Pengubah Rintangan
Diunggah oleh
Nobiah SaharJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pengubah Rintangan
Diunggah oleh
Nobiah SaharHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1.
0 PENGENALAN
Transformer ialah sebuah alat yang digunakan untuk menaikkan atau merendahkan
voltan bekalan a.c mengikut berkurangan atau bertambahnya arus.
Transformer merupakan peranti menukarkan nilai voltan dan bukan peranti yang
menukarkan tenaga elektrik kepada tenaga yang lain seperti yang berlaku dalam
penjana atau motor.
Ianya berkeupayaan mengubah nilai arus ulang alik dari rendah kepada nilai tinggi
ataupun sebaliknya dan juga boleh membalikkan fasa.
Transformer di sambungkan kepada bekalan a.c sebab ia bergantung kepada
perubahan fluks pada d.c tiada perubahan urat daya untuk menghasilkan aruhan
saling.
2.0 PENGUBAH : TRANSFORMER
3.0 BAHAGIAN-BAHAGIAN PENGUBAH
4.0 PRINSIP ASAS KENDALIAN PENGUBAH
TRANSFORMERTakrif
Pengubah ialah alat elektrik yang boleh memindahkan tenaga elektrik dari
satu litar kepada satu ataulebih litar yang lain tanpa sebarang bahagian yang
bergerak secara fizikal pada frekuensi masukandan keluaran yang sama
nilai.Pengubah boleh memindahkan nilai arus dan voltan yang berbeza dari
nilai asalnya dan hanyaberkendali pada voltan ulang-alik atau litar arus terus
yang mengalami perubahan nilai volta atau arus.
BINAAN ASAS
Sebuah pengubah hendaklah mengandungi tiga binaan iaitu teras belitan
dan penutup ataupembalut.!. Teras
"ibuat daripada lapisan-lapisan besi yang diapit bersama.
Terdapat berbagai jenis tetapi umumnya berbentuk tingkap dan kelompong.
Teras merupakan faktor penting bagi menguatkan fliks magnet yang
dihasilkan.
Teras dibuat berlapis-lapis agar kehilangan arus pusar dapat dikurangkan di
dalam terastersebut.#. $elitan
Terbahagi kepada dua iaitu belitan utama dan belitan sekunder
$elitan utama disambungkan ke bekalan masuk sementara belitan sekunder
disambungkanke bekalan keluar. "ari sinilah sama ada nilai voltan atau arus
pengubah itu diambil selepasperpindahannya.
Penambahan atau pengurangan bilangan belitan sekunder dapat memberikan
nilai voltanatau arus yang lebih atau kurang daripada nilai bekalan yang
diberikan.
$elitan dililit secara lapisan sand%ich atau sepusar atau berasingan untuk
mengelakkandaripada kebocoran fliks di samping mengeluarkan fluks yang
berguna.&. Penutup
'enjadi pembalut dan berfungsi untuk menyejukkan pengubah.
(adangkala di abaikan jika penyejukan pengubah tidak diperlikan.
KENDALIAN ASAS
)pabila bekalan arus ulang-alik diberikan pada belitan utama fluks akan
%ujud di sekeliling belitanutama dan aruhan diri akan terhasil pada belitan
itu.*luks yang %ujud akan berpindah ke belitan sekunder melaui teras
pengubah untuk menghasilkanaruhan saling pada belitan sekunder
pula.)pabila keadaan ini berlaku dan jika kehilangan-kehilangan dalam
pengubah diabaikan maka voltanaruhan akan terhasil pada belitan
sekunder.+oltan utama dan sekunder adalah berkadar terus dengan bilangan
belitan teras dan belitan teraspula berkadar songsang dengan arus.
5.0 JENIS-JENIS PENGUBAH
ENIS-JENIS ALATUBAH
Alatubah Jenis Penuruni (Step Down Transforer!
"igunakan untuk menurunkan ,mengurangkan- nilai keluaran voltan ,selalunya atas
alasan keselamatan-
Alatubah Jenis Penai" (Step Up Transforer!
"igunakan untuk menaikkan nilai keluaran voltan. .ontohnya bekalan elektrik yang
dihasilkan oleh Stesen /anakuasa 0lektrik dinaikkan untuk tujuan penghantaran dan
pengagihan pada Sistem 1rid 2asional.
Alatubah Peralatan (Instruent Transforer!
"igunakan di dalam sektor industri dan komersil di mana nilai arus dan voltan yang besar
boleh diukur oleh peralatan elektrik dan elektronik yang berskala kecil.
Alatubah Arus (#urrent Transforer! $ #T
"igunakan apabila sejumlah arus yang besar disambungkan kepada lilitan utama
,primary %inding- sesebuah alatubah dan meter pengukur arus ,ammeter- disambungkan
pada lilitan sekunder ,secondary %inding-. )mmeter ini di tatah ,calibrated- untuk
mengambil kira nisbah bilangan lilitan di mana )mmeter akan memaparkan ,displayed-
jumlah sebenar arus yang digunakan oleh beban elektrik %alaupun )mmeter tersebut
hanya menggunakan nisbah kecil arus sebenar tersebut.
