EEEB113 Chap 1 Notes
Diunggah oleh
NabilahJasmiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EEEB113 Chap 1 Notes
Diunggah oleh
NabilahJasmiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EEEB113
CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I
Chapter 1
Basic Concepts
1
Materials from Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, Alexander & Sadiku 4e, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Basic Concepts - Chapter 1
2
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Systems of Units
1.3 Charge & Current
1.4 Voltage
1.5 Energy & Power
1.6 Circuit Elements
1.1 Introduction
3
What is electric circuit?
Interconnection of electrical elements.
1.2 System of Units (1)
Quantity Basic unit Symbol
1 Length meter m
2 Mass kilogram kg
3 Time second s
4 Electric current ampere A
5 Thermodynamic
temperature
kelvin K
6 Luminous intensity candela cd
4
Six basic units
International System of Units (SI), 1960
1.2 System of Units (2)
5
Common circuit theory SI prefixes
Used to signify powers of 10
e.g.
1,000,000 ohms = 1 x 10
6
ohms
= 1 mega-ohm (M)
100,000 meters = 100 x 10
3
meters
= 100 kilometers (km)
0.001 second = 1 x 10
-3
seconds
= 1 millisecond (ms)
0.0000001 farad = 0.1 x 10
-6
farad
= 0.1 microfarad (F)
1.2 System of Units (3)
6
Example
Convert:
i) 0.01 ms to s
ii) 60 kilometers per hour to meters per second
Solution
i) 0.01 ms = 1x10
-2
x10
-3
s
= 1x10
-5
s
= 1x10x10
-6
s
= 10 s
ii) 60 km/hour = (60x10
3
m)/(60x60 s)
= 16.67 m/s
1.2 Electric Charges (1)
7
Charge, q
an electrical property,
measured in coulombs (C)
Charge is bipolar
(+ve and ve charge)
Charge e on 1electron
= -1.602 10
-19
C
1 coulomb of charge, 1C
= 1/(1.602 10
-19
C)
= 6.24x10
18
electrons
Electric current is due to flow of electronic
charge in a conductor.
Electrical effects:
Charges separate = create electric force
Charges move = create electric flow
i.e. current
1.2 Electric Charges (2)
8
Example
Given nC, find current i at t = 0.5 s
Solution
At t = 0.5 s,
= 152.44 nA
1.3 Current (1)
9
Electric current = time rate of change of charge,
measured in ampere, A.
Charge transferred between time t
0
and t is obtained
by integrating both sides of above equation.
A
dt
dq
i
1 A = 1C/s
t
t
idt q
0
Integrate both sides
1.3 Current (2)
10
direct current (dc)
= current remains constant with time.
alternating current (ac)
= current varies sinusoidally with time.
1.3 Current (3)
Direction of current flow
Conventionally taken as positive charge movement
A current can be represented positively or negative
11
Positive ions Negative ions
(a) Positive current flow
(b) Negative current flow
11
1.3 Current (4)
Example
Calculate the amount of charge represented by four million protons.
Solution
12
1.3 Current (5)
Example
The total charge entering a terminal is given by
.
Calculate the current at t = 0.5s.
Solution
13
1.3 Current (6)
Example
The current flowing through an element is
Calculate the charge entering the element from t=0 to t=2s.
Solution
14
1.4 Voltage (1)
Voltage (or potential difference) = energy required to move a
unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
w is energy in joules (J) and q is charge in coulomb (C).
Electric voltage, v
ab,
is always across the circuit element or
between two points in a circuit.
v
ab
> 0 means the potential of a is higher than potential of b.
v
ab
< 0 means the potential of a is lower than potential of b.
15
dq
dw
v
ab
15
1.4 Voltage (2)
16
16
Point a is at higher potential than point b.
If v
ab
= 3 V, then v
ba
= -3 V because point b is
lower than point a.
