EPC - V - EPCM REV 01
Diunggah oleh
jgarciacochachi100%(4)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (4 suara)
705 tayangan74 halamanepc
Judul Asli
EPC -v- EPCM REV 01
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniepc
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(4)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (4 suara)
705 tayangan74 halamanEPC - V - EPCM REV 01
Diunggah oleh
jgarciacochachiepc
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 74
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
EPC -v- EPCM
2
EPC v- EPCM
Timetable
Timetable
Time Topic
2 mins EPC v- EPCM
2 mins EPC or EPCM?
20 mins Engineering for EPC & EPCM
10 mins Procurement Strategies for EPC & EPCM
10 mins Construction for EPC & EPCM
5 mins Cost Control for EPC and EPCM
5 mins Disputes for EPC & EPCM
10 mins Advantages and Disadvantages of EPC
10 mins Advantages and Disadvantages of EPCM
5 mins Conclusion
Questions & Answers
Richard Chamberlain
3
EPC v- EPCM
The purpose of this presentation is to consider the following:
EPC which is an abbreviation for Engineering (E),
Procurement (P), and Construction (C) and
EPCM which is abbreviation for Engineering (E),
Procurement and Construction Management (CM);
consider the advantages and disadvantages of EPC and
EPCM
understand the pitfalls of EPC and EPCM
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
EPC or EPCM?
5
EPC Standard Forms of Contract
The major EPC/EPCM forms of contract are as follows:
FIDIC Silver Book
Orgalime Turnkey Contract
ICC Turnkey Task Force
ENAA
ICE 7
th
Edition
ECC 3
rd
Edition
MDB Harmonised
6
EPCM Standard Forms of Contract
No standard forms of contract
7
EPC - definition
.procurement by the owner of a
major construction project via a fixed
price, lump sum turnkey route
Worlds Apart: EPC and EPCM Contracts
Risk issues and allocation
Phil Loots and Nick Henchie
8
EPC Contractor
The EPC Contractor is considered to be an expert in this
form of contracting and this is onerous in international
construction projects and must provide:
a project that is fit for purpose
Engineering and design is to a unique standard
not carry out wilful misconduct
not be grossly negligent
9
Typical EPC arrangement
10
EPCM - definition
.an EPCM contract is a professional
services contract which has a radically
different risk allocation
Worlds Apart: EPC and EPCM Contracts
Risk issues and allocation
Phil Loots and Nick Henchie
11
EPCM Contractor
The EPCM Contractor is different to the EPC Contractor and
his duties are carried out to a standard of reasonable skill
and care which is lower than fit for purpose and covers:
performance of design work
preparation of budget cost estimate
preparation of programme and estimated duration
managing procurement and administration of trade
contractors
coordination of design and construction
wilful misconduct and gross negligence are main
causes of breach
12
Typical EPCM arrangement
13
Typical Allocation of Risk for Construction Projects
Moves
towards
Contractor
25%-75%
Contractor
assumes
Risk
10%-90%
Balanced
50%-50%
Client
assumes
Risk
100%
Conclusion:- EPC transfers the majority of risk to the contractor
Construction
Management
EPCM
Traditional
Design and
Build
EPC
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Engineering
EPC & EPCM
15
Basic Engineering (FEED)
Basic engineering is a term commonly used to define
concept design and is commonly known in EPC and
EPCM projects as front-end engineering & design (FEED)
The FEED is normally a separate contract to the EPC
and executed on agreed rates and prices.