Alatubah %oltan (%olta&e Transforer! $ %T
"igunakan apabila bekalan voltan utama disambung kepada lilitan utama ,primary
%inding- sesebuah alatubah dan meter pengukur voltan ,+oltmeter- disambungkan pada
lilitan sekunder ,secondary %inding-. +oltmeter ini di tatah ,calibrated- untuk mengambil
kira nisbah bilangan lilitan di mana +oltmeter akan memaparkan ,displayed- jumlah
sebenar voltan yang digunakan oleh beban elektrik %alaupun +oltmeter tersebut hanya
menggunakan nisbah kecil voltan sebenar tersebut.
Alatubah Berasin&an %oltan Lapau 'en(ah (Separate( E)tra Low
%olta&e Transforer! $ SEL%
)pabila lilitan utama ,primary %inding- dan lilitan sekunder ,secondary %inding- dilakukan
secara berganda ,double %ound- dan di asingkan sambungan pembumian maka
keluaran voltan tersebut adalah terhasil secara berasingan .
)latubah jenis S03+ ini kebiasannya digunakan untuk tujuan keselamatan khusus
peralatan elektrik kecil,contoh 4 pencukur elektrik yang menggunakan !!5+ mesin kecil
pemutar skru- dengan mengambikira kadar kelembapan percikan air Inde6
Perlindungan ,IP- dan ruang kerja berhabuk di tapak pembinaan.
Ianya mempunyai pelbagai saiz dan rupa bentuk mengikut kesesuaian dan kegunaannya.
Binaan asas pengubah terdiri dari dua bahagian iaitu gelong utama (primer) dan gelong kedua (se
kunder) dan dipisahkan oleh teras yang terdiri daripada:-
Pengubah teras besi
Pengubah teras udara
Pengubah bertep tengah
T!B"#"$I %P"&" ' (TI$")
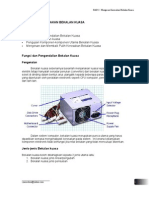
Pengubah kuasa
Pengubah audio
Pengubah !(
Pengubah kuasa
&ireka untuk menangani masalah pengeluaran dan pengagihan kuasa sama
ada untuk bentuk menaik atau menurun .
&igunakan dalam radio) komputer dan sebagainya.
Pengubah *oltan tinggi mempunyai saiz yang besar dan sebaliknya
a. Pengubah peninggi
b. Pengubah Penurun
+. Pengubah Pengasingan
d. Pengubah "uto
Pengubah "udio
Pengubah audio digunakan dalam peralatan radio atau didalam peralatan-peralatan lain
yang mengunakan system suara.
,aiznya agak ke+il dan menggunakan teras besi.
Ber-ungsi men.odohkan isyarat audio ke pembesar suara.
Pengubah !-
Pengubah !( digunakan dalam bahagian penghantaran dan penerimaan -rekuensi radio.
Biasanya digunakan untuk menala atau mendapatkan satu-satu nilai -rekuensi.
Teras yang digunakan sama ada teras -errite atau teras udara.
6.0 KIRAAN ASAS PENGUBAH
78'8S )S)S 030(T7I( (8)S)
7umus asas elektrik kuasa akan digunakan secara meluas dalam bidang elektrik kuasa.
Tak kira tugas anda sebagai 0ngineer .hargeman Technician atau Pengurus perlu
mahir dengan kiraan kuasa.
Secara asasnya kuasa terbahagi kepada & jenis berdasarkan segi tiga kuasa ,po%er
triangle-.
Sudut antara +) dan 9 dipanggil cos :. Sudut ini juga dipanggil faktor kuasa ,Po%er
factor pf-. *aktor kuasa yang ditetapkan oleh T2$ adalah tidak kurang dari 5.; jika
kurang penalti akan dikennakan.
+oltan ,+- yang dibekalkan oleh T2$ adalah tetap< untuk pengiraan< satu fasa = #>5+
dan tiga fasa = >!?+
2ilai voltan ini hanya akan berubah jika T2$ kata nak ubah.
Untuk tiga fasa:
(uasa ,+)- = @& 6 )rus ,I- 6 +oltan ,+-
atau kuasa ,+)- = @& 6 I 6 +
= !.A&# 6 I 6 >!?
(uasa ,9att- = @& 6 )rus ,I- 6 +oltan ,+- 6 pf
atau kuasa ,9- = @& 6 I 6 + 6 pf
atau sama dengan kuasa ,9- = +) 6 pf
Tetapi masa bila kita nak guna +) bila masa nak guna 9B
+) ini boleh dianggap maksimum kuasa 9 adalah kuasa sebenar yang kita guna.
