History: Drinking Pipes Tubing Plumbing Fixtures Plumber Piping Water Heaters Backflow Preventers
Diunggah oleh
AnabelaVillaflorPendonDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
History: Drinking Pipes Tubing Plumbing Fixtures Plumber Piping Water Heaters Backflow Preventers
Diunggah oleh
AnabelaVillaflorPendonHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Plumbing is the system of pipes, drains fittings, valves, valve assemblies, and devices installed in a
building for the distribution of water for drinking, heating and washing, and the removal of
waterborne wastes, and the skilled trade of working withpipes, tubing and plumbing fixtures in such
systems. A plumber is someone who installs or repairs piping systems, plumbing fixtures and
equipment such as water heaters and backflow preventers.Thus, plumbing usually deals with laying
of pipe lines which provide a means of transportation for fluids. The plumbing industry is a basic and
substantial part of every developed economy due to the need for clean water, and sanitary collection
and transport of wastes.
[1]
The word "plumbing" comes from the Latin plumbum for lead, as pipes
were once made from lead.
[2]
Plumbing is usually distinguished from water supply and sewage systems, in that a plumbing system
serves one building, while water and sewage systems serve a group of buildings.
[3]
Contents
[hide]
1 History
2 Materials
3 Components
o 3.1 Sealants
4 Equipment and tools
5 Systems
6 Regulation
7 See also
8 Notes
9 Further reading
10 External links
History[edit]
See also: Sanitation in ancient Rome and History of plumbing
Roman lead pipe with a folded seam, at the Roman Baths in Bath, England
Plumbing originated during ancient civilizations such as the Greek, Roman, Persian, Indian, and
Chinese cities as they developed public baths and needed to provide potable water and drainage of
wastes, for larger numbers of people.
[4]
Standardized earthen plumbing pipes with
broad flanges making use of asphalt for preventing leakages appeared in the urban settlements of
the Indus Valley Civilization by 2700 B.C.
[5]
The Romans used lead pipe inscriptions to prevent water
theft.
Improvement in plumbing systems was very slow, with virtually no progress made from the time of
the Roman system of aqueducts and lead pipes. Plumbing was extremely rare until the growth of
modern densely populated cities in the 1800s. During this period, public healthauthorities began
pressing for better waste disposal systems to be installed, to prevent or control epidemics of
disease. Earlier, the waste disposal system had merely consisted of collecting waste and dumping it
on the ground or into a river. Eventually the development of separate, underground water and
sewage systems eliminated open sewage ditches andcesspools.
Most large cities today pipe solid wastes to sewage treatment plants in order to separate and
partially purify the water, before emptying into streams or other bodies of water. For potable water
use, galvanized ironpiping was commonplace in the United States from the late 1800s until around
1960. After that period, copper piping took over, first soft copper with flared fittings, then with rigid
copper tubing utilizing soldered fittings.
The use of lead for potable water declined sharply after World War II because of increased
awareness of the dangers oflead poisoning. At this time, copper piping was introduced as a better
and safer alternative to lead pipes.
[6][7]
Materials[edit]
It has been suggested that Tap water#Pipe materials be merged into this
article. (Discuss) Proposed since March 2012.
Water systems of ancient times relied on gravity for the supply of water, using pipes or channels
usually made of clay, lead, bamboo, wood, or stone. Hollowed wooden logs wrapped in steel
banding were used for plumbing pipes, particularly water mains. Logs were used for water
distribution in England close to 500 years ago. US cities began using hollowed logs in the late 1700s
through the 1800s.
[6]
Present-day water-supply systems use a network of high-pressure pumps, and pipes in buildings are
now made of copper,
[8]
brass, plastic (particularly cross-linked polyethylene called PEX, which is
estimated to be used in 60% of single-family homes
[9]
), or other nontoxic material. Due to its toxicity,
lead has not been used in modern water-supply piping since the 1930s in the United
States,
[10]
although lead was used in plumbing solder for drinking water until it was banned in
1986.
