Assignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014
Diunggah oleh
Deepak KumarHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Assignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014
Diunggah oleh
Deepak KumarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MAE 311: Machines and Mechanisms I Spring 2014
Assignment #3 Due Date: 3/7/2014
Copyright 2014 Phillip M. Cormier and Jobaidur Khan
Problem 1 (25 Points)
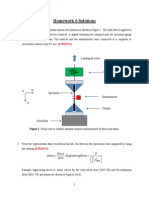
The steel eyebolt shown in Figure 1 is loaded with a force of 75 pounds. The bolt is formed from round
stock with a diameter of 0.25 inches, and has in inner bend radius of 0.5 inches in the eye and at the end
of the shank. Estimate the stress at the inner and outer surfaces of section B, where u = 30.
Figure 1: Problem 1 Diagram
Sol. d = 0.25 in, r
o
= 0.75 on, r
i
= 0.5 in,
From table 3-4, for circular cross-section, we get, R = 0.125 in, r
c
= 0.5 + 0.125 = 0.625 in
( ) ( )
in 618686 . 0
125 . 0 625 . 0 625 . 0 2
125 . 0
r r r 2
r
r
2 2
2
2 2
c c
2
n
=
=
=
in 006314 . 0 618686 . 0 625 . 0 r r e
n c
= = =
in 118686 . 0 5 . 0 618686 . 0 r r c
i n i
= = =
in 131314 . 0 618686 . 0 75 . 0 r r c
i o o
= = =
Cross-section area,
2
2
in 049087 . 0
4
d
A =
t
=
The angle u of the line of radius centers is,
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
+
= u
30
2
1
sin
R d R
2 d R
sin
1 1
Moment, ( ) ( ) in . lbf 44 . 23 30 Sin 2 25 . 0 5 . 0 75 Sin 2 d R F M = + = u + =
kpsi 7 . 18 psi 716 , 18
5 . 0 006314 . 0 049087 . 0
118686 . 0 44 . 23
049087 . 0
30 Sin 75
Aer
Mc
A
FSin
i
i
i
= =
= +
u
= o
psi k 5 . 12 psi 478 , 12
75 . 0 006314 . 0 049087 . 0
131314 . 0 44 . 23
049087 . 0
30 Sin 75
Aer
Mc
A
FSin
o
o
o
= =
=
u
= o
MAE 311: Machines and Mechanisms I Spring 2014
Assignment #3 Due Date: 3/7/2014
Copyright 2014 Phillip M. Cormier and Jobaidur Khan
Problem 2 (25 Points)
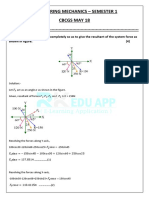
The latch spring shown in Figure 2 supports a load of 3 pounds. Given the noted dimensions, determine
the following:
a) Determine the stresses at the top and bottom of the beam, just before the bend.
b) Using curved beam theory, determine the inner and outer stresses at the bend.
c) Compare the stresses between the curved portion and bent portion to determine an effective
stress concentration factor.
Figure 2: Problem 2 Diagram
Sol. (a)
( )( )
( )
kpsi 02 . 8 psi 8021
12 in 1094 . 0 in 75 . 0
in 1094 . 0 5 . 0 in 4 lb 3
I
Mc
3
= =
= = o
(b) From table 3-4, for rectangular cross-section,
we get, r
i
= 0.125 in, r
o
= r
i
+ h = 0.125 + 0.1094 = 0.2344 in
( ) ( )
in 174006 . 0
125 . 0 2344 . 0 ln
1094 . 0
r r ln
h
r
i o
n
= = =
in 005694 . 0 174006 . 0 1797 . 0 r r e
n c
= = =
in 049006 . 0 125 . 0 174006 . 0 r r c
i n i
= = =
in 060394 . 0 174006 . 0 2344 . 0 r r c
i o o
= = =
Cross-section area,
2
in 08205 . 0 1094 . 0 75 . 0 bh A = = =
M = 3 lb 4 in = 12 lb.in
The negative sign is due to convention, now the stresses,
kpsi 1 . 10 psi 070 , 10
125 . 0 005694 . 0 08205 . 0
049006 . 0 12
Aer
Mc
i
i
i
= =
= = o
kpsi 62 . 6 psi 618 , 6
2344 . 0 005694 . 0 08205 . 0
060394 . 0 12
Aer
Mc
o
o
o
= =
= = o
MAE 311: Machines and Mechanisms I Spring 2014
Assignment #3 Due Date: 3/7/2014
Copyright 2014 Phillip M. Cormier and Jobaidur Khan
(c) Stress concentrations,
26 . 1
02 . 8
1 . 10
K
i
i
=
=
o
o
=
825 . 0
02 . 8
62 . 6
K
o
o
= =
o
o
=
Problem 3 (50 Points Total)
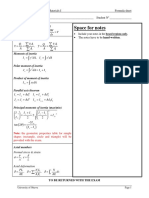
Compute the factor of safety for points A and B using both the distortion energy theory and max shear
stress theory. The bar is made from AISI 1006 cold-drawn steel, and is loaded with force F = 550 N, P
= 4000 N, and T = 25 N-m. Determine the required diameter change to bring the most restrictive case
up to a factor of safety of 3.