The end of FEED is the start point of the EPC which is
executed on the basis of lump sum or reimbursable cost
16
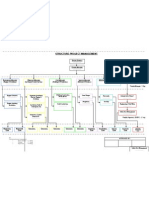
EPC/EPCM FEED & Detailed Design
Exploration and
access
Client
consents
Pre operational
testing
Full production
Client
requirements
Environmental
plan
Basic
engineering
Procurement
plan
Construction
plan
Change control
Material
requisitions
Material
purchasing
Permit to work
Update budget
and schedule
IFC drawings
and
specifications
Material
delivery
Construction of
support
facilities
Engineering
Procurement
Construction
Controls
FEED Basic engineering Detailed engineering
Project release
for construction
Contract
information
Construction
plan for support
facilities
Monitor
engineering
Engineering
support to
construction
Construction of
the project
Progress and
cost reporting
Detailed
engineering
17
1 2 3
Phases
4
Project
Implementation
Start-up and
Operations
Detailed
Engineering
Develop Project
Definition
Feasibility
Study
Select Most
Viable Option
Conceptual
Study Define
Project Options
B
u
s
i
n
e
s
s
P
l
a
n
n
i
n
g
Outcomes:
Excellent operability
Faster project cycle times
Enhanced safety
Capital effectiveness
Improved quality
Skilled resources
Characteristics:
Core to project planning
Progressive, gated
approach
Ensures quality
definition of the project
and the resources
required
FEED phases, characteristics and potential outcomes
18
Quality of FEED
BS 7000 states that properly verified and validated
design leads to cost effective construction
However:
The definition of FEED varies from project to project
and sectors
The slide to follow illustrates the effects of a FEED that
lacks proper verification and validation
19
Results of a Deficient FEED
19
Planned Actual
0
200,000
400,000
600,000
478,230
20
20
Planned Actual
0
200,000
400,000
600,000
600,000
400,000
200,000
0
800,000
1,000,000
1,200,000
1,400,000
478,230
840,000
Results of a Deficient FEED
21
21
Planned
Actual
600,000
400,000
200,000
0
800,000
1,000,000
1,200,000
1,400,000
478,230
840,000
1,280,000
Results of a Deficient FEED
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Procurement
EPC & EPCM
23
EPC/EPCM Synopsis of Risk
Engineering Procurement and Construction (EPC)
High risk for CONTRACTOR and expensive for OWNER
Engineering Procurement and Construction Management (EPCM)
High risk for OWNER, less cost and less onerous for the CONTRACTOR
EPCM Contractor is responsible design, procurement of materials and
management
Professional service as opposed to a party to the contract
EPC/EPCM mix
Bespoke form of CONTRACT, complicated and difficult to make workable
24
EPC & EPCM - Effective Procurement
For either EPC or EPCM to work and especially for PROCUREMENT to
be effective there must be good cooperation and communication
between Owner and Contractor
A key part of EPCM is the effective letting of packages in
conjunction with the FEED
Effective procurement FOR EITHER EPC or EPCM must have a
defined strategy to deal with issues related to:
Contract and commercial
Integration
Contract Management
The slides to follow reveal some of the issues that arise and
potential solutions
25
Procurement strategy
I
s
s
u
e
Fast track procurement
Driven by lack of planning
and understanding of
equipment & vendor supply
chain and end to end logistics
timeframes
S
o
l
u
t
i
o
n
- Improved early market
engagement
- Proactive and robust
procurement planning
- Active management of
inputs
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Costs
Revenue
Time
$
Procurement Strategy
26
Contract and commercial structure
Contract & Commercial Structure
I
s
s
u
e
EPC v EPCM decision-
making
often driven by past poor
experience of one or other
and can shape contract
strategy without
testing/validation
S
o
l
u
t
i
o
n
- Adopt approach that aligns
procurement , contract and
commercial model with
client/project objectives
- Consider developing a
outcome/performance driven
commercial model
- Consider ability to co-