[10]
Drain and vent lines are made of plastic, steel, cast-iron, or lead.
[11][12][13]
The straight sections of plumbing systems are called "pipes" or "tubes". A pipe is typically formed
via casting or welding, whereas a tube is made through extrusion. Pipe normally has thicker walls
and may be threaded or welded, while tubing is thinner-walled and requires special joining
techniques such as brazing, compression fitting, crimping, or for plastics, solvent welding. These
joining techniques are discussed in more detail in the piping and plumbing fittings article.
Components[edit]
See also: Piping and plumbing fittings, Valves and Plumbing fixtures
Piping being placed for a sink
In addition to lengths of pipe or tubing, pipe fittings are used in plumbing systems, such as valves,
elbows, tees, and unions.
[14]
Pipe and fittings are held in place with pipe hangersand strapping.
Plumbing fixtures are exchangeable devices using water that can be connected to a building's
plumbing system. They are considered to be "fixtures", in that they are semi-permanent parts of
buildings, not usually owned or maintained separately. Plumbing fixtures are seen by and designed
for the end-users. Some examples of fixtures include water closets
[15]
(also known
as toilets), urinals, bidets, showers, bathtubs, utility and kitchensinks, drinking fountains, ice makers,
humidifiers, air washers, fountains, and eye wash stations.
Sealants[edit]
Threaded pipe joints are sealed with thread seal tape or pipe dope. Many plumbing fixtures are
sealed to their mounting surfaces with plumber's putty.
[16]
Equipment and tools[edit]
A plumber uses two wrenches to tighten the fitting on a gas supply line.
Plumbing equipment includes devices often hidden behind walls or in utility spaces which are not
seen by the general public. It includes water meters, pumps, expansion tanks, backflow
arrestors, water filters, UV sterilization lights, water softeners, water heaters, heat exchangers,
gauges, and control systems.
Specialized plumbing tools include pipe wrenches, flaring pliers,pipe vice,pipe bending machine,pipe
cutter, dies and joining tools such as soldering torches and crimp tools. New tools have been
developed to help plumbers fix problems more efficiently. For example, plumbers use video cameras
for inspections of hidden leaks or problems, they use hydro jets, and high pressure hydraulic pumps
connected to steel cables for trench-less sewer line replacement.
Systems[edit]
Copper piping system in a building
The major categories of plumbing systems or subsystems are:
Potable cold and hot tap water supply
Plumbing drainage venting
Septic systems
Rainwater, surface, and subsurface water drainage
Fuel gas piping
For their environmental benefit and sizable energy savings, hot water heat recyclingunits are being
installed in residential buildings. Ecological concerns and water shortages have increased interest
in graywater recovery and treatment systems.
Plumbing may also include hydronics, which involves heating and cooling systems utilizing water to
transport thermal energy. The New York City steam system is an example of a large district
heating system.
Regulation[edit]
A pipe wrenchfor holding and turning pipe.
Much of the plumbing work in populated areas is regulated by government or quasi-government
agencies due to the direct impact on the public's health, safety, and welfare. Plumbing installation
and repair work on residences and other buildings generally must be done according to plumbing
and building codes to protect the inhabitants of the buildings and to ensure safe, quality construction
to future buyers. If permits are required for work, plumbing contractors typically secure them from the
authorities on behalf of home or building owners.
In the United Kingdom the professional body is the Chartered Institute of Plumbing and Heating
Engineering (educational charity status) and it is true that the trade still remains virtually
ungoverned;
[17]
there are no systems in place to monitor or control the activities of unqualified
plumbers or those home owners who choose to undertake installation and maintenance works
themselves, despite the health and safety issues which arise from such works when they are
undertaken incorrectly; see Health Aspects of Plumbing (HAP) published jointly by the World Health
Organization (WHO) and the World Plumbing Council (WPC).
