ECG Interpretation
Diunggah oleh
FranspolDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ECG Interpretation
Diunggah oleh
FranspolHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Understanding
Understanding
ECGs
ECGs
February 2003
February 2003
Flight Medic Course (ACLS)
Flight Medic Course (ACLS)
Objectives
Objectives
Describe the basic approach to
Describe the basic approach to
interpretation of ECG strips
interpretation of ECG strips
Explain the five steps used in
Explain the five steps used in
interpretation of ECG strips
interpretation of ECG strips
Explain how to calculate heart rate, PRI,
Explain how to calculate heart rate, PRI,
and QRS complex, given a 6
and QRS complex, given a 6
-
-
second strip
second strip
Identify different types of ECG strips
Identify different types of ECG strips
pertaining to ACLS
pertaining to ACLS
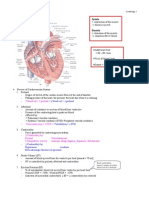
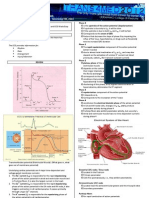
The Electrical Conduction System
The Electrical Conduction System
SA Node
AV Node
Bundle of HIS
Purkinje Fibers
The Electrical Conduction System
The Electrical Conduction System
SA node: Fastest rate of
SA node: Fastest rate of
automaticity
automaticity
.
.
Primary pacemaker of the heart.
Primary pacemaker of the heart.
Rate: 60 to 100
Rate: 60 to 100
bpm
bpm
AV node: Has a delay which allows for
AV node: Has a delay which allows for
atrial
atrial
contraction and a more filling of the
contraction and a more filling of the
ventricles.
ventricles.
Rate: 40
Rate: 40
-
-
60
60
bpm
bpm
The Electrical Conduction System
The Electrical Conduction System
Bundle of His: Has the ability to self
Bundle of His: Has the ability to self
-
-
initiate electrical activity
initiate electrical activity
Rate: 40
Rate: 40
-
-
60
60
bpm
bpm
Purkinje Fibers: Network of fibers that
Purkinje Fibers: Network of fibers that
carry an electrical impulses directly to
carry an electrical impulses directly to
ventricular muscle cells.
ventricular muscle cells.
Rate: 20
Rate: 20
-
-
40
40
bpm
bpm
Information Obtainable from ECG
Information Obtainable from ECG
Rhythm Strip Analysis
Rhythm Strip Analysis
The Electrocardiogram
The Electrocardiogram
Defines the graphic representation of the
Defines the graphic representation of the
electrical activity of the heart
electrical activity of the heart
The printed record of the electrical activity
The printed record of the electrical activity
of the heart is called a rhythm strip or an
of the heart is called a rhythm strip or an
ECG strip.
ECG strip.
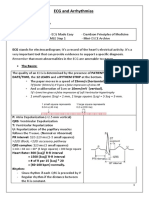
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
P
P
-
-
Wave
Wave
SA node fires, sends
SA node fires, sends
the electrical impulse
the electrical impulse
outward to stimulate
outward to stimulate
both atria and
both atria and
manifests as a P
manifests as a P
-
-
wave.
wave.
Approximately 0.10
Approximately 0.10
seconds in length
seconds in length
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
PR Interval (PRI)
PR Interval (PRI)
Time which impulse
Time which impulse
travels from the SA
travels from the SA
node to the atria and
node to the atria and
downward to the
downward to the
ventricles
ventricles
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
QRS Complex
QRS Complex
Impulse from the
Impulse from the
Bundle of HIS
Bundle of HIS
throughout the
throughout the
ventricular muscles
ventricular muscles
Measures less than
Measures less than
0.12 seconds or less
0.12 seconds or less
than 3 small squares
than 3 small squares
on the ECG paper
on the ECG paper
Breakdown of an ECG
Breakdown of an ECG
T
T
-
-
Wave:
Wave:
Ventricular
Ventricular
repolarization,
repolarization,
meaning no associated
meaning no associated
activity of the
activity of the
ventricular muscle
ventricular muscle
Resting phase of the
Resting phase of the
cardiac cycle
cardiac cycle
Interpretation of an ECG Strip
Interpretation of an ECG Strip
Step 1: Heart Rate
Step 1: Heart Rate
Step 2: Heart Rhythm
Step 2: Heart Rhythm
Step 3: P
Step 3: P
-
-
Wave
Wave
Step 4: PRI
Step 4: PRI
Step 5: QRS Complex
Step 5: QRS Complex
Heart Rate
Heart Rate
6-Second Method: Have a six second strip, count the
QRS complexes and multiple by 10.
