Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Diunggah oleh
Louie Kem Anthony BabaranHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
Diunggah oleh
Louie Kem Anthony BabaranHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
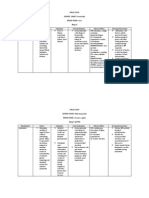
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease
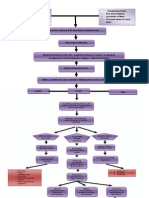
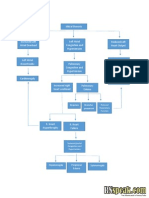
Predisposing Factors:
Family history of RHD
Age (5-15 years old)
Past history of Rheumatic
Fever
Precipitating Factors:
Environmental factors
Low Socioeconomic Status
Geographical Location
Etiology
Group A Beta-
Hemolytic
Streptococcus
Bacteria invades the upper
respiratory tract (tonsils and
pharynx)
Macrophages attack bacteria, and then
present its antigen to the immune system
Production of antibodies (IgG & IgM)
Inflammation of affected tissues
Activation of complement system, opsonic
phagocytosis, production of NK cells to
combat pathogens
Immune system cross-reacts and causes
tissue injury to normal body cells due to
Molecular Mimicry
Multi-systemic effects
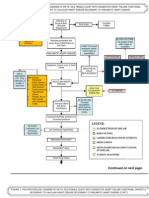
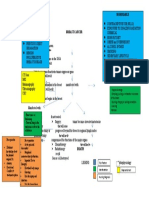
Production of Cytokines, TNF,
Endogenous Pyrogens (IL 1 and IL 6)
A
Release of Prostaglandin
E2
Increased thermostat point
in the hypothalamus
Increased thermostat point
in the hypothalamus
Increased body
temperature
Hyperthermia
Stimulation of liver to produce
acute phase proteins
Increased C
Reactive
Protein
Increased
Fibrinogen
RBCs stick
together
(rouleaux)
Increased
Erythrocyte
Sedimentation
Rate (ESR)
A
Immune system cross-
reacts with Basal Ganglia
Disruption in
motor signals
Involuntary muscle
contractions
(Sydenhams Chorea)
Immune system
cross-reacts with
Synovial membrane
Leakage of plasma
proteins and fluid
Swelling of the joint
Compression of
nerve endings
Pain and tenderness
of the joint
Arthritis migrates
upward to different
joints
Migratory
Polyarthritis
Immune system
cross-reacts with Skin
Presence of ring-like
lesions (Erythema
Marginatum)
Immune system
cross-reacts with
subcutaneous tissue
Immune system
cross-reacts with
myocardial tissue
Presence of
subcutaneous
nodules
Pericarditis
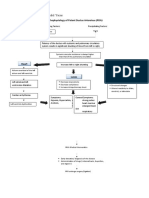
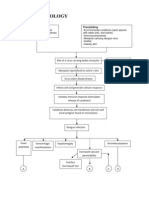
Increased
permeability of
capillaries
Shifting of plasma
and fibrinogen to
pericardial sac
Swelling of
pericardium
C
Endocarditis Myocarditis
Myocardium loses
its contractility
Mechanical injury
caused by
inflammation and
tachycardia
Erosion of mitral
valve leaflets
Aggregation of
platelets and fibrin
along the valve
Fomation of vegetations along
the edges of the leaflets
B
Decreased Cardiac
Output
Decreased Perfusion
Sympathetic
Response: Increased
Heart Rate, Increased
Contractility,
Vasoconstriction
D
E
B C D
Vegetations heal
with fibrosis and
calcifications
Permanent
distortions of the
leaflets of the valve
Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation
E
Pericardial
layers rub
each other
Increased
pressure on
parietal
pericardium
Compression
of nerves
Sharp, stabbing
localized pain
Pericardial
friction rub on
auscultation
Increased Residual Volume of LV
Increased Pressure in LV
Dilatation/Hypertrophy of LV
Increased Volume in LA
Increased Volume in Pulmonary Vein
Increased Pressure in
Pulmonary capillary bed
Pulmonary
edema, dyspnea
Pulmonary
Hypertension
Cor Pulmonale
Dilatation/Hypertrophy of RV
Increased Pressures in the RV and RA
F
F
Decreased CO despite
compensatory mechanisms
Cardiogenic shock
Multi-organ failure
DEATH
Decreased Heart Rate
Hypoperfusion
Hypoxia
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseXtiaR85% (13)
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- Pathophysiology RHDDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology RHDRellette Shane DangdangBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseVince John Sevilla100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Case Study RheumaticDokumen46 halamanCase Study RheumaticJill Anne Balderosa91% (11)
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Dokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDokumen4 halamanDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramGuia Rose Sibayan0% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen4 halamanThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology CHFDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Final Paper Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen16 halamanFinal Paper Rheumatic Heart DiseasePrincess TumambingBelum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen3 halamanRheumatic Heart DiseaseDee SarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanPneumonia PathophysiologyDee Sarajan100% (3)
- Myocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDokumen4 halamanMyocardial Infarction: Nonmodifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsHearty ArriolaBelum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen4 halamanRheumatic Heart DiseaseAlfrin Antony100% (3)
- Patho of MIDokumen2 halamanPatho of MIInchan Montesines0% (1)
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADokumen10 halamanSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- RHD PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanRHD PathophysiologyRichmond LacadenBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Dokumen4 halamanPathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineBelum ada peringkat
