TH236 Tut 1 (Curtin University)
Diunggah oleh
Myo Ko Ko0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
54 tayangan2 halamanThermodynamics 236 Tutorial 1 from curtin unversity
Judul Asli
TH236 Tut 1(curtin university)
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThermodynamics 236 Tutorial 1 from curtin unversity
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
54 tayangan2 halamanTH236 Tut 1 (Curtin University)
Diunggah oleh
Myo Ko KoThermodynamics 236 Tutorial 1 from curtin unversity
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Curtin University of Technology
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Thermodynamics 236
Tutorial 1
1 Identify and mark, if any, boundaries of thermodynamic system (closed system), control
volume (open system) and surroundings for the following operations. Comment whether
the processes can be considered quasi-static. Discuss possible energy interactions across
the boundaries.
(a) A rubber balloon is connected to a rigid tank of helium at high pressure via a
valve which is initially closed. The valve is slowly opened and the balloon is
inflated.
(b) A heated metal billet is dropped into an oil bath for heat treatment.
(c) A gas is contained in a vertical cylinder by a weighted piston. The piston is
initially held in position and the gas is heated to a higher pressure. The piston is
then released.
(d) The air in a room with closed windows is conditioned by an air conditioner in
order to maintain a comfortable temperature and humidity
2 A metal cylinder is fitted with a frictionless piston of mass 10 kg. An additional mass of
150 kg is placed on the piston. A barometer in the neighbourhood indicates a pressure of
760 mm of Hg (density of Hg=13600 kg/m
3
). Calculate the gauge pressure and the
absolute pressure of the gas in the cylinder. The area of the piston is 0.2m
2
.
Heat is supplied to the gas until its absolute pressure becomes 4.0 bar while the piston is
locked in position by a peg. Find the force on the peg.
Ans. 109.2 kPa, 7.85 kPa, 58.2 kN
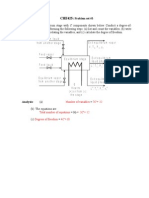
3 A pressure vessel with a spring-loaded relief valve is shown in Fig 1. Initially, the piston
of mass m rests firmly on the shoulder of the vessel due to the initial compression X
o
of
the spring. The excess pressure in the vessel is relieved when the piston moves to a point
X
1
above the shoulder. The area of the piston is A and the spring constant of the spring is
k. The atmospheric pressure in the vicinity is p
o
.
(a) Find an expression for the pressure in the vessel when the piston is just about to rise
from the shoulder.
(b) Show that the pressure in the vessel varies linearly with volume of the gas in the
vessel until the excess pressure is relieved.
(c) Derive an expression for the maximum permissible pressure in the vessel.
Vent for excess
pressure release
X
1
Piston of mass m
and area A
Gas
Volume V
o
Spring constant k
Initial compression X
o
Figure 1
Pressure vessel
4 Describe the characteristics and sketch the paths of the following processes on p-v and T-v
diagrams for a pure substance:
(a) Constant pressure cooling of superheated vapour to liquid phase.
(b) Constant volume heating of wet vapour, passing through the critical point.
(c) Isothermal expansion, starting from subcooled liquid state.
Professor Tilak T Chandratilleke-Department of Mechanical Engineering
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Dari EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Belum ada peringkat
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDokumen37 halamanMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Homework Assignment 2 Winter 2014 McGillDokumen4 halamanHomework Assignment 2 Winter 2014 McGillshwtf1Belum ada peringkat
- Thermo I A1 Feb 2024Dokumen6 halamanThermo I A1 Feb 2024tasmeer khanBelum ada peringkat
- TT P1Dokumen4 halamanTT P1Juan Manuel Uceda PérezBelum ada peringkat
- MMÜ 205 Thermodynamics Suggested Problems - Set # 1Dokumen1 halamanMMÜ 205 Thermodynamics Suggested Problems - Set # 1Onur GökçeBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Engine EfficiencyDokumen8 halamanHeat Engine EfficiencyleisllyBelum ada peringkat
- PomeDokumen17 halamanPomeAnirudh KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- HW 4 3.12Dokumen33 halamanHW 4 3.12Anonymous U3DpVvqVWx0% (3)
- 1.5.2 Gases 00-10Dokumen13 halaman1.5.2 Gases 00-10Murray PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 1 TermodinamicaDokumen3 halamanTarea 1 TermodinamicaMario Gonzalez100% (1)
- PhysicsDokumen15 halamanPhysicssandrosteklegebre100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Practice Problems 3Dokumen13 halamanThermodynamics Practice Problems 3Minh Trương PhúcBelum ada peringkat
- The Exit Velocity of A Compressed Air Cannon3Dokumen9 halamanThe Exit Velocity of A Compressed Air Cannon3tOLBelum ada peringkat
- AS1300: Thermodynamics For Aerospace Engineers Tutorial 4 (13/02/2020)Dokumen2 halamanAS1300: Thermodynamics For Aerospace Engineers Tutorial 4 (13/02/2020)Abdi ZerihunBelum ada peringkat