Heart Rate
Heart Rate
What is the rate on this rhythm strip?
Heart Rhythm
Heart Rhythm
Heart rhythm are classified as regular or
Heart rhythm are classified as regular or
irregular.
irregular.
Can calculate the heart rhythm involves
Can calculate the heart rhythm involves
establishing a pattern of QRS complexes
establishing a pattern of QRS complexes
occurrence.
occurrence.
Measure ventricular rhythm by measuring the
Measure ventricular rhythm by measuring the
interval between R
interval between R
-
-
to
to
-
-
R waves and
R waves and
atrial
atrial
rhythm
rhythm
by measuring the P
by measuring the P
-
-
to
to
-
-
P waves.
P waves.
Interval > than 0.06 seconds, irregular.
Interval > than 0.06 seconds, irregular.
The P
The P
-
-
Wave
Wave
5 questions:
5 questions:
1. Are P
1. Are P
-
-
Waves present?
Waves present?
2. Are P
2. Are P
-
-
Waves occurring regularly?
Waves occurring regularly?
3. Is there a P
3. Is there a P
-
-
Wave for each QRS?
Wave for each QRS?
4. Are the P
4. Are the P
-
-
Waves smooth, rounded, and
Waves smooth, rounded, and
upright in appearance, or are they inverted?
upright in appearance, or are they inverted?
5. Do all P
5. Do all P
-
-
Waves look similar?
Waves look similar?
The PRI
The PRI
Normal length of the PRI is 0.12 to 0.20
Normal length of the PRI is 0.12 to 0.20
second (3
second (3
-
-
5 small squares)
5 small squares)
3 Questions to ask:
3 Questions to ask:
1. Are PRI greater that 0.20 seconds?
1. Are PRI greater that 0.20 seconds?
2. Are PRI less than 0.12 seconds?
2. Are PRI less than 0.12 seconds?
3. Are the PRIs constant across the ECG
3. Are the PRIs constant across the ECG
strip?
strip?
The QRS Complex
The QRS Complex
3 questions to ask:
3 questions to ask:
1. Are QRS intervals greater than 0.12 second
1. Are QRS intervals greater than 0.12 second
(wide)? If so, the complex may be ventricular
(wide)? If so, the complex may be ventricular
in
in
orgin
orgin
.
.
2. Are QRS intervals less than 0.12 seconds
2. Are QRS intervals less than 0.12 seconds
(narrow)? If so, the complex is most likely
(narrow)? If so, the complex is most likely
supraventricular in origin.
supraventricular in origin.
3. Are QRS complexes similar in appearance
3. Are QRS complexes similar in appearance
across the ECG strip?
across the ECG strip?
