Dnapage
Diunggah oleh
api-2583228470 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
41 tayangan2 halamanJudul Asli
dnapage
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
41 tayangan2 halamanDnapage
Diunggah oleh
api-258322847Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary ma-
terial in nearly all organisms. Most eukaryotic DNA is
located in the cell nucleus (a small amount of DNA
can also be found in the mitochondria). Each cell in an
organism contains a copy of the same chromosomes
and DNA. All cells in the same organism have the
same genes, but may have different patterns of genes
turned on and off.
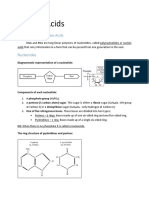
DNA molecules are nucleic acids, made up of two
antiparallel chains of covalently bonded nucleotides. A
nucleotide is composed of a 5-carbon sugar called
deoxyribose covalently bonded to a phosphate
(PO4-) and one of four nitrogen bases. The informa-
tion in DNA is read from the order of the 4 nitrogen
bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and
thymine (T). Adenine and Guanine are purines
(double ring base), and cytosine and thymine are
pyrimidines (single ring base).
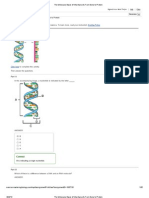
The two strands of DNA molecules are complemen-
tary because the nitrogen bases between the strands
pair up with each other according to the base pair
rules: A bonds T and C bonds G. If one strand of DNA is known, then the other can be determined using
the base pair rules. These particular pairs ensure that the distance between the two DNA strands is equal
along its entire length.The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the base pairs to
form a ladder-like structure with the base pairs as rungs and the sugar- phosphate molecules forming the
vertical rails. This two stranded ladder structure is twisted into a spiral called a double helix. Finally, it is
important to note that the two strands are antiparallel, i.e., the two chains run in opposite directions such
that one chain is upside down relative to the other.
How to complete this lesson:
1. Use the resources listed below to take notes in your notebook.
*Be sure that you can:
Identify DNAs location in a eukaryotic cell
Describe how DNA is packaged to form a chromosome
Explain the relationship between nucleotides and nucleic acids
Explain the relationship between DNA and genes
Draw a simple representation of a single nucleotide that correctly relates the three components: 5-C
sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base
Draw a simple ladder representation of a section of DNA double helix with correct anti-parallel comple-
mentation and label the sugars, phosphates, bases, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds
Explain what complementary, double helix and antiparallel mean
Apply the base pair rules to determine a complementary DNA sequence
Define and use these terms correctly: Nucleotide , nucleic acid, Deoxyribose , Phosphate , Nitroge-
nous Base , Purine , Pyrimidine , Adenine , Thymine , Cytosine, Guanine
DNA Structure
BIOLOGYStraub (2013-14)
Hydrogen bonds
Covalent bonds
1 Nucleotide
N
-B
a
s
e
s
Gene - Wikipedia
Resources:
What is DNA from Learn.Genetics - video on basic DNA
structure
Bozeman Biology What is DNA - video lecture on the
structure of DNA
DNA from the Beginning: Concept 19 - tutorial on DNA:
read the concept, then click the animation tab. Click through
the arrows in the lower right.
The Chemical Structure of DNA from BioInteractive - short video covering the
chemical compounds that are bonded to form DNA
Easy Read DNA structure from IB Biology.
The Structure of DNA - easy to read and understand
The structure of DNA - easy read with good graphic
DNA structure and good definitions from The Guide
Build a DNA molecule. Learn. Genetics - practice base pairing rules by
building a complementary strand of DNA to the one given.
Master your base pairing skills with Play the Double Helix Game
DNA Structure and Replication: Crash Course Biology - Another DNA video lecture
from Hank Green, watch video through 9:18. After this point, he discusses our next
topicDNA replication.
