History of Storage Devices
Diunggah oleh
Zaira Lantican100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
1K tayangan42 halamanHistory of Storage Devices
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHistory of Storage Devices
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
1K tayangan42 halamanHistory of Storage Devices
Diunggah oleh
Zaira LanticanHistory of Storage Devices
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 42
Create by Zaira
1920s 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s Today
1928 Magnetic tape -Fritz Pfleumer, a German engineer,
patented magnetic tape in 1928. He based his invention
off Vlademar Poulsens magnetic wire.
1932 Magnetic Drum -G. Taushek, an Austrian innovator, invented the
magnetic drum in 1932. He based his invention off a discovery credited to Fritz
Pfleumer.
1946 Williams Tube-Professor Fredrick C. Williams and his
colleagues developed the first random access computer memory at the University
of Manchester located in the United Kingdom. He used a series of electrostatic
cathode-ray tubes for digital storage. A storage of 1024 bits of information was
successfully implemented in 1948.
1946 Selectron Tube In 1948, The Radio Corporation of
America (RCA) developed the Selectron tube, an early form of computer
memory, which resembled the Williams-Kilburn design.
1949 Delay Line Memory The delay line memory consists of
imparting an information pattern into a delay path. A closed loop forms to
allow for the recirculation of information if the end of the delay path
connects to the beginning through amplifying and time circuits. A delay
line memory functions similar to inputting a repeating telephone number
from the directory until an individual dials the number.
Magnetic Core-A magnetic core memory, also known as a
ferrite-core memory, uses small magnetic rings made of ceramic to store
information from the polarity to the magnetic field it contains.
1956 Hard disk-A hard disk implements rotating
platters, which stores and retrieves bits of digital information from a
flat magnetic surface.
RAID
On servers and high-end PC workstations (such as those used for high-
end video editing), at least two hard disks are often linked together
using a technology called RAID. This stands for "redundant array of
independent disks" (or sometimes "redundant array of inexpensive
drives"), and stores the data in each user volume on multiple physical
drives.
DAS" OR DIRECT ATTACHED STORAGE DRIVE
DAS external hard disks connect via a USB, firewire or an E-SATA interface (see
the hardware section), with USB being the most common. The highest quality
external hard drives routinely include at least two of these interfaces as
standard
1963 Music tape/Compact Cassete -Philips introduced the compact
audio cassette in 1963. Philips originally intended to use the audio cassette
for dictation machines; however, it became a popular method for distributing
prerecorded music. In 1979, Sonys Walkman helped transformed the use of
the audio cassette tape, which became widely used and popular.
1966 DRAM (PDF) In 1966, Robert H. Dennard invented
DRAM cells. Dynamic Random Access Memory technology (DRAM),
or memory cells that contained one transistor. DRAM cells store bits of
information as an electrical charge in a circuit. DRAM cells increased
overall memory density.
1968 Twistor Memory-Bell Labs developed Twistor memory by
wrapping magnetic tape around a wire that conducts electrical current. Bell
Labs used Twistor tape between 1968 to the mid-1970s before it was
totally replaced by RAM chips.
1970 Bubble Memory In 1970, Andrew Bobeck
invented the Bubble Memory, a thin magnetic film used to store
one bit of data in small magnetized areas that look like bubbles.
The development of the Twistor memory enabled him to create
Bubble Memory.
1971 8 Floppy IBM started its development of an
inexpensive system geared towards loading microcode into the
System/370 mainframes. As a result, the 8-inch floppy emerged. A
floppy disk, a portable storage device made of magnetic film encased in
plastic, made it easier and faster to store data.
1976 5.25 Floppy Allan Shugart developed a the 5.25-
inch floppy disk in 1976. Shugart developed a smaller floppy disk,
because the 8-inch floppy was too large for standard desktop
computers. The 5.25-inch floppy disk had a storage capacity of 110
kilobytes. The 5.25-inch floppy disks were a cheaper and faster
alternative to its predecessor.
1980 CD During the 1960s, James T. Russel thought
of using light to record and replay music. As a result, he invented
the optical digital television recording and playback television in
1970; however, nobody took to his invention. In 1975, Philips
representatives visited Russel at his lab. They paid Russel millions
for him to develop the compact disc (CD). In 1980, Russel
completed the project and presented it to Sony.
1981 3.5 Floppy The 3.5-inch floppy disk had significant
advantages over its predecessors. It had a rigid metal cover that made it
harder to damage the magnetic film inside
1984 CD Rom The CD-ROM, also known as the
Compact Disk Read-Only Memory, used the same physical format
as the audio compact disks to store digital data. The CD-ROM
encodes tiny pits of digital data into the lower surface of the plastic
disc, which allowed for larger amounts of data to be stored.
