Gaussian Input for PCM
Diunggah oleh
Manoel MachadoDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Gaussian Input for PCM
Diunggah oleh
Manoel MachadoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Introduction to
Introduction to
Gaussian
Gaussian
03 Package
03 Package
http://ww.gaussian.com
Gaussian Input file: Section layout
Example of CH
2
O with HF/STO-3G: Input file
More About Gaussian Input file
An array of ab initio methods are available
Gaussian job Route: a sequence of links
Output file
More
PCM in Gaussian 03
PCM in Gaussian 03
G
cav
+ G
elec
+ G
dis-rep
Cavitation
free energy
Electrostatic
free energy
Disp-rep
free energy
Energy and cavity
Energy and cavity
Electrostatic term: solvent-excluded surface (SES) with scaled radii
Cavitation term: van der Waals surface (VDW) with unscaled radii
Disp-rep terms: solvent-accessible surface (SAS) with scaled radii.
) (
4
2
i
cav
spheres
i
i
i
cav
R G
R
A
G
=
Exposed surface of sphere i
Single sphere contribution
( )
solvent solute
atom atom
tesserae
dis rep dis rep
s s i ms mi i
s m i
G N a A r n
=
(6)
6
( )
3
dis
ms
ms ms ms
ms
d
A r r
r
=
(12)
12
( )
9
rep
ms
ms ms ms
ms
d
A r r
r
=
Cavitation term: van der Waals surface (VDW) with unscaled radii
Disp-rep terms: solvent-accessible surface (SAS) with radii scaled to account for
the solvent. A different cavity has to be built for each different solvent atom (s)
Non-Electrostatic terms
Connolly: formal definition
GePol: computational definition
Reentrant (concave) surface Convex surface
Spheres
centered on
solute atoms
Electrostatic interactions:
Solvent-excluded surface (SES)
Electrostatic interactions:
Solvent-excluded surface (SES)
Probe sphere
representing the
solvent
Added sphere
not centered on
atoms
Electrostatic interactions:
Solvent-excluded surface (SES)
Electrostatic interactions:
Solvent-excluded surface (SES)
Which Radii for the spheres centered on the atoms?
van der Waals radius
atomic bond or lone pair charge centers of the
solvent molecules are normally located a bit
further from the solute atoms
vdW
R R f
=
Atom
Scaling factor :
f can be optimized; often for small-medium size solvents:
f = 1.2
f
R
vdW
1.2 1.2 1.2 1.0-1.2
1.55 1.52 1.7 1.2
Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen For
example
Electrostatic interactions:
The boundary element method
Electrostatic interactions:
The boundary element method
s
i
1. Partition of the cavity surface into N finite
elements (tesserae) (Boundary Element
Method, BEM)
2. Discretization of the apparent surface charge into N point-
like charges q
( )
i
s
constant on each
element of area a
i
( )
i i i
q a s =
A sphere: the mesh or tessellation
A sphere: the mesh or tessellation
Polyhedron with
n number of
faces
Projection
on a sphere:
n triangular
spherical
elements
(tesserae)
Refinement of
the mesh
A polyhedron with a
larger number of faces
A sphere intersects a
tessera placed on
another sphere
The part of the tessera
inside the sphere is
eliminated
The area a
i
of all the tesserae
(original or cut) can be calculated
analytically
Cut tessera
A more general cavity: the mesh or
tessellation
A more general cavity: the mesh or
tessellation
Solvent=item
If unspecified, the solvent defaults to water.
Item is a solvent name chosen from the list:
Water or H2O, Acetonitrile or CH3CN, DiMethylSulfoxide or DMSO, Methanol or CH3OH,
Ethanol or CH3CH2OH, Isoquinoline, Quinoline, Chloroform or CHCl3, Ether or DiEthylEther or
CH3CH2OCH2CH3, DiChloroMethane or MethyleneChloride or CH2Cl2, DiChloroEthane or
CH2ClCH2Cl, CarbonTetrachloride or CCl4, Benzene or C6H6, Toluene or C6H5CH3,
ChloroBenzene or C6H5Cl, NitroMethane or CH3NO2, Heptane or C7H16, CycloHexane or
C6H12, Aniline or C5H5NH2, Acetone or CH3COCH3, TetraHydroFuran or THF,
DiMethylSulfoxide or DMSO or CH3SOCH3, Argon or Ar, Krypton or Kr, Xenon or Xe
#p scrf=(iefpcm,solvent=item) hf/3-21G
title
0 1
solute geom
Gaussian Input for PCM
Gaussian Input for PCM
#p scrf=(iefpcm,solvent=item,read) hf/3-21G
title
0 1
solute geom
PCM keywords
Gaussian Input for PCM
Gaussian Input for PCM
PCM keywords:
norep, nodis, nocav: to skip nonelectrostatic terms
scfvac: to do a gas-phase calculation first
eps=XX, epsinf=YY, Rsolv=ZZ, : to change solvent parameters
NOADDSPH, Radii=XX, tsare=YY, nsfe=NN, : to change cavity and meshing
..