1.5 Energy & Power (1)
17
Energy, w is the capacity to do work, measured in Joules (J);
Power, p is the rate of change of energy, measured in Watts
(W)
From the definitions of voltage and current, and
dt
dw
p dt vi dt p w
t
t
t
t
0 0
vi
dt
dq
dq
dw
dt
dw
p
1.5 Energy & Power (2)
Passive sign convention is satisfied:
1. When the current enters through the
positive terminal of an element, the
power is delivered to or absorbed by
the element, p=+vi.
2. When the current enters through the
negative terminal, the power is
delivered from or supplied by the
element, p=-vi.
18
i
+
v
p = +Vi
absorb power
i
+
v p = -Vi
supply power
1.5 Energy & Power (3)
In a circuit,
+ power absorbed = - power supplied
Law of conservation of energy
Algebraic SUM of POWER in a circuit at any instant of time is
ZERO
0 p
19
1.5 Energy & Power (4)
20
20
Example
Find the power delivered to the element at t = 5ms if the current remains the
same but the voltage is:
Solution
1.5 Energy & Power (5)
21
21
Solution cont.
1.5 Energy & Power (6)
22
22
Example
A stove draws 15 A when connected to a 240-V line. How long
does it take to consume 60kJ?
Solution
1.6 Circuit Element (1)
23
2 types of electrical/ circuit elements
Passive elements
1. Resistor
2. Capacitor
3. Inductor
Passive
Active
able to generate
energy
e.g. sources,
batteries,
generators
cannot generate
energy
1.6 Circuit Element (2)
24
Active elements
Sources
1. Independent voltage source
2. Independent current source
3. Dependent sources
Voltage
Current
active element that provides
voltage or current that is
independent of other circuit elements.
active element that depends on
voltage or current of other element.
+
-
+
-
Independent: Dependent:
Voltage Current Voltage Current
1.6 Circuit Element (3)
25
Independent sources:
voltage sources current source
1.6 Circuit Element (4)
26
4 types of Dependent Sources
1. Voltage-controlled voltage source (VCVS)
2. Current-controlled voltage source (CCVS)
3. Voltage-controlled current source (VCCS)
4. Current-controlled current source (CCCS)
2V
0
+
-
2I
0
+
-
2I
2V
0
1.6 Circuit Elements (5)
27
Active Elements Passive Elements
Independent
sources
Dependant
sources
A dependent source is an active
element in which the source quantity
is controlled by another voltage or
current.
They have four different types: VCVS,
CCVS, VCCS, CCCS. Keep in minds the
signs of dependent sources.
1.6 Circuit Elements (6)
28
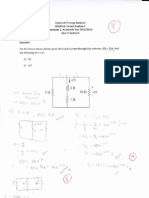
Example
Find the power absorbed or supplied by each component of the circuit
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDokumen61 halamanBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaBelum ada peringkat
- C1 Basic ConceptsDokumen54 halamanC1 Basic ConceptsPEi PAiBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits MidtermDokumen101 halamanFundamentals of Electric Circuits MidtermJohn Lloyd Quiñal MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electricity Chapter OneDokumen76 halamanBasic Electricity Chapter OneGetahun shankoBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDokumen101 halamanCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDokumen96 halamanFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringfrankieyiiBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical and Elecrical SystemDokumen34 halamanMechanical and Elecrical SystemMat ZoulBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Study Abroad Handbook 2023 2024Dokumen114 halamanEngineering Study Abroad Handbook 2023 2024BRAHMJOT SINGH100% (1)
- Grade 8 Biology Binder Final For PrintingDokumen196 halamanGrade 8 Biology Binder Final For PrintingSai YeddanapudiBelum ada peringkat
- Cmos Analog Ic Design Problems and SolutionsDokumen165 halamanCmos Analog Ic Design Problems and SolutionsAnti MatterBelum ada peringkat
- Advances in Analog Circuits PDFDokumen380 halamanAdvances in Analog Circuits PDFnskprasad89100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Dokumen24 halamanCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Công Phạm BáBelum ada peringkat