First Rhythm Strip to Identify
First Rhythm Strip to Identify
Step 1: Heart Rate
Step 1: Heart Rate
Step 2: Heart Rhythm
Step 2: Heart Rhythm
Step 3: P
Step 3: P
-
-
Wave
Wave
Step 4: PRI
Step 4: PRI
Step 5: QRS Complex
Step 5: QRS Complex
Artifact
Artifact
Four Common Causes:
Four Common Causes:
Patient Movement
Patient Movement
Loose or defective electrodes
Loose or defective electrodes
Improper grounding
Improper grounding
Faulty ECG apparatus
Faulty ECG apparatus
Patient assessment is critical
Patient assessment is critical
Types of Rhythms
Types of Rhythms
Rate:
Rate:
Bradycardia = rate of <60
Bradycardia = rate of <60
bpm
bpm
Normal = rate of 60
Normal = rate of 60
-
-
100
100
bpm
bpm
Tachycardia = rate of >100
Tachycardia = rate of >100
-
-
160
160
bpm
bpm
Where its coming from:
Where its coming from:
Sinus; SA node
Sinus; SA node
Atrial
Atrial
; SA node fails, impulse comes from the
; SA node fails, impulse comes from the
atria (
atria (
internodal
internodal
or the AV node)
or the AV node)
Ventricular; SA node or AV junction fails,
Ventricular; SA node or AV junction fails,
ventricles will shoulder responsibility of pacing
ventricles will shoulder responsibility of pacing
the heart
the heart
Sinus Rhythms
Sinus Rhythms
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus Tachycardia
NSR Rhythm
NSR Rhythm
Sinus Bradycardia Rhythm
Sinus Bradycardia Rhythm
Sinus Tachycardia Rhythm
Sinus Tachycardia Rhythm
Atrial
Atrial
Rhythms
Rhythms
SA node fails to generate an impulse, the
SA node fails to generate an impulse, the
atrial
atrial
tissue or areas in the
tissue or areas in the
internodal
internodal
pathways may
pathways may
initiate an impulse.
initiate an impulse.
These are called
These are called
atrial
atrial
dysrhythmias
dysrhythmias
Generally not considered life
Generally not considered life
-
-
threatening or
threatening or
lethal careful and deliberate patient assessment
lethal careful and deliberate patient assessment
must be continuous.
must be continuous.
Types of
Types of
Atrial
Atrial
Rhythms
Rhythms
Atrial
Atrial
Flutter
Flutter
Atrial
Atrial
Fibrillation
Fibrillation
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Atrial
Atrial
Flutter
Flutter
Atrial
Atrial
Fibrillation
Fibrillation
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Rhythms
Ventricular Rhythms
SA node or the AV junctional tissue fails to
SA node or the AV junctional tissue fails to
initiate an electrical impulse, the ventricles will
initiate an electrical impulse, the ventricles will
shoulder the responsibility of pacing the heart.
shoulder the responsibility of pacing the heart.
This group of rhythms are called ventricular
This group of rhythms are called ventricular
dysrhythmias
dysrhythmias
.
.
An electrical impulse can be instigated from any
An electrical impulse can be instigated from any
pacemaker cell in the ventricles, including the
pacemaker cell in the ventricles, including the
bundle branches or the fibers of the Purkinje
bundle branches or the fibers of the Purkinje
fibers.
fibers.
Types of Ventricular Rhythms
Types of Ventricular Rhythms
Premature Ventricular Complexes
Premature Ventricular Complexes
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia
Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de Pointes
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Fibrillation
Asystole
Asystole
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
Premature Ventricular
Premature Ventricular
Complexes (PVCs)
Complexes (PVCs)
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia
Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de Pointes
French term that signifies the twisting of the
French term that signifies the twisting of the
points.
points.
May wax and wane in amplitude and may flip
May wax and wane in amplitude and may flip
or twist on its electrical axes.
or twist on its electrical axes.
Similar to ventricular tachycardia
Similar to ventricular tachycardia
Caused by
Caused by
hypomagnesemia
hypomagnesemia
or by
or by
antiarrhythmic
antiarrhythmic
drugs
drugs
Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de Pointes
V. Fibrillation
V. Fibrillation
Asystole
Asystole
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
The absence of a palpable pulse and myocardial
The absence of a palpable pulse and myocardial
muscle activity with the presence of organized
muscle activity with the presence of organized
electrical activity (excluding VT and VF) on
electrical activity (excluding VT and VF) on
cardiac monitor.
cardiac monitor.
It is
It is
not
not
an actual rhythm, it represents a
an actual rhythm, it represents a
clinical condition wherein the patient is clinically
clinical condition wherein the patient is clinically
dead, despite the fact that some type of
dead, despite the fact that some type of
organized rhythm appears on the monitor.
organized rhythm appears on the monitor.