Default (UA0): Spheres centered only
on heavy atoms (effective radii)
Cavities
Cavities
Rmin=0. ofac=0.8
simplified scheme for
the added spheres:
computationally more
efficient
Radii=bondi : spheres centered on
each atom including the hydrogens
Simplification
of the topology
Further
simplification
of the topology
Green spheres are centered on
carbons, red spheres on oxygens,
white spheres on hydrogens and
added spheres are in black
O
Aceto-phenone
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
United AtomTopological Model (UA0 parameters set).
Nord Group Hybr Charge Alpha Radius Bonded to
1 C * 0.00 1.00 1.925 C2 [s] O3 [d] C4 [s]
2 CH3 * 0.00 1.00 2.525 C1 [s]
3 O * 0.00 1.00 1.750 C1 [d]
4 C * 0.00 1.00 1.925 C1 [s] C5 [s] C9 [s]
5 CH * 0.00 1.00 2.125 C4 [s] C6 [s]
6 CH * 0.00 1.00 2.125 C5 [s] C7 [s]
7 CH * 0.00 1.00 2.125 C6 [s] C8 [s]
8 CH * 0.00 1.00 2.125 C7 [s] C9 [s]
9 CH * 0.00 1.00 2.125 C4 [s] C8 [s]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Polarizable Continuum Model (PCM)
=================================
Model : PCM.
Atomic radii : UA0 (Simple United AtomTopological Model).
Polarization charges : Total charges.
Charge compensation : None.
Solution method : Matrix inversion.
Cavity : GePol (RMin=0.500 OFac=0.800).
Default sphere list used, NSphG= 9.
Tesserae with average area of 0.200 Ang**2.
Solvent : Cyclohexane, Eps = 2.023000
Eps(inf)= 2.028000
RSolv = 2.815000 Ang.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GePol: Number of tesserae being generated = 1185
GePol: Average area of tesserae = 0.15 Ang**2
GePol: Minimum area of tessera = 0.12D-02 Ang**2
GePol: Maximumarea of tessera = 0.30586 Ang**2
GePol: Number of small tesserae = 16
GePol: Fraction of small tesserae (<1% of avg) = 1.35%
GePol: Total count of vertices = 3905
GePol: Maximumnumber of vertices in a tessera = 6
GePol: Cavity surface area = 175.984 Ang**2
GePol: Cavity volume = 182.113 Ang**3
In the output
In the output
#p scrf=(iefpcm, solvent=cyclohexane, read) ....
title
0 1
solute geom
nodis nocav norep rmin=0.5 ofac=0.8
Input
Spheres centered only on heavy atoms.
Computationally efficient but it loses accuracy in describing
the interaction of acidic hydrogens with solvent
When the default (UA0) cavity is not sufficient?
Default: UA0
When hydrogens play a role
OH
OH
OH
O
HO
+
rmin=0.5 ofac=0.8
Gallic acid
When the default (UA0) cavity is not sufficient?
When hydrogens play a role
OH
OH
OH
O
HO
Mixed
Spheres centered on the heavy atoms and on acidic hydrogens
More accurate in the description of solute-solvent interactions
Gallic acid
Gallic acid
#p scrf=(iefpcm,read) ....