A.5 +) banyak digunakan untuk mengungkap nilai kuasa sesebuah 1enset atau
8PS.
;.5 .ontohnya jika sebuah genset berkapasiti !55(+) dan faktor kuasa 5.;? maka
kuasa ,9- adalah !55(+) 6 pf = ;?(9. $ermaksud %alaupun kekuatan kapasiti
maksimum 1enset adalah !55(+) tetapi kita tidak boleh menggunakan
semaksimumnya bagi mengelakkan kerosakan. "an jika terlebih maka faktor
kuasa juga terlebih dan penalti akan dikenakan.
Pengubah mempunyai belitan primer dan belitan sekunder. Nisbah bilangan belitan primer
kepada bilangan belitan sekunder adalah n!"#$ %%&#n '(n)*"#$.
Nisbah voltan berkadaran kepada voltan teraruh di lilitan primer kepada lilitan sekunder.
Apabila jumlah lilitan sekunder sedikit dibandingkan dengan lilitan primer, voltan di sekunder
lebih rendah dari voltan di primer. Voltan sekunder boleh dikira dengan.
Contoh :
Nisbah lilitan transformer =
Ns
Np
Ns
Np
Vs
Vp
=
Vp
Np
Ns
Vs =
Rajah 4.3 : Pengubah Tap Tengah
Rajah 4.2 : Transformer
Satu pengubah dengan nisbah lilitan 4: dibekalkan dengan voltan !4" V #"$%. &irakan
voltan sekundernya.
Penyelesaian :
+.0 PENGUJIAN TRANSFORMER
+.1 O'(n An, S$-.& /.0*& T(!& O1 T.#n!1-.2(.
D. Pengujian Transistor
Pada dasarnya transistor merupakan dua dioda yang dipertemukan, sehingga cara pengujian transistor
hampir sama dengan pengujian dioda. Pengujian transistor ini dibedakan menjadi dua, yaitu jenis
NPN dan jenis PNP. Berikut ini adalah tabel yang merangkumkan hasil pengujian transistor yang
dinyatakan dalam keadaan baik.
NO
TRANSSTOR
NPN PNP
!AB"# $O#O! %AR&'
'&#T'"T"R
!AB"# $O#O! %AR&'
'&#T'"T"R
POST( N")AT( POST( N")AT(
Vs = 1 x 24V
4
= ! V
Vs = x Vp
*. B $ T+A!
B"R)"RA!
B $ B"R)"RA!
,. B " T+A!
B"R)"RA!
B " B"R)"RA!
-. $ B B"R)"RA! $ B T+A!
B"R)"RA!
.. " B B"R)"RA! " B T+A!
B"R)"RA!
/. $ " T+A!
B"R)"RA!
$ " T+A!
B"R)"RA!
0. " $ T+A!
B"R)"RA!
" $ T+A!
B"R)"RA!
Adapun langkah1langkah pengujian transistor NPN adalah 2
*. 'enyiapkan alat dan bahan yang dibutuhkan.
,. 'engarahkan saklar jangkah pada posisi ohm, contohnya pada posisi 3*k.
-. 'enempelkan colok hitam pada kaki basis 4B5 dan colok merah pada kaki emitor 4"5. Apabila jarum
penunjuk bergerak maka transistor dinyatakan baik. Selanjutnya memindahkan colok merah pada kaki
kolektor 4$5, apabila jarum penunjuk bergerak maka transistor juga dinyatakan dalam keadaan baik.
.. Selanjutnya apabila pengujian dibalik, colok merah pada kaki basis, sedangkan kaki emitor dan kaki
kolektor dihubungkan dengan colok itam secara bergantian, maka jika jarum penunjuk bergerak,
transistor dinyatakan rsak, mungkin bocor.
/. 'engembalikan perlengkapan pengujian pada tempat semula.
Sedangkan langkah1langkah dalam menguji transistor PNP adalah 2
*. 'enyiapkan alat dan bahan yang dibutuhkan.
,. 'engarahkan saklar jangkah pada posisi ohm, contohnya pada posisi 3*k.
-. 'enempelkan colok merah pada kaki basis 4B5 dan colok hitam pada kaki emitor 4"5. Bila jarum
bergerak maka transistor dinyatakan baik.
.. Setelah itu memindahkan colok hitam pada kaki kolektor 4$5. %ika jarum meter bergerak, maka
transistor dinyatakan baik. Apabila dalam pengujian jarum meter tidak bergerak sama sekali, maka
transistor dinyatakan rusak 4mungkin putus5.
/. !emudian, jika pengujian dibalik, yaitu colok hitam pada kaki basis, sedangkan kaki emitor dan
kolektor dihubungkan dengan colok merahsecara bergantian, maka bila jarum penunjuk bergerak,
transistor tersebut dinyatakan rusak. Apabila jaum pennjuk tersebt bergerak menunjukkan nilai ohm
yang rendah, maka dapat disimpulkan transistor tersebut bocor.