- Ac Final PresentationDokumen128 halamanAc Final PresentationHoney Lynne AnitoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDokumen51 halamanBasic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringJayniti Kumari100% (1)
- Current Electricity. MiaDokumen42 halamanCurrent Electricity. MiaVerla MfeerBelum ada peringkat
- BUET SuggestionsDokumen3 halamanBUET SuggestionsTanvir Alam ShishirBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Alternative Forms of Pull-UpDokumen15 halaman7 Alternative Forms of Pull-UpRajesh Pyla100% (1)
- What Is A Resistor - Types, Uses, Details Electronics NotesDokumen7 halamanWhat Is A Resistor - Types, Uses, Details Electronics NotesKimberly Camacho CatubigBelum ada peringkat
- Phys 1121 Kinematic NotesDokumen17 halamanPhys 1121 Kinematic NoteshardkntBelum ada peringkat
- Ohm's Law Lab ExperimentDokumen1 halamanOhm's Law Lab ExperimentAira Cannille LalicBelum ada peringkat
- AS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesDokumen17 halamanAS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesAryan KingerBelum ada peringkat
- Current & Charge Calculations WorksheetDokumen8 halamanCurrent & Charge Calculations WorksheetSumolmal SrisukriBelum ada peringkat
- Everything Science Grade 12Dokumen461 halamanEverything Science Grade 12sikakhane321Belum ada peringkat
- ACElectricalCircuitsWorkbook PDFDokumen159 halamanACElectricalCircuitsWorkbook PDFArunBelum ada peringkat
- IBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSDokumen10 halamanIBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSle 。 gexBelum ada peringkat
- Digital ElectronicsDokumen228 halamanDigital ElectronicsMujeeb AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge 2010 - Physics - Five Edition - TsokosDokumen849 halamanCambridge 2010 - Physics - Five Edition - TsokosAngelBelum ada peringkat
- Formula List New STPM - 2nd TermDokumen6 halamanFormula List New STPM - 2nd TermOne_sofian2715Belum ada peringkat
- 9781292035444Dokumen7 halaman9781292035444Bwn Jangyeswar KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Particle PhysicsDokumen44 halamanIntroduction to Particle Physicssyazwan100% (1)
- Common Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1Dokumen3 halamanCommon Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1RidwanAbrarBelum ada peringkat
- PYTHAGORAS WORKSHEET SOLVERDokumen4 halamanPYTHAGORAS WORKSHEET SOLVERBranson Kaution Peters IIBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Emagnet Teacher - EditedDokumen46 halamanChapter 8 Emagnet Teacher - EditedSuadrifRunDamahum100% (1)
- Topic 11 Electromagnetic Induction (HL) - IB PhysicsDokumen1 halamanTopic 11 Electromagnetic Induction (HL) - IB PhysicsFortNite KIDBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Effect of Current ExerciseDokumen12 halamanMagnetic Effect of Current Exercisemaatla monkgeBelum ada peringkat
- Madeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsDokumen23 halamanMadeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsmadhujayanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter19pp171 180 PDFDokumen10 halamanChapter19pp171 180 PDFInderMahesh0% (1)
- PC To PC Data CommDokumen41 halamanPC To PC Data CommParshant GargBelum ada peringkat
- WPH05 01 Que 20160121Dokumen28 halamanWPH05 01 Que 20160121josekadaBelum ada peringkat
- Slides 2 Atomic Structure (Handout)Dokumen40 halamanSlides 2 Atomic Structure (Handout)Seng Sy Keath100% (1)
- Takeapeek PDFDokumen20 halamanTakeapeek PDFRohit AdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- Alternating Current FundamentalsDokumen154 halamanAlternating Current FundamentalsRK KBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise Short Questions F.sc. Part 2Dokumen35 halamanExercise Short Questions F.sc. Part 2Gulshair KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Fabrication Organic Solar CellsDokumen48 halamanFabrication Organic Solar CellsSwaroop RBelum ada peringkat
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDokumen6 halaman12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamBelum ada peringkat
- Ch02 BLawsDokumen67 halamanCh02 BLawsThomas WondwosenBelum ada peringkat