operate/collaborate with
EPCM contractor
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Costs
Revenue
Time
$
27
Integrated process
Integrated Procurement/Engineering/Project Controls Process
I
s
s
u
e
Poor integration between
engineering and project
controls and procurement
functions
S
o
l
u
t
i
o
n
- Planning that addresses
integration of functions
(linking outputs with inputs)
- Improved definition of
engineering deliverables and
estimation/alignment of man
hours
- Procurement process and
governance that aligns with
engineering progression and
project controls
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Costs
Revenue
Time
$
28
Contract management
Contract Management
I
s
s
u
e
Contractor non-compliant
with client management
and project process
S
o
l
u
t
i
o
n
Integration of owner policies
and standards, functions and
inclusion of process
requirements e.g. Project
Controls reporting, cost,
financial, schedule within
contract
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Costs
Revenue
Time
$
29
Typical Procurement Failure
29
82 tons of steel shipped to site
wrong earth quake design by Contractor
30
Conclusion
Communication, cooperation and a
defined strategy are essential tools in
ensuring successful procurement for
either EPC or EPCM
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Construction
EPC & EPCM
32
EPC/EPCM Network and Programme Management
Exploration and
access
Client
consents
Pre operational
testing
Full production
Client
requirements
Environmental
plan
Basic
engineering
Procurement
plan
Construction
plan
Change control
Material
requisitions
Material
purchasing
Permit to work
Update budget
and schedule
IFC drawings
and
specifications
Material
delivery
Construction of
support
facilities
Engineering
Procurement
Construction
Controls
Basic engineering Detailed engineering
Project release
for construction
Contract
information
Construction
plan for support
facilities
Monitor
engineering
Engineering
support to
construction
Construction of
the project
Progress and
cost reporting
Detailed
engineering
33
Construction and Programme Risks
EPC
CONTRACTOR is responsible for the programme,
coordinates all interested parties and is responsible for
completion on time
EPCM
CONTRACTOR is responsible for coordinating the
schedule and safety during construction
34
EPC/EPCM Construction and Programme
Responsibilities
EPC Contractor is responsible for the construction programme
and any culpable delays result in liquidated damages
EPCM Contractor is responsible for:
managing the coordination of trade contractors
design and procurement
development and agreement of an overall programme
EPCM projects are prone to difficulties when deficient FEED
and late design changes are encountered
35
Deficient FEED
Deficient FEED and Programme Consequences
Root causes
Programme Consequences
Lack of trained operatives and poor
engineering
Construction planning breaks down
and leads to delay
Lack of information and records Reliance upon wrong information
leads to over payment and incorrect
scheduling
Late changes to the FEED Delay and disruption to the
progress of construction leading to
claims and disputes
36
EPC/EPCM Deficient FEED, Late Changes and Delay
EPCM projects are prone to difficulties when deficient FEED
and late design changes are encountered
The slides to follow demonstrate how a deficient FFED causes
late design changes and results in prolongation
37
Deficient FEED leads to late changes and delay
37
Monthly
Progress
Report
Field Change
Requests
Field
Change
Requests
Engineering
Percent
Complete
38
Deficient FEED leads to late changes and delay
38
Field Change
Requests
Monthly
Progress
Report to
Field
Change
Requests
Engineering
Percent
Complete
39
Deficient FEED leads to late changes and delay
39
Field
Change
Requests
Engineering
Percent
Complete
Field Change
Requests
Monthly
Progress
Report
40
EPC/EPCM Mixing
It is now becoming common to mix EPC and EPCM
responsibilities on major projects.