1987 DAT In 1987, Sony introduced the Digital Audio
Tape (DAT), a signal recording and playback machine. It resembled the
audio cassette tape on the surface with a 4 millimeter magnetic tape
enclosed into a protective shell.
1989 DDS In 1989, Sony and Hewlett Packard
introduced the Digital Data Storage (DDS) format to store and
back up computer data on magnetic tape. The Digital Data
Storage (DDS) format evolved from Digital Audio Tape (DAT)
technology.
1990 MOD (PDF) -The Magneto-Optical disc emerged
onto the information technology field in 1990. This optical disc
format used a combination of optical and magnetic technologies
to store and retrieve digital data. A special magneto-optical
drive is necessary to retrieve the data stored on these 3.5 to
5.25-inch discs.
1992 MiniDisc -The MiniDisk stored any kind of digital
data; however, it was predominately used for audio. Sony
introduced MiniDisk technology in 1991. In 1992, Philips
introduced the Diigtal Compact Cassette System (DCC). MiniDisk
was intended to replace the audio cassette tape before it
eventually phased out in 1996.
1993 DLT (PDF) - The Digital Equipment Corporation invented
the Digital Linear Tape (DLT), an alternative to the magnetic tape
technology used for computer storage.
1994 Compact Flash -CompactFlash (CF), also known as
flash drives, used flash memory in an enclosed disc to save
digital data. CF devices are used in digital cameras and
computers to store digital information.
Zip -The Zip drive became commonly used in 1994 to
store digital files. It was a removable disk storage system
introduced by Iomega.
1995 DVD -DVD became the next generation of digital
disc storage. DVD, a bigger and faster alternative to the
compact disc, serves to store multimedia data.
SmartMedia-Toshiba launched the SmartMedia, a flash
memory card, in the summer of 1995 to compete with MiniCard
and SanDisk.
Phasewriter Dual -The Phasewriter Dual (PD) was the
first device that used phase-change technology to store
digital data. Panasonic introduced the Phasewriter Dual
device in 1995. It was replaced by the CD-ROM and DVD.
CD-RW The Compact Disc Rewritable disc, a
rewritable version of the CD-ROM, allows users to record digital
data over previous data.
1997 Multimedia Card - The Multimedia Card (MMC)
uses a flash memory card standard to house digital data. It was
introduced by Siemens and SanDisk in 1997.
1999 Microdrive A USB Flash Drive uses a NAND-
type flash memory to store digital data. A USB Flash Drive
plugs into the USP interface on standard computers.
SD Card The Secure Digital (SD) flash memory format incorporates DRM
encryption features that allow for faster file transfers. Standard SD cards measure 32
millimeters by 32 millimeters by 2.1 millimeters. A typical SD card stores digital media
for a portable device.
2003 Blu Ray (PDF) Blu-Ray is the next generation of
optical disc format used to store high definition video (HD) and
high density storage. Blu-Ray received its name for the blue laser
that allows it to store more data than a standard DVD. Its
competitor is HD-DVD.
xD-Picture Card Olympus and Fujifilm introduced the xD-
Picture Card in 2002, which are exclusively used for Olympus
and Fujifilm digital cameras.
2004 WMV-HD The Windows Media High Definition
Video (WMV-HD) references high definition videos encoded with
Microsoft Media Video nine codecs. WMV-D is compatible for
computer systems running Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows XP.
In addition, WMV-D is compatible with Xbox-360 and Sonys
PlayStation 3.
HD-DVD -High-Density Digital Versatile Disc (HD-DVD),
a digital optical media format, uses the same disc size as Blu-
Ray. It is promoted by Toshiba, NEC, and Sanyo.
Holographic (PDF)The future of computer memory resides in holographic
technology. Holographic memory can store digital data at high density inside
crystals and photo-polymers. The advantage of holographic memory lies in its
ability to store a volume of recording media, instead of just on the surface of
discs. In addition, it enables a 3D aspect that allows a phenomenon known as
Bragg volume to occur.
Cloud Backup Solutions Zettas cloud enables
businesses to protect data using backup, recover from a disaster,
and archive unused files using only a lightweight sofware client
and Zettas bi-coastal datacenters. As storage hardware and
internet bandwidth continue to develop, so will Zettas
performance.