- Schaum - S Electromagnetics (PDFDrive)Dokumen303 halamanSchaum - S Electromagnetics (PDFDrive)dummy accountBelum ada peringkat
- Arham WB 6th ClassDokumen11 halamanArham WB 6th ClassArham JainBelum ada peringkat
- Physics DC CircuitsDokumen24 halamanPhysics DC CircuitsJenessaBelum ada peringkat
- Electricity: An Introduction to Atomic Structure, Charge, Potential, Current and CircuitsDokumen24 halamanElectricity: An Introduction to Atomic Structure, Charge, Potential, Current and CircuitsPremela PremelaBelum ada peringkat
- GCSE Chemistry Revision QuestionsDokumen31 halamanGCSE Chemistry Revision QuestionsMarina Jaubert ✩Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Exam Quick Revision NotesDokumen40 halamanPhysics Exam Quick Revision NotesPinky Ann DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Static Electricity and Current FlowDokumen26 halamanStatic Electricity and Current FlowAirul YantiBelum ada peringkat
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDokumen2 halamanRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- ECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaDokumen24 halamanECE1311 Ch1 - FarahIsaMuhd NaimBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic ConceptsDokumen47 halamanLinear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 1: Basic Conceptsrizwanspirit11Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 BNJ 10903 E&ETECHDokumen45 halamanChapter 1 BNJ 10903 E&ETECHMuhammad NaufalBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical Concepts ExplainedDokumen19 halamanBasic Electrical Concepts ExplainedWasim MagsiBelum ada peringkat
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDokumen61 halamanEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanBelum ada peringkat
- Charge and Electrical VariableDokumen44 halamanCharge and Electrical VariableNeverson RusipinBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation Report FormDokumen2 halamanInvestigation Report FormNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Energy ManagementDokumen2 halamanAssignment Energy ManagementNabilahJasmi0% (1)
- Vector Cross Product and Its ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanVector Cross Product and Its ApplicationsNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- NOTES2Dokumen97 halamanNOTES2NabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- NDT Assignments for Machine Vision, Jet Engines, and Work ProceduresDokumen1 halamanNDT Assignments for Machine Vision, Jet Engines, and Work ProceduresNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal SWM SustainDokumen8 halamanProposal SWM SustainNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics LAB OKDokumen42 halamanFluid Mechanics LAB OKNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- DataLab 2Dokumen9 halamanDataLab 2NabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen22 halamanLecture 1Vinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual MeasurementDokumen74 halamanLab Manual MeasurementNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Eng AnalysisDokumen7 halamanEng AnalysisAbera ZewduBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Power Gearbox TechnologiesDokumen8 halamanWind Power Gearbox TechnologiesNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Dokumen9 halamanCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavBelum ada peringkat
- CH 02 - Atomic Structure & BondingDokumen27 halamanCH 02 - Atomic Structure & BondingNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- MEHB221 Prelab 2012 Part 1Dokumen4 halamanMEHB221 Prelab 2012 Part 1NabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Fluid LabDokumen6 halamanAssignment Fluid LabNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- GearboxDokumen19 halamanGearboxNabilahJasmi100% (1)