This is complex and difficult to manage and the slides to
follow demonstrate this statement
41
Mixing EPC and EPCM Construction Risks
42
Mine workings location Mine workings location
Mine EPCM
El =+3000m
El =+3000m
Tunnel from mine to grinder EPCM
SAG Mill EPC
Typical mix of EPC & EPCM Construction Risk
El =+3000m
El =+800m
Molybdenum plant EPC
55KMm pipeline to plant EPC
43
Summary
In both EPC and EPCM projects the programme is an essential
tool to carry out effective construction
EPC Contractor is responsible for the construction programme
EPCM Contractor is responsible for the design and
procurement programme
EPCM trade contractors are responsible for the construction
programme
EPCM programme relationships results in difficulties in settling
delay claims
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Cost Control
EPC & EPC
45
Cost Control
EPC Contractors are paid by means of a lump sum or
reimbursable cost
This provides certainty to the Owner as long as the FEED is
properly verified and validated
EPCM Contractors are paid by means of a professional fee and
target cost
This process does not provide certainty because the FEED is
not fully developed for procurement and there is a high risk of
late changes
46
Owner Claims
EPC Contractors are turnkey contractors and if they are late
the contract provides certainty for the Owner by means of
liquidated damages for delayed completion
EPCM Contractor is a professional role and if they are in breach
the recourse is a claim for negligence and which is difficult to
prove and uncertain
Both EPC and EPCM forms of contract have a common cause of
claim i.e. a deficient FEED, which can cause disputes
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Disputes
EPC & EPC
48
Deficient FEED and Disputes
A deficient FEED creates:
excessive post contract changes to scope (variations)
variations create additional administration
variations create additional work
variations create additional cost
variations cause a breakdown in planning
All the above lead to claims, potential disputes and delay
49
Variations
Poor project set up
and planning
Imprecise contract
/ specification
programming
issues
Claims / variations
leading to Delay
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Time
Delay
50
Lack of funding
Lack of funding
Delays
Project funding concerns
Financial Arrangements
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Time
Delay
51
EPC poor engineering control
Poor engineering
Claims and variations lead
to Delay
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Time
Delay
52
Lack of administration
Poor administration
Contractors claims, un
agreed variations lead to
Delay
Step 1
FEED / Concept
Step 2
Detail
Design
Step 3
Procure
Step 4
Schedule
Step 5
Construction
Step 6
Commissioning
and operation
Time
Delay
53
Conclusion
A deficient FEED creates variations together with
Owner and Contractor tension which leads to a
breakdown in job planning
Excessive variations can lead to disputes and delay
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Advantages and Disadvantages
EPC
55
EPC Advantages 1. Single Point Responsibility
1
Single Point
2
Certainty
3
Quality
4
Legal
Contractors risk
and responsible for
all vendor design
and field
engineering
Engineering Procurement
The purchasing of
resources and
materials are
contractors risk as
is inflation and
escalation
Field engineering
and constructability
and functionality is
contractors risk
Single Point Responsibility
Construction
56
EPC Advantages 2. Certainty in respect of time and cost
1
Single Point
2
Certainty
3
Quality
4
Legal
Contractors risk to
complete design
and field
engineering where
time is of the
essence and cost is
a lump sum. Owner
controls variations
to the lump sum
Engineering Procurement
Placement of
orders in good time
is driven by
Engineering. Thus
the purchasing of
resources and
materials are
contractors risk as
is inflation and
escalation
Construction being
completed on time
is driven by
Engineering and
Procurement and if
the contractor is
late then liquidated
damages are
applied
Certainty in respect of time and cost
Construction
57
EPC Advantages 3. Quality is standard of fit for purpose
1
Single Point
2
Certainty
3
Quality
4
Legal
Design warranties
protect the owner
with regard to
quality
Engineering Procurement
Design warranties
and performance
bond protect the
owner
Quality of design and work
Construction
Design warranties
protect the owner
with regard to
quality
58
EPC Advantages 4. Legal
1
Single Point
2
Certainty
3
Quality
4
Legal
Legal fees tend to be lower because owner negotiates one
contract with the EPC contractor, thus single point for any
dispute
Engineering Procurement
Legal
Construction
59
EPC Disadvantages 1. Precise and accurate owner requirements
1
Requirements
2
Variations
3
Cost
4
Financing
Owner must clearly specify requirements
Engineering Procurement
Precise and accurate owner requirements
Construction
60
EPC Disadvantages 2. Variations
1
Requirements
2
Variations
3
Cost
4
Financing
Owner ordered variations are expensive and can delay
completion
Engineering Procurement
Owner ordered variations
Construction
61
EPC Disadvantages 3. Cost
1
Requirements
2
Variations
3
Cost
4
Financing
Tends to be costly because of the imbalance in risk
Engineering Procurement
Cost
Construction
62
EPC Disadvantages 4. Cost
1
Requirements
2
Variations
3
Cost
4
Financing
Tends to be costly because of the imbalance in risk
Engineering Procurement
Cost
Construction
Turner & Townsend plc December 11
making the difference
Advantages and Disadvantages
EPCM
64
EPCM Advantages 1. Earlier commencement
1
Commencemen
t
2
Concurrent
3
Cost
4
Control
The owners requirements do not have to be as precise and
accurate and the cost of post contract changes is managed by
the EPCM contractor on behalf of the owner
Engineering Procurement
Earlier commencement
Construction
Management
65
EPCM Advantages 2. Concurrent engineering and procurement
1
Commencemen
t
2
Concurrent
3
Cost
4
Control
The owners requirements do not have to be as precise and
accurate and the cost of post contract changes is managed by
the EPCM contractor on behalf of the owner
Engineering Procurement
Concurrent engineering and procurement
Construction
Management
66
EPCM Advantages 3. Cost
1
Commencemen
t
2
Concurrent
3
Cost
4
Control
The cost is lower because the owners requirements do not have
to be as precise and accurate and the cost of post contract
changes is managed by the EPCM contractor on behalf of the
owner. The risk is then spread across multiple trade contracts
which again provides a lower overall construction cost.