- Patho MIDokumen2 halamanPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Acs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoDokumen2 halamanAcs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoJerom YamatBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue PoathoDokumen6 halamanDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- NCP 2Dokumen5 halamanNCP 2Donna Co IgBelum ada peringkat
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiologynursing concept maps50% (4)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDokumen1 halamanAcute GlomerulonephritisTaz Bagul MutiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarBelum ada peringkat
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - CSDokumen88 halamanRheumatic Heart Disease - CSMASII100% (8)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDokumen3 halamanCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahBelum ada peringkat
- Final Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDokumen3 halamanFinal Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDave JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniamatrixtrinityBelum ada peringkat
- NCP RHDDokumen7 halamanNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDokumen3 halamanMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- RHD Case StudyDokumen94 halamanRHD Case StudyGel Jovenal100% (1)
- NCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen3 halamanNCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseAdrian Mallar71% (28)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen23 halamanRheumatic Heart DiseaseRashid Khaliff Enok Dignadice100% (3)
- Wilm's Tumor PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanWilm's Tumor PathophysiologyJonalene Suarez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseCyril Jane Caanyagan Acut50% (2)
- 1.pathophysiology of MeningitisDokumen1 halaman1.pathophysiology of Meningitisshielamaygo05100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDokumen1 halamanBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoBelum ada peringkat
- Pleural Effusion - Case StudyDokumen25 halamanPleural Effusion - Case StudyLilian Linogao94% (18)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDokumen2 halamanPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMaynelle Caspe100% (2)
- Malaria PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanMalaria Pathophysiologykaye040375% (4)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen25 halamanRheumatic Heart DiseaseMag5Belum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of AMLDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- Rheumatic FeverDokumen27 halamanRheumatic FeverMalueth AnguiBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac Disease: DR A. Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (K)Dokumen9 halamanBacterial Aspect of The Cardiac Disease: DR A. Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (K)Kuro ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseDokumen9 halamanBacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseNova SuryatiBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2.3.6 Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseDokumen9 halaman3.2.3.6 Bacterial Aspect of The Cardiac DiseaseRizky Putra IsmeldiBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic InflammationDokumen24 halamanChronic InflammationTommys100% (1)
- Rheumatic Fever (Caypuno, Isaac-Lee P.)Dokumen15 halamanRheumatic Fever (Caypuno, Isaac-Lee P.)Carlojay IniegoBelum ada peringkat
- PBL: Breathing Through Fish MouthDokumen7 halamanPBL: Breathing Through Fish MouthPraveen DuraiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseIJ Ayop86% (7)
- Inflammation KundieDokumen4 halamanInflammation KundieTadiwanashe ManyandeBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology of CVSDokumen44 halamanMicrobiology of CVSsultan khabeebBelum ada peringkat
- RHDokumen6 halamanRHAMOS MELIBelum ada peringkat
- Downloaded From Perfect Notes and Guitar Tabs SearcherDokumen30 halamanDownloaded From Perfect Notes and Guitar Tabs SearcherLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- BEC-1A June 19, 2016Dokumen134 halamanBEC-1A June 19, 2016Louie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Pain Assessment ScalesDokumen9 halamanPain Assessment ScalesElham AlsamahiBelum ada peringkat
- National Prayer For Papal VisitDokumen4 halamanNational Prayer For Papal VisitLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Pork Binagoongan RecipeDokumen1 halamanPork Binagoongan RecipeLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Providing Care of A Chest TubeDokumen11 halamanProviding Care of A Chest TubeLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- The Moral Issue of Paternalism and Truth TellingDokumen4 halamanThe Moral Issue of Paternalism and Truth TellingLouie Kem Anthony Babaran0% (2)
- Medicinal Plant PandanDokumen1 halamanMedicinal Plant PandanLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- DivingDokumen11 halamanDivingLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals in NursingDokumen2 halamanFundamentals in NursingLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- The Urinary System Is Made Up of The Kidneys, Ureters, Urethra and BladderDokumen4 halamanThe Urinary System Is Made Up of The Kidneys, Ureters, Urethra and BladderdodongcharingBelum ada peringkat