Figure 3: Problem 3 Diagram
Sol. Using Table A-20, o
yp
= 280 MPa
Lets analyze the point B,
o
x from bending
x z
y
t
T
o
x from P
MAE 311: Machines and Mechanisms I Spring 2014
Assignment #3 Due Date: 3/7/2014
Copyright 2014 Phillip M. Cormier and Jobaidur Khan
For point B the bending stress from F will cause a normal stress in the x direction,
( )
MPa Pa
m
m N
d
M
I
c M
F F
bend x
166 10 166
015 . 0
1 . 0 550 32 32
6
3 3
= =
= = =
t t
o
For point B the axial stress (tension) from P will cause a normal stress in the x direction,
( )
MPa Pa
m
N
d
P
A
P
axial
6 . 22 10 6 . 22
015 . 0
4000 4 4
6
2 2
= =
= = =
t t
o
So, total axial stress at B, o
x
= o
x,bend
+ o
axial
= 188.6 MPa
Shear stress for torsion,
( )
MPa 7 . 37
m 015 . 0
m . N 25 16
d
T 16
J
Tr
3 3
T
=
t
=
t
= = t
So, total shear stress, MPa 7 . 37
T xy
= t = t
So, according to DE, ( ) ( ) 4 . 1 7 . 37 3 6 . 188
280
3
2 2 2 2
= + = + = n
n n
xy x
yp
t o
o
So, according to MSST, ( ) ( ) 38 . 1 7 . 37 4 6 . 188
280
4
2 2 2 2
= + = + = n
n n
xy x
yp
t o
o
Lets analyze the point A,
For point A the axial stress (tension) from P will cause a normal stress in the x direction,
( )
MPa Pa
m
N
d
P
A
P
axial
6 . 22 10 6 . 22
015 . 0
4000 4 4
6
2 2
= =
= = =
t t
o
o
x from P
x z
y
t
T
t
F
MAE 311: Machines and Mechanisms I Spring 2014
Assignment #3 Due Date: 3/7/2014
Copyright 2014 Phillip M. Cormier and Jobaidur Khan
Shear stress for torsion,
( )
MPa 7 . 37
m 015 . 0
m . N 25 16
d
T 16
J
Tr
3 3
T
=
t
=
t
= = t
Shear stress from F,
( )
MPa
m
N
d
F
A
F
F
15 . 4
015 . 0 3
550 16
3
16
3
4
2 2
=
= = =
t t
t
So, total shear stress, MPa
F T xz
55 . 33 15 . 4 7 . 37 = + = + = t t t
So, according to DE, ( ) ( ) 27 . 4 55 . 35 3 6 . 22
280
3
2 2 2 2
= + = + = n
n n
xz x
yp
t o
o
So, according to MSST, ( ) ( ) 75 . 3 55 . 35 4 6 . 22
280
4
2 2 2 2
= + = + = n
n n
xz x
yp
t o
o
This is obvious from the previous calculation that MSST in point B gives most restrictive case. So, the
design calculation becomes,
3 3 3
F F
bend x
d
2 . 560
d
m 1 . 0 N 550 32
d
M 32
I
c M
=
t
=
t
= = o
For point B the axial stress (tension) from P will cause a normal stress in the x direction,
2 2 2
5093 4000 4 4
d d
N
d
P
A
P
axial
=
= = =
t t
o
So, total axial stress at B,
2 3
5093 2 . 560
d d
axial bend x x
+ = + = o o o
Shear stress for torsion,
3 3 3
T
d
3 . 127
d
m . N 25 16
d
T 16
J
Tr
=
t
=
t
= = t
So, total shear stress,
3
T xy
d
3 . 127
= t = t
So, according to MSST,
( ) ( ) ( ) | |
mm m d
d d
d d d n
xy x
yp
20 02 . 0
0 3 . 127 4 5093 2 . 560 9 10 280
3 . 127
4
5093 2 . 560
3
10 280
4
2 2
2
3 6
2
3
2
2 3
6
2 2
= ~
= + +
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
+ = t o
o
The diameter needs to be increased by 33%.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Engineers Precision Data Pocket ReferenceDari EverandEngineers Precision Data Pocket ReferencePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Ub Mae 311Dokumen7 halamanUb Mae 311Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ub Mae 311Dokumen6 halamanUb Mae 311Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MAE311 Test 1 SolutionsDokumen9 halamanMAE311 Test 1 SolutionsStephenBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 6Dokumen1 halamanHomework 6Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #3: (8 Points)Dokumen7 halamanAE 321 - Solution of Homework #3: (8 Points)Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- (5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Dokumen4 halaman(5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 6 Solutions: (4 Points)Dokumen7 halamanHomework 6 Solutions: (4 Points)Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σDokumen8 halamanAE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σArthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 4Dokumen2 halamanHomework 4Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- AE321 - Solutions For Homework 9: F F F GDokumen13 halamanAE321 - Solutions For Homework 9: F F F GArthur Ding100% (1)
