Diversity of Lifeapi-302715570Belum ada peringkat
- SLE123 - Sample Quiz 04 QuestionsDokumen17 halamanSLE123 - Sample Quiz 04 QuestionsNinaBelum ada peringkat
- OctanitrocubaneDokumen6 halamanOctanitrocubaneAndrew Cecil Earhart SchneckBelum ada peringkat
- Application TA 018e 2Dokumen2 halamanApplication TA 018e 2Goni GoniBelum ada peringkat
- BIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Dokumen13 halamanBIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Phenyo MmerekiBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics CH 01 PDFDokumen75 halamanGeneral Physics CH 01 PDFAnonymous 0rIj5j1iBelum ada peringkat
- 6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide PropertiesDokumen70 halaman6.23 Equation of State Prediction of Carbon Dioxide Propertiessaulatlone100% (1)
- AP-102 - Detailed SyllabusDokumen3 halamanAP-102 - Detailed Syllabusshivam dharyaalBelum ada peringkat
- D 2251 - 96 R00 - RdiynteDokumen2 halamanD 2251 - 96 R00 - RdiynteRuben YoungBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesDokumen12 halamanStudy On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesTJPRC PublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Ec 6702Dokumen22 halamanEc 6702Madhan ReddyBelum ada peringkat