Engineering Procurement
Cost
Construction
Management
67
EPCM Advantages 4. Control
1
Commencemen
t
2
Concurrent
3
Cost
4
Control
The owner has more control over the whole process and
ultimately with time and cost.
Engineering Procurement
Cost
Construction
Management
68
EPCM Disadvantages 1. Owner bears the greater risk
1
Risk
2
Uncertainty
3
Concept
4
Legal
Owner bears the greater risk
Engineering Procurement
Owner bears the greater risk
Construction
Management
Capped professional indemnity insurance for design
Construction manager errors are owner errors and cost
Defects are difficult to attribute
69
EPCM Disadvantages 2. Greater uncertainty with time and cost
1
Risk
2
Uncertainty
3
Concept
4
Legal
Owner bears the greater risk
Engineering Procurement
Greater uncertainty with time and cost
Construction
Management
Capped professional indemnity insurance for design
Construction manager errors are owner errors and cost
Defects are difficult to attribute
Delay and disruption and associated costs are difficult to
attribute
70
EPCM Disadvantages 3. Concept design not fully verified and
validated
1
Risk
2
Uncertainty
3
Concept
4
Legal
Owner bears the risk for design development
Engineering Procurement
Concept design not fully verified and validated
Construction
Management
Value Engineering can be expensive
Construction manager errors are capped by professional
insurance indemnity
Defects are difficult to attribute
Delay and disruption and associated costs of post contract
changes are difficult to attribute in both time and cost
71
EPCM Disadvantages 4. Legal
1
Risk
2
Uncertainty
3
Concept
4
Legal
Multiple contract drafting
Engineering Procurement
Legal
Construction
Management
Multiple disputes
Drafting errors and law of contract can be difficult to impose
making the difference
Conclusion
EPC or EPCM?
73
Conclusion
EPC and an EPCM are two different forms of contract
Mixing EPC and EPCM is to be avoided
EPC is the transfer of risk to the Contractor at a high cost to
the Owner
EPCM places more risk on the Owner with a lower cost
Properly verified and validated FEED provides cost effective
EPC and EPCM
making the difference
Thank You
Questions & Answers
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Gold Investor S ManualDokumen57 halamanGold Investor S Manualdrkwng100% (1)
- Temporary Auto Identification CardDokumen1 halamanTemporary Auto Identification CardNercilia Santana de Azevedo0% (1)
- Allergan 2017 J.P. Morgan PresentationDokumen19 halamanAllergan 2017 J.P. Morgan Presentationmedtechy100% (1)
- Engineering, Procurement and Construction Contracts For Large Scale ProjectsDokumen252 halamanEngineering, Procurement and Construction Contracts For Large Scale ProjectsIgor Sherstnev100% (6)
- Port OperationsDokumen41 halamanPort OperationsAllan Jason Burga50% (2)
- EPC Project Management PDFDokumen28 halamanEPC Project Management PDFRuna Jully100% (1)
- EPC 4.0 - Engineering Procurement ConstructionDokumen38 halamanEPC 4.0 - Engineering Procurement ConstructionManoj Kumar Singh50% (2)
- EPC and ERGP - The NexusDokumen37 halamanEPC and ERGP - The NexusOyinleye AdebowaleBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Risk Factors in Oil & Gas Epc ProjectsDokumen79 halamanCritical Risk Factors in Oil & Gas Epc ProjectsSairam Ravula100% (1)