[13][18]
WPC has subsequently
appointed a representative to the World Health Organization to take forward various projects related
to Health Aspects of Plumbing.
[13]
In the United States, plumbing codes and licensing are generally controlled by state and local
governments. At the national level, the Environmental Protection Agency has set guidelines about
what constitutes lead-free plumbing fittings and pipes, in order to comply with the Safe Drinking
Water Act.
Some widely used Standards in the United States are:
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Plumbing ReportDokumen29 halamanPlumbing ReportJohn Orland67% (3)
- 1.-LECTURE For Engineering UtilitiesDokumen27 halaman1.-LECTURE For Engineering Utilitiescutie4everrBelum ada peringkat
- Wells O&M ManualDokumen80 halamanWells O&M Manualpatitay036817100% (1)
- 4-2953 - 55 Final Manual - Eng 05-08-11 PDFDokumen225 halaman4-2953 - 55 Final Manual - Eng 05-08-11 PDFVladimirBelum ada peringkat
- PlumbingDokumen5 halamanPlumbingmico alilayaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDokumen8 halamanLecture 1 Introductionpatrick kivutiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Plumbing Level 1 Rev 2Dokumen10 halamanIntroduction To Plumbing Level 1 Rev 2Florence KisengeseBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing PortfolioDokumen32 halamanPlumbing PortfolioAllan DeGuzman Dela VegaBelum ada peringkat
- Masonry AND Concrete Works: "Plumbing System in Relation To Masonry" & "Plumbing Terms"Dokumen7 halamanMasonry AND Concrete Works: "Plumbing System in Relation To Masonry" & "Plumbing Terms"mitch willyBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing Engineering: Design & EstimateDokumen24 halamanPlumbing Engineering: Design & EstimateGintokiBelum ada peringkat
- Term Paper - PlumbingDokumen5 halamanTerm Paper - PlumbingTristan Torres TanguidBelum ada peringkat
- PlumbingDokumen11 halamanPlumbingTeodoro Miguel Carlos IsraelBelum ada peringkat
- IndustrialArts Group5 PlumbingDokumen6 halamanIndustrialArts Group5 Plumbingsrain092Belum ada peringkat
- Tle q4 M1to3Dokumen12 halamanTle q4 M1to3Syrart's Digitally Art'sBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing Project1Dokumen11 halamanPlumbing Project1DANI AFROBelum ada peringkat
- Tap Water - WikipediaDokumen7 halamanTap Water - Wikipediaramthecharm_46098467Belum ada peringkat
- Plumbing: Plumbing Is The System of Pipes, Drains Fittings, Valves, Valve Assemblies, and Devices Installed in ADokumen1 halamanPlumbing: Plumbing Is The System of Pipes, Drains Fittings, Valves, Valve Assemblies, and Devices Installed in ALGCPBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Plumbing DefinitionDokumen18 halaman1 Plumbing DefinitionVikram DhabaleBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing System: Prepared By: Group 7Dokumen56 halamanPlumbing System: Prepared By: Group 7Glenn Midel Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Final Building UtiDokumen18 halamanFinal Building UtiJalenmoriena PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing SystemsDokumen7 halamanPlumbing SystemsManjunath HrmBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of PlumbingDokumen4 halamanProperties of PlumbingvicentiopaulBelum ada peringkat
- PlumbingDokumen13 halamanPlumbingJonathan Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- BuDokumen2 halamanBuMARVEL SHOWSBelum ada peringkat
- Ei 395Dokumen48 halamanEi 395Edward MagangaBelum ada peringkat