Gene Graphic . (2003). Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved July 4, 2014, from http://
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Deoxyribo Nucleic AcidDokumen26 halamanDeoxyribo Nucleic AcidJoshua EbenezerBelum ada peringkat
- NAT SCI 9 Nucleic AcidsDokumen12 halamanNAT SCI 9 Nucleic Acidskjgbitoon00125Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDokumen63 halamanTopic 1 - A1.2 Nucleic AcidsOlatundeBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Dokumen20 halamanGenetics BS - 6 Semester: Assignment # 1Hassan JavedBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Components and Structure WSDokumen3 halamanDNA Components and Structure WSmoadhmoayedBelum ada peringkat
- Notes C22 121Dokumen20 halamanNotes C22 121Gopi NathBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Study Guide 8 2 - 8 3 ANSWERS 2Dokumen6 halaman02 Study Guide 8 2 - 8 3 ANSWERS 2KenzieBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleic AcidsDokumen9 halamanNucleic AcidsRex Blanco NuñezBelum ada peringkat
- Dna - CotDokumen39 halamanDna - CotJcob BangcayaBelum ada peringkat
- Dna Molecule Model Exercise No. 3 NAME: Shanica E. Surigao Course and Year: Bsed I - ScienceDokumen8 halamanDna Molecule Model Exercise No. 3 NAME: Shanica E. Surigao Course and Year: Bsed I - ScienceShamaica SurigaoBelum ada peringkat
- Dna 053215Dokumen13 halamanDna 053215Baninla NerusBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleotide and DNADokumen38 halamanNucleotide and DNAProttoyBelum ada peringkat
- C6 Nucleic AcidsDokumen57 halamanC6 Nucleic AcidsSoraya Al-obinayBelum ada peringkat
- 1934 FdocDokumen6 halaman1934 Fdoctyleryawh2072Belum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDokumen18 halamanCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaBelum ada peringkat
- The DNA StructureDokumen16 halamanThe DNA StructureJourneia AustriaBelum ada peringkat
- Biotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNADokumen20 halamanBiotechnology: Guided Learning Activity Kit DNA Versus RNAKimberly Esmelo100% (1)
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dokumen9 halamanDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Biology Unit 2 (DNA & RNA)Dokumen40 halamanMolecular Biology Unit 2 (DNA & RNA)Fuz Nas100% (2)
- Nucleic Acids BC21C 2018 StudentDokumen120 halamanNucleic Acids BC21C 2018 StudentPheona BlagroveBelum ada peringkat
- REPLICATIONDokumen9 halamanREPLICATIONdineshBelum ada peringkat
- 7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study GuideDokumen2 halaman7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study Guideelursgod1Belum ada peringkat
- Molecular Biology and Genetics of CK 12 Life Science Concepts For Middle School CH v23 C4e s1Dokumen79 halamanMolecular Biology and Genetics of CK 12 Life Science Concepts For Middle School CH v23 C4e s1garotaBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 5-GeneticsDokumen9 halamanMODULE 5-GeneticsDivine Grace CincoBelum ada peringkat
- Science10 Q3 Week4Dokumen22 halamanScience10 Q3 Week4Samad Recca T. NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Central Board Od Secondary EducationDokumen17 halamanCentral Board Od Secondary EducationSk Samir UddinBelum ada peringkat
- 3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodeDokumen27 halaman3.9 DNA Replicaton and The Genetic CodePratika MBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics 1Dokumen13 halamanGenetics 1Shivam PatelBelum ada peringkat
- EXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialDokumen3 halamanEXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialMohamidin MamalapatBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDokumen11 halaman1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesBelum ada peringkat
- Genetic EngineeringDokumen218 halamanGenetic EngineeringSrramBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleic Acids. Dna. Rna. Nucleic AcidsDokumen7 halamanNucleic Acids. Dna. Rna. Nucleic Acidsm_tankovaBelum ada peringkat
- DNA ReplicationDokumen3 halamanDNA ReplicationGirish AdapaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 Genetic Control My NotesDokumen51 halamanTopic 4 Genetic Control My NotesrukashablessingBelum ada peringkat
- The Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokumen35 halamanThe Molecular Basis of Inheritanceprehealthhelp80% (5)
- Module 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsDokumen15 halamanModule 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsMadhuri Gupta100% (1)
- Dna StructureDokumen9 halamanDna StructureVivi Chávez CalzadaBelum ada peringkat
- GGL DNA Replication PDF VersionDokumen7 halamanGGL DNA Replication PDF VersionlloaanaBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01Dokumen40 halamanNucleicacids Dnarna 100618205106 Phpapp01InerTiaOpheliaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsDokumen3 halamanAssignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsRuel John RanayBelum ada peringkat
- Nucleic AcidsDokumen42 halamanNucleic AcidsJulianne AnikaBelum ada peringkat
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Dokumen7 halamanWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaBelum ada peringkat
- A. Unit y Diversity 1. 2 Nucleic AcidsDokumen34 halamanA. Unit y Diversity 1. 2 Nucleic AcidshzunigaBelum ada peringkat
- Orca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Dokumen9 halamanOrca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Mic Houston Mar T. ParroBelum ada peringkat