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Dokumen9 halamanAE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 8Dokumen3 halamanHomework 8Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 5Dokumen2 halamanHomework 5Arthur DingBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionDokumen51 halamanChapter 8 Two-Dimensional Problem SolutionJoseph Daguio JrBelum ada peringkat
- Ee5101 Ca1 PDFDokumen24 halamanEe5101 Ca1 PDFHamid FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Problems From Solving Dynamics Problems in Mathcad: by Brian D. Harper Ohio State UniversityDokumen9 halamanSample Problems From Solving Dynamics Problems in Mathcad: by Brian D. Harper Ohio State UniversityMario Jucharo LaymeBelum ada peringkat
- Under, Over and Critical DampingDokumen6 halamanUnder, Over and Critical Dampingxeron7126Belum ada peringkat
- May 2018 With SolutionDokumen34 halamanMay 2018 With SolutionSagar AhireBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional FormulationDokumen18 halamanChapter 7 Two-Dimensional FormulationHk Lorilla QuongBelum ada peringkat
- MDSolidsDokumen1 halamanMDSolidsJosé BritesBelum ada peringkat
- Trig No Metric FormulasDokumen4 halamanTrig No Metric FormulasZee Shan100% (1)
- Be First Year Engineering Semester 1 2019 December Engineering Mechanics Emrev 2019'c' SchemeDokumen43 halamanBe First Year Engineering Semester 1 2019 December Engineering Mechanics Emrev 2019'c' Schemesinghsitturaj78Belum ada peringkat
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDokumen14 halamanWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsShubham mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Static FailureDokumen6 halamanLecture Static FailureKelly MooneyBelum ada peringkat
- Sample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellDokumen24 halamanSample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellMaryam ʚiïɞBelum ada peringkat
- Design-II, 2016 Bevel Gear Design ProcedureDokumen1 halamanDesign-II, 2016 Bevel Gear Design ProcedureenggsantuBelum ada peringkat
- hwk6 SolDokumen5 halamanhwk6 SolDylan Ler0% (1)
- Frekans Cevap AnaliziDokumen25 halamanFrekans Cevap AnalizineredemaliBelum ada peringkat
- A Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossDokumen2 halamanA Rectangular Steel Bar Having A CrossHitesh PrajapatBelum ada peringkat
- EE5101 Linear Systems Project Report: Semester - I, 2010/11Dokumen22 halamanEE5101 Linear Systems Project Report: Semester - I, 2010/11Jie RongBelum ada peringkat
- Green's Functions For The Stretched String Problem: D. R. Wilton ECE DeptDokumen34 halamanGreen's Functions For The Stretched String Problem: D. R. Wilton ECE DeptSri Nivas ChandrasekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix A: Piezoelectric Constitutive EquationsDokumen6 halamanAppendix A: Piezoelectric Constitutive EquationsAniruddh FaujdarBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductors MathcadDokumen5 halamanSemiconductors MathcadGerardo Silva OelkerBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 Due 1-16-2014Dokumen4 halamanAssignment 1 Due 1-16-2014Evan Baxter0% (1)
- Assignment 3 SolutionDokumen9 halamanAssignment 3 SolutionMurat BayrakBelum ada peringkat
- CVG2140 Final Exam Formula SheetDokumen4 halamanCVG2140 Final Exam Formula SheetFadey FaridBelum ada peringkat
- Bitsat Paper 03Dokumen21 halamanBitsat Paper 03Arnab SenBelum ada peringkat
- Bevel GearDokumen17 halamanBevel Gearparesh09Belum ada peringkat
- MAT244 Quiz3Dokumen2 halamanMAT244 Quiz3RevownSadaBelum ada peringkat
- PaperDokumen14 halamanPaperSayan Kumar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- SDOF - Free Vibration - DampedDokumen4 halamanSDOF - Free Vibration - DampedJr BongabongBelum ada peringkat
- Fatigue Failure CriteriaDokumen17 halamanFatigue Failure CriteriaAmrMashhourBelum ada peringkat
- Matched Asymptotic Expansion Solution5Dokumen7 halamanMatched Asymptotic Expansion Solution5Michael James Miller100% (1)