CHARACTERISTICS OF STORAGE
Storage technologies at all levels of the storage hierarchy can be
differentiated by evaluating certain core characteristics as well as measuring
characteristics specific to a particular implementation. These core characteristics
are volatility, mutability, accessibility, and addressibility. For any particular
implementation of any storage technology, the characteristics worth measuring
are capacity and performance
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- HD & HDTV: PAL NTSC 576i (Digital PAL) 480i (Digital NTSC) S Resolution Frame Rate Aspect RatiosDokumen9 halamanHD & HDTV: PAL NTSC 576i (Digital PAL) 480i (Digital NTSC) S Resolution Frame Rate Aspect Ratioscr0zzb0wBelum ada peringkat
- VideoDokumen24 halamanVideoSindhu SmilyBelum ada peringkat
- Development of The Principles of EditingDokumen5 halamanDevelopment of The Principles of Editingapi-264459464Belum ada peringkat
- Digital Cinema: By: Mahaveer.j.Aski 4SN06EC022 E&C Dept, SITDokumen21 halamanDigital Cinema: By: Mahaveer.j.Aski 4SN06EC022 E&C Dept, SITpankaj88orangeBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Video? Basics of Video, Analog and Digital Video. by Shobhit JainDokumen2 halamanWhat Is Video? Basics of Video, Analog and Digital Video. by Shobhit JainShobhit JainBelum ada peringkat
- Digital IntermediateDokumen3 halamanDigital IntermediateMoji PiyapongBelum ada peringkat
- Combined VE SLMDokumen150 halamanCombined VE SLMAnzar khanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Introduction To MultimediaDokumen42 halamanChapter 1 Introduction To MultimediaAbhijit BahlBelum ada peringkat
- "Trabajo Monográfico - Almacenamiento Magnético": Curso: Ingles TécnicoDokumen12 halaman"Trabajo Monográfico - Almacenamiento Magnético": Curso: Ingles TécnicoChambilla Lanchipa Alfredo LuisBelum ada peringkat
- A111l #3Dokumen12 halamanA111l #3Aanstein YalungBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Storage EvolutionDokumen2 halamanComputer Storage EvolutionRics SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- 1) History of Storage (Origin To Present)Dokumen8 halaman1) History of Storage (Origin To Present)Veanne Jhannyca Espiritu VerilBelum ada peringkat
- External Storage DDokumen4 halamanExternal Storage DAkash SagarBelum ada peringkat
- Data StorageDokumen14 halamanData Storageapi-327731606Belum ada peringkat
- TechnologyDokumen3 halamanTechnologyquigaojoanneBelum ada peringkat
- MIL Lesson 8Dokumen33 halamanMIL Lesson 8Caitlin SanoyBelum ada peringkat
- Floppy Disk - WikipediaDokumen123 halamanFloppy Disk - Wikipediayannaungsoe890Belum ada peringkat
- Evolution of MemoryDokumen12 halamanEvolution of MemorySuparn SalujaBelum ada peringkat
- Floppy DiskDokumen10 halamanFloppy DiskBryan AremadoBelum ada peringkat
- Technological University of Panama West Regional Headquarters of Panama Faculty of Computer Systems EngineeringDokumen21 halamanTechnological University of Panama West Regional Headquarters of Panama Faculty of Computer Systems EngineeringIsrael Alexis Tejada QuintanaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System (Csc1033) Ver. 2003Dokumen20 halamanComputer System (Csc1033) Ver. 2003izzul_125z1419Belum ada peringkat
- Storage Devices and Its UsesDokumen4 halamanStorage Devices and Its UsesSanjay SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Disc: Collection of Various Optical Disc and Cassette Tape FormatsDokumen10 halamanOptical Disc: Collection of Various Optical Disc and Cassette Tape FormatsJohann S M MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Minidisc: Mini Disk Navigation Search Minidisc (Album) VM (Operating System)Dokumen11 halamanMinidisc: Mini Disk Navigation Search Minidisc (Album) VM (Operating System)ramkishore_krkBelum ada peringkat
- Product Life Cycle (PLC) : Floppy DiskDokumen4 halamanProduct Life Cycle (PLC) : Floppy DiskSajid100% (1)
- ThreatDokumen5 halamanThreatTechLead Co. LTDBelum ada peringkat