- MEHB221 Prelab 2012 Part 1Dokumen4 halamanMEHB221 Prelab 2012 Part 1NabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- ElectricalDokumen12 halamanElectricalNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 1 Pelton Wheel TurbineDokumen8 halamanExp 1 Pelton Wheel TurbineNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Exam: Flow in PipesDokumen13 halamanFluid Mechanics Exam: Flow in PipesNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 5 SolutionDokumen2 halamanQuiz 5 SolutionNabilahJasmiBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Radio Waves and ApplicationsDokumen11 halamanTypes of Radio Waves and Applicationsultra dubsBelum ada peringkat
- Mpe ReadingDokumen2 halamanMpe ReadingShekhar NagarBelum ada peringkat
- UPII Spring 2008 Course Guide on Magnetism and OpticsDokumen485 halamanUPII Spring 2008 Course Guide on Magnetism and OpticsErica Gale Joseph100% (1)
- Problem StatemenetDokumen7 halamanProblem StatemenetlitonBelum ada peringkat
- Jan 2017Dokumen7 halamanJan 2017kirthikaBelum ada peringkat
- Biophysics Final QuestionsDokumen4 halamanBiophysics Final Questionshadigy1001Belum ada peringkat
- Equations of PlanesDokumen35 halamanEquations of PlanesRakibHasanBhashaBelum ada peringkat
- Phys259 L2 ElectricForces FinalDokumen13 halamanPhys259 L2 ElectricForces FinalKatelyn KnudsgaardBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanLesson PlanElgaliza Karina DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Flange LeakageDokumen48 halamanFlange LeakageAnjani Prabhakar83% (6)
- Static Equib WorksheetDokumen7 halamanStatic Equib Worksheetsitinasarath100% (1)
- Generator synchronization challengesDokumen6 halamanGenerator synchronization challengesabdulyunus_amirBelum ada peringkat
- Lamé ParametersDokumen3 halamanLamé ParametersKamineni JagathBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Stability, Swelling Behaviour and Dielectric Proper-Ties of Nbr/Pvc-Pvac BlendsDokumen8 halamanThermal Stability, Swelling Behaviour and Dielectric Proper-Ties of Nbr/Pvc-Pvac BlendssdfsdfssdfsdBelum ada peringkat
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 1 Sura Guide em 214945Dokumen62 halamanNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Unit 1 Sura Guide em 214945Lakshitha SivakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iv PDFDokumen17 halamanUnit Iv PDFephBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor Examples PDFDokumen16 halamanTransistor Examples PDFGuganesan PerumalBelum ada peringkat
- Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam Institut Teknologi Bandung Studi Fisika Modul Tutorial 7 Gelombang ElektromagnetikDokumen4 halamanFakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam Institut Teknologi Bandung Studi Fisika Modul Tutorial 7 Gelombang ElektromagnetikHazelnut ChocoBelum ada peringkat
- Fracture Toughness Testing - TwiDokumen5 halamanFracture Toughness Testing - TwiSergio MunhosBelum ada peringkat
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions MCQDokumen6 halamanInverse Trigonometric Functions MCQAshmita GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Nov 2006 PhysicsDokumen12 halamanPaper 2 Nov 2006 PhysicssolarixeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics of SkatingDokumen12 halamanPhysics of SkatingCeline YâùBelum ada peringkat
- EE8391 QB 04 - by LearnEngineering - inDokumen20 halamanEE8391 QB 04 - by LearnEngineering - inKeerthiSahaBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual MethodDokumen1 halamanVirtual Methodsuganthi1711Belum ada peringkat
- Iit Chemistry 4Dokumen11 halamanIit Chemistry 4Shailendra Agarwal100% (1)
- Jest2022 QP and Revised AnswersDokumen22 halamanJest2022 QP and Revised AnswersSkSBelum ada peringkat
- PYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NATURAL AND MAN-MADE FIBERSDokumen16 halamanPYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NATURAL AND MAN-MADE FIBERSKhandaker Sakib FarhadBelum ada peringkat
- ES4423 Lec01 CourseIntroduction 4OWLDokumen31 halamanES4423 Lec01 CourseIntroduction 4OWLMJKHTBelum ada peringkat
- OU Open University SM358 2012 Exam SolutionsDokumen20 halamanOU Open University SM358 2012 Exam Solutionssam smithBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic High Tension SeparatorsDokumen37 halamanMagnetic High Tension SeparatorsAdel Niño Liza IliganBelum ada peringkat