Pathophysio Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Diunggah oleh
Ran Ma100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
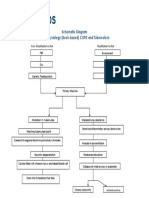
347 tayangan1 halamanChronic glomerulonephritis is caused by either unknown direct damage to the glomeruli or secondary causes like SLE or infection. This results in inflammation and fibrosis of the glomeruli, reducing the glomerular filtration rate and leading to renal failure. Symptoms include edema, hypertension, proteinuria, and decreased urine output as the kidneys fail to filter blood properly and retain fluids and salts. Treatment focuses on controlling hypertension with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, modifying diet, and fluid restrictions.
Deskripsi Asli:
CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS.
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniChronic glomerulonephritis is caused by either unknown direct damage to the glomeruli or secondary causes like SLE or infection. This results in inflammation and fibrosis of the glomeruli, reducing the glomerular filtration rate and leading to renal failure. Symptoms include edema, hypertension, proteinuria, and decreased urine output as the kidneys fail to filter blood properly and retain fluids and salts. Treatment focuses on controlling hypertension with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, modifying diet, and fluid restrictions.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
347 tayangan1 halamanPathophysio Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Diunggah oleh
Ran MaChronic glomerulonephritis is caused by either unknown direct damage to the glomeruli or secondary causes like SLE or infection. This results in inflammation and fibrosis of the glomeruli, reducing the glomerular filtration rate and leading to renal failure. Symptoms include edema, hypertension, proteinuria, and decreased urine output as the kidneys fail to filter blood properly and retain fluids and salts. Treatment focuses on controlling hypertension with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, modifying diet, and fluid restrictions.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
1
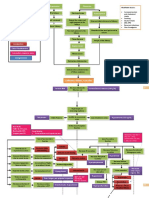
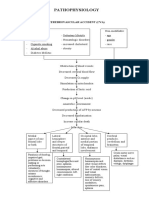
Pathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis
PRIMARY CAUSES
Unknown
Direct glomerular
damage
SECONDARY CAUSES
SLE, Good pastures,
Infection
Damage to the glomerular
membrane
Release of inflammatory
mediators
Lodging of antigen-antibody
complexes in the glomerular
membrane
Inflammation
Fibrosis, scarring, sclerosis
of the glomerulus
Decrease in glomerular
filtration rate
Renal failure Hyperpermeability of the
glomerular membrane
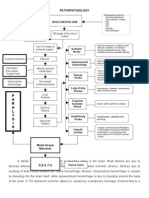
Decreased urinary output,
Edema, Hypertension
Sodium and water
retention
Increased urinary
frequency, proteinuria,
albuminuria, hematuria
Fatigue, difficulty of
breathing, anemia,
nausea and vomiting
Congestive heart failure,
Pulmonary edema
Dark frothy urine
Diuretics
Angiotensin Converting
Enzyme Inhibitors,
Amgiotensin II receprotr
blockers for hypertension
Diet modifications: low
salt, low fat, low protein
diet. Fluid restrictions as
advised
LEGEND:
Causes
Disease process
Reaction/compensation
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Treatment and management
Pain and
tenderness
on the back
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CKD - For Concept MappingDokumen7 halamanCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- CKD PathoDokumen5 halamanCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDokumen2 halamanPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Belum ada peringkat
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDokumen3 halaman"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisAprille Rose UrbanoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Renal FailureDokumen3 halamanChronic Renal FailureAura Salve Ildefonso AllasBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology CVDDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinBelum ada peringkat
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaBelum ada peringkat
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDokumen2 halamanEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageAlvin RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHCarly Beth Caparida LangerasBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Belum ada peringkat
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDokumen22 halamanLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoBelum ada peringkat
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDokumen3 halamanAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseDokumen15 halamanNon-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseWiljohn de la CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Qtsoi Concept MapDokumen5 halamanQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarBelum ada peringkat