- Session Design HerbalDokumen10 halamanSession Design HerbalLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Gds137 Slide HyperthyroidismDokumen30 halamanGds137 Slide HyperthyroidismLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Trisomy S&SXDokumen3 halamanTrisomy S&SXLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Kahit Maputi Na Ang Buhok KoDokumen13 halamanKahit Maputi Na Ang Buhok KoLouie Kem Anthony Babaran100% (1)
- Rocky Mountain Spotted FeverDokumen4 halamanRocky Mountain Spotted FeverLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - Case Pre FINALDokumen14 halamanDrug Study - Case Pre FINALLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- I Wont Give UpDokumen9 halamanI Wont Give UpRose AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Borrelia SPP Are Gram Negative Helical Bacteria: Rickketsia Tsutsugamushi Is The CausativeDokumen1 halamanBorrelia SPP Are Gram Negative Helical Bacteria: Rickketsia Tsutsugamushi Is The CausativeLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- P.A JeromeDokumen6 halamanP.A JeromeLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Mental Health and Mental DisordersDokumen24 halamanMental Health and Mental DisordersLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- AtherosclerosisDokumen11 halamanAtherosclerosisLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- WCV Egyptian ArchitectureDokumen62 halamanWCV Egyptian ArchitectureLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Who Am IDokumen30 halamanWho Am ILouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- CakesDokumen8 halamanCakesLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative NursingDokumen9 halamanPerioperative NursingLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- Pie Details Fact or FictionDokumen2 halamanPie Details Fact or FictionLouie Kem Anthony BabaranBelum ada peringkat
- On Pies and PastriesDokumen44 halamanOn Pies and PastriesLouie Kem Anthony Babaran100% (2)
- Pathophysiology PP FinalDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology PP FinalLouie Kem Anthony Babaran0% (1)
- 实用多元统计分析Dokumen611 halaman实用多元统计分析foo-hoat LimBelum ada peringkat
- Agriculture: PAPER 3 Practical TestDokumen8 halamanAgriculture: PAPER 3 Practical Testmstudy123456Belum ada peringkat
- Sector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringDokumen12 halamanSector San Juan Guidance For RepoweringTroy IveyBelum ada peringkat
- Theoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Dokumen3 halamanTheoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Rizza Manabat PacheoBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Final 2 Number c1-c5Dokumen167 halamanThesis Final 2 Number c1-c5Kimverly DomaganBelum ada peringkat
- Course: Consumer Behaviour: Relaunching of Mecca Cola in PakistanDokumen10 halamanCourse: Consumer Behaviour: Relaunching of Mecca Cola in PakistanAnasAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Post Market Surveillance SOPDokumen8 halamanPost Market Surveillance SOPgopinathBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen45 halamanUntitledjemBelum ada peringkat
- Liebherr PR 712 Litronic Final DrivesDokumen8 halamanLiebherr PR 712 Litronic Final DrivesLiebherr75% (4)
- NCS V5 1.0 Layer Name FormatDokumen4 halamanNCS V5 1.0 Layer Name FormatGouhar NayabBelum ada peringkat
- Buzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & BeyondDokumen15 halamanBuzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & Beyondyossara26100% (3)
- State Partnership Program 101 Brief (Jan 2022)Dokumen7 halamanState Partnership Program 101 Brief (Jan 2022)Paulo FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Binary To DecimalDokumen8 halamanBinary To DecimalEmmanuel JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- UKAYUNIK Chapter 1 To 12Dokumen31 halamanUKAYUNIK Chapter 1 To 12Chiesa ArellanoBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationDokumen14 halamanAssignment 2 Management Perspective Son Leadership MotivationHoneyVasudevBelum ada peringkat
- Psych PresurgicalDokumen31 halamanPsych Presurgicalriham ammar100% (1)
- Examples Week1 CompressDokumen6 halamanExamples Week1 CompressAngel HuitradoBelum ada peringkat
- Helena HelsenDokumen2 halamanHelena HelsenragastrmaBelum ada peringkat
- User Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveDokumen12 halamanUser Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveMauricio Contreras R.Belum ada peringkat
- Nail Malformation Grade 8Dokumen30 halamanNail Malformation Grade 8marbong coytopBelum ada peringkat
- Theater InstallationDokumen7 halamanTheater InstallationtemamBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report - Performance Anaylysis of Mutual Funds in IndiaDokumen52 halamanProject Report - Performance Anaylysis of Mutual Funds in Indiapankaj100% (1)
- Shaira Narrative Report (Final)Dokumen7 halamanShaira Narrative Report (Final)Sheryll TamangBelum ada peringkat
- Norman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsDokumen35 halamanNorman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsJorge Luis Echeverry González100% (1)
- AP1 Q4 Ip9 v.02Dokumen4 halamanAP1 Q4 Ip9 v.02Fayenah Pacasum Mindalano100% (1)
- Power Factor Improvement SystemDokumen25 halamanPower Factor Improvement SystemBijoy SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Keras N0vember 2021Dokumen137 halamanObat Keras N0vember 2021antonBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialDokumen2 halaman02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialIshang VashishthaBelum ada peringkat
- Research PaperDokumen14 halamanResearch PaperNeil Jhon HubillaBelum ada peringkat
- ISO StandardsDokumen7 halamanISO StandardsHusnain BaigBelum ada peringkat