- SonyDokumen3 halamanSonysony67% (6)
- Blue Ray DiskDokumen6 halamanBlue Ray DiskManpreet SachdevaBelum ada peringkat
- CD and DVD Technologies and Their DifferencesDokumen17 halamanCD and DVD Technologies and Their DifferencesAmrinder SinghBelum ada peringkat
- History of Hard Disk Drives: Marlene A. Caliste Cse111L/Rc7: Hard Drives Part 1 BSIT, CSE111L/IT41P1-COMTECH LAB, S 1-5Dokumen28 halamanHistory of Hard Disk Drives: Marlene A. Caliste Cse111L/Rc7: Hard Drives Part 1 BSIT, CSE111L/IT41P1-COMTECH LAB, S 1-5Meldrid CalisteBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment:-2: Magnetic Tapes Floppy Disc CD - Rom Blue Ray TechnologyDokumen15 halamanAssignment:-2: Magnetic Tapes Floppy Disc CD - Rom Blue Ray TechnologyRevan GaikwadBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture5 - Hardware Comp For MM SystemDokumen29 halamanLecture5 - Hardware Comp For MM SystemHasniza HarunBelum ada peringkat
- History of The Floppy Disk: 8-Inch, 5 - Inch, and 3 - Inch Floppy DisksDokumen11 halamanHistory of The Floppy Disk: 8-Inch, 5 - Inch, and 3 - Inch Floppy DisksYuvaraj BhaduryBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Audio TapeDokumen3 halamanDigital Audio Tapepablete82Belum ada peringkat
- Input Devices: KeyboardDokumen4 halamanInput Devices: KeyboardvaishaliBelum ada peringkat
- ÷M ÷M ÷M ÷M ÷MDokumen9 halaman÷M ÷M ÷M ÷M ÷MJiby JhnBelum ada peringkat
- Components of ComputerDokumen12 halamanComponents of ComputerRaskshannaBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 History of The Compact DiscDokumen22 halaman2.1 History of The Compact Discanon_926978759Belum ada peringkat
- Evolution of The Major Computer Storage Devices: Gamze ZeytinciDokumen34 halamanEvolution of The Major Computer Storage Devices: Gamze ZeytinciVarun DhuriaBelum ada peringkat
- E Storage DeviceDokumen8 halamanE Storage DevicePanopio EnterpBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary MemoriesDokumen4 halamanSecondary MemoriesAizik Lessik AreveBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary StorageDokumen15 halamanSecondary StorageKyle CaguladaBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Disk StorageDokumen24 halamanOptical Disk StorageShahjahan SialBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of Computer EquipmentDokumen11 halamanEvolution of Computer EquipmentK. Légrádi FruzsinaBelum ada peringkat
- MHD (Final) DocumentDokumen4 halamanMHD (Final) Documentngatatpyar420Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8: Storage: MultimediaDokumen28 halamanLecture 8: Storage: MultimediaAgung RizqiBelum ada peringkat
- Storage DevicesDokumen32 halamanStorage Devicesdairyl.virreyBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 - Secondary Storage DevicesDokumen55 halamanAssignment 1 - Secondary Storage DevicesDeepak Gurbani70% (10)
- Covermount: Covermount (Sometimes Written Cover Mount) Is The Name Given To StorageDokumen4 halamanCovermount: Covermount (Sometimes Written Cover Mount) Is The Name Given To StoragehurlyhutyoBelum ada peringkat
- Multimedia StorageDokumen11 halamanMultimedia StorageAjay Joshy0% (1)
- Cit463 Summary From NoungeeksDokumen49 halamanCit463 Summary From NoungeeksBrian CopperBelum ada peringkat
- Pendrive 5Dokumen2 halamanPendrive 5EINSTEINBelum ada peringkat
- Hard Disk DrivesDokumen36 halamanHard Disk DrivesSagar ParikhBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution of Storage MediaDokumen13 halamanEvolution of Storage MediaLutfan NessaBelum ada peringkat
- CDintroductionDokumen32 halamanCDintroductionSaadBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology: Topic: Secondary Storage Device Teacher: Miss Group Name: Tech Army DUE DATE: 10/19/2020Dokumen9 halamanInformation Technology: Topic: Secondary Storage Device Teacher: Miss Group Name: Tech Army DUE DATE: 10/19/2020Maduri JaikaranBelum ada peringkat
- Storage Systems-UNIT-IstDokumen20 halamanStorage Systems-UNIT-IstpbpscBelum ada peringkat