0. 'engembalikan perlengkapan pengujian pada tempat semula.
!erusakan1kerusakan yang sering terjadi pada sebuah transistor adalah 2
*. Adanya pemutusan hubungan dari rangkaian elektronik.
,. Terjadinya konsleting ata hubungan singkat antara elektroda1elektroda transistor.
-. Terjadi kebocoran diantara elektroda1elektroda transistor.
Adapun penyebab terjadinya kerusakan pada sebuah transistor adalah 2
*. Penanganan yang tidak tepat saat pemasangan pada rangkaian.
,. Transistor terlalu panas karena suhnya melebihi batas maksimumnya. &ntuk transistor yang terbuat
dai bahan germanium, suhu maksimumnya 67/8$, sedangkan transistor silicon suhu maksimumnya
mencapai 6*/98$.
-. !esalahan Pengkuran.
.. Pemasangan yang salah pada rangkaian.
10.0 SISTEM PENGIRAAN TRANSFORMER 3TRANSFORMER /OOLING
S4STEM5
11.0 AUTO TRANSFORMER
12.0 3 PHASE TRNSFORMER
3 Phase Transformers
To Buy - Phase Trans:ormers
;e Recommend T"'$o Brand.
$all *1/*91.<91,*=7
;eb #ink2 - Phase Trans:ormers
3 Phase Electrical Power Transformer
) & phase transformer there is a three-legged iron core as sho%n belo%. 0ach leg has a respective
primary and secondary %inding.
'ost po%er is distributed in the form of three-phase ).. Therefore before proceeding any further you
should understand %hat is meant by & phase po%er. $asically the po%er company generators
produce electricity by rotating ,&- coils or %indings through a magnetic field %ithin the generator .
These coils or %indings are spaced !#5 degrees apart. )s they rotate through the magnetic field they
generate po%er %hich is then sent out on three ,&- lines as in three-phase po%er. 3 phase
transformers must have ,&- coils or %indings connected in the proper seCuence in order to match
the incoming po%er and therefore transform the po%er company voltage to the level of voltage %e
need and maintain the proper phasing or polarity.
3 Phase Power Is More Efficient Than Single Phase
Three phase electricity po%ers large industrial loads more efficiently than single-phase electricity.
9hen single-phase electricity is needed It is available bet%een any t%o phases of a three-phase
system or in some systems bet%een one of the phases and ground. $y the use of three conductors
a & phase system can provide !A&D more po%er than the t%o conductors of a single-phase system.
Three-phase po%er allo%s heavy duty industrial eCuipment to operate more smoothly and efficiently. &
phase po%er can be transmitted over long distances %ith smaller conductor size.
Also read about - phase isolation trans:ormers here. *or an e6cellent source for these all
transformer types check out T0'.o - phase trans:ormers. Er check %ith solation Trans:ormer
Sales for - phase isolation trans:ormers. These t%o companies manufacture some of the most
recognized high Cuality & phase transformers available today.
In a three-phase transformer there is a three-legged iron core as sho%n belo%. 0ach leg has a
respective primary and secondary %inding.
The three primary %indings ,P! P# P&- %ill be connected at the factory to provide the proper
seCuence ,or correct polarity- reCuired and %ill be in a configuration kno%n as "elta. The three
secondary %indings ,S! S# S&- %ill also be connected at the factory to provide the proper seCuence
,or correct polarity- reCuired. Fo%ever the secondary %indings depending on our voltage
reCuirements %ill be in either B"eltaB or a B9yeB configuration.
3 Phase Transformer Delta and We !onnections
n a - phase trans:ormer, there is a three1legged iron core as sho>n belo>. "ach leg has
a respecti?e primary and secondary >inding.
3 Phase Transformer Winding !om"ination
)s can be seen the three-phase transformer actually has G %indings ,or coils- & primary and &
secondary. These G %indings %ill be pre-connected at the factory in one of t%o configurations4
.onfiguration !. Three primary 9indings in "elta and Three Secondary 9indings in 9ye
Note: These are the designations %hich are marked on the leads or terminal boards provided for
customer connections and they %ill be located in the transformer %iring compartment.
In both single and 3 phase transformers the high voltage terminals are designated %ith an HhI and
the lo% voltage %ith an HJI
.onfiguration #. Three Primary 9indings in "elta and Three Secondary 9indings in "elta
Note4 These are the designations %hich are marked on the leads or terminal boards provided for the
customer connections and they %ill be located in the transforming %iring compartment.
In both single and three-phase transformers the high voltage terminals are designated %ith an HFI
and the lo% voltage %ith an HJI.