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDokumen3 halamanHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial InfarctionSheana TmplBelum ada peringkat
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Uremic EncephalopathyDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of Uremic EncephalopathyKristen Leigh Mariano100% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF2 - RevisedDokumen1 halamanPathophysio CRF2 - Reviseddeborah malnegroBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Kidney DiseaseSTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- CVA PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Renal FailureDokumen3 halamanChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaBelum ada peringkat
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDokumen8 halamanSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanPathophysiologynitlihpBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Diseases PathophysiologyDokumen6 halamanRenal Diseases PathophysiologyBilly Gayados100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilBelum ada peringkat
- PatofkuDokumen3 halamanPatofkunisaaa88Belum ada peringkat
- Liver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Dokumen8 halamanLiver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoBelum ada peringkat
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Dokumen7 halamanStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFDokumen2 halamanBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFgailBelum ada peringkat
- Soapie Charting: Date/ Time/ ShiftDokumen2 halamanSoapie Charting: Date/ Time/ Shiftspain michaelisBelum ada peringkat
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableDokumen2 halamanV. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableMary Grace BanezBelum ada peringkat
- Goal Not MetDokumen4 halamanGoal Not MetAyaBasilioBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDokumen3 halamanChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDaniel GeduquioBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Dokumen3 halamanDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Dokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY PancreatitisDokumen1 halamanPATHOPHYSIOLOGY PancreatitisMicahEuranneCastillo-GoliBelum ada peringkat
- Liver CancerDokumen1 halamanLiver CancerTarantado67% (3)
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDokumen1 halamanSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaBelum ada peringkat
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Dokumen10 halamanSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Concept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDDokumen1 halamanConcept Map On CVA Bleed Left Thalamo-Ganglionic Bleed Patient Name: Mr. DGDBert Brian Bolido100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen36 halamanChronic Kidney Diseasejabir100% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDokumen54 halamanChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaBelum ada peringkat
- Jaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainDokumen7 halamanJaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorBelum ada peringkat
- Renal SystemDokumen20 halamanRenal SystemRahul DasBelum ada peringkat
- KidneyDokumen18 halamanKidneyRacha MougharbelBelum ada peringkat
- Anesthetic Concerns For The Patient With Renal and Hepatic DiseaseDokumen43 halamanAnesthetic Concerns For The Patient With Renal and Hepatic Diseasekamel6Belum ada peringkat
- T104 - TranscribeMe TR Handbook June 2017Dokumen18 halamanT104 - TranscribeMe TR Handbook June 2017Tuklu SenBelum ada peringkat
- TranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Dokumen24 halamanTranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Juan Zhao67% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaBelum ada peringkat
- Cranial Nerves Assessment FormDokumen3 halamanCranial Nerves Assessment FormCristina CenturionBelum ada peringkat
- TranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Dokumen24 halamanTranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Juan Zhao67% (6)
- Common Board Question1Dokumen2 halamanCommon Board Question1Ran MaBelum ada peringkat
- Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeDokumen2 halamanSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock SyndromeRan MaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma GuideDokumen4 halamanPharma GuidegudoloveBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Aspects of Nursing Definition of Terms Board of Registered NursingDokumen14 halamanLegal Aspects of Nursing Definition of Terms Board of Registered NursingAdrian FurigaoBelum ada peringkat
- Crisis and Crisis Intervention Quick FactsDokumen1 halamanCrisis and Crisis Intervention Quick FactsRan MaBelum ada peringkat