- Design Calculations Velocity and Acceleration Analysis Analytic TechniquesDokumen15 halamanDesign Calculations Velocity and Acceleration Analysis Analytic TechniquesAjinkya Kulkarni100% (1)
- Ex 2Dokumen2 halamanEx 2api-3708873Belum ada peringkat
- CH 5Dokumen56 halamanCH 5Jesús Javier Santana PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Common Distributions and Their Properties (From Epps, 2007)Dokumen1 halamanCommon Distributions and Their Properties (From Epps, 2007)salehina974Belum ada peringkat
- Midterm SolutionDokumen8 halamanMidterm SolutionAnonymous 94I9knBelum ada peringkat
- Real Mode and Complex ModeDokumen2 halamanReal Mode and Complex ModeTao Lai100% (2)
- Mini Project 2016Dokumen7 halamanMini Project 2016khooteckkienBelum ada peringkat
- 14 IC SolutionDokumen4 halaman14 IC SolutionNurul AsyilahBelum ada peringkat
- Mathcad - Extra33Dokumen1 halamanMathcad - Extra33Desejo Sozinando50% (2)
- CN2116-HW7-Solution (XJP - 2011)Dokumen12 halamanCN2116-HW7-Solution (XJP - 2011)Brian WatsonBelum ada peringkat
- Ispravci - Cvrstoca 2Dokumen10 halamanIspravci - Cvrstoca 2Mile Konfuzije JunglistBelum ada peringkat
- 125 - 201review Problems SolnsDokumen6 halaman125 - 201review Problems SolnsdfgdfgdfgaaBelum ada peringkat
- 307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFDokumen9 halaman307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFNusret MeydanlikBelum ada peringkat
- 00 Calculator Techniques 01Dokumen2 halaman00 Calculator Techniques 01vincelord92% (12)
- Module 2: Analysis of Stress: 2.3.1 GENERAL S S T D C C SDokumen21 halamanModule 2: Analysis of Stress: 2.3.1 GENERAL S S T D C C SManish SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Static FailureDokumen10 halamanStatic FailureQ_TBelum ada peringkat
- UB Mae 311Dokumen4 halamanUB Mae 311Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ub Mae 311Dokumen8 halamanUb Mae 311Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ub Mae 311Dokumen9 halamanUb Mae 311Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #4 Solution - Spring 2014Dokumen11 halamanAssignment #4 Solution - Spring 2014Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #2 Solution - Spring 2014Dokumen11 halamanAssignment #2 Solution - Spring 2014Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #1 Solution - Spring 2014Dokumen8 halamanAssignment #1 Solution - Spring 2014Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Decision MatrixDokumen1 halamanDecision MatrixDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment #0 - 2014 SolutionDokumen10 halamanAssignment #0 - 2014 SolutionDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MAE 423 Prject ReportDokumen18 halamanMAE 423 Prject ReportDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Final Document - Group 5Dokumen31 halamanFinal Document - Group 5Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MAE 376 HW 4Dokumen4 halamanMAE 376 HW 4Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MAE 376 Final ReportDokumen2 halamanMAE 376 Final ReportDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 2-17, Hydrostatic Eq, Vertical Plate, Composite AreaDokumen2 halaman2-17, Hydrostatic Eq, Vertical Plate, Composite AreaDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Review: Science, Medicine, and The FutureDokumen4 halamanClinical Review: Science, Medicine, and The FutureDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Project1 UpdatedDokumen2 halamanProject1 UpdatedDeepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Dkumar+1986 Ultrasonography in Radio Logic 1 58.Dokumen9 halamanDkumar+1986 Ultrasonography in Radio Logic 1 58.Deepak KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Classification of HormonesDokumen65 halamanChemical Classification of HormonesetBelum ada peringkat
- Makerere University Is Inviting Applications For Undergraduate Admissions On Private Sponsorship For Academic Year 2015/2016Dokumen9 halamanMakerere University Is Inviting Applications For Undergraduate Admissions On Private Sponsorship For Academic Year 2015/2016The Campus TimesBelum ada peringkat