Types of Heart Blocks
Types of Heart Blocks
First Degree AV Block
First Degree AV Block
Second
Second
-
-
Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type I) or
Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type I) or
Wenckebach
Wenckebach
Second
Second
-
-
Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type II)
Degree AV Block (Mobitz Type II)
Third Degree AV Block (Complete)
Third Degree AV Block (Complete)
First Degree AV Block
First Degree AV Block
Second
Second
-
-
Degree AV Block
Degree AV Block
(Mobitz Type I) or Wenckebach
(Mobitz Type I) or Wenckebach
Second
Second
-
-
Degree AV Block
Degree AV Block
(Mobitz Type I) or Wenckebach
(Mobitz Type I) or Wenckebach
Second
Second
-
-
Degree AV Block
Degree AV Block
(Mobitz Type II)
(Mobitz Type II)
Third Degree AV Block
Third Degree AV Block
(Complete)
(Complete)
Third Degree AV Block
Third Degree AV Block
(Complete)
(Complete)
Artificial Pacemaker
Artificial Pacemaker
Practice Strips
Practice Strips
Atrial Fibrillation with PVCs
NSR
Sinus Bradycardia
Practice Strips
Practice Strips
Ventricular Fibrillation
Third-Degree Heart Block
Asystole
Practice Strips
Practice Strips
Sinus Tachycardia
Second-Degree AV Block
Mobitz Type I, Wenckebach
Atrial Flutter
Questions/Confused
Questions/Confused
Student Brain
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NBME Subject ExamsDokumen40 halamanNBME Subject ExamsMedSchoolStuff89% (9)
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationDari EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasDari EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (5)
- Chapter 47 EKG WorksheetDokumen4 halamanChapter 47 EKG WorksheetChris CamarilloBelum ada peringkat
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsDari EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsBelum ada peringkat
- Ekg PracticeDokumen7 halamanEkg PracticeMichelle Cobb Matthews100% (1)
- Easy ECG GuideDokumen17 halamanEasy ECG GuideDr.Chinmay Kulkarni83% (12)
- ACLS EKG Rhythms and InterpretationDokumen10 halamanACLS EKG Rhythms and Interpretationdonheyzz_02Belum ada peringkat
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDokumen3 halamanDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- Personality TestDokumen5 halamanPersonality Testapi-215089876Belum ada peringkat
- GHS Health Declaration Form PDFDokumen2 halamanGHS Health Declaration Form PDFFattah AfawBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Terminology Workbook-Iii: NAME: Abdullah Hani Kaltham I.D: 211110066Dokumen14 halamanMedical Terminology Workbook-Iii: NAME: Abdullah Hani Kaltham I.D: 211110066Abod -vo-Belum ada peringkat
- Ecg Made EasyDokumen130 halamanEcg Made EasyJOHN ARBIE TATTAO, RN96% (49)
- Learning ECGDokumen187 halamanLearning ECGPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Dari EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Belum ada peringkat
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Dari EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Belum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisDari EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Heart Arrhythmias, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandHeart Arrhythmias, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!Dari EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!Belum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookDari EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookBelum ada peringkat
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXDari EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Mini Test QUIZDokumen9 halamanMini Test QUIZAbdul RohimBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg InterpretationDokumen3 halamanEcg Interpretationman0billi0% (1)
- Cardiac PacingDokumen89 halamanCardiac Pacingsandwhale056Belum ada peringkat
- Ecg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointDokumen37 halamanEcg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointJara Maris Moreno BudionganBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg InterpretationDokumen9 halamanEcg InterpretationEthan Rodriguez100% (3)
- Quick Ekg ReferenceDokumen23 halamanQuick Ekg Referencekowaikowar100% (2)
- Medsurg Cardio Ana&PhysioDokumen6 halamanMedsurg Cardio Ana&Physiorabsibala80% (10)