- Common Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsDokumen16 halamanCommon Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsWilliam Franz SyBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of ShockDokumen1 halamanClassification of ShockKaisun TeoBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Medicinal Plants Approved by The DOHDokumen4 halaman10 Medicinal Plants Approved by The DOHAlyssa Jane Gaitan LauBelum ada peringkat
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDokumen1 halamanPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerRan Ma73% (11)
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDokumen49 halamanCongestive Heart Failure PDFVerinice NañascaBelum ada peringkat
- IM SyllabusDokumen7 halamanIM Syllabusepah1925100% (1)
- Wikipedia - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (CHECKED)Dokumen7 halamanWikipedia - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (CHECKED)pixoguiasBelum ada peringkat
- TOFPA: A Surgical Approach To Tetralogy of Fallot With Pulmonary AtresiaDokumen24 halamanTOFPA: A Surgical Approach To Tetralogy of Fallot With Pulmonary AtresiaRedmond P. Burke MD100% (1)
- Mitral StenosisDokumen31 halamanMitral StenosisArtemisBelum ada peringkat
- MKSAP 16: Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment ..Dokumen3 halamanMKSAP 16: Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment ..ellokarioBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Medicine Report 2019Dokumen49 halamanDepartment of Medicine Report 2019Taylor LaframboiseBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Residen CardioDokumen13 halamanContoh Soal Residen CardioLusyAlwiBelum ada peringkat
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Pathophysiology, Nursing, Treatment, Symptoms Heart Failure Part 1Dokumen6 halamanCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) Pathophysiology, Nursing, Treatment, Symptoms Heart Failure Part 1ParallelBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Mitral Regurgitation and Aortic Regurgitation: Have Indications For Surgery Changed?Dokumen9 halamanChronic Mitral Regurgitation and Aortic Regurgitation: Have Indications For Surgery Changed?mamuyaBelum ada peringkat
- Alcapa FinalDokumen22 halamanAlcapa FinalCardiacCareCenterMCHBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg CompiledDokumen65 halamanEcg CompiledVstreamhdBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Treatment WorkflowsDokumen75 halamanStandard Treatment WorkflowsIndranil DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Quick Reference Chart PDFDokumen4 halamanEKG Quick Reference Chart PDFrodney subaranBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Benefits Enrollment Expert in Chicago IL Resume Paulette BarrettDokumen2 halamanEmployee Benefits Enrollment Expert in Chicago IL Resume Paulette BarrettPauletteBarrettBelum ada peringkat
- Chan, Johnson - TreatmentGuidelines PDFDokumen0 halamanChan, Johnson - TreatmentGuidelines PDFBogdan CarabasBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Heart attack-हृदय घात का इलाज-by Shri Rajiv DixitDokumen5 halamanTreatment of Heart attack-हृदय घात का इलाज-by Shri Rajiv Dixitvirendrak11100% (1)
- ECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookDokumen118 halamanECG Mastery Yellow Belt WorkbookOana Anghel100% (8)
- MR - Nagula Prashanth (Corpahcrya1711230377) Male 26 Years: This Document Holds The Written Radiology Report ForDokumen3 halamanMR - Nagula Prashanth (Corpahcrya1711230377) Male 26 Years: This Document Holds The Written Radiology Report Forp13607091Belum ada peringkat
- Ronco - Textbook of Cardiorenal Medicine 2021Dokumen381 halamanRonco - Textbook of Cardiorenal Medicine 2021Adiel OjedaBelum ada peringkat
- Dysrhythmias ChartDokumen6 halamanDysrhythmias Chartjkrix100% (1)
- Chapter 28: Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflammatory Cardiac DisordersDokumen19 halamanChapter 28: Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, and Inflammatory Cardiac DisordersBrian BileckyBelum ada peringkat
- Buku Panduan ACLS Perki Cetakan 2021 - Hal 11Dokumen1 halamanBuku Panduan ACLS Perki Cetakan 2021 - Hal 11yandriasBelum ada peringkat
- American Heart Association: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Written ExamsDokumen36 halamanAmerican Heart Association: Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Written ExamsAndrew Sefain56% (9)
- Pacienti 2020 1-220Dokumen28 halamanPacienti 2020 1-220crilala23Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Assignment 08 HEMODIALYSISDokumen1 halamanChemistry Assignment 08 HEMODIALYSISAxel FangBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Basics - NAVEENDokumen65 halamanEcg Basics - NAVEENNaveen MathieuBelum ada peringkat
- Peadiatric ECGDokumen54 halamanPeadiatric ECGshalini0580% (5)
- Congenital heart disease overviewDokumen8 halamanCongenital heart disease overviewgolagani praveenkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Test QUIZDokumen9 halamanMini Test QUIZAbdul RohimBelum ada peringkat