- EPC and FEEDDokumen19 halamanEPC and FEEDBaghdadi AbdelillahBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges and Opportunities For Insurance Business in Volatile EnvironmentDokumen20 halamanChallenges and Opportunities For Insurance Business in Volatile EnvironmentKamauWafulaWanyama100% (1)
- EPC Contracts in The Oil & Gas SectorDokumen43 halamanEPC Contracts in The Oil & Gas Sectorsuryadiwang86% (14)
- Epc in NutshellDokumen83 halamanEpc in NutshellBilal A Barbhuiya100% (2)
- Engineering Procurement and ConstructionDokumen84 halamanEngineering Procurement and ConstructionAayushi Arora75% (4)
- EPC Structure Project ManagementDokumen1 halamanEPC Structure Project ManagementArif Rachman100% (3)
- EPC Contracting Issues in The Oil and Gas Industry PDFDokumen359 halamanEPC Contracting Issues in The Oil and Gas Industry PDFAhmed M. Hashim100% (1)
- EPC Schedule Levels ExplanationDokumen1 halamanEPC Schedule Levels ExplanationJoe_Average0% (1)
- Personal BudgetDokumen4 halamanPersonal BudgetIvana GrinfelderBelum ada peringkat
- FEED or No FEEDDokumen15 halamanFEED or No FEEDjohndagheBelum ada peringkat
- Contract Strategies for Major Projects: Mastering the Most Difficult Element of Project ManagementDari EverandContract Strategies for Major Projects: Mastering the Most Difficult Element of Project ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Assisgnment No. 4 Contract ManagementDokumen39 halamanAssisgnment No. 4 Contract ManagementAshutosh Kumar50% (2)
- Mining Guide Epc and Epcm Contracts 104178Dokumen40 halamanMining Guide Epc and Epcm Contracts 104178mohantyom100% (1)
- EPC PracticeDokumen4 halamanEPC PracticeSaid Ahmed SalemBelum ada peringkat
- Epc Overview: Stands For Engineering, Procurement and ConstructionDokumen15 halamanEpc Overview: Stands For Engineering, Procurement and ConstructionPrince75% (4)
- Risk Management ExamDokumen260 halamanRisk Management ExamItebogeng Iteza MosupyeBelum ada peringkat
- Epc Epcm ChartDokumen1 halamanEpc Epcm ChartSylvester Mokgokone Rakgate89% (9)
- Conceiving and Drafting The Terms of Epc ContractsDokumen8 halamanConceiving and Drafting The Terms of Epc Contractsaugustaq100% (2)
- EPC ProcessesDokumen37 halamanEPC ProcessesSagar Garg100% (3)
- Ed Merrow PresentationDokumen42 halamanEd Merrow Presentationinitiative1972Belum ada peringkat
- EPC Vs EPCMDokumen3 halamanEPC Vs EPCMArun MunjalBelum ada peringkat
- EPC Contract Tool For Project FinanceDokumen29 halamanEPC Contract Tool For Project Financeshalw100% (2)
- Epc Contracts Process Plant SectorDokumen30 halamanEpc Contracts Process Plant Sectorlimpama100% (2)
- Pce Sample Questions 2016 - EngDokumen39 halamanPce Sample Questions 2016 - EngImran Azman100% (1)
- Prediction of Project Performance-FluorDokumen159 halamanPrediction of Project Performance-FluorCüneyt Gökhan Tosun100% (4)
- EPC & EPCM Definition and ComparisonDokumen4 halamanEPC & EPCM Definition and Comparisonconstp1Belum ada peringkat
- EPC Contracts - Project Management Perspective Rev02 PDFDokumen42 halamanEPC Contracts - Project Management Perspective Rev02 PDFMustafa UsalanBelum ada peringkat
- EPC V EPCM TableDokumen8 halamanEPC V EPCM TableChris Eggleton100% (1)
- EPC - V - EPCM REV 01Dokumen74 halamanEPC - V - EPCM REV 01jgarciacochachi100% (4)
- Allocating Risk in An EPC Contract - Patricia GallowayDokumen13 halamanAllocating Risk in An EPC Contract - Patricia Gallowayjorge plaBelum ada peringkat