- MMS - Chapter 4 - Optical StorageDokumen29 halamanMMS - Chapter 4 - Optical StorageAbebaw GebreBelum ada peringkat
- Videotape: Videotape Is Magnetic Tape Used ForDokumen43 halamanVideotape: Videotape Is Magnetic Tape Used ForpraveenBelum ada peringkat
- PDFUnit 9 MediaDokumen5 halamanPDFUnit 9 MediaNunaBelum ada peringkat
- IC-MF644CDW - MF741CDW BrochureDokumen8 halamanIC-MF644CDW - MF741CDW BrochureosvaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Building A Simple Web ServerDokumen6 halamanBuilding A Simple Web ServerAnh WeasleyBelum ada peringkat
- 200910Dokumen130 halaman200910Som SuperBelum ada peringkat
- Pirated GamesDokumen6 halamanPirated GamesVladNeculaBelum ada peringkat
- 11-BICC and IPBCP Protocol-29Dokumen37 halaman11-BICC and IPBCP Protocol-29Sajid BashirBelum ada peringkat
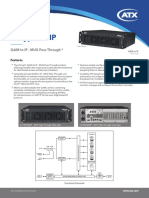
- Ucrypt Q2Ip: Qam To Ip - Mux Pass ThroughDokumen3 halamanUcrypt Q2Ip: Qam To Ip - Mux Pass ThroughbiggenaBelum ada peringkat
- Gamma 2.2 Setup or Linear Workflow: Before You StartDokumen13 halamanGamma 2.2 Setup or Linear Workflow: Before You Startjelena1004Belum ada peringkat
- Pl2303hx Usb To Rs485-422 Manual v1.0Dokumen4 halamanPl2303hx Usb To Rs485-422 Manual v1.0famaral_hotmail_comBelum ada peringkat
- Nokia HDM 5.1 Data SheetDokumen5 halamanNokia HDM 5.1 Data SheetLuis Angel ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Operation Guide: Prismasync Remote ManagerDokumen70 halamanOperation Guide: Prismasync Remote ManagerJPauloBelum ada peringkat
- GSM Short Message ServiceDokumen13 halamanGSM Short Message ServiceihabgamilBelum ada peringkat
- Motorola Canopy Wireless Broadband Platform: Configuration GuideDokumen59 halamanMotorola Canopy Wireless Broadband Platform: Configuration GuideLola Blasco CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Outdoor PTZ Camera (Axis Q6034-E)Dokumen2 halamanOutdoor PTZ Camera (Axis Q6034-E)Usman ZouqueBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering Guide To AudioDokumen20 halamanMastering Guide To AudioLuke Haqq100% (4)
- 4KP6800 enDokumen36 halaman4KP6800 enbeethoven015Belum ada peringkat
- OpenScape Business V1, OpenScape Business X3R - X5R, Getting Started Guide, Issue 1Dokumen4 halamanOpenScape Business V1, OpenScape Business X3R - X5R, Getting Started Guide, Issue 1Noel SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Multimedia in IctDokumen25 halamanMultimedia in IctAllyssa Mae ValderramaBelum ada peringkat
- Calix Understanding Deployment Costs FTTHDokumen9 halamanCalix Understanding Deployment Costs FTTHWei Jung Shih HungBelum ada peringkat
- Klisipcam 2 MirudvengDokumen2 halamanKlisipcam 2 MirudvengShareef KoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Peter Norton - Introduction To Computers Part 1Dokumen18 halamanPeter Norton - Introduction To Computers Part 1jony50% (2)
- RX-A700 Manual PDFDokumen143 halamanRX-A700 Manual PDFFilimone ThumboBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco SD Wan and UmbrellaDokumen3 halamanCisco SD Wan and UmbrellabuendiaisauroBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA Discovery Practice Final ExamDokumen10 halamanCCNA Discovery Practice Final ExamMel BaaBelum ada peringkat
- MikroTik Web-Proxy Rev1.2 PDFDokumen24 halamanMikroTik Web-Proxy Rev1.2 PDFRony Dettmar Celis ReateguiBelum ada peringkat
- Digimerge M42044 Data SheetDokumen3 halamanDigimerge M42044 Data SheetJMAC SupplyBelum ada peringkat
- DX DiagDokumen30 halamanDX DiagJake BardinasBelum ada peringkat
- Sewoo SLK TS400Dokumen2 halamanSewoo SLK TS400Estrella LopezBelum ada peringkat
- A Distributed Protocol To Serve Dynamic Groups For Peer-To-peer StreamingDokumen35 halamanA Distributed Protocol To Serve Dynamic Groups For Peer-To-peer StreamingYerri SwamyBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco IconosDokumen26 halamanCisco IconosTheo DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Trust ModelsDokumen9 halamanTrust Modelssaurabmi275% (4)