- Workbook FMDokumen66 halamanWorkbook FMSubhash JhurawatBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment # 3 (Chapter 2) Due 3:00 PM of January 31, 2008Dokumen2 halamanAssignment # 3 (Chapter 2) Due 3:00 PM of January 31, 2008Adam SchellBelum ada peringkat
- ExercisesDokumen19 halamanExercisesNhật MinhBelum ada peringkat
- Scribd Download - Com Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersDokumen6 halamanScribd Download - Com Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersRomil ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Cylinder T (K) P (Bar) V (M)Dokumen3 halamanCylinder T (K) P (Bar) V (M)Harshit MittalBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1 2014Dokumen7 halamanTutorial 1 2014sotdeBelum ada peringkat
- Subjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsDokumen5 halamanSubjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsTanvir ShafalBelum ada peringkat
- 4 5927173555606259377 PDFDokumen5 halaman4 5927173555606259377 PDFabel derejeBelum ada peringkat
- FORM 4 REVISION ON HEAT WORKSHEET 2021 SolnDokumen6 halamanFORM 4 REVISION ON HEAT WORKSHEET 2021 SolnRuqayya ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set (10 Questions) of First-Second Law of ThermodynamicsDokumen4 halamanProblem Set (10 Questions) of First-Second Law of Thermodynamicscoolcool2167Belum ada peringkat
- CH 1Dokumen7 halamanCH 1Asad IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Heat and Thermodynamics-SubjectiveDokumen8 halamanHeat and Thermodynamics-SubjectiveNeeraj KalraBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Laws Questions - NAT 5Dokumen6 halamanGas Laws Questions - NAT 5Uniyals AcademyBelum ada peringkat
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Dokumen3 halamanChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71Belum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics question bank analyzedDokumen10 halamanThermodynamics question bank analyzedRaj PratyushBelum ada peringkat
- ChE204 20181HWIIDokumen1 halamanChE204 20181HWIIGG MMBelum ada peringkat
- ME-1100 Thermodynamics May - June 2022 - Trimester Tutorial - 1Dokumen2 halamanME-1100 Thermodynamics May - June 2022 - Trimester Tutorial - 1Aiswarya Ramesh me21b011Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 ThermodynamicsDokumen1 halamanAssignment 1 ThermodynamicsMarvin BayanayBelum ada peringkat
- D C & E E H81ETD/CHEE1016 E T: Xample HeetDokumen2 halamanD C & E E H81ETD/CHEE1016 E T: Xample HeetPrakkash RajantheranBelum ada peringkat
- Eng1460 TT1 Solutions Wi10Dokumen7 halamanEng1460 TT1 Solutions Wi10Favelax895Belum ada peringkat
- Work sheet.1Dokumen6 halamanWork sheet.1tfkthe46Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics 1: Tutorial 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction to Fluid MechanicsDokumen3 halamanFluid Mechanics 1: Tutorial 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction to Fluid MechanicsAh WenBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Properties (HW1)Dokumen4 halamanFluid Properties (HW1)Jamiel CatapangBelum ada peringkat
- CompressibleFlow PracticeProblemsDokumen42 halamanCompressibleFlow PracticeProblemsGautam KadianBelum ada peringkat
- Homework solutions fluid mechanics problemsDokumen25 halamanHomework solutions fluid mechanics problemsHirman De NovaBelum ada peringkat
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Dokumen7 halamanChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Propulsion and Rocket Chapter 1 QuestionsDokumen3 halamanPropulsion and Rocket Chapter 1 QuestionsRiyad Mohammed0% (1)
- ME301 Paper ADokumen2 halamanME301 Paper AMitesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTDokumen34 halamanCHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTZohaib Ali0% (1)
- Ejercicios de Cinematica en Mecanica de Los Medios ContinuosDokumen3 halamanEjercicios de Cinematica en Mecanica de Los Medios ContinuoscuetaracremaBelum ada peringkat
- ENG 1460 Term Test 1 Thermal Sciences Fall 2011Dokumen7 halamanENG 1460 Term Test 1 Thermal Sciences Fall 2011Favelax895Belum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 3-4 - Winter 2010Dokumen2 halamanProblem Set 3-4 - Winter 2010nayudu narasimhaBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Thermodynamics TutorialDokumen4 halamanBasics of Thermodynamics TutorialKaka ZettyBelum ada peringkat
- MAE651 AdvancedThermo 2017 HWK2Dokumen2 halamanMAE651 AdvancedThermo 2017 HWK2JonBelum ada peringkat
- Problems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirDokumen3 halamanProblems Chapter 2 Introduction To Aircraft Technology Use: G 9.81 M/S 1 Atm. 101325 N/M R 287 J/KGK For AirKynn VargasBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersDokumen5 halamanFluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersAlex LakeBelum ada peringkat
- ME2121 Tutorial 2Dokumen2 halamanME2121 Tutorial 2joshua_chan_10Belum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics ProblemsDokumen16 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics ProblemsMahantesh ChulakiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 Soln PDFDokumen13 halamanAssignment 1 Soln PDFJawahar Khetan100% (1)
- PRINT AndersonDokumen7 halamanPRINT AndersonCed Sison100% (1)