3 Phase Transformer #oltage in Delta and We !onnections
+i::erent brands o: 3 phase transformers handle the >indings in di::erent manners. )ll
*ederal Pacific & phase transformers have their primary %indings pre-connected in a "elta
configuration. Therefore %hen connected to a three-phase source each primary %inding %ill have the
same voltage across it.
For Exam!e: >;5+ & Phase Source
If the secondary %indings are also connected "elta then they have eCual voltages across each
%inding. Ef course this voltage %ill be either higher or lo%er than the primary depending upon the
Hturns ratioI.
>;5+ Primary Source %ith #>5+ Secondary Eutput K #L! Turns 7atio ,"elta-"elta-
Note: it is important to note that three-phase transformers %ith "elta-connected primaries %hen
connected to a &5 >-%ire supply system do not utilize the >th %ire or neutral.
9ye4 If the secondary is not connected in "elta it %ill be pre-connected at the factory as a 9ye
secondary. )ll 9ye connections provide t%o voltages due to the common point or neutral connection.
) typical rating %ould be #5;L!#5+. The #5;M indicates the voltage bet%een phases of the secondary
%indings.
For Exam!e:
The !#5 volt portion indicates the voltage from each phase to the common point or neutral
For Exam!e:
This Phase-to-2eutral voltage in a 9ye is al%ays eCual to the Phase-to-Phase voltage divided by
For Exam!e:
Therefore a 3 phase transformer %ith its secondary connected in a 9ye configuration for #5;ML!#5
volts %ill have the available4 .ommon Three-Phased Transformer +oltage .ombinations
13.0 /URRENT TRANSFORMER
"en#a$u!uan%
! . N . u r r e n t t r a n s f o r m e r O , . T - a t a u d i k e n a l i s e b
a g a i p e n g u b a h a r u s b a n y a k digunakan dalam litar pengukuran
dan perlindungan elektrik di industri.*ungsi utamanya adalah mengubah nilai arus
primer kepada nilai arus sekunder iaitu nilai yang mampu diukur oleh jangka dalam
keadaan selamat."i d a l a m l i t a r u t a ma mu n g k i n arus yang mengalir ialah
!555 )atau #555 ) atau mungkin
lebiht i nggi l agi . Ti ada j angka yangber kebol ehan mengukur t er usnilai
yang sebegitu tinggi tanpa mengunakan kaedah pengubahan arus."alam perkara ini
pengubah arus mestilah digunakan bagi merendahkan nilai
ygs e l a ma t d i s a mp i n g i t u j u g a l i t a r p e n d a %a i a n s e k u n d e r , Pe r
me t e r a n d a n Perlindungan- akan menjadi lebih kecil saiz
pengalirnya.)r us maksi ma sekunder adal ah 5 - ? ampi ar bagi kebanya
kan si st em 3+manakala 5 -! ampiar bagi sistem
FT.# . ( e n d a l i a n N . T O a d a l a h b e r b e z a d a r i a l a t
u b a h k u a s a % a l a u p u n p r i n s i p kendaliannya adalah sama.
3ilitan penduanya mengandungi belitan yang banyakdan disambungkan kepada
ammeter.)mmeter yang menggunakan N.TO ini telah dipia%aikan samada
menggunakankadaran !) atau ?). )mmeter dipilih berdasarkan kepada nilai
pendua N.TO.
Pengiraan nisbah N.TO adalah seperti berikut...+p IsPPP = PPPPP +s
Ip3 i l i t a n p r i m e r d i l i l i t h a n y a d e n g a n b e b e r a p a l i l i t a n s
a h a j a a t a u p u n biasanya di%akili bus bar sebagai lilitanprimer. "alam
keadaan ini arus utamaadal ah mengal i r mel al ui bus bar danmelalui
teras
N.TO.& . . o n t o h . Satu )mmeter mempunyai skil p e
s o n g a n p e n u h i a l a h ? ) d i gunakan mengukur arus utama#55).
/i ka lilitan utamaLPrimer sebanyak # belitan ki rakan jumlah
bel itansekunder yang diperlukan bagi memberikan nilai skil pesongan penuh.2p
IsPPP = PPPPP 2s Ip2p 6 Ip2s = PPPPPPPPP Is
Zam (transformer)
&
2s= B2p= #T)
.urrent Transformer $asics
T$e &urrent Transformer ' &%T% () is a t*e of +instrument
transformer, t$at is #esigne# to ro#u-e an a!ternating
-urrent in its se-on#ar* .in#ing .$i-$ is roortiona! to t$e
-urrent /eing measure# in its rimar*%
Current transformers reduce high voltage currents to a much
lo%er value and provide a convenient %ay of safely monitoring
the actual electrical current flo%ing in an ). transmission line
using a standard ammeter. The principal of operation of a current
transformer is no different from that of an ordinary transformer.
T*i-a! &urrent Transformer
8nlike the voltage or Po%er Transformer looked at previously the
current transformer consists of only one or very fe% turns as its
primary %inding. This primary %inding can be of either a single
flat turn a coil of heavy duty %ire %rapped around the core or just
a conductor or bus bar placed through a central hole as sho%n.