Gallic acid
0 1
C -1.70224259 0.12750348 0.11298551
O -2.28678088 1.19484792 -0.04380417
C -0.20894647 0.05080826 0.00724215
C 0.50951011 1.22655781 -0.27366334
C 1.89851189 1.19842744 -0.38034127
C 2.59066606 -0.00676889 -0.20769622
C 1.88685577 -1.18183291 0.07185998
C 0.49446587 -1.15391970 0.17894851
H -0.04009200 2.15431340 -0.40529346
H -0.03600514 -2.07642759 0.39663425
O -2.44243558 -1.06194043 0.39975636
H -3.37923874 -0.85540077 0.43637888
O 2.58890857 -2.41498234 0.24895983
H 3.53135335 -2.26504814 0.14447268
O 4.01617040 -0.03602505 -0.31715599
H 4.34088853 0.84642460 -0.51065213
O 2.61592210 2.40192899 -0.66635985
H 1.99714443 3.13057680 -0.75460133
rmin=0.5 ofac=0.8 nsfe=16
1 1.925
2 1.750
3 1.925
4 2.125
5 1.925
6 1.925
7 1.925
8 2.125
11 1.520 1.2
12 1.000 1.2
13 1.520 1.2
14 1.000 1.2
15 1.520 1.2
16 1.000 1.2
17 1.520 1.2
18 1.000 1.2
O
O
O
O
O
H
H
H
H
From UA0
vdW
R R f
=
0 R
H H V E
= + =
0
0
1 1
2 2
1
2
el R R R
R
G E V H V V
H V
= = +
= +
To get the free energy we have to subtract the work spent in polarizing the solvent
By solving the equation we get
E H =
The internal energy of
the solvated system
0 el el
G G G =
Electrostatic solvation free energy:
Electrostatic interactions
Gaussian Output
Gaussian Output
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Variational PCM results
=======================
<psi(f)| H |psi(f)> (a.u.) = -98.568013
<psi(f)|H+V(f)/2|psi(f)> (a.u.) = -98.573228
Total free energy in solution:
with all non electrostatic terms (a.u.) = -98.569083
--------------------------------------------------------------------
(Polarized solute)-Solvent (kcal/mol) = -3.27
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Cavitation energy (kcal/mol) = 5.34
Dispersion energy (kcal/mol) = -3.08
Repulsion energy (kcal/mol) = 0.34
Total non electrostatic (kcal/mol) = 2.60
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Output
Output
1
2
R
V
0
1
2
el R
G H V = +
Nonelectrostatic
terms
E H =
By doing first a gas-phase calculation: keyword = scfvac
Variational PCM results
=======================
<psi(0)| H |psi(0)> (a.u.) = -509.799632
<psi(0)|H+V(0)/2|psi(0)> (a.u.) = -509.821720
<psi(0)|H+V(f)/2|psi(0)> (a.u.) = -509.823898
<psi(f)| H |psi(f)> (a.u.) = -509.797139
<psi(f)|H+V(f)/2|psi(f)> (a.u.) = -509.823917
(Unpolarized solute)-Solvent (kcal/mol) = -13.86
(Polarized solute)-Solvent (kcal/mol) = -16.80
Solute polarization (kcal/mol) = 1.56
Total electrostatic (kcal/mol) = -15.24
0 0 0 0
H H
1
2
R
V
0 0
1
2
R
V
0 0 0 el el
G G H =
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Example in ElectrostaticsDokumen36 halamanExample in ElectrostaticsJoseMiguelDomingo75% (4)
- Gas Solubility in Aqueous SolutionDokumen93 halamanGas Solubility in Aqueous SolutionArgie Adduru73% (11)
- Tester, Modell - Answers To Selected ProblemsDokumen12 halamanTester, Modell - Answers To Selected ProblemsCoronel MustangBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsDari EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsBelum ada peringkat
- 21 Great Answers To: Order ID: 0028913Dokumen13 halaman21 Great Answers To: Order ID: 0028913Yvette HOUNGUE100% (1)
- Introduction To GemologyDokumen286 halamanIntroduction To GemologyEhtesham Siddiqui100% (2)
- EtomDokumen1 halamanEtomarthryxBelum ada peringkat
- Continuum Solvation Models in Gaussian 03Dokumen31 halamanContinuum Solvation Models in Gaussian 03AlejandroWiernaBelum ada peringkat
- 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science: Mit OpencoursewareDokumen11 halaman5.111 Principles of Chemical Science: Mit OpencoursewareÁlvaro Alvites RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 4th Edition WWW - Elsolucionario.org 573 680Dokumen108 halamanSolution Manual Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 4th Edition WWW - Elsolucionario.org 573 680Jose Maria Quintas GironBelum ada peringkat
- Chem II AP PacketDokumen4 halamanChem II AP PacketAmanda Rose DalyBelum ada peringkat
- Solucoes ICHO28 A ICHO24Dokumen38 halamanSolucoes ICHO28 A ICHO24Leonardo FagundesBelum ada peringkat
- Homework Ed Kinetics2Dokumen5 halamanHomework Ed Kinetics2Edrian A. MañalongBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Handout Chapter1 Applied EMDokumen13 halamanAdditional Handout Chapter1 Applied EMWaddah AbdoBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1st Edition Reisel Solutions ManualDokumen48 halamanPrinciples of Engineering Thermodynamics Si Edition 1st Edition Reisel Solutions Manualraftbungofqy6100% (27)