- Reading EKGs For BeginnersDokumen30 halamanReading EKGs For BeginnersMark Hammerschmidt100% (8)
- ECG Interpretation BookDokumen57 halamanECG Interpretation BookLouis Plan100% (2)
- ECGDokumen6 halamanECGMatthew MackeyBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac SystemDokumen7 halamanCardiac Systemsccctutor100% (3)
- ECG InterpretationDokumen40 halamanECG InterpretationMuhammad BadrushshalihBelum ada peringkat
- Ventricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)Dokumen3 halamanVentricular Rhythms Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)goobyyplssBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Study GuideDokumen70 halamanECG Study GuideFatima Chrystelle NuñalBelum ada peringkat
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDokumen15 halamanAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Basics of EKG InterpretationDokumen132 halamanBasics of EKG InterpretationSiddhant GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Aclsrhythmtest11 PDFDokumen7 halamanAclsrhythmtest11 PDFmonir610% (1)
- Cardiac DysrythmiasDokumen190 halamanCardiac DysrythmiasKoRnflakes100% (4)
- Basic Ecg 2016Dokumen75 halamanBasic Ecg 2016api-284503860Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Acls For DummiesDokumen3 halamanSample Acls For DummiesTodd Cole100% (1)
- ECG StripsDokumen5 halamanECG StripsNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- Basic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALDokumen16 halamanBasic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALCharlotte James100% (5)
- Cardiac DisordersDokumen15 halamanCardiac Disordersgold_enriquez100% (3)
- Name That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticeDokumen5 halamanName That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticelcascolanBelum ada peringkat
- Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDokumen70 halamanJoseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPcarmsBelum ada peringkat
- How To Read An EKG StripDokumen9 halamanHow To Read An EKG StripRavi PandeBelum ada peringkat
- Heart FailureDokumen1 halamanHeart Failurehannahhwolf100% (3)
- Rhythm Interpretation and Its ManagementDokumen6 halamanRhythm Interpretation and Its Managementjh_ajjBelum ada peringkat
- Dysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFDokumen105 halamanDysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFtvrossyBelum ada peringkat
- Mnemonic SDokumen78 halamanMnemonic SJoevet T. TadlasBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineDokumen88 halamanAdvanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineRoroBelum ada peringkat
- ECG and ArrhythmiasDokumen25 halamanECG and ArrhythmiasRashed ShatnawiBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiography: ECG StandardizationDokumen4 halamanElectrocardiography: ECG StandardizationRayan OlivaBelum ada peringkat
- Pakya ECG BasicsDokumen5 halamanPakya ECG BasicsFrederick CokroBelum ada peringkat
- My Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Anatomy Physiology PDFDokumen22 halamanCardiovascular Anatomy Physiology PDFMahesh ChendakeBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Guide To Ecg InterpretationDokumen53 halamanSimple Guide To Ecg Interpretationedy suyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert Test BankDokumen14 halamanEcgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert Test BankQuinn50% (2)
- Basic Ear Anatomy: or Whats in An EarDokumen23 halamanBasic Ear Anatomy: or Whats in An EarFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustkaDokumen2 halamanDaftar PustkaFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Behrbohm H, Et Al. 2009. Mouth and Phrynx. Ear, Nose, and Throat Diseases: With Head and Neck Surgery, P 268Dokumen1 halamanBehrbohm H, Et Al. 2009. Mouth and Phrynx. Ear, Nose, and Throat Diseases: With Head and Neck Surgery, P 268FranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Behrbohm HDokumen1 halamanBehrbohm HFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Dependence of The Middle EarDokumen6 halamanDependence of The Middle EarFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Progressive Hearing Loss Following Acquired Cytomegalovirus Infection in An Immunocompromised ChildDokumen4 halamanProgressive Hearing Loss Following Acquired Cytomegalovirus Infection in An Immunocompromised ChildFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Karsinoma LaringDokumen84 halamanKarsinoma LaringFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- Interventional BronchosDokumen323 halamanInterventional BronchosFranspol100% (1)