"ue to this type of arrangement the current transformer is often
referred too as a Hseries transformerI as the primary %inding
%hich never has more than a very fe% turns is in series %ith the
current carrying conductor.
The secondary %inding may have a large number of coil turns
%ound on a laminated core of lo%-loss magnetic material %hich
has a large cross-sectional area so that the magnetic flu6 density
is lo% using much smaller cross-sectional area %ire depending
upon ho% much the current must be stepped do%n. This
secondary %inding is usually rated at a standard ! )mpere or ?
)mperes.
There are three basic types of current transformers4 H%oundI
HtoroidalI and HbarI.
Q 9ound current transformers R The transformers
primary %inding is physically connected in series %ith the
conductor that carries the measured current flo%ing in the
circuit. The magnitude of the secondary current is
dependent on the turns ratio of the transformer.
Q Toroidal current transformers R These do not contain
a primary %inding. Instead the line that carries the current
flo%ing in the net%ork is threaded through a %indo% or
hole in the toroidal transformer. Some current transformers
have a Hsplit coreI %hich allo%s it to be opened installed
and closed %ithout disconnecting the circuit to %hich they
are attached.
Q $ar-type current transformers R This type of current
transformer uses the actual cable or bus-bar of the main
circuit as the primary %inding %hich is eCuivalent to a
single turn. They are fully insulated from the high operating
voltage of the system and are usually bolted to the current
carrying device.
&urrent transformers can reduce or Hstep-do%nI current levels
from thousands of amperes do%n to a standard output of a
kno%n ratio to either ? )mps or ! )mp for normal operation.
Thus small and accurate instruments and control devices can be
used %ith .TOs because they are insulated a%ay from any high-
voltage po%er lines. There are a variety of metering applications
and uses for current transformers such as %ith %attmeterOs
po%er factor meters %att-hour meters protective relays or as
trip coils in magnetic circuit breakers or '.$Os.
.urrent Transformer
1enerally current transformers and ammeters are used together
as a matched pair in %hich the design of the current transformer
is such as to provide a ma6imum secondary current
corresponding to a full-scale deflection on the ammeter. In most
current transformers an appro6imate inverse turns ratio e6ists
bet%een the t%o currents in the primary and secondary %indings.
This is %hy calibration of the .T is generally for a specific type of
ammeter.
*or most current transformers the primary and secondary
currents are e6pressed as a ratio such as !55L?. This means that
%hen !55 )mps is flo%ing in the primary %inding it %ill result in ?
)mps flo%ing in the secondary %inding. $y increasing the
number of secondary %indings 2# the secondary current can be
made much smaller than the current in the primary circuit being
measured. In other %ords as 2# increases I# goes do%n by a
proportional amount.
9e kno% from our tutorial on double %ound voltage transformers
that its turns ratio is eCual to4
from %hich %e get4
)s the primary usually consists of one or t%o turns %hilst the
secondary can have several hundred turns the ratio bet%een the
primary and secondary can be Cuite large. *or e6ample assume
that the current rating of the primary %inding is !55). The
secondary %inding has the standard rating of ?). Then the ratio
bet%een the primary and the secondary currents is !55)-to-?)
or #54!. In other %ords the primary current is #5 times greater
than the secondary current.
It should be noted ho%ever that a current transformer rated as
!55L? is not the same as one rated as #5L! or subdivisions of
!55L?. This is because the ratio of !55L? e6presses the
HinputLoutput current ratingI and not the actual ratio of the primary
to the secondary currents. )lso note that the number of turns and
the current in the primary and secondary %indings are related by
an inverse proportion.
$ut relatively large changes in a current transformers turns ratio
can be achieved by modifying the primary turns through the .TOs
%indo% %here one primary turn is eCual to one pass and more
than one pass through the %indo% results in the electrical ratio
being modified.
So for e6ample a current transformer %ith a relationship of say
&55L?) can be converted to another of !?5L?) or even !55L?) by
passing the main primary conductor through its interior %indo%
t%o or three times as sho%n. This allo%s a higher value current
transformer to provide the ma6imum output current for the
ammeter %hen used on smaller primary current lines.
.urrent Transformer Primary Turns 7atio
.urrent Transformer 06ample 2o!
) bar-type current transformer %hich has ! turn on its primary
and !G5 turns on its secondary is to be used %ith a standard
range of ammeters that have an internal resistance of 5.#SOs. The
ammeter is reCuired to give a full scale deflection %hen the
primary current is ;55 )mps. .alculate the ma6imum secondary
current and secondary voltage across the ammeter.