- Gifted Black Females Attending Predominantly White Schools Compressed 1 CompressedDokumen488 halamanGifted Black Females Attending Predominantly White Schools Compressed 1 Compressedapi-718408484Belum ada peringkat
- Your Bentley Bentayga V8: PresentingDokumen9 halamanYour Bentley Bentayga V8: PresentingThomas SeiferthBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Leukemia The Scientist's Perspective and ChallengeDokumen438 halamanAcute Leukemia The Scientist's Perspective and ChallengemedskyqqBelum ada peringkat
- Wits Appraisalnof Jaw Disharmony by JOHNSONDokumen20 halamanWits Appraisalnof Jaw Disharmony by JOHNSONDrKamran MominBelum ada peringkat
- Story 1Dokumen3 halamanStory 1api-296631749Belum ada peringkat
- GSM Radio ConceptsDokumen3 halamanGSM Radio ConceptsMD SahidBelum ada peringkat
- A Short History of Denim: (C) Lynn Downey, Levi Strauss & Co. HistorianDokumen11 halamanA Short History of Denim: (C) Lynn Downey, Levi Strauss & Co. HistorianBoier Sesh PataBelum ada peringkat
- Altura Architect & Interior Design BriefDokumen56 halamanAltura Architect & Interior Design BriefDave WongBelum ada peringkat
- Genie PDFDokumen264 halamanGenie PDFjohanaBelum ada peringkat
- Robbie Hemingway - Text God VIP EbookDokumen56 halamanRobbie Hemingway - Text God VIP EbookKylee0% (1)
- Caldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignDokumen6 halamanCaldon Lefm 240ci Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Integral Manifold DesignJim LimBelum ada peringkat
- GT I9100g Service SchematicsDokumen8 halamanGT I9100g Service SchematicsMassolo RoyBelum ada peringkat
- A Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixDokumen12 halamanA Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixPraveen KumarBelum ada peringkat
- EC105Dokumen14 halamanEC105api-3853441Belum ada peringkat
- D15 Hybrid P1 QPDokumen6 halamanD15 Hybrid P1 QPShaameswary AnnadoraiBelum ada peringkat
- ERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingDokumen3 halamanERBS UPDATE John Doe ProceedingtpeppermanBelum ada peringkat
- Growing Onion Management and Water NeedsDokumen25 halamanGrowing Onion Management and Water NeedsKATE NAVAJABelum ada peringkat
- Cash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oDokumen1 halamanCash Budget Sharpe Corporation S Projected Sales First 8 Month oAmit PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Case StudyDokumen2 halamanCase StudyFadhlin Sakina SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Regulated and Non Regulated BodiesDokumen28 halamanRegulated and Non Regulated Bodiesnivea rajBelum ada peringkat
- License Fee PaidDokumen1 halamanLicense Fee Paidmy nBelum ada peringkat
- Free PDF To HPGL ConverterDokumen2 halamanFree PDF To HPGL ConverterEvanBelum ada peringkat
- Tanque: Equipment Data SheetDokumen1 halamanTanque: Equipment Data SheetAlonso DIAZBelum ada peringkat
- Enzyme Immobilization - Advances in Industry, Agriculture, Medicine, and The Environment-Springer International Publishing (2016)Dokumen141 halamanEnzyme Immobilization - Advances in Industry, Agriculture, Medicine, and The Environment-Springer International Publishing (2016)Komagatae XylinusBelum ada peringkat
- Industry and Community Project: Jacobs - Creating A Smart Systems Approach To Future Cities Project OutlineDokumen14 halamanIndustry and Community Project: Jacobs - Creating A Smart Systems Approach To Future Cities Project OutlineCalebBelum ada peringkat
- Mang-May-Tinh - 03a.-Dns1 - (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Dokumen52 halamanMang-May-Tinh - 03a.-Dns1 - (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Anh Quân TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12Dokumen15 halamanChapter 12kk5522Belum ada peringkat
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipDokumen44 halamanReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliBelum ada peringkat