- A Case of Acquired Tracheal Diverticulum Presenting With Globus PharyngeusDokumen3 halamanA Case of Acquired Tracheal Diverticulum Presenting With Globus PharyngeusFranspolBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE - Underground Clinical Vignettes BiochemistryDokumen114 halamanUSMLE - Underground Clinical Vignettes BiochemistryFranspol100% (4)
- Medical Syndromes Internal Medicine NoteDokumen4 halamanMedical Syndromes Internal Medicine NoteFranspol100% (1)
- Usmle CK StepDokumen74 halamanUsmle CK StepIrfan Majeed100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDokumen30 halamanAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeNikhil GhubadeBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics For Elementary Teachers 5th Edition Beckmann Test BankDokumen26 halamanMathematics For Elementary Teachers 5th Edition Beckmann Test BankDonnaMoorefspo98% (59)
- Anemia in Sports: A Narrative ReviewDokumen12 halamanAnemia in Sports: A Narrative ReviewRomana VulturarBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Hypertension - Blood PressureDokumen8 halamanPediatric Hypertension - Blood PressureMUV Class of 2016Belum ada peringkat
- LearnFM Clinical Card Book 2020Dokumen67 halamanLearnFM Clinical Card Book 2020Aqilah Syafiqah100% (1)
- Snake BiteDokumen29 halamanSnake BiteIgbashioBelum ada peringkat
- 2002 Magnetom Flash 3Dokumen104 halaman2002 Magnetom Flash 3Herick Savione100% (3)
- Class-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesDokumen39 halamanClass-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesAyi FurqonBelum ada peringkat
- PRINTTTDokumen6 halamanPRINTTTEy EmBelum ada peringkat
- One Shot Revision Patho by DR PraveenDokumen19 halamanOne Shot Revision Patho by DR PraveenTauqueer AlamBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrotic Syndrome FinalDokumen20 halamanNephrotic Syndrome FinalAndrew AdelBelum ada peringkat
- Ospe HistologyDokumen17 halamanOspe Histologyaimi BatrisyiaBelum ada peringkat
- Sudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportDokumen4 halamanSudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportAnonymous JXEtV98KjPBelum ada peringkat
- Veratrum VirideDokumen5 halamanVeratrum VirideSuhas IngaleBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia OrderDokumen25 halamanPulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia OrderRizqon RohmatussadeliBelum ada peringkat
- CPAP For Prevention CVE in OSADokumen13 halamanCPAP For Prevention CVE in OSAenBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmo Viewboxes BLOCK 8Dokumen251 halamanPulmo Viewboxes BLOCK 8U.P. College of Medicine Class 2014100% (2)
- Heart Reviewer 1Dokumen6 halamanHeart Reviewer 1tokzzBelum ada peringkat
- Work Tests To Evaluate Cardio Respiratory FitnessDokumen40 halamanWork Tests To Evaluate Cardio Respiratory FitnessJawad Ahmed100% (1)
- Glomerular Diseases in Pregnancy - Kidney (2023)Dokumen18 halamanGlomerular Diseases in Pregnancy - Kidney (2023)cheve glzBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio QuestionsDokumen21 halamanCardio QuestionsJenna AbuanBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory System of OxDokumen14 halamanThe Respiratory System of OxHemant JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- CPC Year 5 Heart FailureDokumen84 halamanCPC Year 5 Heart FailureIhsan Mustapha AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Corticosteroids and Anabolic SteroidsDokumen32 halamanCorticosteroids and Anabolic SteroidsSudhakar LakavathBelum ada peringkat
- Left Ventricular Non-CompactionDokumen20 halamanLeft Ventricular Non-CompactionlawlietBelum ada peringkat
- CSF & Lumbar PunctureDokumen26 halamanCSF & Lumbar Punctureaz.rah.e.khudiBelum ada peringkat
- Adachi Autopsy ReportDokumen25 halamanAdachi Autopsy ReportMissionLocalBelum ada peringkat
- Mattox Trauma 8th Edition - PDF 2Dokumen16 halamanMattox Trauma 8th Edition - PDF 2Meri YeghiazaryanBelum ada peringkat