- Chem 36: General ChemistryDokumen13 halamanChem 36: General ChemistryAbdulhakeemSolimanBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry: Practice ExamplesDokumen35 halamanElectrochemistry: Practice ExamplesJudith Del Valle Morejon100% (2)
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDokumen9 halamanWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsShubham mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Continuous Mode)Dokumen6 halamanFull-Wave Controlled Rectifier RL Load (Continuous Mode)hamza abdo mohamoud100% (1)
- Gas Technology-4th Stage Lecture 2 12 November 2017Dokumen7 halamanGas Technology-4th Stage Lecture 2 12 November 2017muhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Micro4EXSol6 PDFDokumen22 halamanMicro4EXSol6 PDFDeivasigamani SubramaniyanBelum ada peringkat
- 20 Petrucci10e CSMDokumen66 halaman20 Petrucci10e CSMAlexBelum ada peringkat
- EE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13Dokumen43 halamanEE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13ozanistzBelum ada peringkat
- Chap3 1Dokumen4 halamanChap3 1Jose Eduardo MoralesBelum ada peringkat
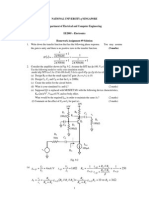
- Code: Name:: Total Scores: 38 Points Total Points 4 4 4 4 6 4 8 4 38 ReceivedDokumen24 halamanCode: Name:: Total Scores: 38 Points Total Points 4 4 4 4 6 4 8 4 38 ReceivedMacxsimusBelum ada peringkat
- PS1 08-SolutionDokumen7 halamanPS1 08-SolutionNguyễn Vũ Quang Thành100% (1)
- Modeling Speaker Impedance & Circuit CompensationDokumen7 halamanModeling Speaker Impedance & Circuit CompensationChristian JeguesBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 321 Midterm SolutionDokumen13 halamanCHE 321 Midterm SolutionDtf6969Belum ada peringkat
- Department of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Dokumen9 halamanDepartment of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Anelin OsiriknaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal (1) (Repaired)Dokumen9 halamanSoal (1) (Repaired)Inda AlwanBelum ada peringkat
- EjercicosDokumen8 halamanEjercicosdavidBelum ada peringkat
- Taller Ingenieria de Las Reacciones - Determinacion Del Orden de ReaccionDokumen15 halamanTaller Ingenieria de Las Reacciones - Determinacion Del Orden de ReaccionJesus JulioBelum ada peringkat
- New Updates of The First Ed.Dokumen6 halamanNew Updates of The First Ed.Filston RukerandangaBelum ada peringkat
- MIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Third Hour ExamDokumen11 halamanMIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Third Hour ExamÁlvaro Alvites RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen24 halamanChapter 2FARUK3725Belum ada peringkat
- Answer Key: (Jee Mains)Dokumen18 halamanAnswer Key: (Jee Mains)ssjatav128Belum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics of CellsDokumen11 halamanThermodynamics of Cellsjonathan_raimanBelum ada peringkat
- PS9Soln 2014Dokumen13 halamanPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Cdamp TheveninDokumen9 halamanCdamp TheveninssyellampalliBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Analysis: Newton-Raphson Power FlowDokumen29 halamanPower System Analysis: Newton-Raphson Power Flowselvan90Belum ada peringkat
- EE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionDokumen6 halamanEE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionKL ChiangBelum ada peringkat
- Reactor Design for Multiple ReactionsDokumen16 halamanReactor Design for Multiple ReactionsSchannBelum ada peringkat
- Amplifier StagesDokumen5 halamanAmplifier StagesNelsonLucioRodriguezPenagosBelum ada peringkat
- 01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceDokumen46 halaman01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceLatif Nurohman Bayu Nugroho60% (5)
- Lecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsDokumen13 halamanLecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsSaneesh KarayilBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Propeller Matching: Kelompok 1 Rega Ardian Syah Angga Wahyu P Pandika DarmawanDokumen15 halamanEngine Propeller Matching: Kelompok 1 Rega Ardian Syah Angga Wahyu P Pandika DarmawanyuniardimzBelum ada peringkat
- Basis Set OptimizationDokumen16 halamanBasis Set OptimizationNdhoz Los GandhozBelum ada peringkat