- EPC Contract Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandEPC Contract Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBelum ada peringkat
- EPC Vs EPCMDokumen4 halamanEPC Vs EPCMNemanja KlisaraBelum ada peringkat
- Alimentador VibratorioDokumen24 halamanAlimentador VibratoriojgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- Choosing The Project Strategy EPCM EPC PMC Bilfinger TebodinDokumen2 halamanChoosing The Project Strategy EPCM EPC PMC Bilfinger TebodinFirasAlnaimi100% (1)
- 01 - Developing A Contracting StrategyDokumen67 halaman01 - Developing A Contracting Strategyali deveboynuBelum ada peringkat
- 04 - Contracting For EPC PhaseDokumen45 halaman04 - Contracting For EPC PhaseJJ Welding100% (4)
- EPCM - The Special Engineering ContractDokumen13 halamanEPCM - The Special Engineering ContractHarsh SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Epcm JacobDokumen19 halamanEpcm JacobjgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- Epcm JacobDokumen19 halamanEpcm JacobjgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- EPCM TheMisunderstoodContractDokumen6 halamanEPCM TheMisunderstoodContractmonikatickoo4412100% (2)
- EPC or EPCM Contracts - AusencoDokumen3 halamanEPC or EPCM Contracts - AusencoEduardo Mena100% (1)
- 03 Epc Contract ManagementDokumen37 halaman03 Epc Contract Managementzhangj5100% (4)
- EPC ContractsDokumen5 halamanEPC ContractsAbdul Rahman Sabra100% (1)
- Mega Project Construction Contracts - An Owner's PerspectiveDokumen16 halamanMega Project Construction Contracts - An Owner's Perspectivesevero97Belum ada peringkat
- Ausenco EPCM Vs EPCDokumen7 halamanAusenco EPCM Vs EPCJavier IgnacioBelum ada peringkat
- Epic Projectinterdepency Promo 150417084058 Conversion Gate02Dokumen101 halamanEpic Projectinterdepency Promo 150417084058 Conversion Gate02eddyronaldycBelum ada peringkat
- Pe D A09134227266 Ge Sow 003 01 E - Sow Epcm Sgi MunteniDokumen13 halamanPe D A09134227266 Ge Sow 003 01 E - Sow Epcm Sgi MunteniIoana PopescuBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of EPC ContractingDokumen39 halamanEvolution of EPC Contractingsyafiq100% (1)
- Lecture 3-Bid Package PreparationDokumen23 halamanLecture 3-Bid Package PreparationnhojtrenrewBelum ada peringkat
- The Statoil BookDokumen77 halamanThe Statoil BookAlexandra Gabriela Grecu100% (1)
- Loadstar Shipping vs. Malayan Insurance (Decision)Dokumen2 halamanLoadstar Shipping vs. Malayan Insurance (Decision)John Mark RevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentacion Edward MerrowDokumen53 halamanPresentacion Edward MerrowDaniel HuacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ni 617 July 2014 PDFDokumen46 halamanNi 617 July 2014 PDFTi AnnelBelum ada peringkat
- Fidic - Condictions of Contract For Epc-Turnkey ProjectsDokumen49 halamanFidic - Condictions of Contract For Epc-Turnkey Projectssharon gradosBelum ada peringkat
- Modelling A Global Epcm Engineering Procurement and Construction Management EnterpriseDokumen8 halamanModelling A Global Epcm Engineering Procurement and Construction Management EnterprisejgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- Mega Project Interface ManagementDokumen3 halamanMega Project Interface ManagementLTE002100% (2)
- EPCM-Delivering The ImpossibleDokumen9 halamanEPCM-Delivering The ImpossibleralucastanescuBelum ada peringkat
- EPC AnalysisDokumen46 halamanEPC AnalysisVinaya NayakBelum ada peringkat