- Reaserch PaperDokumen5 halamanReaserch PaperJohn Michael PascuaBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Technology - Topic 4Dokumen14 halamanCivil Technology - Topic 4Zyla Balandra SorillaBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing Key AnswerDokumen7 halamanPlumbing Key AnswerStanley Scott ArroyoBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range ofDokumen1 halamanPlumbing Is Any System That Conveys Fluids For A Wide Range ofJoseph BelisarioBelum ada peringkat
- Project WorkDokumen41 halamanProject WorkOlogunleko Seun damiBelum ada peringkat
- Interm 1Dokumen4 halamanInterm 1Masroor AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Group A - Case Study - Building ServicesDokumen17 halamanGroup A - Case Study - Building ServicesEmmanuel AndenyangBelum ada peringkat
- Group A - Case Study - Building ServicesDokumen17 halamanGroup A - Case Study - Building ServicesEmmanuel AndenyangBelum ada peringkat
- History of SanitationDokumen11 halamanHistory of SanitationPooja K A NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing: Plumbing Is Any System That ConveysDokumen58 halamanPlumbing: Plumbing Is Any System That Conveysstallone21Belum ada peringkat
- PlumbingDokumen15 halamanPlumbingLoraine June MenesesBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1. Principles of Plumbing: Principle 1Dokumen4 halaman3.1. Principles of Plumbing: Principle 1M MBelum ada peringkat
- M1 - Plumbing FixturesDokumen19 halamanM1 - Plumbing FixturesazulaBelum ada peringkat
- Sewerage Systems & Drainage StructuresDokumen13 halamanSewerage Systems & Drainage StructuresErald EnriquezBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Plumbing Definition and HistoryDokumen19 halaman2 - Plumbing Definition and HistoryMark Danilo CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Reporting ME 01Dokumen84 halamanReporting ME 01Diane Fe CajaroBelum ada peringkat
- BTM 5 TOPIC 10 Drainage PipesDokumen14 halamanBTM 5 TOPIC 10 Drainage PipesJanetCablaoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 - The Plumbing ProfessionDokumen19 halamanModule 1 - The Plumbing Professionnicholas yeo chun ekBelum ada peringkat
- History of PlumbingDokumen45 halamanHistory of PlumbingWinnieBlancoAlabanJr.Belum ada peringkat
- Design of Water Supply SystemDokumen4 halamanDesign of Water Supply SystemVivek Thakur Sujanian100% (2)
- Lecture PlumbingDokumen215 halamanLecture PlumbingHope PilloraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 20 Plumbing Plans PDFDokumen24 halamanChapter 20 Plumbing Plans PDFmimahmoud50% (2)
- THESIS PLUMBING GROUP Part 2Dokumen5 halamanTHESIS PLUMBING GROUP Part 2jj magallanesBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On The Application of A Proper PlumbingDokumen25 halamanCase Study On The Application of A Proper PlumbingJeremie SaragaBelum ada peringkat
- WRE BlOCK DDokumen9 halamanWRE BlOCK DIcaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Utilities 2: Me-223 (Basic Mechanical Engineering)Dokumen57 halamanEngineering Utilities 2: Me-223 (Basic Mechanical Engineering)Jommel GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- University of Gondar Institute of Technology Department of CotmDokumen39 halamanUniversity of Gondar Institute of Technology Department of CotmYasichalew sefinehBelum ada peringkat
- Phe Microproject ReportDokumen20 halamanPhe Microproject ReportAbrar Khan100% (2)
- REVIEWER MPDokumen6 halamanREVIEWER MPAn-gela Dar-lene MangahisBelum ada peringkat
- BSD 7 LaicaDokumen11 halamanBSD 7 LaicaLaica AbadescoBelum ada peringkat
- Dr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaDokumen40 halamanDr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaID Pritesh ModiBelum ada peringkat