Secondary .urrent4
+oltage across )mmeter4
9e can see above that since the secondary of the current
transformer is connected across the ammeter %hich has a very
small resistance the voltage drop across the secondary %inding
is only !.5 volts at full primary current. If the ammeter is removed
the secondary %inding becomes open-circuited and the
transformer acts as a step-up transformer resulting in a very high
voltage eCual to the ratio of4 +p,2sL2p- being developed across
the secondary %inding.
So for e6ample assume our current transformer from above is
connected to a >;5 volt three-phase po%er line. Therefore4
This AG.;k+ is %hy a current transformer should never be left
open-circuited or operated %ith no-load attached %hen the main
primary current is flo%ing through it. If the ammeter is to be
removed a short-circuit should be placed across the secondary
terminals first to eliminate the risk of shock.
This is because %hen the secondary is open-circuited the iron
core of the autotransformer operates at a high degree of
saturation %hich produces an abnormally large secondary
voltage and in our simple e6ample above this %as calculated at
AG.;k+T. This high secondary voltage could damage the insulation
or cause electric shock if the .TOs terminals are accidentally
touched.
Fandheld .urrent Transformers
There are many specialized types of current transformers no%
available. ) popular and portable type %hich can be used to
measure circuit loading are called Hclamp metersI as sho%n.
.lamp meters open and close around a current carrying
conductor and measure its current by determining the magnetic
field around it providing a Cuick measurement reading usually on
a digital display %ithout disconnecting or opening the circuit.
)s %ell as the handheld clamp type .T split core current
transformers are available %hich has one end removable so that
the load conductor or bus bar does not have to be disconnected
to install it. These are available for measuring currents from !55
up to ?555 amps %ith sCuare %indo% sizes from !U to over !#U
,#?-to-&55mm-.
Transformer "esign Principles4 9ith )pplications to .ore-*orm Po%er
Transformers Second 0dition
List "ri-e4 .lick to see...
&urrent "ri-e4 .lick to see...
Price "isclaimer
Then to summarise the &urrent Transformer) '&T( is a type of
instrument transformer used to convert a primary current into a
secondary current through a magnetic medium. Its secondary
%inding then provides a much reduced current %hich can be used
for detecting overcurrent undercurrent peak current or average
current conditions.
) current transformers primary coil is al%ays connected in series
%ith the main conductor giving rise to it also being referred to as
a series transformer. The nominal secondary current is rated at
!) or ?) for ease of measurement. .onstruction can be one
single primary turn as in Toroidal "oughnut or $ar types or a
fe% %ound primary turns usually for lo% current ratios.
.urrent transformers are intended to be used as proportional
current devices. Therefore a current transformers secondary
%inding should never be operated into an open circuit just as a
voltage transformer should never be operated into a short circuit.
+ery high voltages %ill result from open circuiting the secondary
circuit of an energized .T so their terminals must be short-
circuited if the ammeter is to be removed or %hen a .T is not in
use before po%ering up the system.
In the ne6t tutorial about Transformers %e %ill look at %hat
happens %hen %e connect together three individual transformers
in a star or delta configuration to produce a larger po%er
transformer called a T$ree "$ase Transformer used to supply &-
phase supplies.
14.0 6OLTAGE TRANSFORMER
RUJUKAN
$&&':77888.!0.",.0-27,-07954649337T.#n!1-.2(.-A!#!
$&&':77(%(:&.:#%,#n#.0-n."%-)!'-&.0-2720137047.*2*!-#!#!-(%(:&.:-:*#!#.$&2%
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- KertasDokumen38 halamanKertasNoorhasnizam AzmiBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Transformer#Dokumen7 halaman01 Transformer#aimiza100% (1)
- Faktor Kepelbagaian 2Dokumen20 halamanFaktor Kepelbagaian 2ZULHILMIBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT8Dokumen72 halamanUNIT8noorazuBelum ada peringkat
- Cikgu Issey 2Dokumen27 halamanCikgu Issey 2Amelia Natasha100% (1)
- PenukardcdcDokumen12 halamanPenukardcdcimran_84Belum ada peringkat
- Aktiviti 2 Praktikal 6Dokumen9 halamanAktiviti 2 Praktikal 6Shee YingBelum ada peringkat