- Paper - IV Molecular BiologyDokumen236 halamanPaper - IV Molecular BiologyNaruto UzumakiBelum ada peringkat
- 12 2 WKSTDokumen4 halaman12 2 WKSTapi-262378640Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 Nucleic AcidsDokumen62 halamanUnit 7 Nucleic AcidsGlory MuedaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of MoleculesDokumen5 halamanStructure of MoleculesHanimBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Structure & ReplicationDokumen25 halamanDNA Structure & Replicationivanam0202Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)Dokumen20 halamanIntroduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)DeMetrius Sam DanielBelum ada peringkat
- 09NucAMO SuarezDokumen14 halaman09NucAMO SuarezscasuarezBelum ada peringkat
- The Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyDokumen3 halamanThe Story of DNA - Script and Answer KeyAdam SimpsonBelum ada peringkat
- How Genes WorkDokumen47 halamanHow Genes WorkJelly Joy CampomayorBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeDokumen8 halamanGenetics: For A Non-Technical Introduction To The Topic, See - For Other Uses, SeeElenaDiSavoiaBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Replication PDFDokumen7 halamanDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-9 Regression AnalysisDokumen20 halamanUnit-9 Regression AnalysisPRASANT KUMAR SAMALBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Dokumen3 halamanLesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Marc Laurence LadoresBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam..Dokumen6 halamanFinal Exam..Joezer AlamoBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test BankDokumen13 halamanEssential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test Bankmeaganstephensonmdbapgcjfezt100% (45)
- Mechanism of Tissue RepairDokumen22 halamanMechanism of Tissue RepairWalidad AarbiBelum ada peringkat
- Overview On Mechanisms of Antibacterial Resistance: Alemayehu Toma, Serawit DeynoDokumen10 halamanOverview On Mechanisms of Antibacterial Resistance: Alemayehu Toma, Serawit DeynowaelBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen926 halamanUntitledNicola BourdillonBelum ada peringkat
- Pierce Chapter 2Dokumen30 halamanPierce Chapter 2Sarah HanBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer Biology Raymond W. Ruddon M.D PDFDokumen545 halamanCancer Biology Raymond W. Ruddon M.D PDFEsha SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Genomics and Crop ImprovementDokumen56 halamanGenomics and Crop Improvementsenguvelan100% (6)
- Amino Acids - ProteinsDokumen138 halamanAmino Acids - ProteinsWael OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- The Sexual Differentiation of Cannabis Sativa L.: A Morphological and Molecular StudyDokumen12 halamanThe Sexual Differentiation of Cannabis Sativa L.: A Morphological and Molecular StudyEmanuel PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Powerpoint LecturesDokumen161 halamanMolecular Biology of The Gene: Powerpoint Lecturesİrem SarıkocaBelum ada peringkat
- The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity: ReviewDokumen15 halamanThe Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity: ReviewNandkumar ChinaiBelum ada peringkat
- Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies: An Overview: Taishan Hu, Nilesh Chitnis, Dimitri Monos, Anh DinhDokumen11 halamanNext-Generation Sequencing Technologies: An Overview: Taishan Hu, Nilesh Chitnis, Dimitri Monos, Anh DinhNina FajsBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins Classification of ProteinDokumen7 halamanProteins Classification of ProteinKrishnanand NagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Year Biochemistry Guidance BookletDokumen67 halaman1st Year Biochemistry Guidance Bookletusama HafeezBelum ada peringkat
- Neve CellDokumen5 halamanNeve CellAaron WallaceBelum ada peringkat
- SNP MicroarraysDokumen10 halamanSNP MicroarraysTiger DsixtytwoBelum ada peringkat
- Biomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. DwivediDokumen39 halamanBiomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. Dwivedipavan7443Belum ada peringkat
- DEPC Treated Water RecipeDokumen3 halamanDEPC Treated Water RecipeAnisam AbhiBelum ada peringkat
- Tasks CareerNaksha Short Internship ProjectDokumen23 halamanTasks CareerNaksha Short Internship ProjectDarshil DalwadiBelum ada peringkat
- E-Bio 206 - Translation WorksheetDokumen3 halamanE-Bio 206 - Translation WorksheetAmna BaigBelum ada peringkat
- Biology PQMSDokumen12 halamanBiology PQMSnayipranav8Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Size and ShapeDokumen23 halamanCell Size and ShapenmsarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral StrategiesDokumen386 halamanAntiviral StrategiesGourisankar Roul67% (3)
- Stoeckle Thaler Final Reduced 002Dokumen30 halamanStoeckle Thaler Final Reduced 002Júnior SenseyBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesDokumen4 halamanStructure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.Belum ada peringkat
- Meselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedDokumen1 halamanMeselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedCarolina RelvaBelum ada peringkat
- Lipoprotein MetabolismDokumen6 halamanLipoprotein MetabolismVincent MwirigiBelum ada peringkat
- GEP Worksheets EnzymesDokumen5 halamanGEP Worksheets Enzymesprameeta100% (1)
- BCH 3053 Spring2015 Syllabus IGelisDokumen6 halamanBCH 3053 Spring2015 Syllabus IGelisadmiralrevBelum ada peringkat