- Me 312Dokumen20 halamanMe 312John Angelo MarzanBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsDokumen9 halamanReaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsMiguel Magat Joves100% (1)
- Peng-Robinson EOS For Z-FactorDokumen29 halamanPeng-Robinson EOS For Z-FactorCHANADASBelum ada peringkat
- Submitted To: DR Khurram Naveed Lab 11Dokumen32 halamanSubmitted To: DR Khurram Naveed Lab 11Amna EjazBelum ada peringkat
- School of Chemical Engineering: Experiment 3: Problem Statement Date:06 August 2019Dokumen4 halamanSchool of Chemical Engineering: Experiment 3: Problem Statement Date:06 August 2019RishavBelum ada peringkat
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsDari EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)Dari EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)Belum ada peringkat
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Dari EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Penilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (3)
- ADL MATRIX STRATEGY FOR BPCL'S GROWTHDokumen17 halamanADL MATRIX STRATEGY FOR BPCL'S GROWTHSachin Nagar100% (1)
- Test Unit 7 m.2Dokumen6 halamanTest Unit 7 m.2Petchara SridakunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - 31-05-2023Dokumen163 halamanChapter 6 - 31-05-2023Saumitra PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Xiaomi Mi Drone 4K User Manual GuideDokumen47 halamanXiaomi Mi Drone 4K User Manual GuideΜιχάλης ΛαχανάςBelum ada peringkat
- Crafting and Executing StrategyDokumen33 halamanCrafting and Executing Strategyamoore2505Belum ada peringkat
- WORK ORDER TITLEDokumen2 halamanWORK ORDER TITLEDesign V-Tork ControlsBelum ada peringkat
- Alaris 8210 and 8220 SpO2 Module Service ManualDokumen63 halamanAlaris 8210 and 8220 SpO2 Module Service ManualNaveen Kumar TiwaryBelum ada peringkat
- 199-Article Text-434-1-10-20200626Dokumen11 halaman199-Article Text-434-1-10-20200626ryan renaldiBelum ada peringkat
- Travel Agency ManagementDokumen47 halamanTravel Agency ManagementKatherine BarretoBelum ada peringkat
- Sulzer MC EquipmentDokumen12 halamanSulzer MC EquipmentsnthmlgtBelum ada peringkat
- Exp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorDokumen8 halamanExp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorWaseem Nawaz MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Math 101Dokumen3 halamanMath 101Nitish ShahBelum ada peringkat
- A Sample of Directory or Instruction:: World Temperatures February 16Dokumen1 halamanA Sample of Directory or Instruction:: World Temperatures February 16eksaBelum ada peringkat
- Proejcr ManduaDokumen552 halamanProejcr ManduaDanny NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- MI 276 Rev B - Conversion of Turbochargers For Opposite Engine RotationDokumen15 halamanMI 276 Rev B - Conversion of Turbochargers For Opposite Engine RotationJesse BarnettBelum ada peringkat
- Y06209 November 2015Dokumen28 halamanY06209 November 2015Fredy CoyagoBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 13: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDokumen28 halamanManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 13: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaBelum ada peringkat
- Calibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraDokumen8 halamanCalibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraHapsari DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Vega Plus 69Dokumen3 halamanVega Plus 69yashBelum ada peringkat
- Small Healthcare Organization: National Accreditation Board For Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (Nabh)Dokumen20 halamanSmall Healthcare Organization: National Accreditation Board For Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (Nabh)Dipti PatilBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Lecher AntennaDokumen4 halamanWhat Is A Lecher AntennaPt AkaashBelum ada peringkat
- Penomoran Bantex - K64&COMPDokumen8 halamanPenomoran Bantex - K64&COMPVigour Rizko MurdyneBelum ada peringkat
- COP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDokumen4 halamanCOP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDavid CarrilloBelum ada peringkat
- RB450G Trouble ShootingDokumen9 halamanRB450G Trouble Shootingjocimar1000Belum ada peringkat
- Workflowy - 2. Using Tags For NavigationDokumen10 halamanWorkflowy - 2. Using Tags For NavigationSteveLangBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Micro EncapsulationDokumen5 halamanA Review On Micro EncapsulationSneha DharBelum ada peringkat