- ThermodynamicDokumen6 halamanThermodynamicWilliam Arthur MacklorenBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Depressurization of Pressure VesselsDokumen4 halamanRapid Depressurization of Pressure VesselsChristian CândidoBelum ada peringkat
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 623, December 10, 1887Dari EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 623, December 10, 1887Belum ada peringkat
- Small Cylinder Over Big Cylinder DyamicsDokumen9 halamanSmall Cylinder Over Big Cylinder DyamicsMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- EFPC Site Visit Report FinalDokumen17 halamanEFPC Site Visit Report FinalMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics 236 Semester 2 2014 Bentley Campus INTDokumen10 halamanThermodynamics 236 Semester 2 2014 Bentley Campus INTMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco SummaryDokumen1 halamanCisco SummaryMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- PlanDokumen1 halamanPlanMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco SummaryDokumen1 halamanCisco SummaryMyo Ko KoBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 05 - Upthrust in Fluids, Archidems' Principle and FloatationDokumen2 halamanCHP 05 - Upthrust in Fluids, Archidems' Principle and FloatationKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ABelum ada peringkat
- JIANYE Air Dryer Filter CatalogueDokumen19 halamanJIANYE Air Dryer Filter CatalogueAriantoBelum ada peringkat
- CNG Facility Process NarrativeDokumen4 halamanCNG Facility Process NarrativeArnel MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science: SciencedirectDokumen8 halamanExperimental Thermal and Fluid Science: SciencedirectHanner Cantillo RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Ternary Systems ReviewDokumen7 halamanTernary Systems Reviewtensai no tenshiBelum ada peringkat
- NDT TableDokumen16 halamanNDT Tablekamlesh kumar singh engineers pvt ltd kkseplBelum ada peringkat
- Vapour Power Cycle 1Dokumen129 halamanVapour Power Cycle 1Chadaram JagadishBelum ada peringkat
- Ion-Solid InteractionsDokumen41 halamanIon-Solid InteractionsHorácioBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular ShapeDokumen25 halamanChemical Bonding and Molecular Shapeshivakafle039Belum ada peringkat
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDokumen4 halaman9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics Real GasesDokumen16 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics Real Gasesonel badroBelum ada peringkat
- 2.eng - Ternary Mixtures As Long Term - DR P Sekhar BabuDokumen8 halaman2.eng - Ternary Mixtures As Long Term - DR P Sekhar BabuImpact JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Set 3 AnsDokumen13 halamanSet 3 Ansluis fernando santos narvaezBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDokumen6 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDivine Grace Valenzuela100% (4)
- Chemical Bonding Lewis Structure Formal Charges Molecular GeometryDokumen29 halamanChemical Bonding Lewis Structure Formal Charges Molecular GeometryChristine FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- M14Dokumen28 halamanM14Vijay RajaindranBelum ada peringkat
- Control Valve Process Sizing: Corporate CriteriaDokumen36 halamanControl Valve Process Sizing: Corporate CriteriaMohammad Ben ShenshenBelum ada peringkat
- Bernouli S Theorem DemonstrationDokumen14 halamanBernouli S Theorem DemonstrationHarris ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Genting Lanco PowerDokumen49 halamanGenting Lanco PowerbhargavBelum ada peringkat
- Gaugler, R. S. (1944) - U.S.A. Patent No. 2350348.Dokumen5 halamanGaugler, R. S. (1944) - U.S.A. Patent No. 2350348.pathiBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 4-Energy Analysis of Closed SystemDokumen26 halamanCHAPTER 4-Energy Analysis of Closed SystemChelsie Patricia Demonteverde MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- INA-Naftaplin's Development of Oil and Gas Production, Gathering and Transportation TechnologyDokumen16 halamanINA-Naftaplin's Development of Oil and Gas Production, Gathering and Transportation TechnologyStefano SinožićBelum ada peringkat
- A-Science-8-Q3-Module 2 OdogDokumen23 halamanA-Science-8-Q3-Module 2 OdogMA EDYLYN NOGUERRABelum ada peringkat
- Mass Transfer Unit Operation - Robert E. TreybalDokumen5 halamanMass Transfer Unit Operation - Robert E. Treybalግደይ ዓደይ ዓይነይ ኪሮስBelum ada peringkat
- Phase DiagramsDokumen79 halamanPhase DiagramsArun V NairBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Entry #4Dokumen67 halamanChem Entry #4Vivialyn YumulBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics - TocDokumen3 halamanIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics - TocNguyễn Hồng Quân100% (2)
- Mud Viscocities and Other Rheological PropertiesDokumen23 halamanMud Viscocities and Other Rheological PropertiesMuhammad Naqiuddin Bin Zahid67% (3)
- Me 321: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. A.B.M. Toufique HasanDokumen10 halamanMe 321: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. A.B.M. Toufique HasanankitaBelum ada peringkat
- Recrystallization: Activity No. 6Dokumen6 halamanRecrystallization: Activity No. 6Mary Jean SteffenBelum ada peringkat