- Dr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, NizwaDokumen50 halamanDr.S.Sreedhar Reddy, Assistant Professor University of Nizwa, Nizwassreedharreddy0% (1)
- Final Plumbing 2Dokumen215 halamanFinal Plumbing 2Paolo Ocampo88% (8)
- s6 BMC Module 204Dokumen53 halamans6 BMC Module 204SureshKollatBelum ada peringkat
- ContinueDokumen2 halamanContinuegovind krishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Protection Symbols and AbreviationsDokumen1 halamanFire Protection Symbols and AbreviationsMr. ABelum ada peringkat
- ClapeDokumen320 halamanClapeJean-Noël LerouxBelum ada peringkat
- Enerpac RRH-Series, Hollow Plunger CylindersDokumen2 halamanEnerpac RRH-Series, Hollow Plunger CylinderstdzeienBelum ada peringkat
- BS 1600Dokumen2 halamanBS 1600visio2004Belum ada peringkat
- 8171 FLOMAX 15 316 SS Self Priming Centrifugal PumpDokumen11 halaman8171 FLOMAX 15 316 SS Self Priming Centrifugal PumprianandiyahooBelum ada peringkat
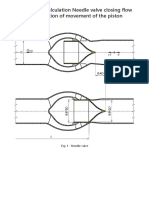
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The PistonDokumen23 halamanHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The Pistonmet-calcBelum ada peringkat
- Project Ruby: As Built DrawingDokumen1 halamanProject Ruby: As Built DrawingTôn Huỳnh ĐoànBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Circuit Design and AnalysisDokumen10 halamanHydraulic Circuit Design and Analysisshreya malviyaBelum ada peringkat
- PDF To Cad PDFDokumen32 halamanPDF To Cad PDFKyle ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- Flow Control Valves: Figure 4A.1 Symbol For Flow Control Valves One Way Flow Control ValveDokumen4 halamanFlow Control Valves: Figure 4A.1 Symbol For Flow Control Valves One Way Flow Control ValveKhaled MahranBelum ada peringkat
- Solenoid Valve Piping PC200-5Dokumen4 halamanSolenoid Valve Piping PC200-5Charlene DiocadizBelum ada peringkat
- 50 Question Related To ValvesDokumen24 halaman50 Question Related To ValvesNjat HakimBelum ada peringkat
- Total Pack SprinklerDokumen54 halamanTotal Pack SprinklerEdgar FloresBelum ada peringkat
- WFA Hose Fittings PDFDokumen46 halamanWFA Hose Fittings PDFjoebrazBelum ada peringkat
- Web Catalogue Maximator Valves Fittings and Tubings 2013Dokumen112 halamanWeb Catalogue Maximator Valves Fittings and Tubings 2013pmmparanaBelum ada peringkat
- New Sheet - CorrectedDokumen19 halamanNew Sheet - CorrectedklashincoviskyBelum ada peringkat
- GNFC - Cause and Effect DiagramDokumen5 halamanGNFC - Cause and Effect DiagramRaymond Clark100% (1)
- Data and Specifications: HMR Regulated MotorsDokumen21 halamanData and Specifications: HMR Regulated MotorsBeniamin KowollBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 - Centrifugal PumpDokumen104 halamanLecture 5 - Centrifugal Pumphasan bishBelum ada peringkat
- ValvesDokumen44 halamanValvesأحمد محمد قدريBelum ada peringkat
- Import Items TemplateDokumen15 halamanImport Items TemplateTech AkshatBelum ada peringkat
- Thuy Luc Drd100-200Dokumen27 halamanThuy Luc Drd100-200ANH LÊBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Sprinkler System NFPA 13 Plan Review ChecklistDokumen10 halamanFire Sprinkler System NFPA 13 Plan Review ChecklistTanveer Aziz100% (2)
- Singer PRV ManualDokumen3 halamanSinger PRV ManualAdityaBelum ada peringkat
- New Price List CPVC 2021Dokumen2 halamanNew Price List CPVC 2021Yash ShanishvaraBelum ada peringkat
- SMC Hidrolic No Quantity Designation SerialDokumen2 halamanSMC Hidrolic No Quantity Designation SerialAnnysa UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Pump Design Excel SheetDokumen5 halamanPump Design Excel SheetAkshay AdarshBelum ada peringkat