- EPC March17 (Sanjay)Dokumen37 halamanEPC March17 (Sanjay)Dundi Kumar T & D Dept.0% (1)
- EPC or EPCM Contracts: Which One Can Drive Stronger Outcomes For Project Owners?Dokumen7 halamanEPC or EPCM Contracts: Which One Can Drive Stronger Outcomes For Project Owners?Đặng Trung AnhBelum ada peringkat
- Iif 8 Epcm Contracts Feb16 3Dokumen22 halamanIif 8 Epcm Contracts Feb16 3Jorge RammBelum ada peringkat
- EPC Vs EPCMDokumen22 halamanEPC Vs EPCMmohantyom100% (2)
- Financial Risks and Bankability in EPC ContractsDokumen5 halamanFinancial Risks and Bankability in EPC ContractsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Catálogo GA 200Dokumen16 halamanCatálogo GA 200jgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- Monatcarga H400Dokumen16 halamanMonatcarga H400jgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- Seamless Rock Floor/sandDokumen2 halamanSeamless Rock Floor/sandjgarciacochachiBelum ada peringkat
- SPM 14 en Binding Web Fin Rev 04Dokumen68 halamanSPM 14 en Binding Web Fin Rev 04Dušan DimitrijevićBelum ada peringkat
- SM ICICI Change Management FreeDokumen36 halamanSM ICICI Change Management FreeHimanshu Oza100% (1)
- Product StrategyDokumen2 halamanProduct StrategyS. M.Belum ada peringkat
- Meaning and Definition of InsuranceDokumen40 halamanMeaning and Definition of InsurancekanikaBelum ada peringkat
- Aftermath Adjusters & Consulting Clarifies Burst Pipe CoverageDokumen3 halamanAftermath Adjusters & Consulting Clarifies Burst Pipe CoveragePR.comBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome To UCR BookletDokumen8 halamanWelcome To UCR BookletGabija VerbaitėBelum ada peringkat
- Marine InsuranceDokumen8 halamanMarine InsuranceSyed Saqlain HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Ce 1402 Estimation and Quantity SurveyingDokumen26 halamanCe 1402 Estimation and Quantity SurveyingNagaraja Prasanna RassBelum ada peringkat
- Erm ProcessDokumen2 halamanErm ProcessSejal VibhuteBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Business Studies Lesson 4 XI ComDokumen4 halamanNotes Business Studies Lesson 4 XI Comadarshchoudhary2796Belum ada peringkat
- Ra 10607 PDFDokumen68 halamanRa 10607 PDFMae Jansen Doroneo100% (1)
- Quality Management in Health Care: Concepts, Principles and StandardsDokumen8 halamanQuality Management in Health Care: Concepts, Principles and StandardsMartin BringasBelum ada peringkat
- All Lines TemplateDokumen1 halamanAll Lines Templatejohnbbb111Belum ada peringkat
- How To File A Claim-For GSISDokumen2 halamanHow To File A Claim-For GSISZainal Abidin AliBelum ada peringkat
- Continental Casualty Company v. William S. Burton, Audrey H. Buckner, Mary R. Thweatt, 795 F.2d 1187, 4th Cir. (1986)Dokumen11 halamanContinental Casualty Company v. William S. Burton, Audrey H. Buckner, Mary R. Thweatt, 795 F.2d 1187, 4th Cir. (1986)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- The Costs of Accidents at WorksDokumen64 halamanThe Costs of Accidents at Worksイセ ジュ100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Corporate FinanceDokumen3 halamanChapter 1 Introduction To Corporate FinanceLimBelum ada peringkat
- Final Internship Report - PES1PG19MB116 - Pavan MDokumen61 halamanFinal Internship Report - PES1PG19MB116 - Pavan MPavan ManjunathBelum ada peringkat
- Pol IctDokumen4 halamanPol Ictrajrane8784Belum ada peringkat
- HR Budget TrainingDokumen32 halamanHR Budget Trainingsaidul islamBelum ada peringkat