- En ZharifDokumen18 halamanEn ZharifQhalilah BashahBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer PDFDokumen2 halamanTransformer PDFElly Sayuti0% (1)
- Transistor Horizontal Jebol Terus Sering Terjadi Pada Kerusakan Televisi Yang Berjenis CRTDokumen9 halamanTransistor Horizontal Jebol Terus Sering Terjadi Pada Kerusakan Televisi Yang Berjenis CRTAlfin DahlanBelum ada peringkat
- Ete 7014 Power TransformerDokumen26 halamanEte 7014 Power Transformersyahadah98Belum ada peringkat
- Penatahan (Calibration)Dokumen22 halamanPenatahan (Calibration)Mohamad Syukri Abd Rahaman50% (10)
- TransformerDokumen77 halamanTransformerAhmad Jamil Tahir100% (3)
- 03 Standby AC GeneratorDokumen8 halaman03 Standby AC Generatoraimiza100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 (Asas Elektrik 1)Dokumen56 halamanCHAPTER 1 (Asas Elektrik 1)Noorfadhilah Binti KhairiBelum ada peringkat
- Menentukan Saiz KabelDokumen7 halamanMenentukan Saiz KabelAbdulIzzatSaroni80% (5)
- Elektrik - Kuasa Dan TenagaDokumen19 halamanElektrik - Kuasa Dan Tenagaaizuddin_zaihan100% (4)
- VoltmeterDokumen4 halamanVoltmeterTaufiq RabbaniBelum ada peringkat
- Penyegerakan Janakuasa Slot 1 - PengenalanDokumen32 halamanPenyegerakan Janakuasa Slot 1 - PengenalanAmirul Amran100% (1)
- Bab-10 Gangguan Tiga Fase SimetrisDokumen25 halamanBab-10 Gangguan Tiga Fase SimetrisMudarrisBelum ada peringkat
- Kuantiti Dan Unit ElektrikDokumen33 halamanKuantiti Dan Unit ElektrikJily ToomisBelum ada peringkat
- TranduserDokumen12 halamanTranduseranon-668182Belum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 - Power Supply - Bekalan KuasaDokumen17 halamanBab 4 - Power Supply - Bekalan KuasaMohd Syamsul Ariff94% (16)
- Lecture1 (Pengubah)Dokumen99 halamanLecture1 (Pengubah)Ramakrisnna Gunasegaran50% (2)
- Alat Ukur Dan Alat Uji MultimeterDokumen8 halamanAlat Ukur Dan Alat Uji MultimeterFakhrul RoziBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Ukuran Dan RalatDokumen22 halaman1-Ukuran Dan RalatLian Ai ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 9Dokumen12 halamanUnit 9Zhan RunZhi 詹润之Belum ada peringkat
- BAB 1 Pengenalan Kawalan Motor PDFDokumen35 halamanBAB 1 Pengenalan Kawalan Motor PDFAmeerul SalimBelum ada peringkat
- Penerangan Inductor N TransformerDokumen17 halamanPenerangan Inductor N TransformerHafiz ZukafleBelum ada peringkat
- Nota PengubahDokumen28 halamanNota PengubahMuhammad AfeefBelum ada peringkat
- Kawalan MotorDokumen11 halamanKawalan MotorAnonymous 4l98Wh6rBelum ada peringkat
- Bekalan Kuasa Arus Terus ATDokumen32 halamanBekalan Kuasa Arus Terus ATHisham Ayob100% (1)
- Bekalan KuasaDokumen2 halamanBekalan KuasaSyukri SreeBelum ada peringkat
- Litar Pengguna 1 FasaDokumen5 halamanLitar Pengguna 1 FasaSiti Haja'sBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 4 Alat PanduDokumen43 halamanBAB 4 Alat PanduZamrisharif100% (5)
- PENDAWAIAN ELEKTRIK Assignmet.Dokumen50 halamanPENDAWAIAN ELEKTRIK Assignmet.عزيزي أحمد نوردين100% (2)
- MODUL Elektrik Elektif T1Dokumen16 halamanMODUL Elektrik Elektif T1YenLing ChinBelum ada peringkat
- Asas ElektrikDokumen20 halamanAsas ElektrikAzliana Mohd TaibBelum ada peringkat
- Panduan MultimeterDokumen9 halamanPanduan MultimeterMuhd QemryBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5Dokumen32 halamanUnit 5syafikahlBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Bengkel ElektromekanikDokumen6 halamanLaporan Bengkel ElektromekanikHendraBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT5Dokumen31 halamanUNIT5Azlan Abd Hanib100% (1)
- Alat - Alat Pengukur ElektrikDokumen45 halamanAlat - Alat Pengukur ElektrikHelmi HalimBelum ada peringkat
- Nota ElektrikDokumen59 halamanNota ElektrikGeorge RaymondBelum ada peringkat
- 9a Asas Mesin Elektrik (Penjana)Dokumen43 halaman9a Asas Mesin Elektrik (Penjana)schaBelum ada peringkat
- TransformerDokumen1 halamanTransformerAiman HarithBelum ada peringkat
- Apakah Itu TransformerDokumen9 halamanApakah Itu TransformerZakiah Hayati100% (1)
- INDUKTANDokumen16 halamanINDUKTANMahayudin SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Pengasutan MotorDokumen11 halamanPengasutan MotorYogi Fathur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 5 - Komponen Pengendali ElektromagnetikDokumen28 halamanBAB 5 - Komponen Pengendali ElektromagnetikIrfan KristiawanBelum ada peringkat
- PMG JanakuasaDokumen10 halamanPMG JanakuasaMuhrif MaharoffBelum ada peringkat